
Dr. Zainab F. Hassan Lecture Four
1
Circulatory shock
Circulatory shock means generalized inadequate blood flow
through the body, to the extent that the body tissues are
damaged because of too little flow.
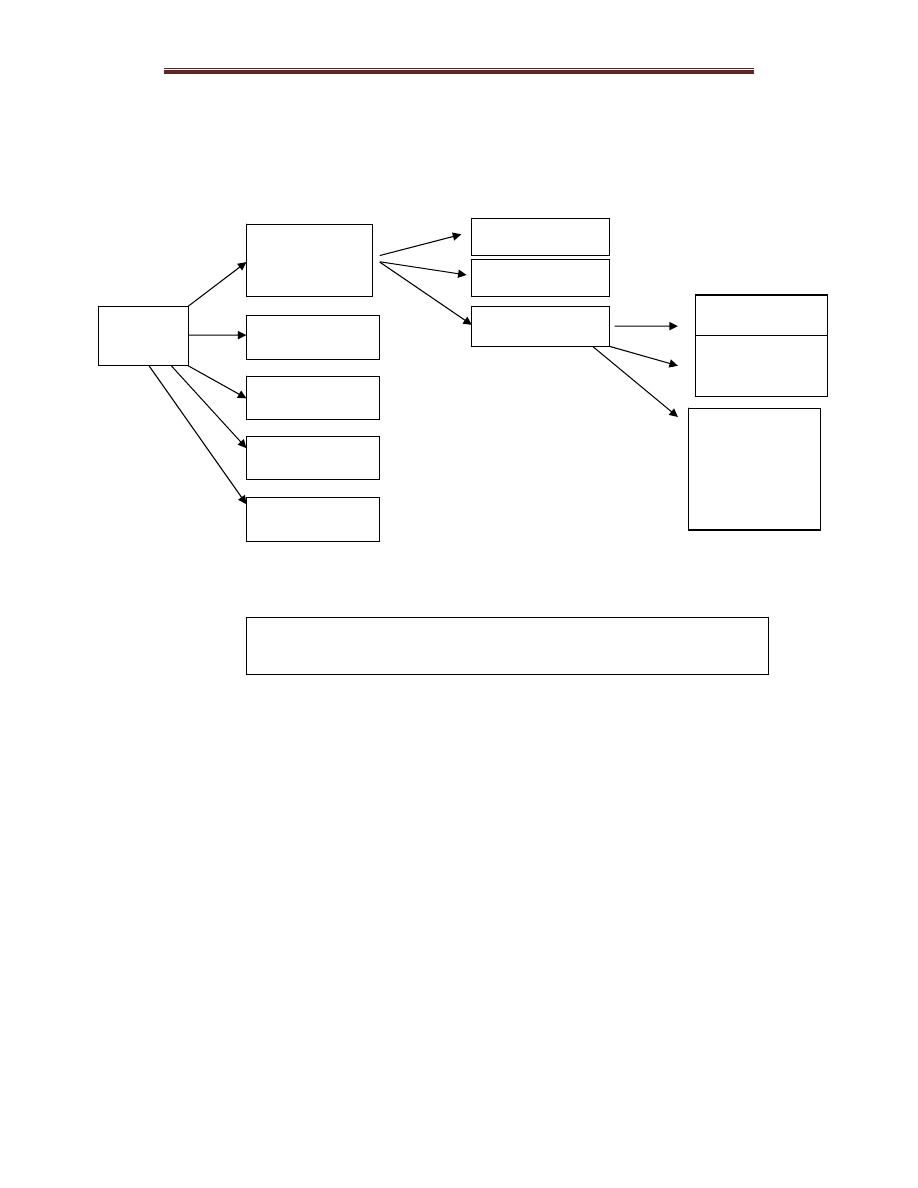
Types of shock according to their underline cause:
1-Hypovolemic shock: which include
I-Hemorrhagic shock: Hemorrhage is the most common
cause of hypovolemic shock. Hemorrhage decreases the filling
pressure of the circulation and, as a consequence, decreases
venous return. As a result, the cardiac output falls below normal.
II-Hypovolemic caused by plasma loss: Loss of plasma from
the circulatory system, even without loss of red blood cells, can
sometimes be severe enough to reduce the total blood volume.
Severe plasma loss occurs in the following conditions:
A-Intestinal obstruction is often a cause of severely reduced
plasma volume.
B-severe burns cause loss of large amount of plasma from the
burned areas.
C-Dehydration: Some of the causes of this type of shock are
(1) excessive sweating, (2) fluid loss in severe diarrhea or
vomiting, (3) excess loss of fluid by nephrotic kidneys, (4)
inadequate intake of fluid and electrolytes, or (5) destruction of
the adrenal cortices, with loss of aldosterone secretion and
consequent failure of the kidneys to reabsorb sodium, chloride,
and water.
III-Traumatic shock: caused by extensive contusion of the
body can damage the capillaries sufficiently to allow excessive
loss of plasma into the tissues. This results in greatly reduced
plasma volume, although there might also be a moderate degree
of concomitant neurogenic shock caused by the pain.

Dr. Zainab F. Hassan Lecture Four
2
2-Cardiogenic shock. This circulatory shock caused by
inadequate cardiac pumping. after acute heart attacks and often
after prolonged periods of slow progressive cardiac
deterioration, the heart becomes incapable of pumping even the
minimal amount of blood flow required to keep the body alive.
all the body tissues begin to suffer and even to deteriorate. Once
a person develops cardiogenic shock, the survival rate is often
less than 15 per cent.
3-Neurogenic shock. sudden loss of vasomotor tone throughout
the body, resulting especially in massive dilation of the veins
lead to Diminish venous return cause decrease cardiac output.
(Diminished venous return caused by vascular dilation is called
venous pooling of blood).causes of neurogenic shock include:a-
deep general anesthesia. b. Spinal anesthesia. C. Brain damage
that cause vasomotor depression.
4-Anaphylactic shock is an allergic condition results from an
antigen-antibody reaction that takes place immediately after an
antigen to which the person is sensitive enters the circulation.
This antigen-antibody reaction stimulate mast cell and
basophiles to release histamine which cause massive
vasodilatation and increased capillary permeability, with rapid
loss of fluid and protein into the tissue spaces.
5-Septic shock. This refers to widely disseminated bacterial
infection to many areas of the body by the blood and causing
extensive damage. Examples of causes of septic shock include
Peritonitis caused by rupture of the gastrointestinal system and
spread of a skin infection such as streptococcal or
staphylococcal infection .A special type of septic shock is
endotoxin shock this is caused especially by gram negative
bacteria mainly colon bacilli that contain a toxin called
Dr. Zainab F. Hassan Lecture Four
3
endotoxin , as in strangulation of gut, this endotoxin on entering
the circulation cause an effect similar to anaphylaxis.
Shock
Hypovolemic
shock
hemorrhagic
Traumatic
Plasma loss
Cardiogenic
Neurogenic
Anaphylactic
Septic shock
Dehydration:
(e.g)diarrhea and
vomiting,
nephrotic
syndrom
Intestinal
obstruction
Sever burn
Fig-1 Diagram showing types of circulatory shock
