
1
Assessment of malnutrition
Causes of malnutrition:
Major causes poverty – food process – dietary practices.
Consequences of health issues like gastroenteritis – chronic illness – HIV.
Diarrhea and other infections.
Parasitic infections.
Abnormal nutrient loss.
Lack of adequate breast feeding.
Degree of malnutrition:
Mild malnutrition abdominal sub-cutaneous fat is decreased.
Moderate malnutrition Thigh and buttock sub-cutaneous fat is decreased.
Severe malnutrition old face appearance.
Protein and calories deficiency:
Kwashiorkor (protein deficiency) change in mod – dull patient – loss of appetite –
skin change (dermatitis) – change in skin color – thin hair – wasting – liver enlargement
- focal edema (swelling in the limbs and belly).
Marasmus (calories deficiency) good appetite – alert – low weight – severe wasting
– little or no edema – minimal subcutaneous fat – severe muscle wasting.
Marasmic-Kwashiorkor (Protein and calories deficiency) weight less than 60% of
ideal weight – edema.
Ibnlatef
Notes
Pediatrics

2
Vitamins deficiency:
Vit A white spot in the eye.
Vit B1 (thiamine) beriberi "dry & wet”.
Vit B2 angular stomatitis – glossitis.
Vit B3 (Niacin) pellagra "diarrhea, dementia, dermatitis".
Vit B6 neurological change.
Vit B7 (Biotin) hypotonia, ataxia.
Vit B9 (folate) anemia.
Vit B12 Megaloblastic anemia.
Vit C gum hypertrophy.
Vit D rickets rosary – widening of wrest – developmental delay – bowing of the
lower limbs.
Vit E ecchymosis – petechiae.
Vit K bleeding.
Minerals deficiency:
Iron iron deficiency anemia.
Zinc acro-dermatitis in napkin area ((also occur with candidiasis and atopy like
contact dermatitis)).
General signs of malnutrition:
Face moon face (kwashiorkor) – simian face (marasmus).
Eye dry eye – pale conjunctiva – Bitot's spots (Vit A) peri-orbital edema.
Mouth Angular stomatitis – cheilitis – glossitis – parotid enlargement – spongy
bleeding gums (Vit C).
Teeth enamel mottling – delayed eruption.
Hair dull – sparse – brittle – hypo-pigmentation – flag sign – alopecia.
Skin loose and wrinkled (marasmus) – shiny and edematous (kwashiorkor) dry –
poor wound healing – erosions – hypo or hyper pigmentation.
Nail koilonychia – thin and soft nail plates – fissures or ridges.
Musculature muscles wasting (buttocks and thigh).
Skeletal deformities (Vit C, Vit D, Calcium deficiency).
Abdomen distended – hepatomegaly – fatty liver – ascites.
Cardiovascular bradycardia – hypotension – reduced cardiac output – small vessel
vasculopathy.
Neurologic global developmental delay – loss of knee and ankle reflexes – poor
memory.
Hematological pallor – petechiae – bleeding diathesis.
Behavior lethargic – apathetic.
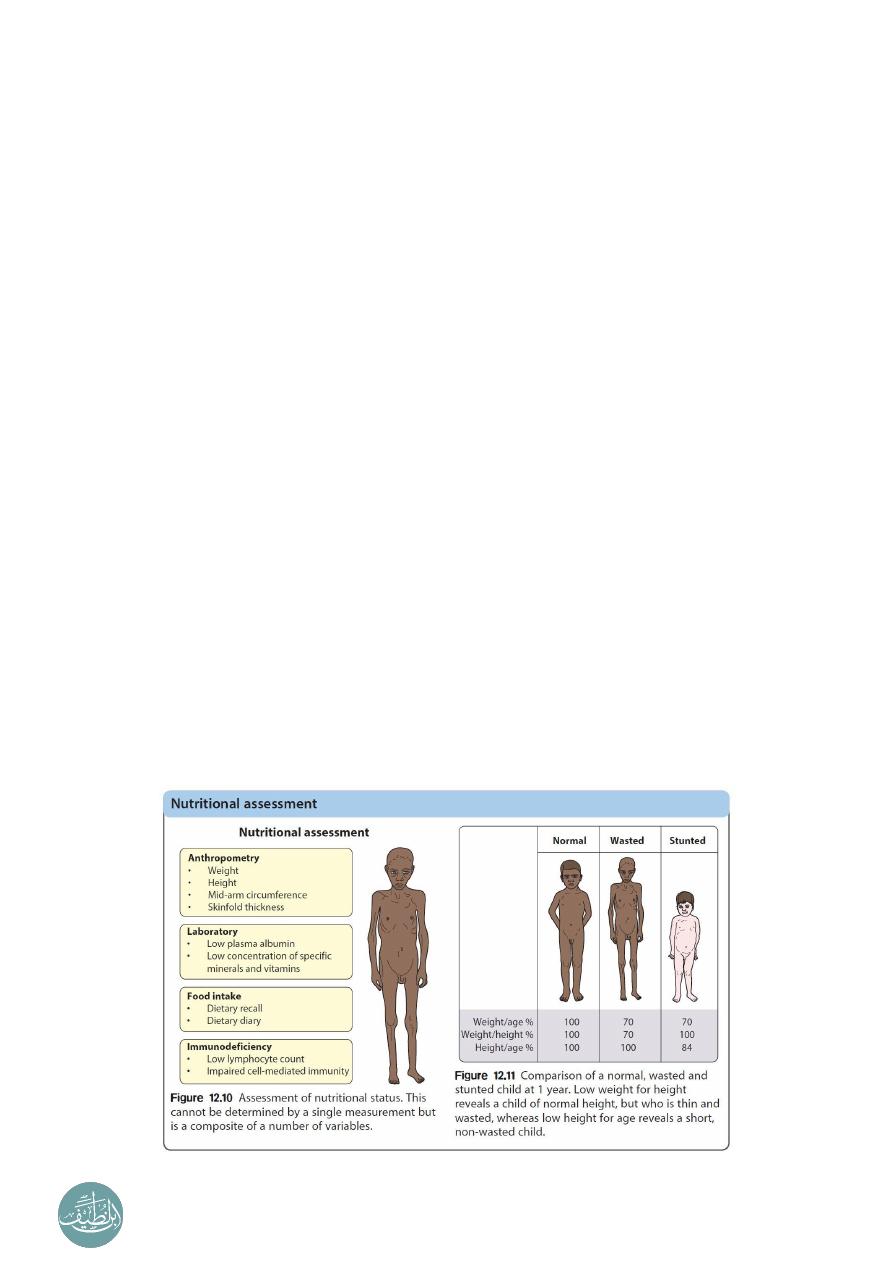
3
Approach and management to faltering growth:
Recheck wright-plot weight against centile chart.
Check type and amount of feeding.
Observe feeding technique.
Assess stool.
Examine for underlying illness – appropriate investigations.
Consider admission to observe response to feeding.
Dietician involvement.
Inform general practitioner / health visitor / community nurse.
Calories calculation for baby:
Normal baby need (100-120 kcal/kg) - preterm baby (150) - less than 6 months age
(110) - after one year (100).
Each ounce = 30 cc of water = 20 kcal.
We multiply the number of daily requirement of calories (100-120 kcal/kg) by the ideal
weight of the child.
To calculate the ideal weight you should use the chart or use the following equation
ideal weight of the infant = (age in months + 9)/2.
Then we divide it by 20 (the number of ounces that the milk spoon carry)( Ounce=20
Kcal), the result will be the numbers that the child should feed in the day.
Example in the child ideal wt. is 5kg , 5*100 = 500 kcal/day, divided by 20, this
equals to 25 numbers, that means if the child feeds 5 times/day every bottle should
contain 5 numbers.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
www.facebook.com/ibnlatef
https://goo.gl/RpvNsl
