Lab 10
Mammals
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Super class: Tetrapoda
Class: Mammalia
Sub class: Eutheria
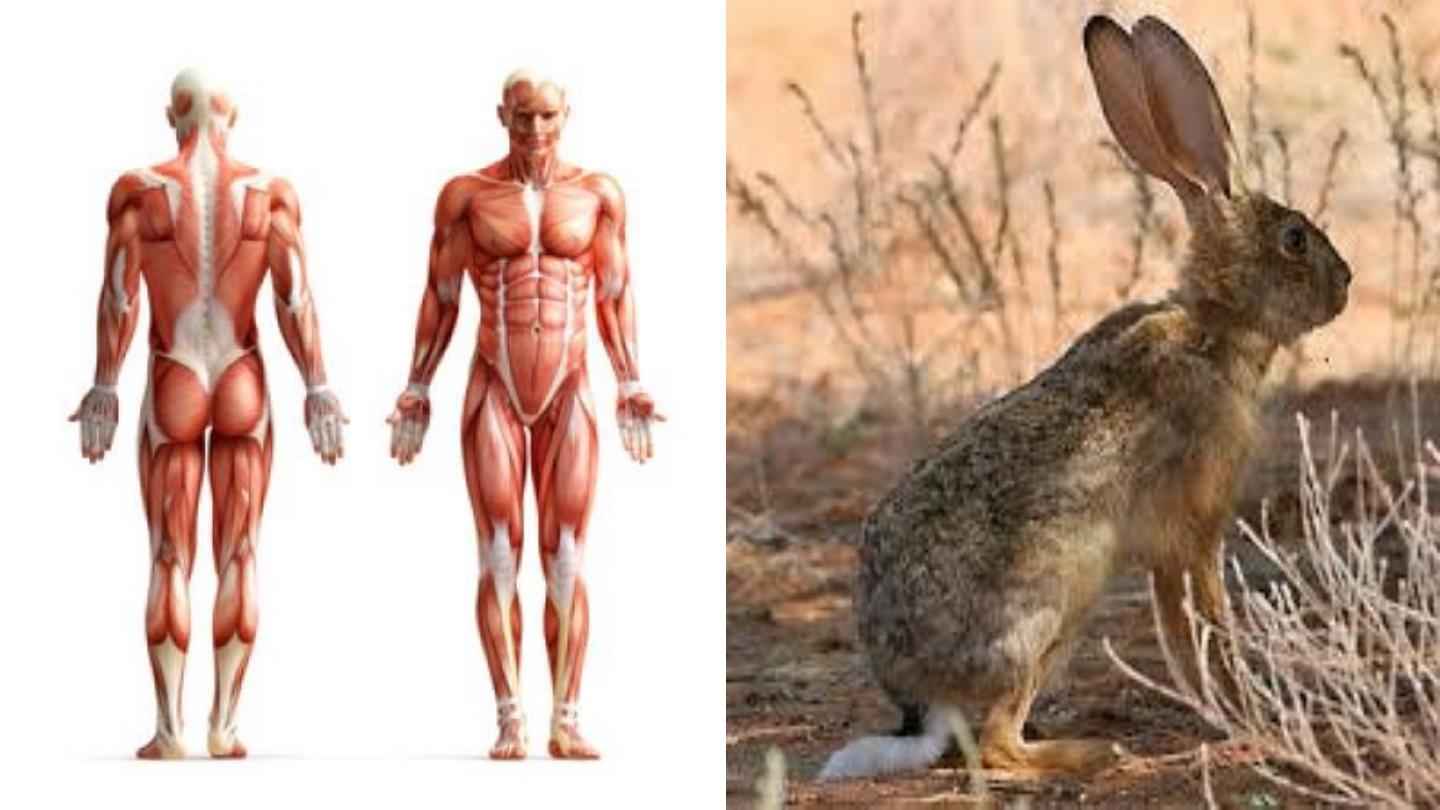
Order: Lagmorpha
Scientific name: Lepus capensis arabicus
Common name: Arabic rabbit
II. Order: Primates
Scientific name: Homo sapiens
Common name: Human

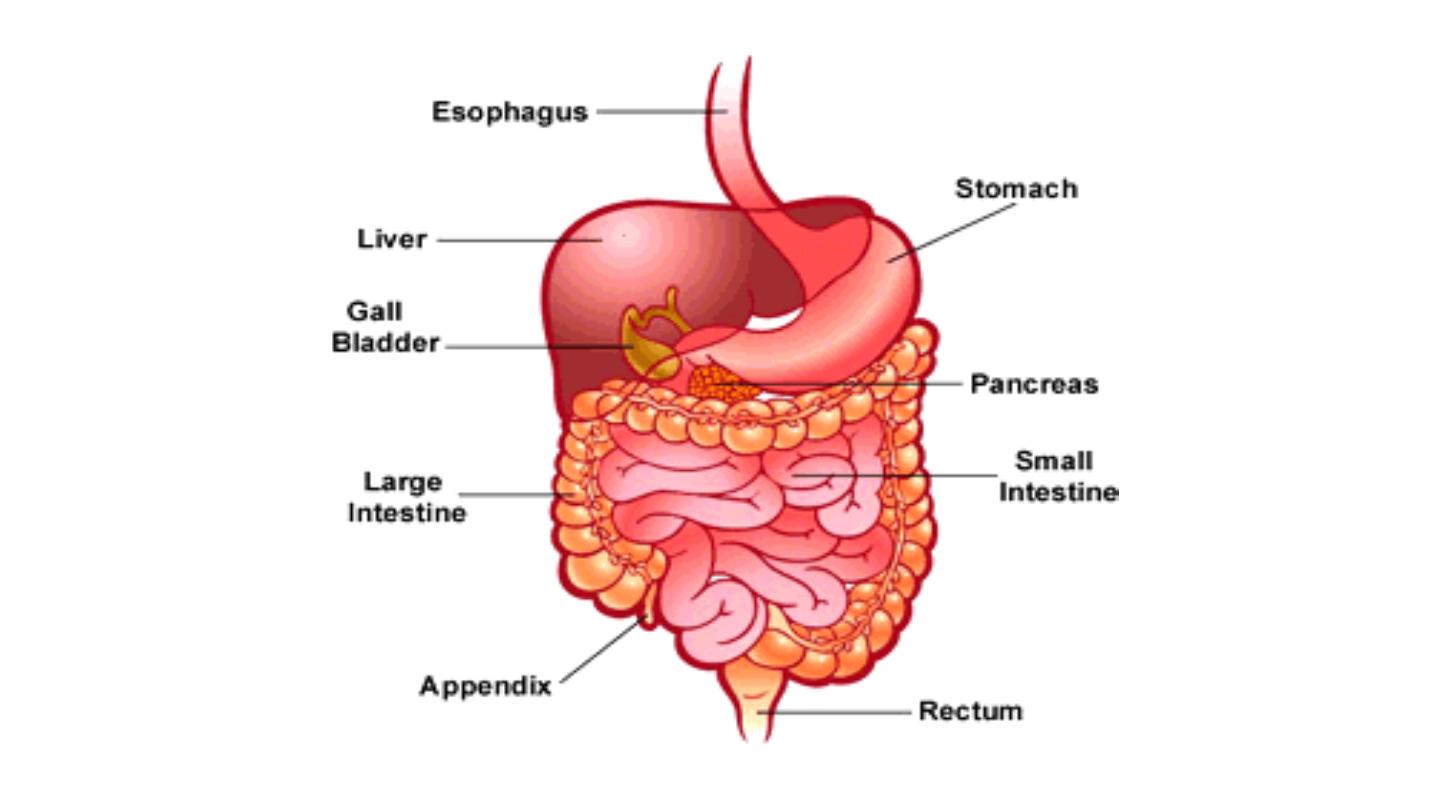
Digestive System
• The oral cavity begins at the mouth & ends at the
pharynx.
• Pharynx: an epiglottis is positioned over the glottis so
that, when a mammal swallows, the epiglottis blocks the
glottis (which prevents food or liquids from entering the
trachea).
• Esophagus: A distensible
connecting the
pharynx & the stomach.
• Stomach: A muscular chamber at end of esophagus.
• The intestine is located between the stomach & the anus.

long & coiled and differentiated into
duodenum, jejunum, & ileum.
• The large intestine (colon and rectum) is often relatively long
(but not as long as the small intestine). A caecum is often
present at the junction of the small & large intestines.
• Liver & gall bladder: liver produces bile which is stored in the
gall bladder.
• Pancreas: secretes pancreatic juice into the intestine
•
The intestine opens directly to the exterior via anus.
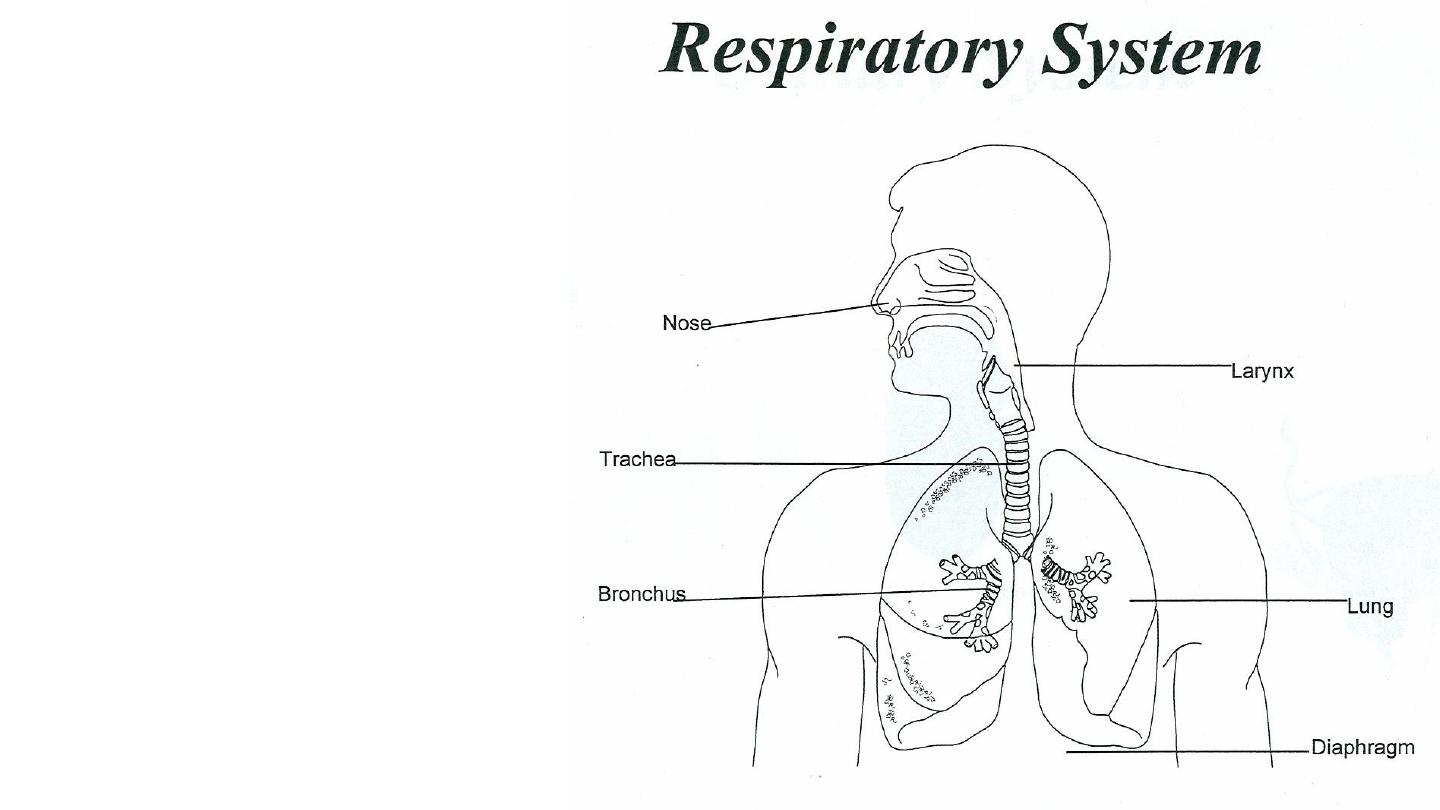
• Nostrils
• Nasopharynx
• Glottis
• Trachea
• Left & right bronchi
• Bronchioles
• Alveoli
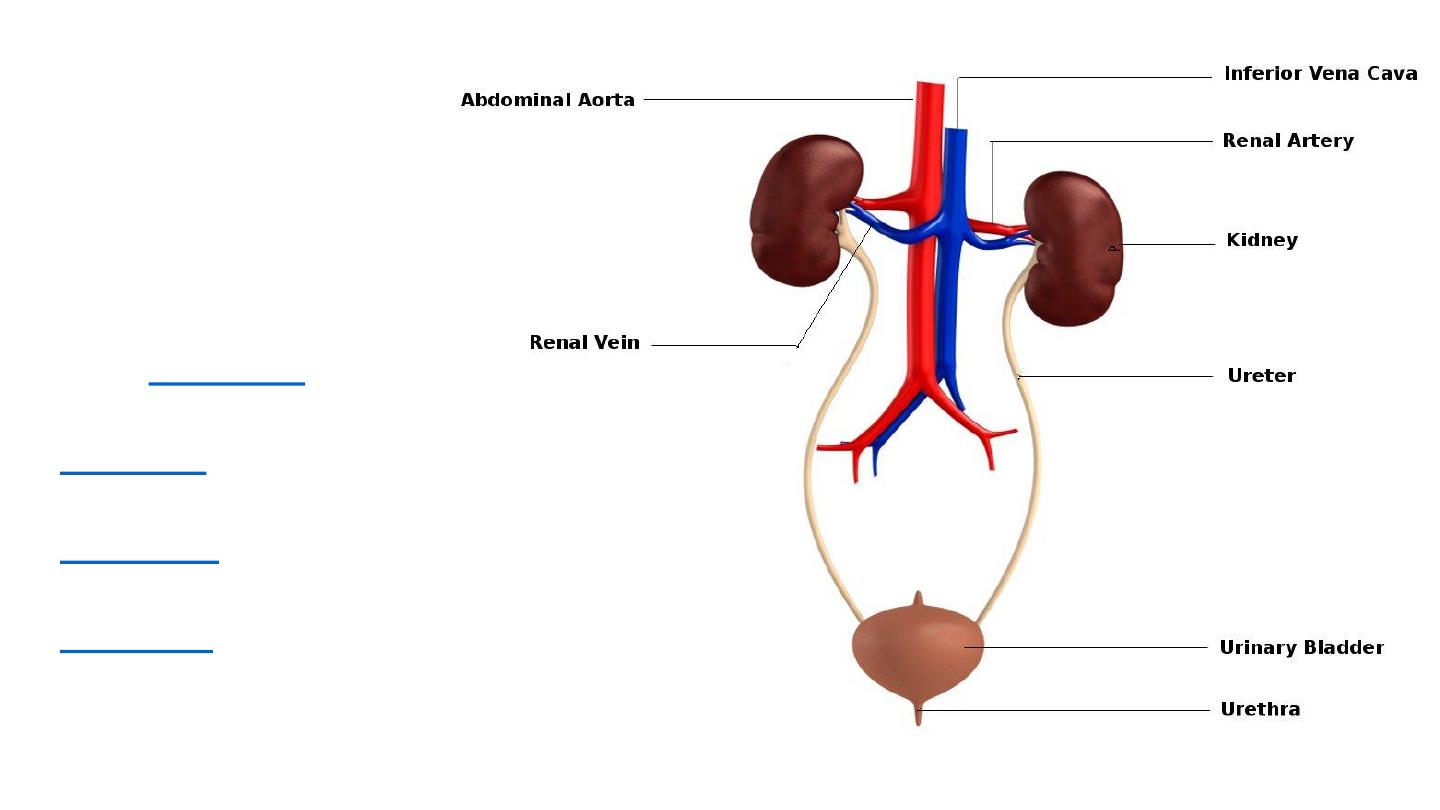
Urinary System
• In humans it includes
two
, two
, the urinary
and the

Reproductive System
Female Reproductive System
• Ovaries: The ovaries are small, oval-shaped glands that are located on
either side of the uterus. The ovaries produce eggs and hormones.
• Fallopian tubes (Oviducts): These are narrow tubes that are attached
to the upper part of the uterus and travel the ova (egg cells) from the
ovaries to the uterus.
• Uterus: The uterus is a hollow, pear-shaped organ that is the home to
a
. The uterus is divided into two parts: the cervix,
which is the lower part that opens into the vagina, and the corpus
(the main body of the uterus). The corpus can easily expand to hold a
developing baby.
• Vagina: The vagina is a canal that joins the cervix (the lower part of
uterus) to the outside of the body. It also is known as the birth canal.

Male Reproductive System
• Testes: The testes are oval organs that lie in the scrotum, secured at
either end by a structure called the spermatic cord.
• Epididymis: The epididymis is a long, coiled tube that rests on the
backside of each testis. It functions in the transport and storage of
the sperm cells that are produced in the testes.
• Vas deferens: The vas deferens is a long, muscular tube that travels
from the epididymis into the pelvic cavity, behind the bladder.
• Seminal vesicles: The seminal vesicles are sac-like pouches that
attach to the vas deferens near the base of the bladder.
• Prostate gland: The prostate gland is a walnut-sized structure that is
located below the urinary bladder in front of the rectum.
• Bulbourethral glands: The bulbourethral glands, or Cowper’s glands,
are pea-sized structures located on the sides of the urethra below the
prostate gland.
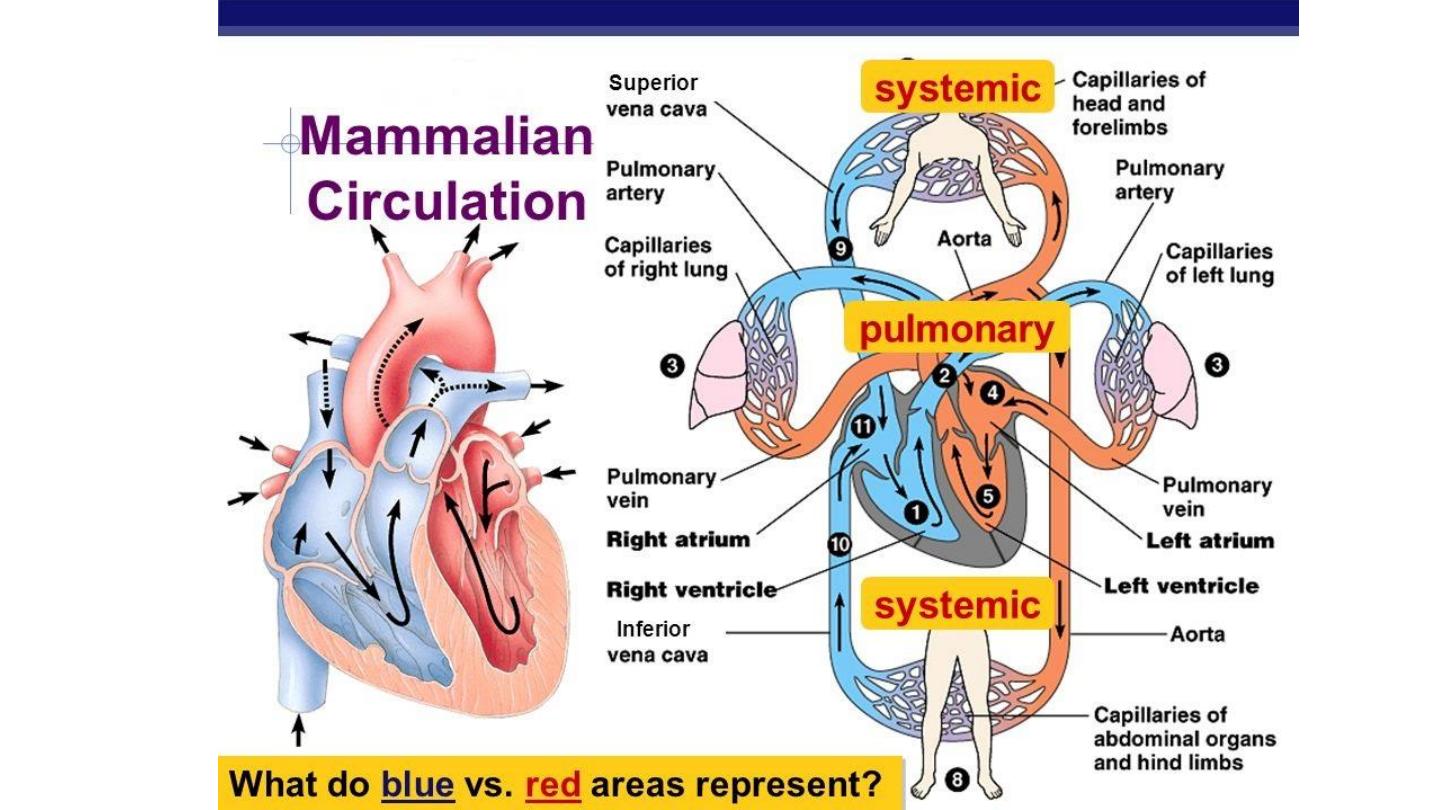
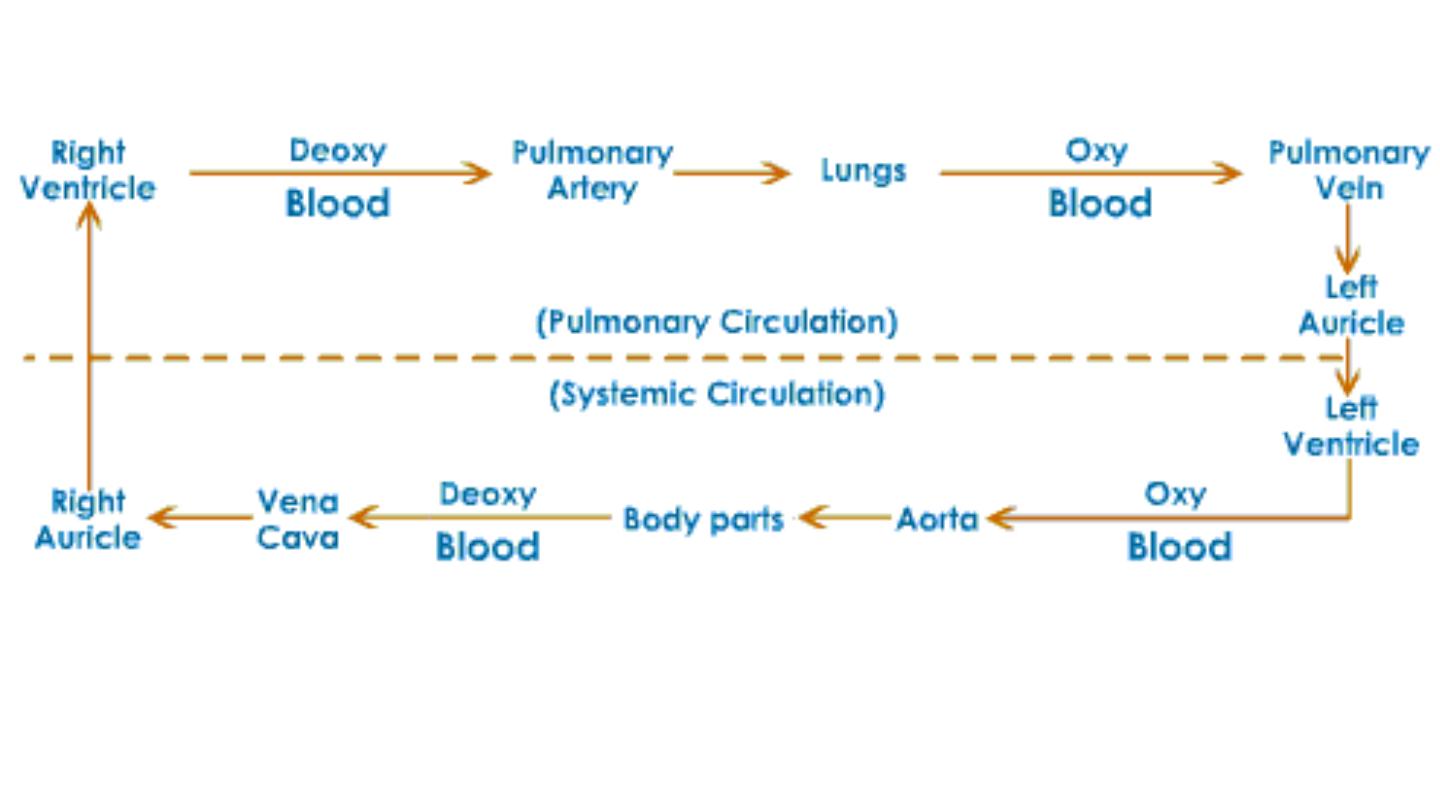
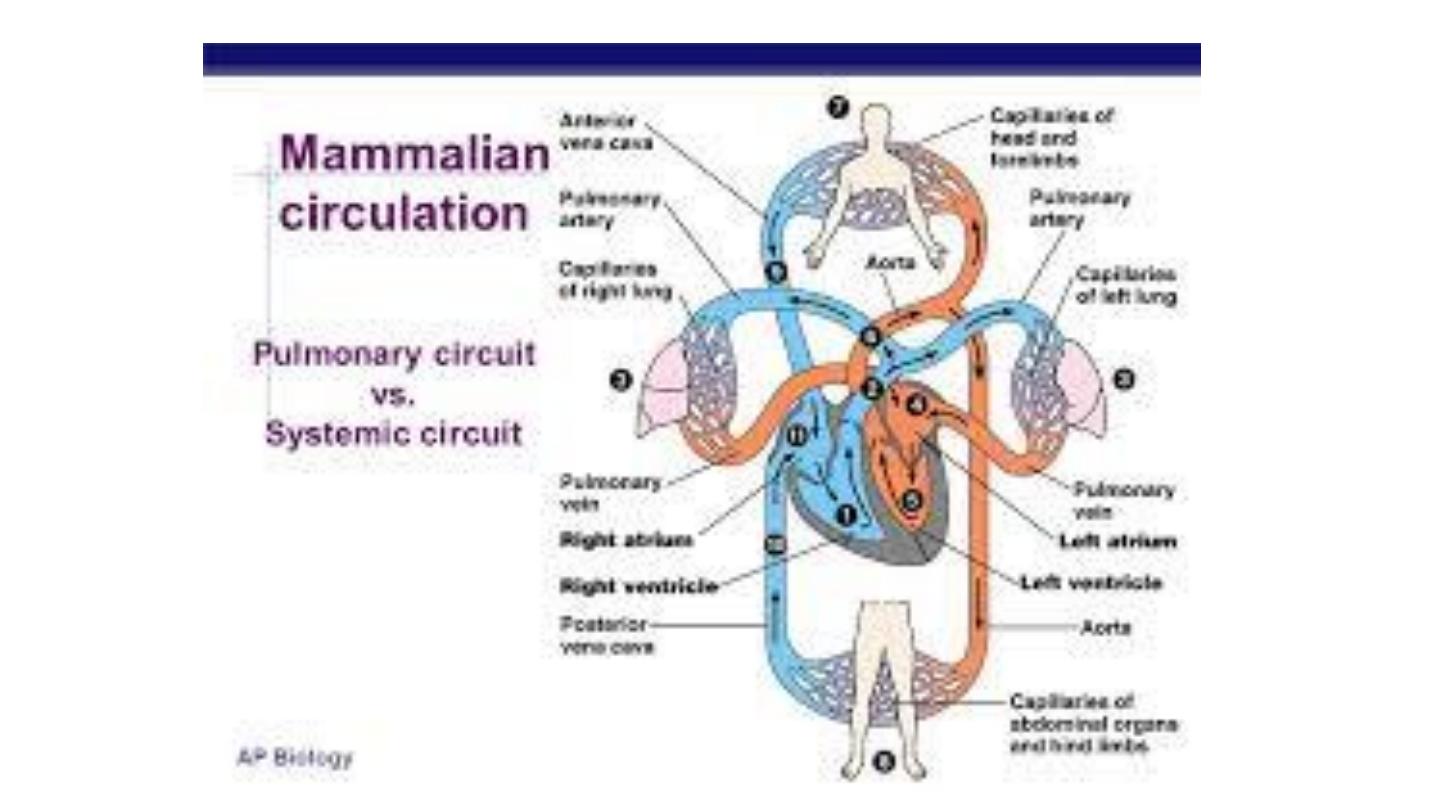
Circulatory System
Heart
• There are four chambers:
and
.
• The blood that is returned to the right atrium is
deoxygenated and passed into the right ventricle to be
pumped through the pulmonary artery to the lungs
for re-oxygenation and removal of carbon dioxide.
• The left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the
lungs which is passed into the strong left ventricle to
be pumped through the aorta to the different organs
of the body.