
Lec.16 Dr:Buthaina Al-Sabawi
Date:24/12/2016
Cellular Activity
Protein synthesis:
Protein synthesis, is the process whereby biological cells
generate new proteins; it is balanced by the loss of cellular
proteins via degradation or export.
The events involved in gene expression that results in a protein
synthesis.
1- DNA contains genetic information. The sequence of its bases
determines the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptides.
2- During transcription one strand of DNA serves as a template for
formation of mRNA. The bases in mRNA are complementary to those in
DNA, every three bases is a codon that codes for amino acid.
3- Messenger RNA (mRNA) is processed before it leaves the nucleus,
during which time the introns are removed.
4- Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries a sequence of codons to the
ribosomes, which are composed of rRNA and proteins.
5- Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules, each of which is bonded to a
particular amino acid, have anticodons that pair complementarily to the
codons in mRNA.
6- During translation, tRNA molecules and their attached amino acids
arrive at ribosomes, and the linear sequence of codons of the mRNA
determines the order in which the amino acids become incorporated
into a protein.
1
Proteins
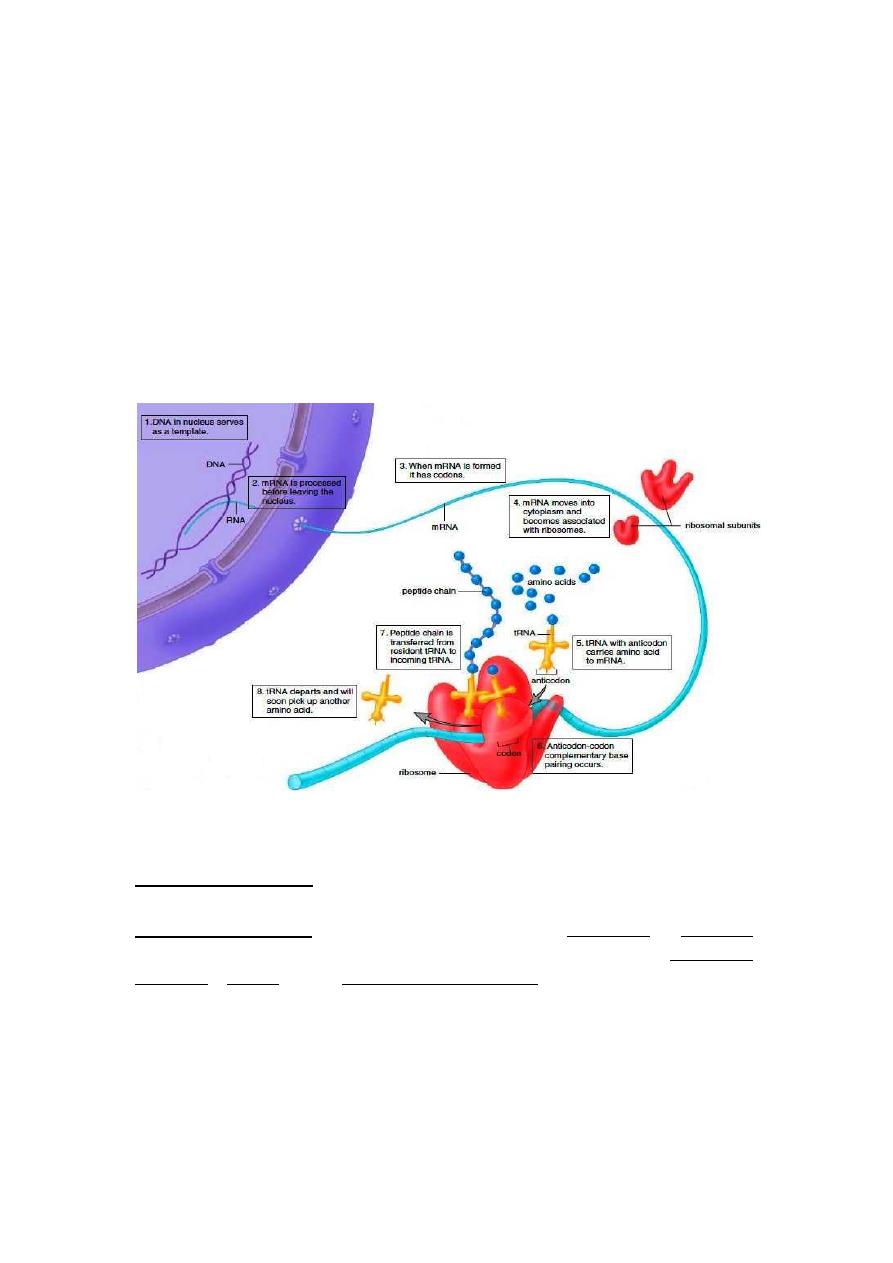
7- They have release factors that recognize the signals and terminate
Protein synthesis.
The release factors bind to a termination codon at the A site and
stimulate hydrolysis of the bond between the tRNA and the polypeptide
chain at the P site, resulting in release of the completed polypeptide
from the ribosome. The tRNA is then released, and the ribosomal
subunits and the mRNA template dissociate.
Stages of Protein Synthesis
Protein secretion:
A secretory protein is any protein, whether it be endocrine or exocrine,
which is secreted by a cell. Secretory proteins include many hormones,
enzymes, toxins, and antimicrobial peptides. Secretory proteins are
synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum.
Proteins traveled from the Golgi apparatus to the cell surface in
secretory vesicles, which then fused with the plasma membrane to release
defined contents outside of the cell.
2
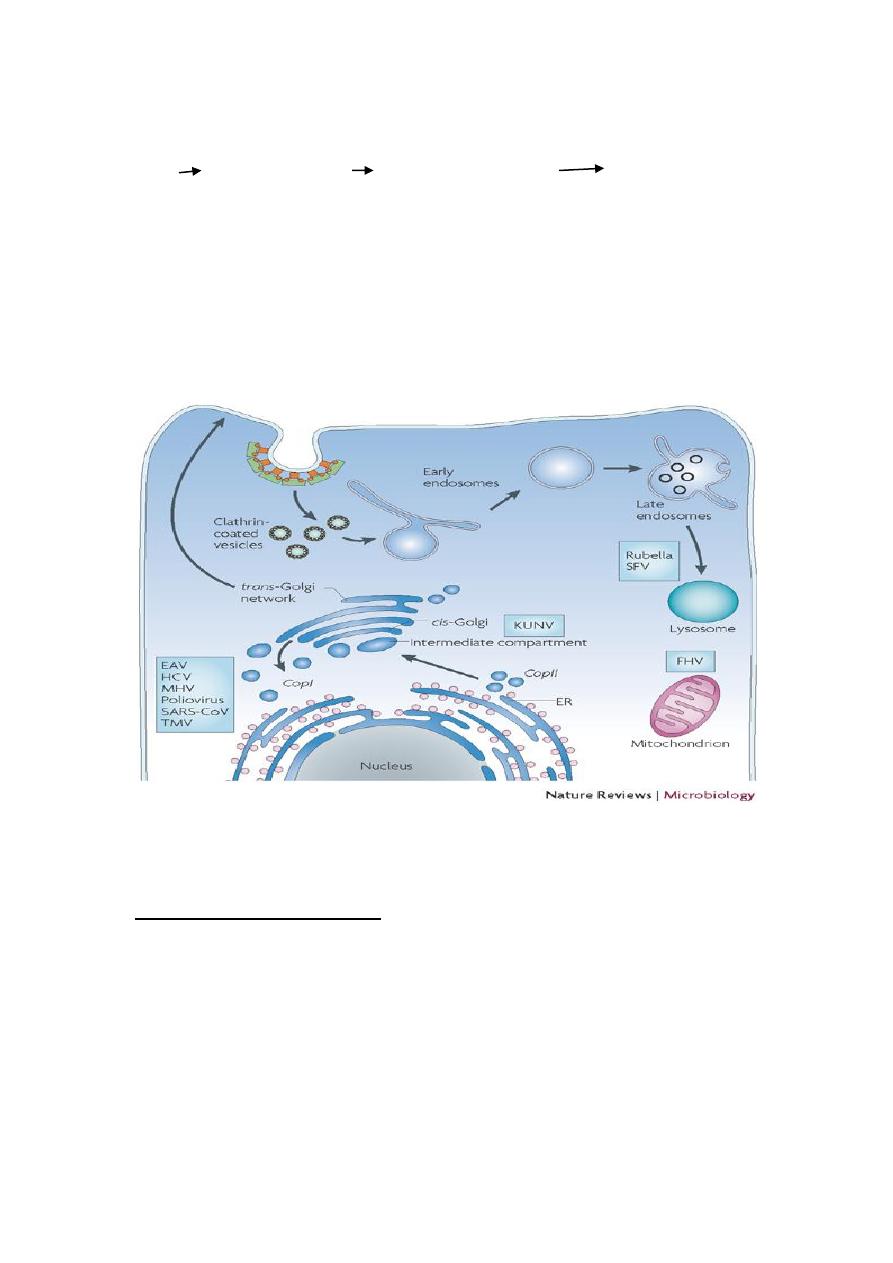
The secretory pathway:
RER Golgi apparatus secretory vesicles cell exterior.
Plasma membrane and lysosomal proteins also travel from the RER to
the Golgi apparatus and then to their final destinations.
Proteins as well as lipids and polysaccharides are transported from the
Golgi apparatus to their final destinations through the secretory
pathway. This involves, which bud from the trans Golgi network and
deliver their contents to the appropriate cellular locations.
Lipids
Lipids synthesis & secretion:
Lipids are important energy storage molecules and the major
constituent of cell membranes. They are synthesized from acetyl CoA,
which is formed from the breakdown of carbohydrates, in a series of
reactions that resemble the reverse of fatty acid oxidation.
The major product of fatty acid biosynthesis, which occurs in the cytosol
of eukaryotic cells, is the 16-carbon fatty acid palmitate.
3
The principal constituents of cell membranes (phospholipids,
spingomylin, and glycolipids) are then synthesized from fatty acids in the
endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus.
The ER is the major site at which membrane lipids are synthesized in
eukaryotic cells. Because they are extremely hydrophobic, lipids are
synthesized in association with already existing cellular membranes
rather than in the aqueous environment cytosol. They are then
transported from the ER to their ultimate destination either in vesicles
or by carrier proteins.
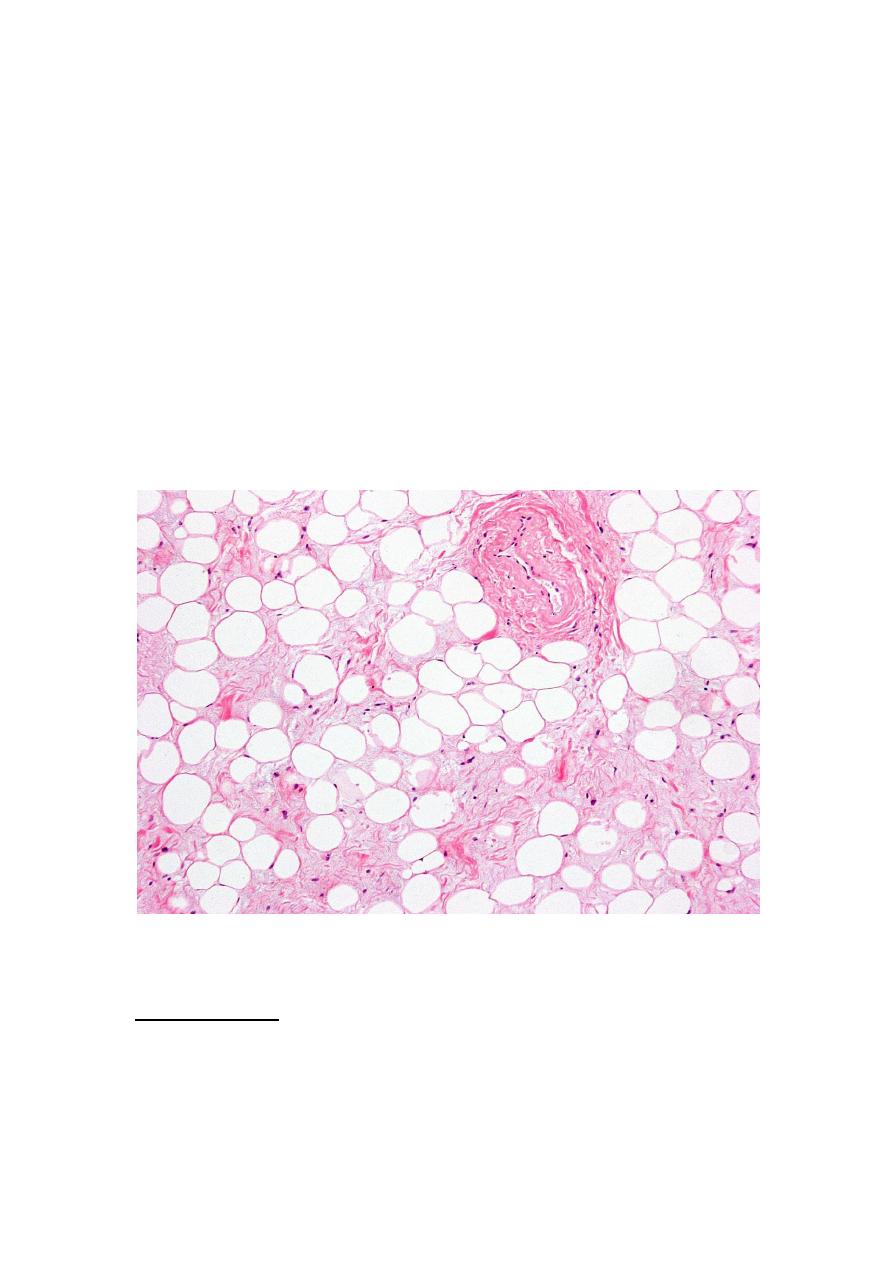
Adipose Tissue
Lipids storage:
Lipids may accumulates as non-membrane vacuoles, which appear as
large clear spaces in the cytoplasm. Large fat vacuoles are a special
4

feature of fat storage cells called adipocytes. Fat also accumulates in
certain cells such as hepatocytes in the liver in response to sublethal
metabolic damage. The most common cause in chronic high alcohol
ingestion.
