
Lec.17 Dr:Buthaina Al-Sabawi
Date:24/12/2016
Carbohydrates Biosynthesis
In addition to being obtained directly from food or generated by
photosynthesis, glucose can be synthesized from other organic
molecules. In animal cells, glucose synthesis (gluconeogensis) usually
starts with lactate (produce by an anaerobic glycolsis).
Amino acid (produced by the breakdown of proteins) or glycerol
(produced by the breakdown of lipids).
Glucose in the body undergoes catabolism in all peripheral tissue,
particularly in brain, muscle and kidney to produce ATP. Excess glucose is
charged into glycogen by the process of glycogenesis (anabolism) and
stored as glycogen in liver and muscle or converted to fatty acid and is
stored in adipose tissue as triglycerides. Epinephrine and glycogen
hormones are secreted to stimulate the conversion of glycogen to
glucose when blood glucose level become low. This process is called
glucogenolysis (catabolism).
Gluconeogensis involves the conversion of pyruvate to glucose-
essentially the reverse of glucolysis.
In both plant & animal cells, glucose is stored in the form of
polysaccharides (starch and glycogen, respectively).
The synthesis of polysaccharides like that of all other macromolecules is
an energey-requiring reaction.
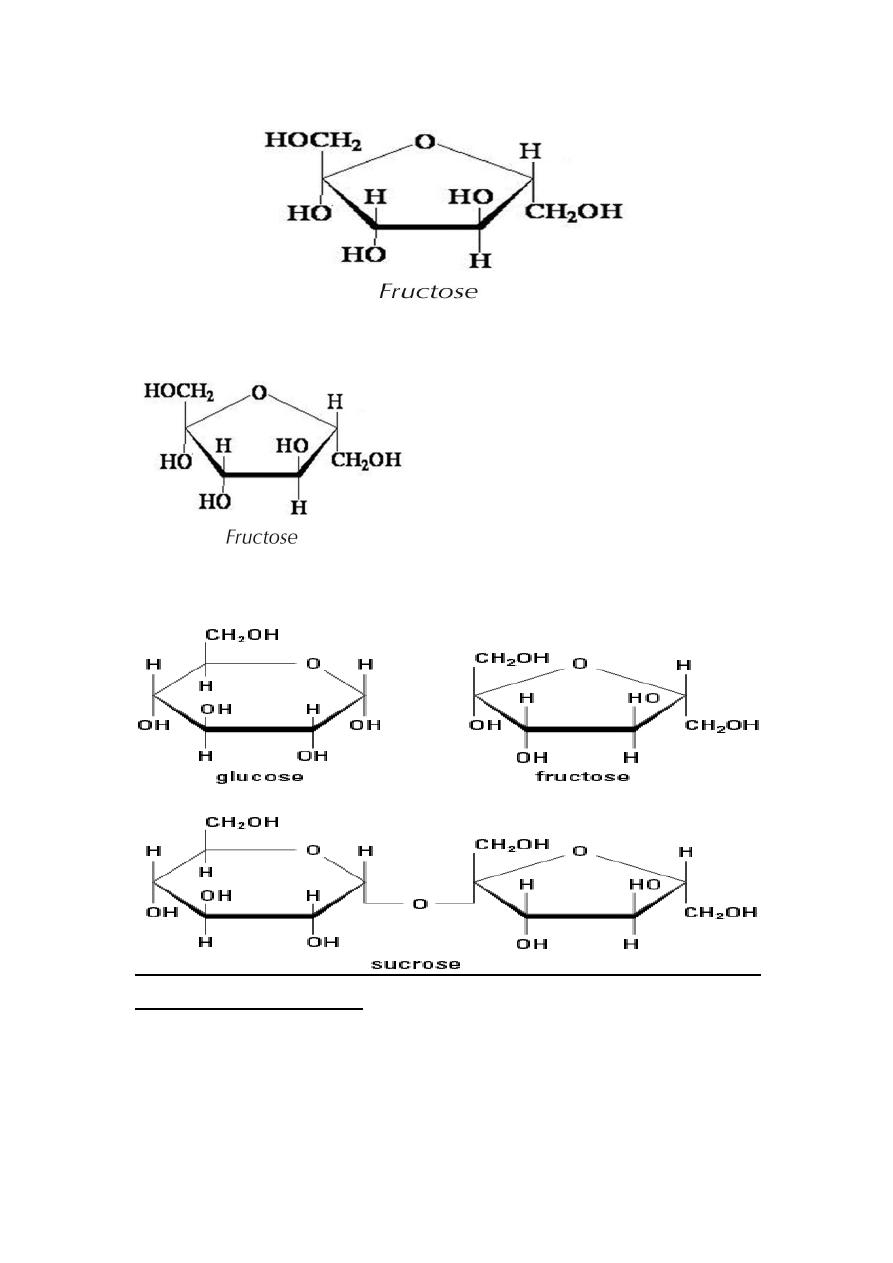
The linkage of two sugars by glycosidic bond can be written as a
dehydration reaction, in which H2O is removed.
5
(5)
Carbohydrates storing:
Glycogen, a polymer and storage product of glucose, forms as granules
in the cell cytoplasm and is only visible by electron microscopy.
Demands for energy are met by conversion of glycogen to glucose.
6
In a certain cells, the presence of large amounts of glycogen causes pale
staining or apparent vacuolation of cell cytoplasm. Glycogen can be
stained by the PAS method.
Nucleic Acids
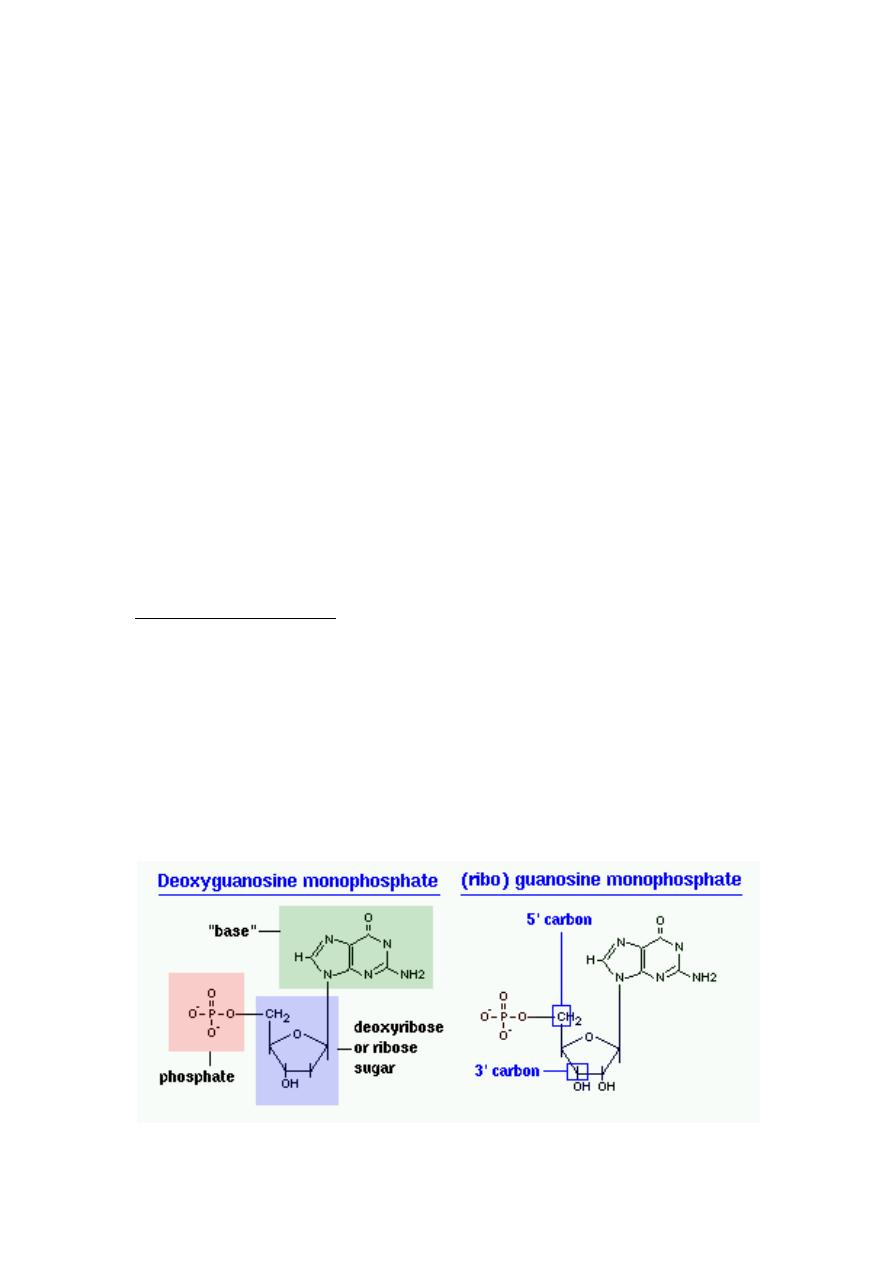
The precursors of nucleic acids, the nucleotides, are composed of
phosphorylated five - carbon sugars joined to nucleic acid bases.
They are obtained from:
Dietary source
Or reused following nucleic acid breakdown.
The starting point for nucleotide synthesis is the phosphorylated sugar
ribose-5- phosphate.
Different pathways then lead to the synthesis of purine and pyrimidine
ribonucleotides, which are the immediate precursors for RNA synthesis.
Thesis ribonucleotides are converted to deoxyribonucleotides, which
serve as the monomeric building blocks of DNA.
Watson & Crick Model:
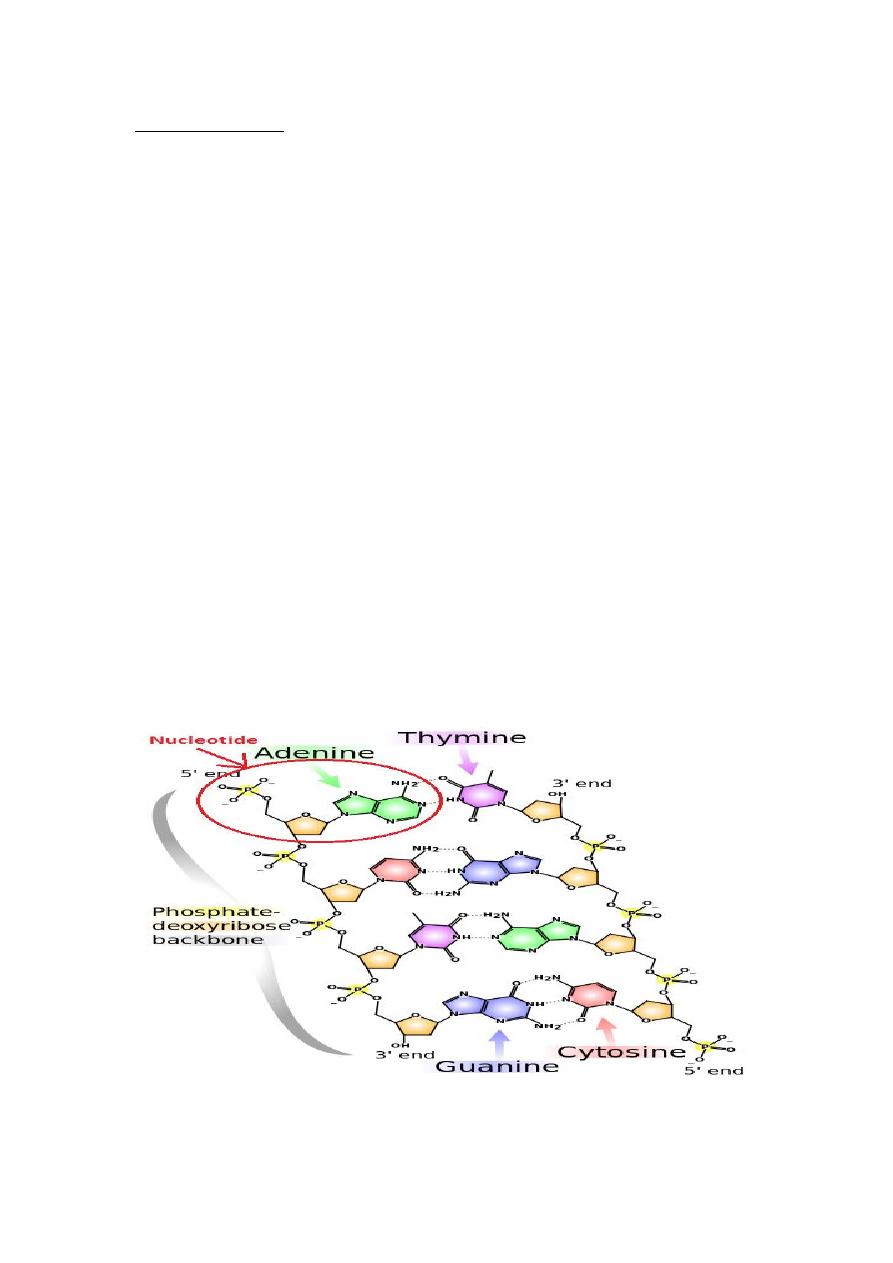
The Watson & Crick model shows that DNA is a double helix with sugar-
phosphate backbones on the outside and paired bases on the inside.
Chargaff”s rules said that A=T and G=C. The model shows that A is
hydrogen-bonded to T and G is hydrogen bonded to C.
This is so-called complementary base pairing means a purine is always
bonded to pyrimidine.
7
DNA Replication:
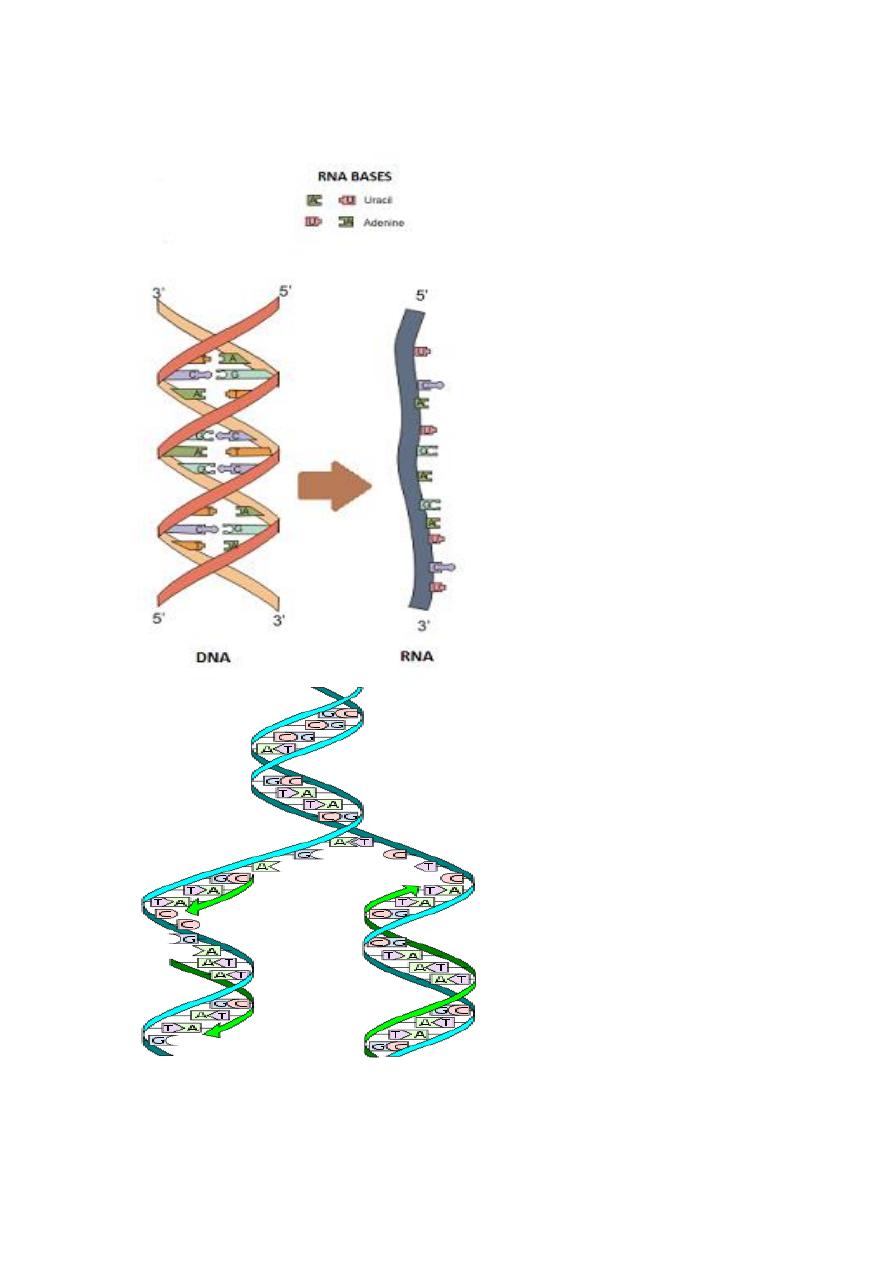
It has now been confirmed that DNA is replicated by means of
complementary base pairing. During replication, each old DNA strand of
the parent molecules serves as a template for a new strand in a
daughter molecule. DNA replication is termed semiconsevative
replication because each daughter helix contains an old strand and a
new strand.
Replication requires the following steps
1- Unwinding:
The old strands that make up the parent DNA molecule are unwound
and “unzipped” (the weak hydrogen bonds between the paired bases
are broken). There is a special enzyme
called helicase that unwinds the molecule.
2- Complementary base pairing:
New complementary nucleotides, always present in the nucleus, are
positioned by the process of complementary base pairing.
3- joining:
The complementary nucleotides join to form new strands. Each daughter
DNA molecule contains an old strand and a new strand.
(8)
(9)
10
