1
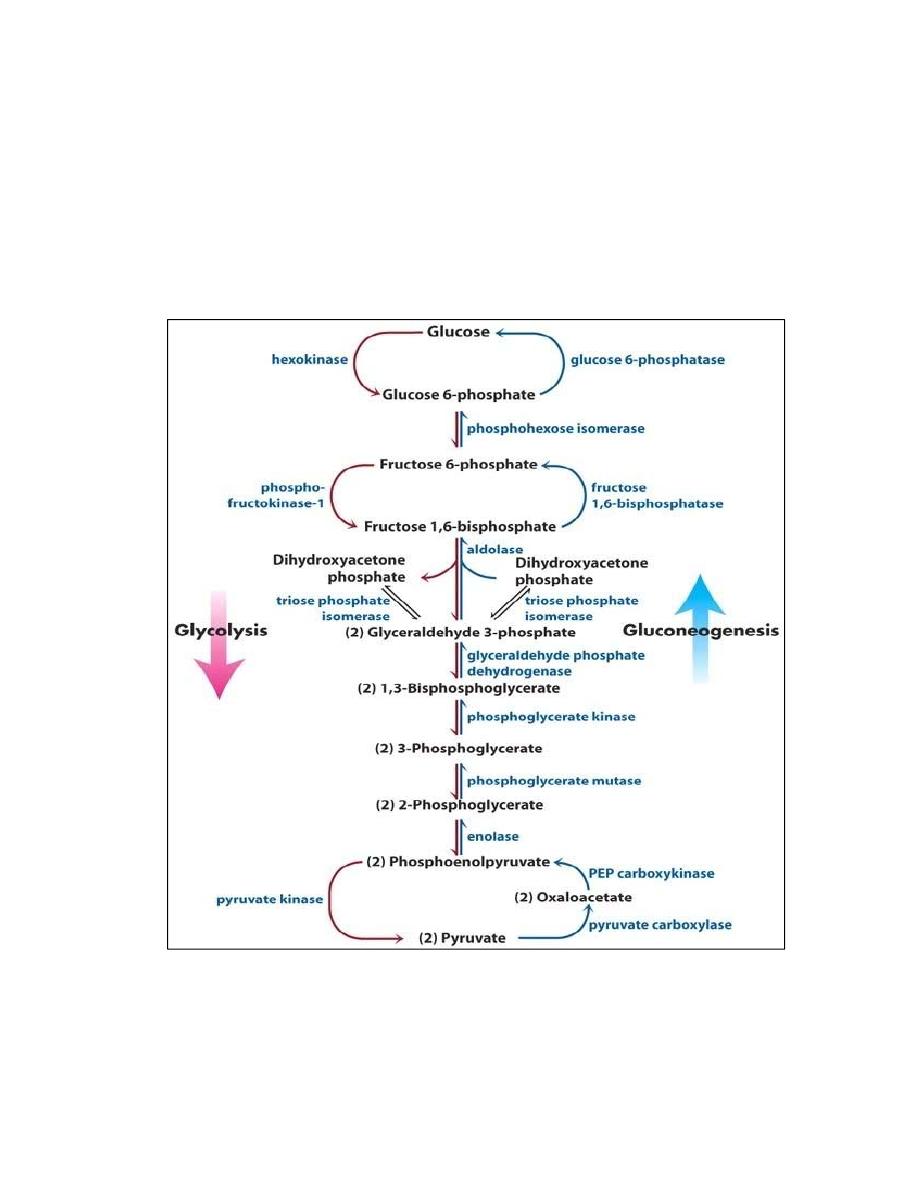
GLUCONEOGENESIS
It is the process by which glucose molecules are produced from non-
carbohydrate precursors, which include lactate, glucogenic amino acids,
glycerol part of fat and propionyl CoA derived from odd chain fatty
acids.
Gluconeogenesis occurs mainly in the liver, and to a lesser extent in the
kidney. The pathway is partly mitochondrial and partly cytoplasmic.
Gluconeogenesis involves several enzymes of glycolysis, but it is not a
reversal of glycolysis. The irreversible steps in glycolysis are
circumvented by four enzymes which are designated as the key enzymes
of gluconeogenesis, these enzymes are:
1
2
3
4

2
1. Pyruvate Carboxylase
Pyruvate in the cytoplasm enters the mitochondria. Then, carboxylation
of pyruvate to oxaloacetate is catalysed by a mitochondrial enzyme,
Pyruvate carboxylase. It needs the co-enzymes biotin and ATP.
2. Phosphoenol Pyruvate Carboxy Kinase (PEPCK)
In the cytoplasm, PEPCK enzyme converts oxaloacetate to phosphoenol
pyruvate by removing a molecule of CO2. GTP donates the phosphate.
The net effect of these two reactions is the conversion of pyruvate to
phosphoenol pyruvate. This circumvents the irreversible step 9 of
glycolysis.
Partial Reversal of Glycolysis
The phosphoenol pyruvate undergoes further reactions catalyzed by the
glycolytic enzymes to form fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (see glycolysis
steps 8,7,6,5 and 4; all these reactions are freely reversible).
3. Fructose-1, 6-bisphosphatase
Fructose-1, 6-bisphosphate is then converted by fructose 1,6-
bisphosphatase to form fructose -6-phosphate. This will bypass the step
of PFK reaction (see step 3 of glycolysis). Then fructose-6-phosphate is
isomerized to glucose-6-phosphate by the freely reversible reaction
catalyzed by hexose phosphate isomerase (step2 in glycolysis).
4. Glucose-6-phosphatase Reaction
The glucose 6-phosphate is hydrolysed to free glucose by glucose-6-
phosphatase.
Glucose-6-phosphatase is active in liver. It is also present in kidney and
intestinal mucosa to a lesser extent, but it is absent in muscle.
Substrates for Gluconeogenesis
Lactate and glucogenic amino acids are the most important substrates for
gluconeogenesis.
1. Lactate
The lactate formed in the muscle is transported to the liver through Cori's
cycle. In the liver cell lactate dehydrogenase converts lactate to pyruvate.
The pyruvate enters the gluconeogenic pathway to form glucose.

3
2. Glucogenic amino acids
Glucogenic amino acids are alanine, glutamic acid, aspartic acid, etc.
When glucose is not readily available (starvation or diabetes mellitus),
the glucogenic amino acids are transaminated to corresponding carbon
skeletons. These then enter the TCA cycle and form oxaloacetate or
pyruvate. Alanine released from the muscle is the major substrate for
gluconeogenesis.
3. Glycerol
The glycerol part of fat is phosphorylated in the liver cytosol by ATP to
glycerol-3-phosphate. It is then oxidized to dihydroxy acetone phosphate
by NAD+ dependent dehydrogenase and enter pathway to form lastly
glucose.
4. Propionyl CoA
Propionyl CoA is formed either from odd chain fatty acids and carbon
skeleton of some amino acids. It is converted to succinyl CoA which also
enter TCAcycleto form oxaloacetate and terminate by formation of
glucose. It is a minor source for glucose
Notes about Gluconeogenesis
1. Only liver can replenish blood
glucose through gluconeogenesis,
because glucose-6- phosphatase is present mainly in liver. So liver plays
the major role in maintaining the blood glucose level.
2. During starvation, Gluconeogenesis maintains normal blood glucose
level. The stored glycogen is depleted within the first 12-18 hours of
fasting. On prolonged starvation, the gluconeogenesis is speeded up and
protein catabolism provides the substrates ( glucogenic amino acids).
3. Energy Requirement, The reactions catalyzed by Pyruvate
carboxylase, phosphoenol Pyruvate carboxy kinase and phospho
glycerate kinase require one ATP each; so 3 ATPs are used by one
pyruvate residue to produce one-half molecule of glucose; or 6 ATPs are
required to generate one glucose molecule.
2 pyruvate →2 oxaloacetate = 2 ATP
2 oxaloacetate → 2 phosphoenol pyruvate = 2 ATP
2 ( 3-phosphoglycerate) →2 ( 1,3-bisphospho glycerate) = 2 ATP
Total = 6 ATP

4
Regulation of Gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis and glycolysis are reciprocally regulated so that one
pathway is relatively inactive when the other is active.
Pyruvate Carboxylase
It is an allosteric enzyme. Acetyl CoA is an activator of Pyruvate
carboxylase so that generation of oxaloacetate is favored when acetyl
CoA level is sufficiently high.
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase
Citrate is an activator while fructose-2,6-bisphosphate and AMP are
inhibitors. All these three effectors have an exactly opposite effect on the
phosphofructokinase (PFK) .
Hormonal Regulation of Gluconeogenesis
The hormones glucagon and glucocorticoids increase gluconeogenesis.
Glucocorticoids induce the synthesis of hepatic amino transferases
thereby providing substrate for gluconeogenesis. The high glucagon-
insulin ratio also favors induction of synthesis of gluconeogenic enzymes
(PEPCK, Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase and glucose-6-phosphatase).At the
same time, synthesis of glycolytic enzymes HK, PFK and PK are
depressed. Insulin inhibits this process.
Clinical Significance of Gluconeogenesis
Pyruvate carboxylase deficiency: It is seen as an inborn error of
metabolism, where mental retardation is manifested. Its incidence is 1 in
25,000 births. Lactic acidosis is noticed.
