i
7
th
lesson Biology
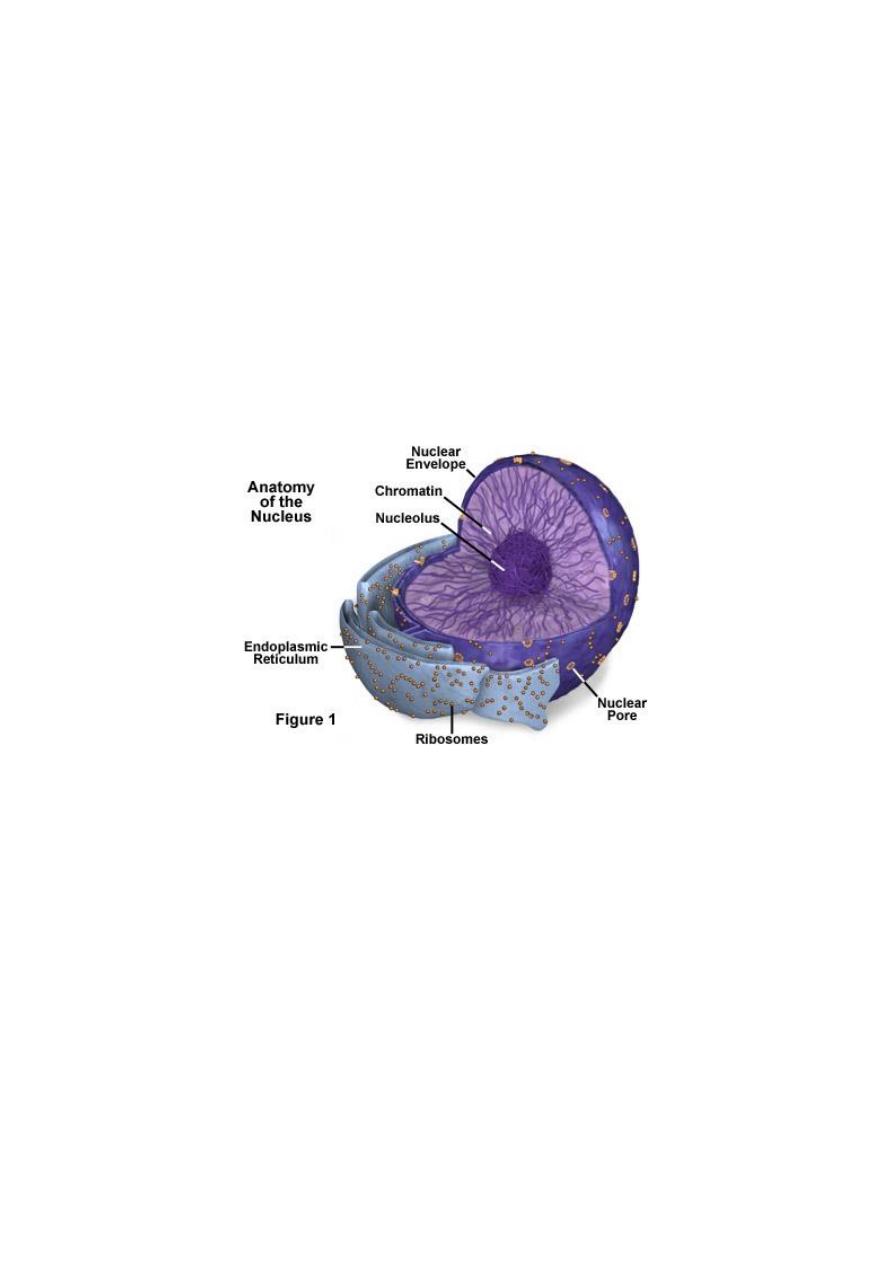
The Cell Nucleus
The cell nucleus is a membrane bound structure that contains the cell's
genetic information and controls the cell's growth and reproduction. It is
the command center of a eukaryotic cell and is commonly the most
prominent organelle in a cell.
The Nucleus consists of:
Nuclear envelope:
The cell nucleus is bound by a double membrane called the nuclear
envelope. This membrane separates the contents of the nucleus from
the cytoplasm. Like the cell membrane, the nuclear envelope consists
of phospholipids that form a lipid bilayer. The envelope helps to maintain
the shape of the nucleus and assists in regulating the flow of molecules
into and out of the nucleus through nuclear pores.

ii
The nuclear envelope is perforated with holes called nuclear pores. These
pores regulate the passage of molecules between the nucleus and
cytoplasm, permitting some to pass through the membrane, but not
others. Building blocks for building DNA and RNA are allowed into the
nucleus as well as molecules that provide the energy for constructing
genetic material.
Chromosomes:
are located within the nucleus. Chromosomes consists of DNA, which
contains genetic information and instructions for cell growth,
development, and reproduction. the chromosomes are organized into long
entangled structures called chromatin.
The Nucleolus:
Contained within the nucleus is a dense structure composed
of RNA and proteins called the nucleolus. The nucleolus contains
nucleolar organizers, which are parts of chromosomes with the genes for
ribosome
synthesis
on
them.
The
nucleolus
helps
to
synthesize ribosomes by transcribing and assembling ribosomal RNA. A
ribosome is composed of ribosomal RNA and proteins.

iii
Functions of the Nucleus:
It controls the heredity characteristics of an organism.
It is responsible for protein synthesis, cell division, growth and
differentiation.
Stores heredity material in the form of deoxy-ribonucleic acid
(DNA) strands.
Also stores proteins and ribonucleic acid (RNA) in the nucleolus.
It is a site for transcription process in which messenger RNA
(m RNA) are produced for protein synthesis.
Aids in exchange of DNA and RNA (heredity materials) between
the nucleus and the rest of the cell.
Nucleolus produces ribosomes and are known as protein factories

iv
The Lysosomes
Lysosomes are spherical membranous sacs of enzymes. These enzymes
are acidic hydrolase enzymes that can digest cellular macromolecules.
The lysosome membrane helps to keep its internal compartment acidic
and separates the digestive enzymes from the rest of the cell. Lysosomes
are formed by budding from the Golgi complex.
Four types of Lysosomes:
1. Primary lysosome (storage granules)
2. Secondary lysosomes (digestive vacuole or heterophagosome)
3. Residual bodies
4. Autophagic vacuole (cytolysosome or autophagosome)
Lysosome Function:
Lysosomes act as the "garbage disposal" of a cell. They are active in
recycling the cell's organic material and in the intracellular digestion
of macromolecules. Some cells, such as white blood cells, have many
more lysosomes than others. These cells destroy bacteria, dead
cells, cancerous
and
foreign
matter
through
cell
digestion. Lysosomes are also necessary for the degradation of internal
cell components such as organelles. In many organisms, lysosomes are
also involved in programmed cell death.
