

To define separate bones of the upper limb
To identify the specific parts of each bone
To describe the relations of each bone with
adjacent ones
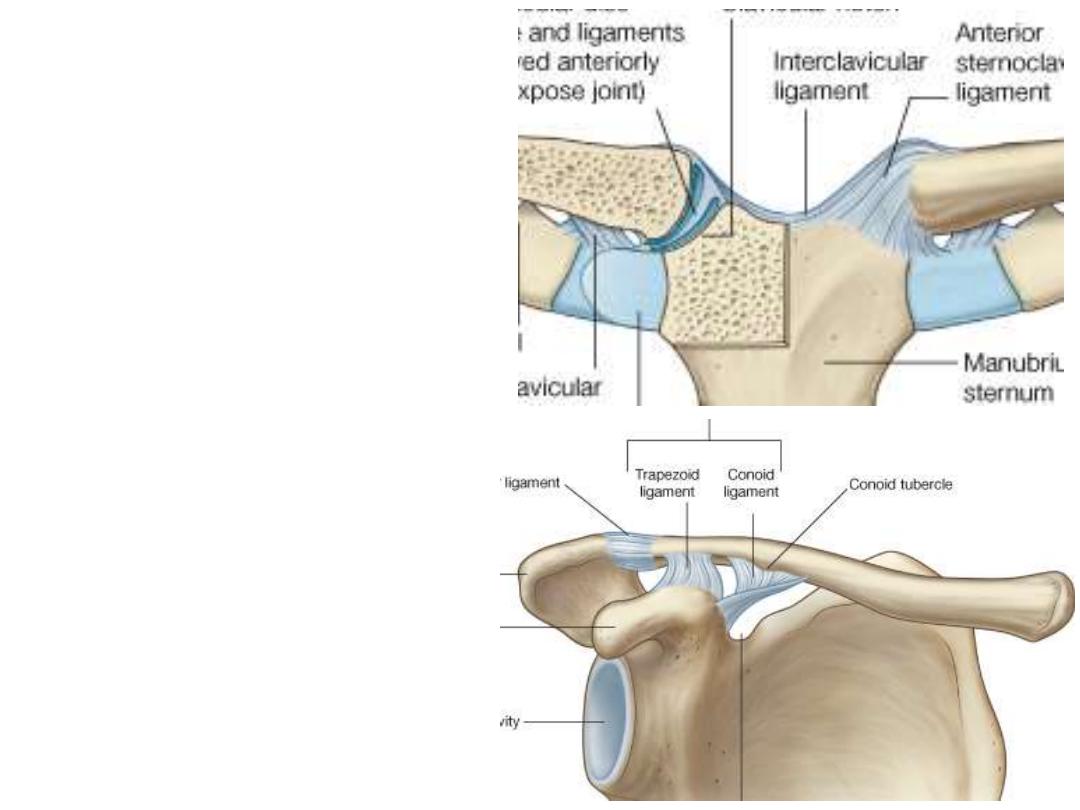
The Clavicle:
-The clavicle props the shoulder
out of the trunk to give the UL
maximum freedom of movement
-The bone is S-shaped (the most
commonly fractured bone in the
body)
-Medial articulation; manubrium
sterni (sternoclavicular joint)
-Laterally;
scapula
(acromio-
clavicular joint)
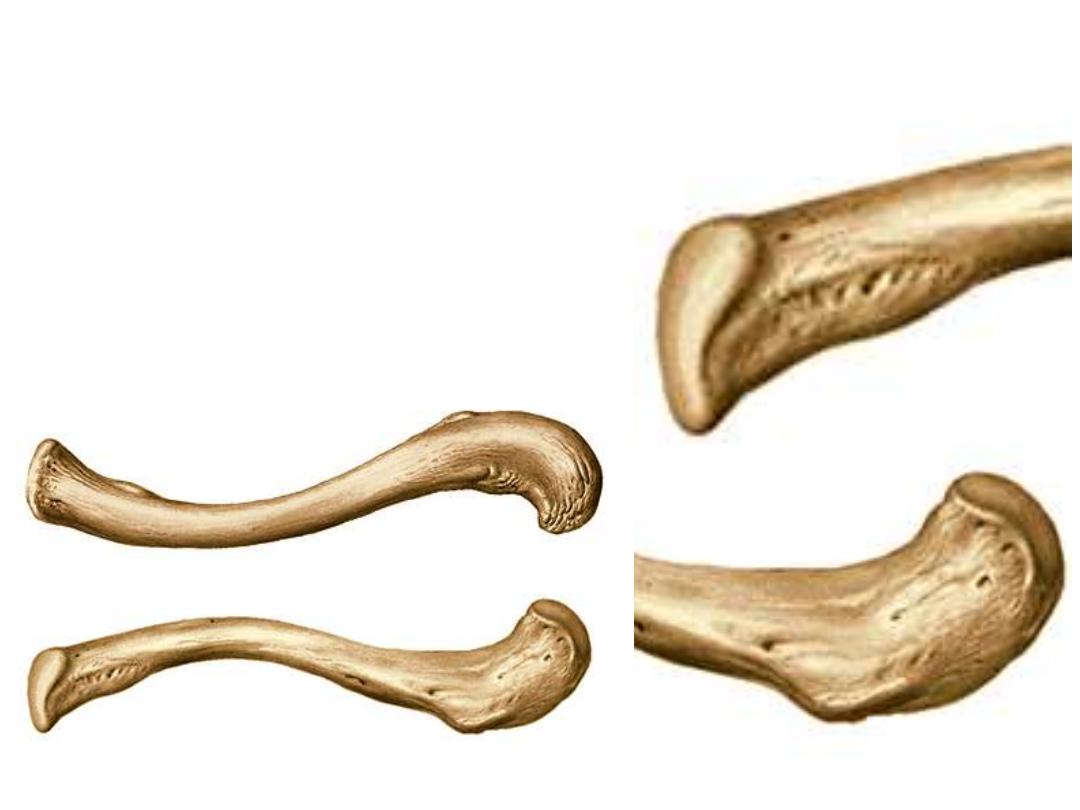
-The medial 2/3 is quadrangular & is convex forward
-The lateral end is flat & convex backward
-The undersurface shows the following landmarks:
1- Costal tuberosity
2- Conoid tubercle & trapezoid ridge
3- Subclavius groove
-The costal facet is saddle shape
-The acromial facet is elongated
Medial
Lateral
1
2
3
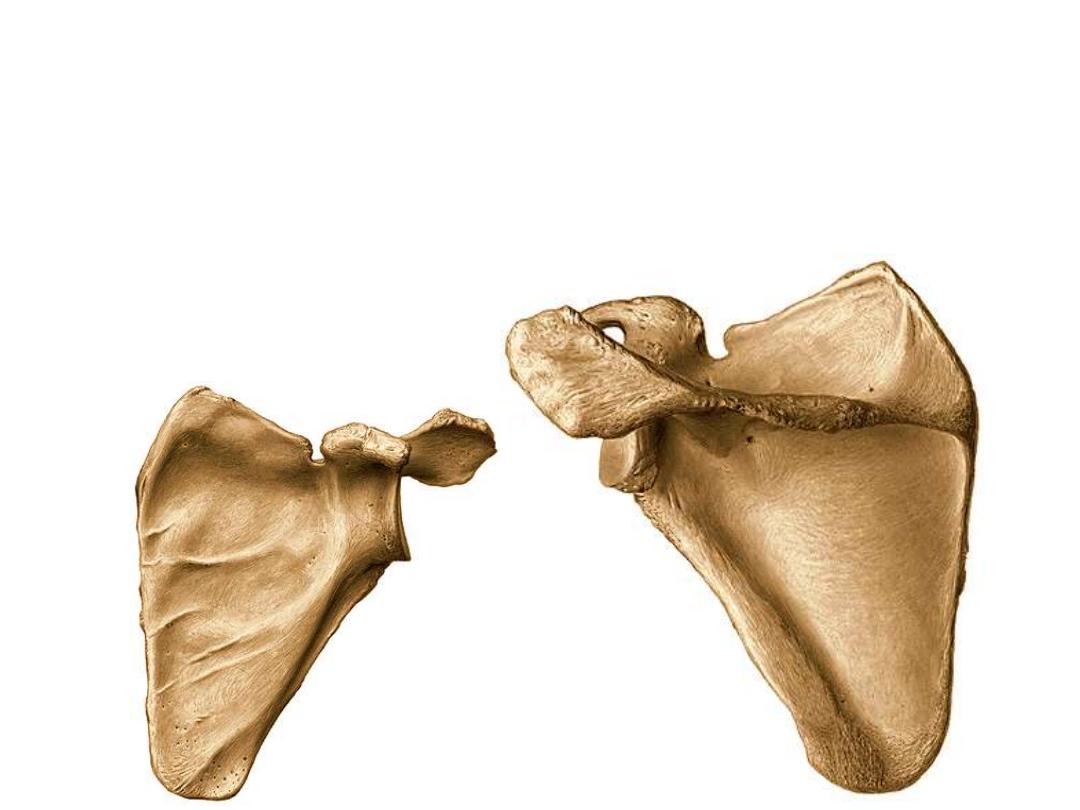
The Scapula:
Flat triangular bone lying against the back of the thoracic cage (ribs 2-7)
Borders:
1- Medial border: the longest, it is directed vertically along the vertebral furrow
2- Lateral border: directed superolaterally
3- Superior border: the shortest, shows the scapular notch near the lateral angle
Angles:
1- Superior angle
2- inferior angle
3- lateral angle: carries the glenoid cavity
Lateral
Medial
Medial
Ventral
Dorsal
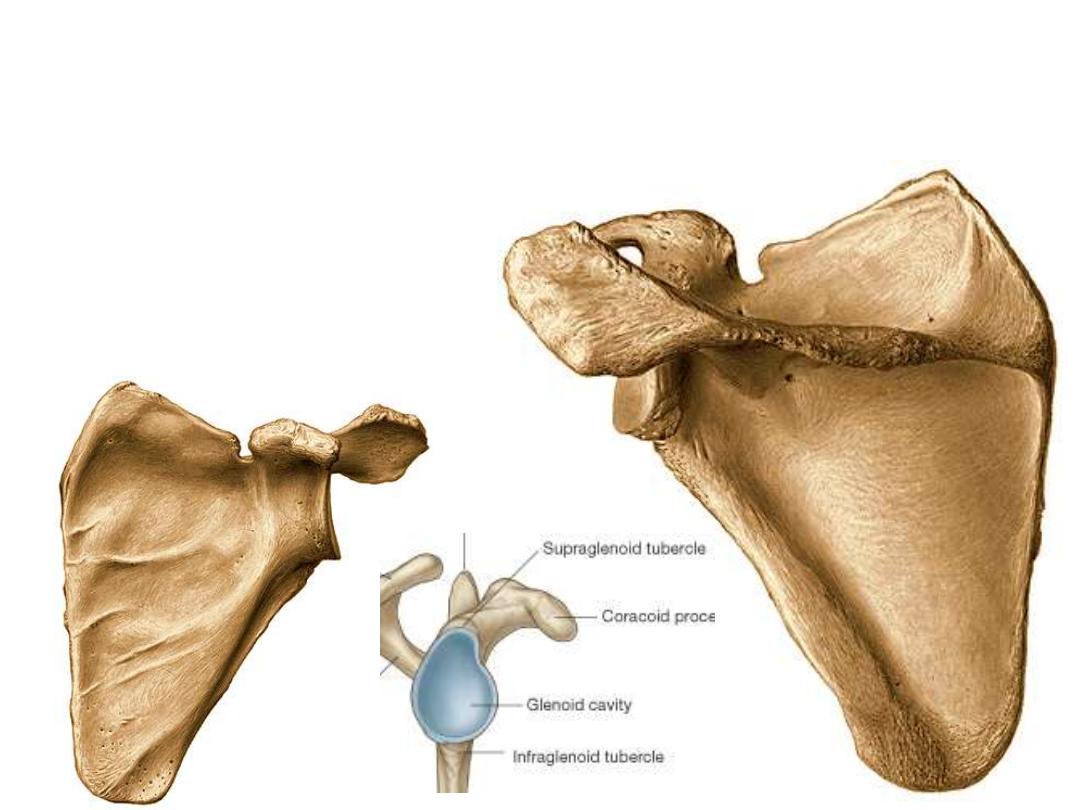
Parts of he Scapula:
1. The subscapular fossa
2. The scapular spine divides the dorsal surface of the blade into small supraspinous
& large infraspninous fossae
3. The teres major ridge
4. The acromion
5. The coracoid process
6. The glenoid cavity
7. The supraglenoid & infraglenoid tubercles
1
2
3
4
5
6
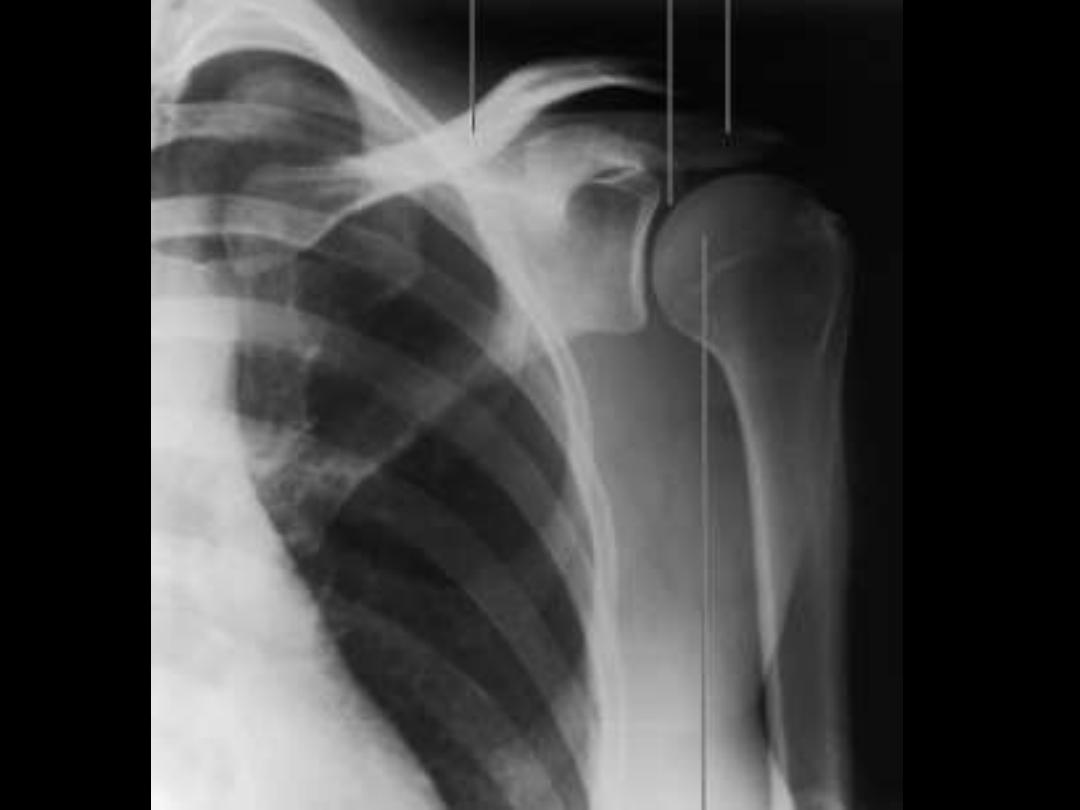
The Humerus:
The main bone of the UL, equals 1/5 of the body height
Parts:
1- The head:
¾ a sphere, articulates with the glenoid cavity
2- The anatomical neck:
lies at the margin of the head
3- The surgical neck:
the thinnest & highest part of the shaft
1
2
3
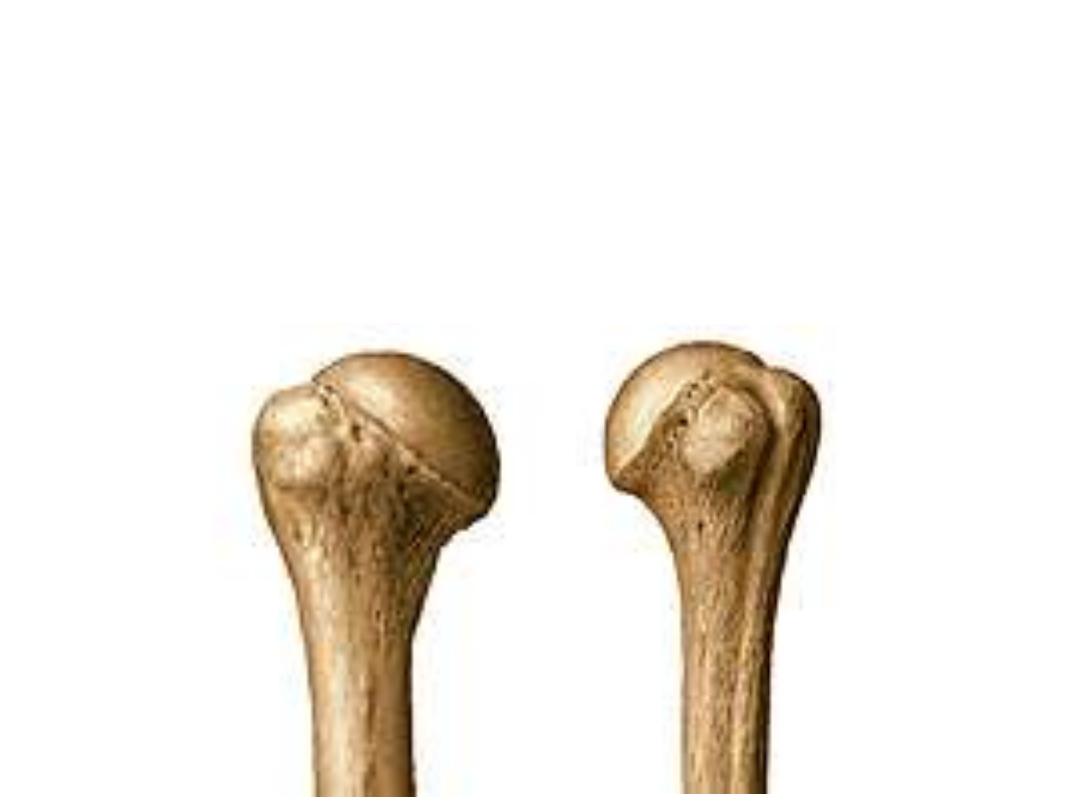
4- The greater tuberosity:
-It is the most laterally projecting part of the bone
-It carries three facets on its postero-superior
aspect
5- The lesser tuberosity:
smaller then the greater
one & lies medial & inferior to it
6- The bicepital groove:
between the two tubercles
The shaft:
7- Deltoid tuberosity
8- Medial supracondylar ridge
, ends in the medial
epicondyle
9- Lateral supracondylar ridge,
ends in the lateral
epicondyle
10- Radial groove
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
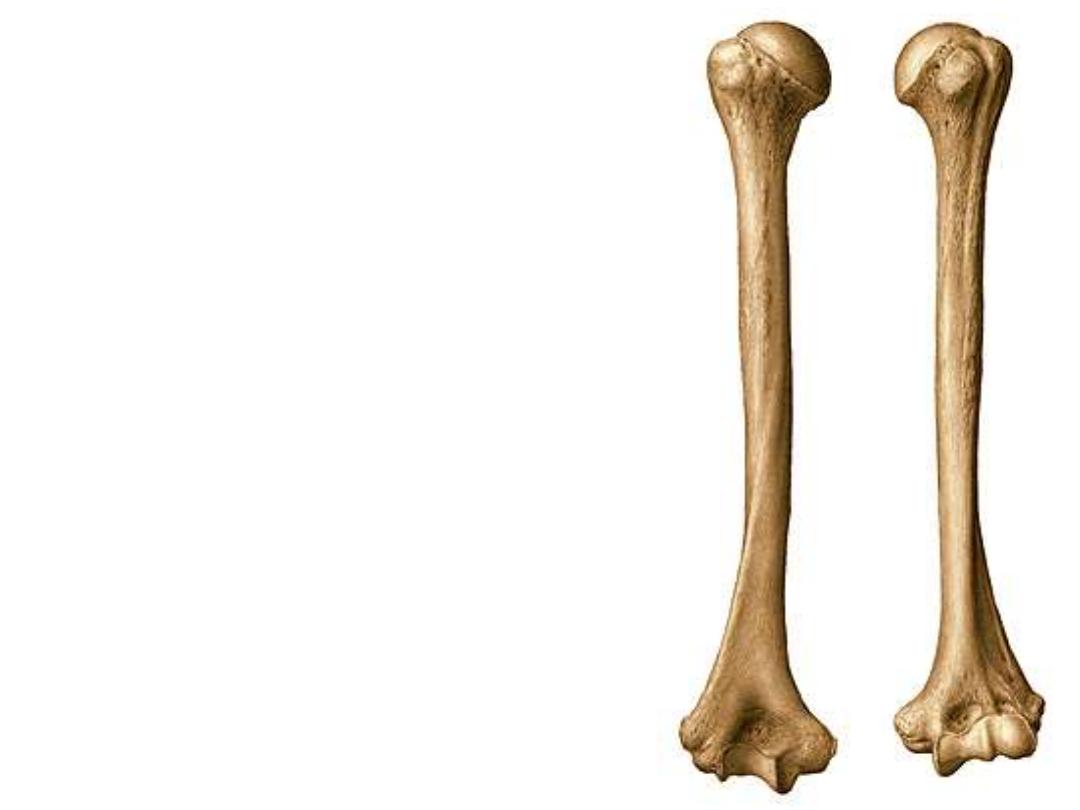
The lower extremity:
11- Lateral epicondyle
12- Medial epicondyle;
very prominent, projects
posteromedially
13- Trochlea;
fits the trochlear notch of the ulna
14- Capitulum;
for articulation with the upper
surface of the head of radius
15- Coronoid (ulnar) fossa;
receives the
coronoid process during flexion
16- Radial fossa;
fits for the head of radius
during flexion
17- Olecranon fossa;
receives the olecranon
process during elbow extension
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
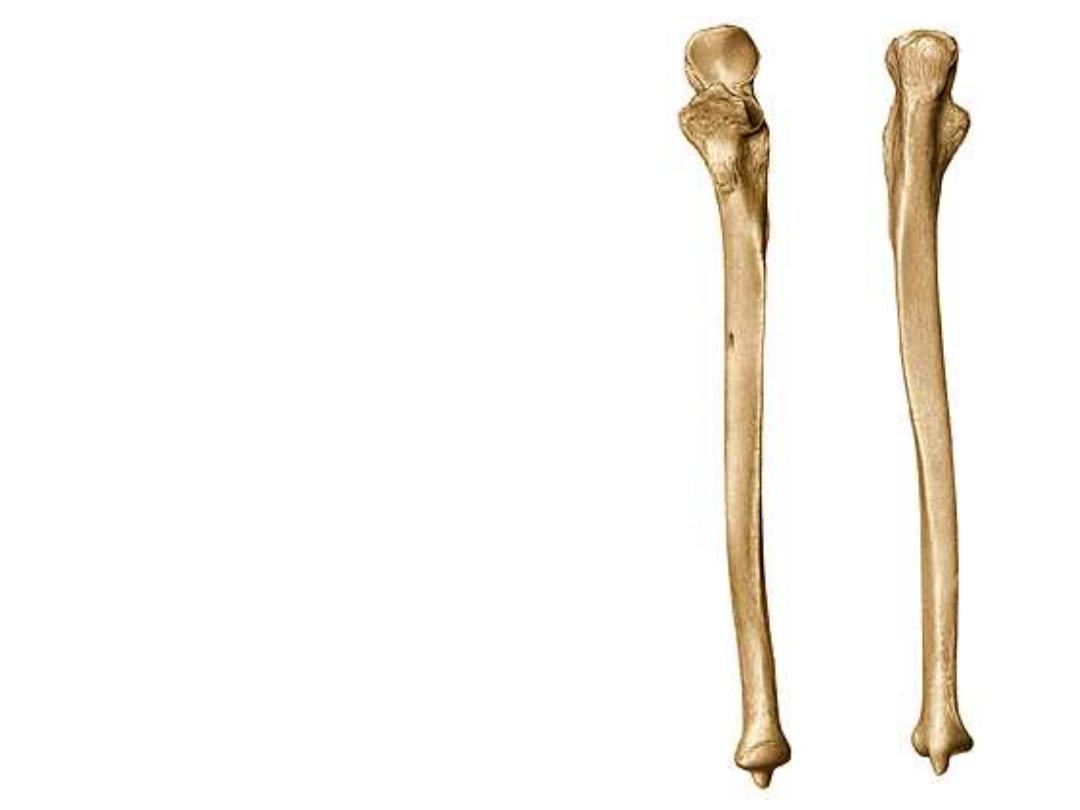
The Ulna:
-This is the prime bone of the medial
side of the forearm
-It is firmly connected to the humerus
but only indirectly connected to the
hand bones
-It is therefore, more robust proximally
where its two processes ( olecranon &
coronoid) form an open jaw-like end to
clasp the humeral trochlea
-Its lower end is reduced where it is
replaced by the broadened end of the
radius which takes almost the full
contact with the carpal bones
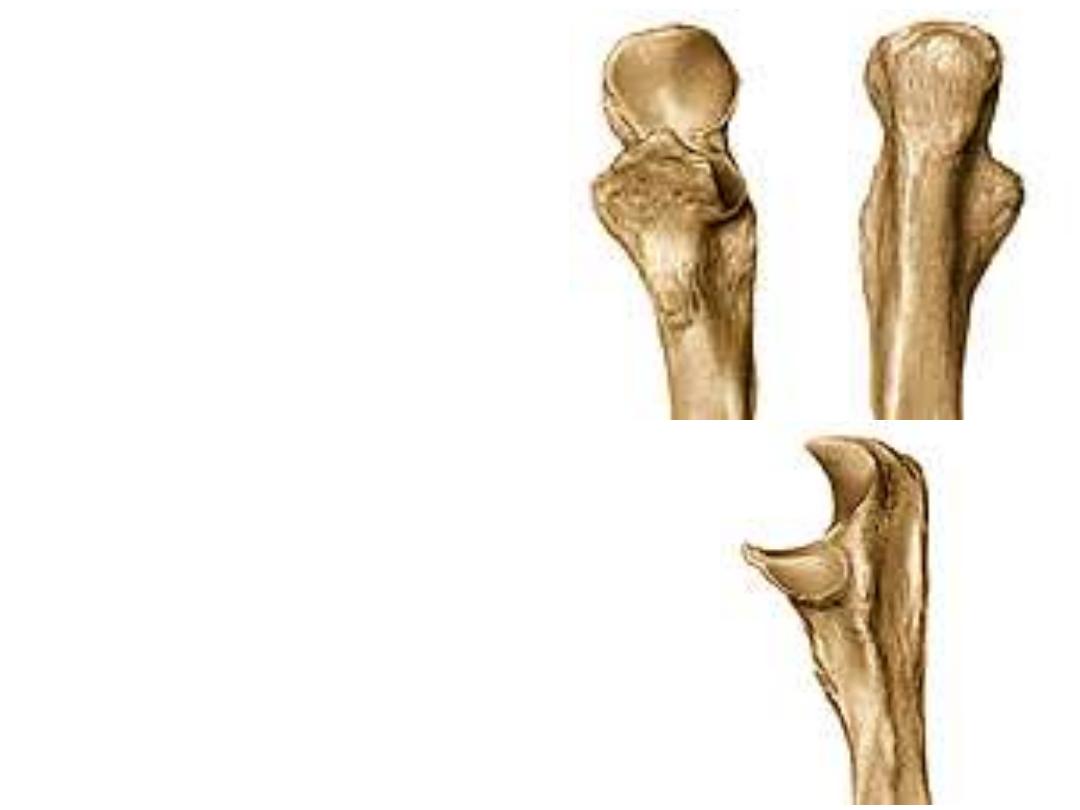
The upper end:
1- Trochlear notch;
a concavity describes
1/3 a circle to fit the humeral trochlea
2- Olecranon process;
forms the point of
the wrist & participates in the formation
of the trochlear notch, it receives the
tendon of triceps muscle
3- Coronoid process;
projects anteriorly
from the trochlear notch, it receives the
insertion of brachialis
4- Ulnar tuberosity;
lies at the junction of
the coronoid process with the shaft of
ulna
5- Radial notch;
lies lateral to the
coronoid process, fits the radius head to
form the superior radio-ulnar joint
1
2
3
2
4
5
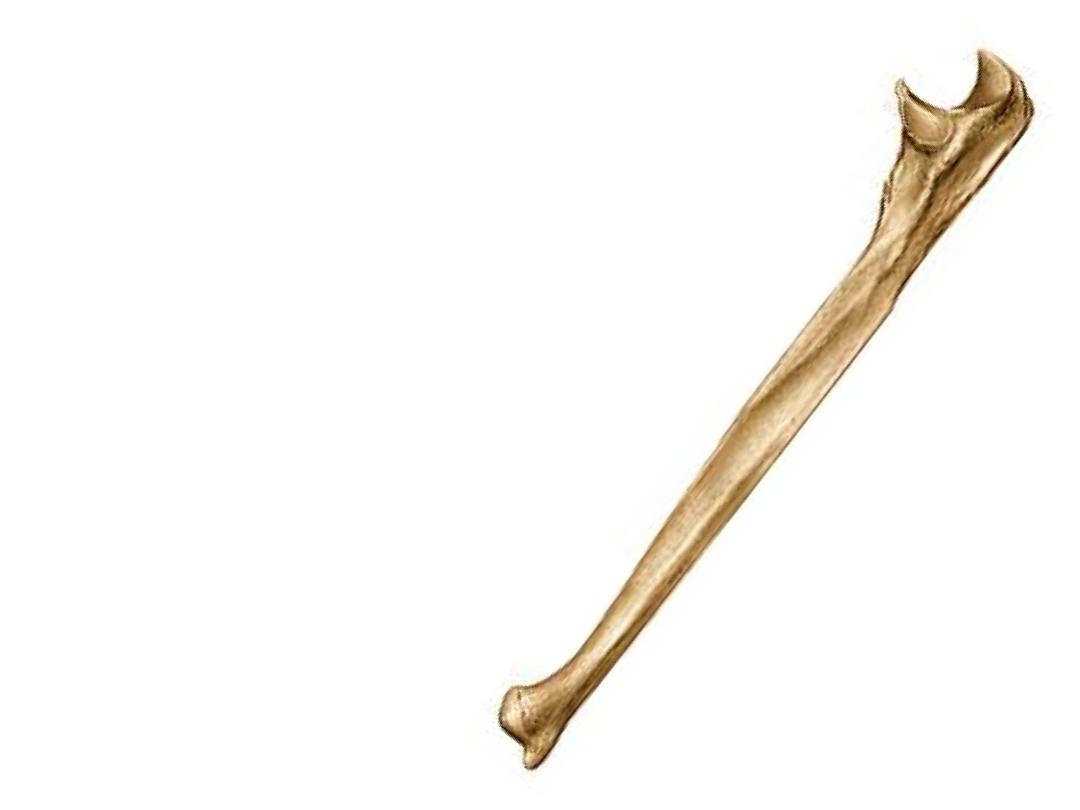
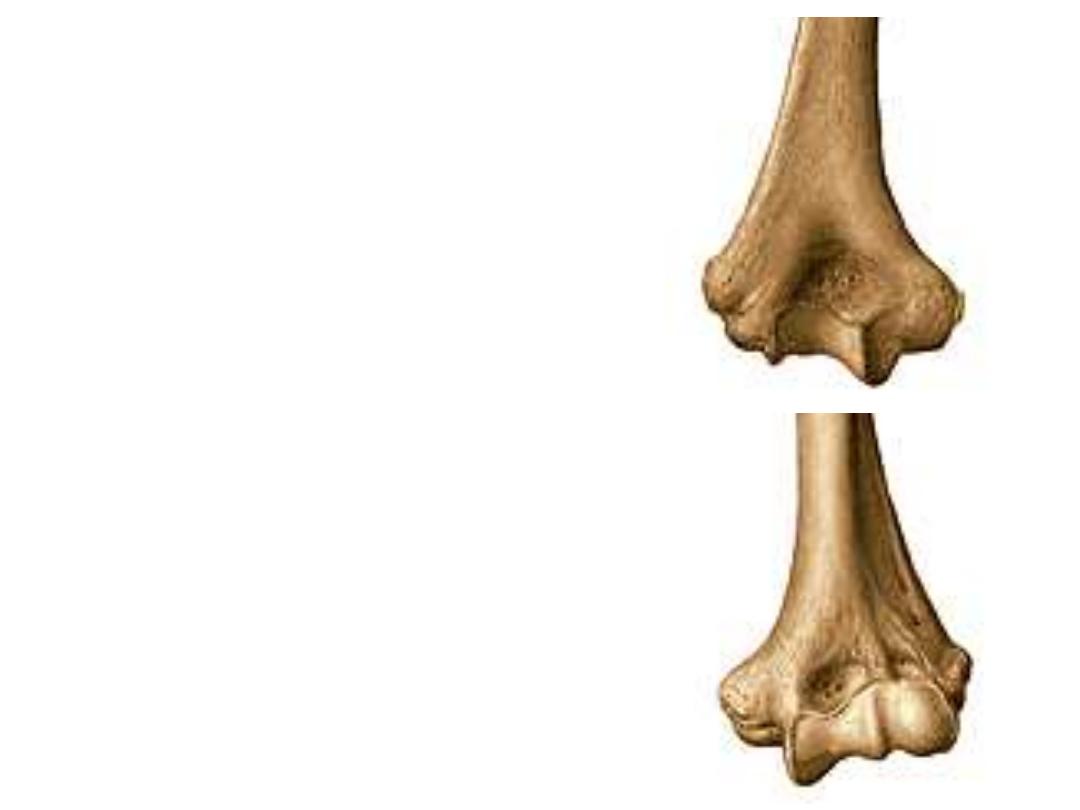
The body (shaft):
6- Subcutaneous border,
starts at the dorsum of
the olecranon & ends in the styloid process
7- Supinator crest;
extends between the radial
notch & the posterior border
8- Interosseous margin;
projects as a sharp
margin from the lateral side of the body & gives
attachment to the interosseous membrane
6
7
8
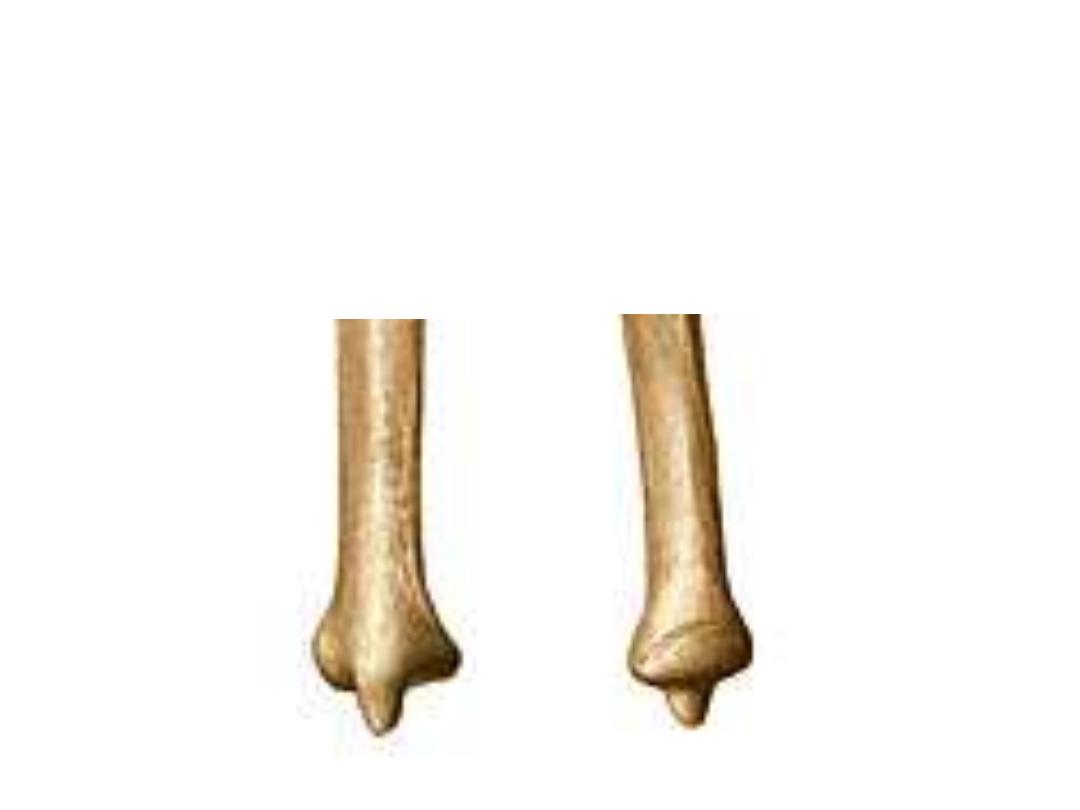
The lower end:
9- Styloid process;
in continuity with the posterior border
10- Head;
is larger than the styloid, & fits the ulnar notch in the lower
end of the radius to form the inferior R-U joint
9
10
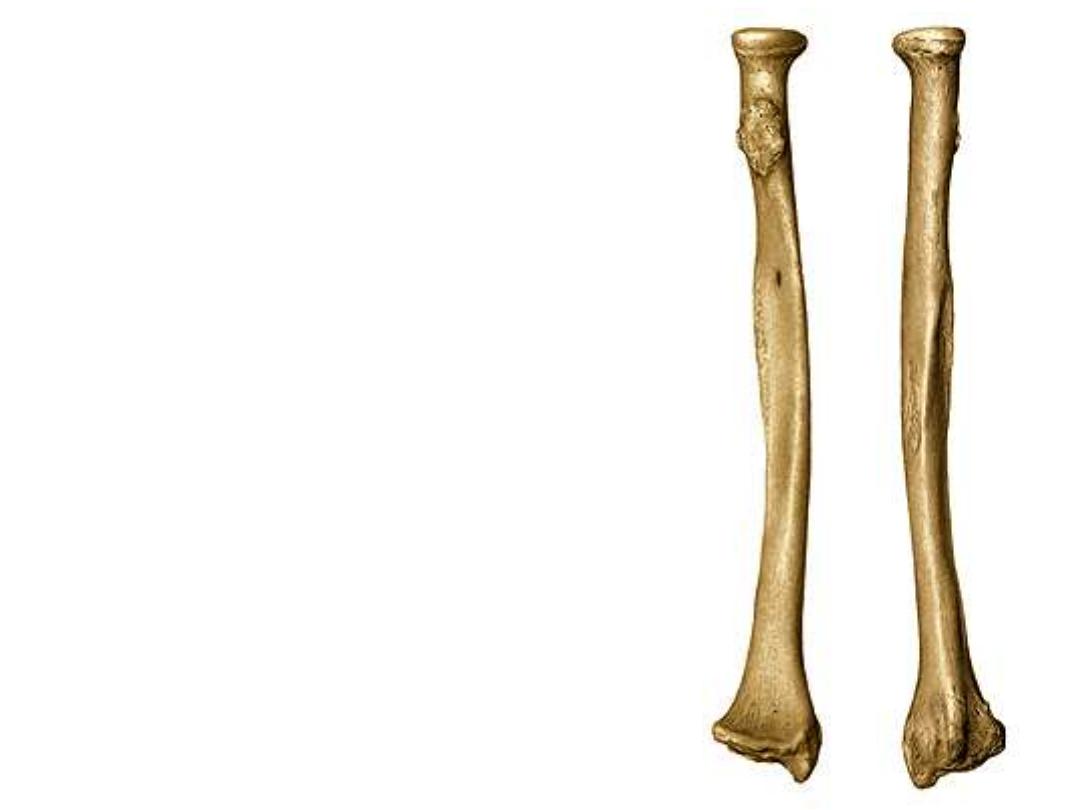
The Radius:
This bone is shorter & laterally placed in
relation to the ulna
1- The head
is disk-like part articulates with its
upper surface with the capitulum of the
humerus & by its circumference with the radial
notch of the ulna
2- The neck
Is the constriction just below the
head
3- Biceps tuberosity
is an oval prominence
distal to the neck , faces medially for the
insertion of biceps tendon
4- The shaft
is characterized by being convex
laterally to keep the radius away from the ulna
during pronation-supination movements
5- Interosseous border
1
2
3
2
4
5
5
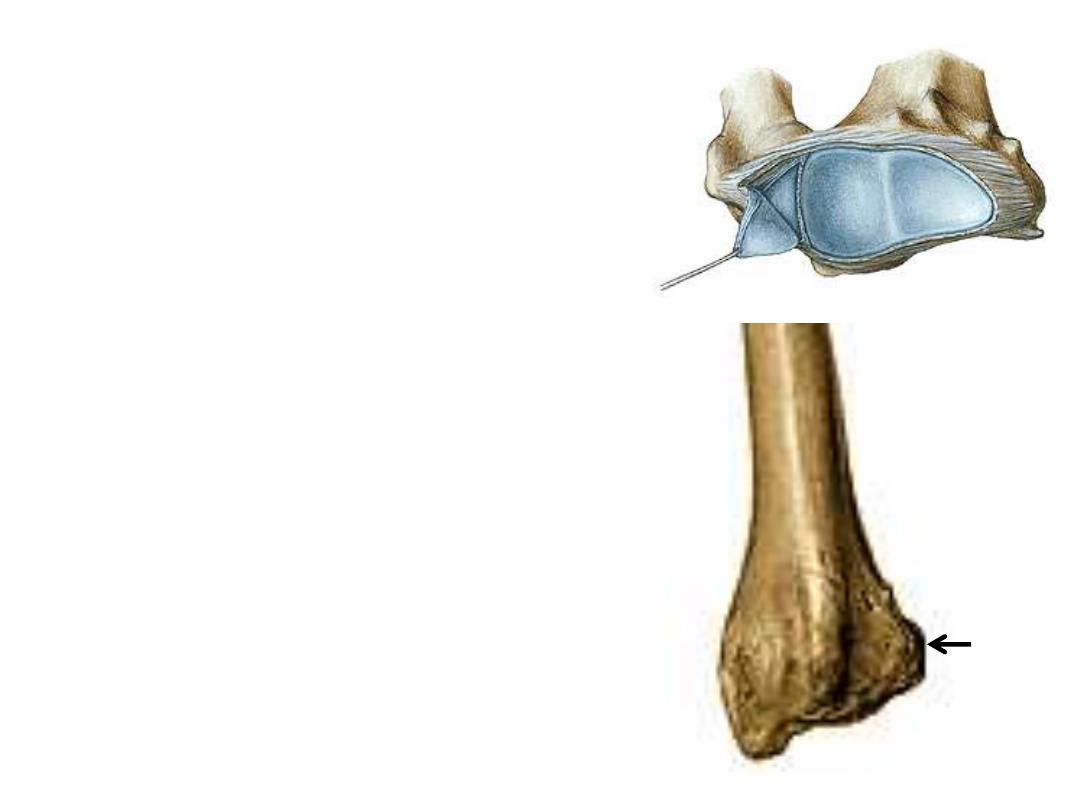
The lower end:
6- Carpal articular surface;
is concave &
separated by a ridge into a lateral triangular
area for articulation with the scaphoid &
medial quadrangular area for the lunate
7- Ulnar notch;
is a concavity in the medial
surface of this extremity for reception of the
ulnar head
8- Styloid process;
is the pointed lower end of
the lateral border, its radial side shows a
flattened area for passage of tendons of APL &
EPB
9- The dorsal surface;
shows
the dorsal radial
tubercle
& many other shallow ridges &
grooves for passage of extensor tendons
6
7
8
9
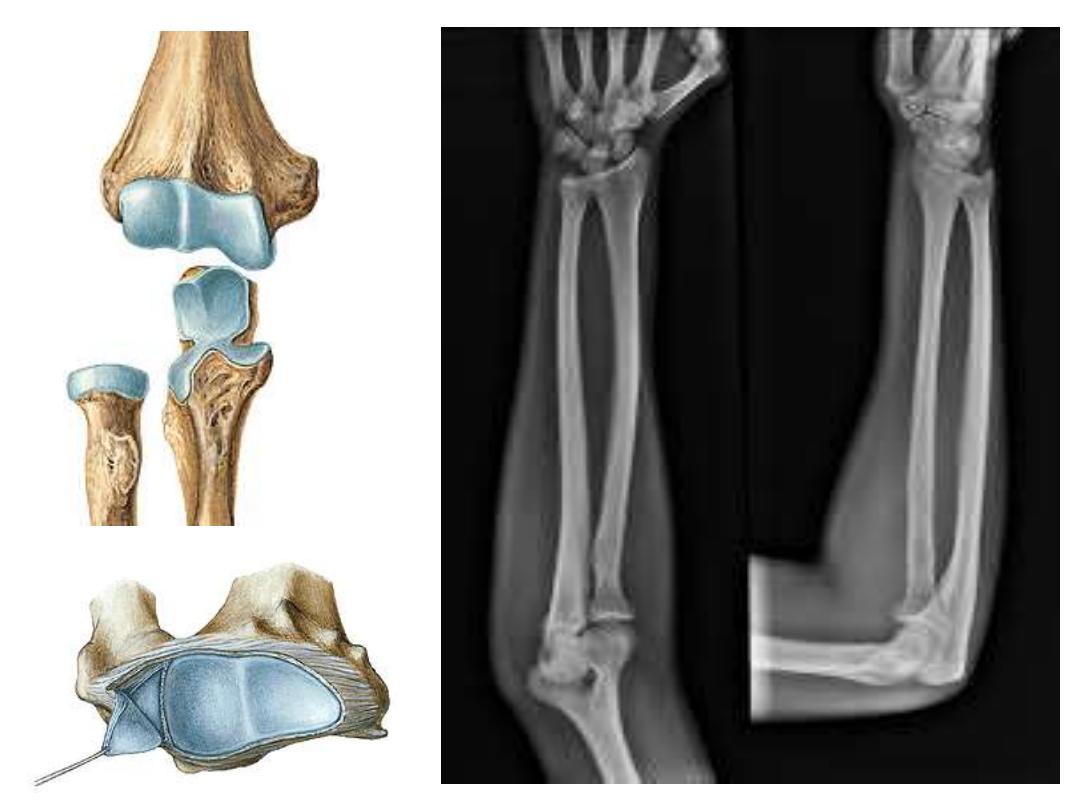
The Carpal Bones:
These are eight bones arranged in two rows:
1- The proximal row; from radial to ulnar side:
-Scaphoid
– Lunate – Triquetral - Pisiform
2- The distal row; from radial to ulnar side:
-Trapezium - Trapezoid - Capitate - Hamate
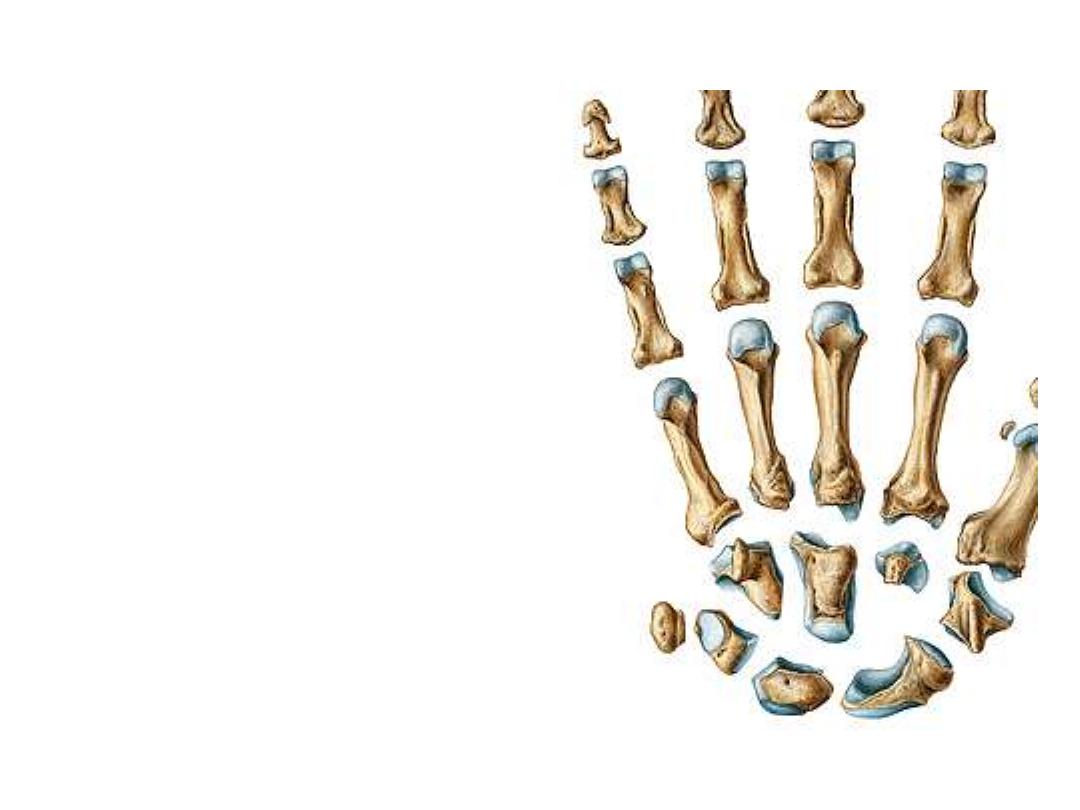
-In spite of the different shapes of
these bones, one should think of them
as cubes, each has six surfaces
-The palmar & dorsal surfaces of each
are non articular, other surfaces
articulate with adjacent bones
-Joints are synovial of different shapes
-Scaphoid & lunate are the bones
which hang the hand to the radius
forming the wrist joint
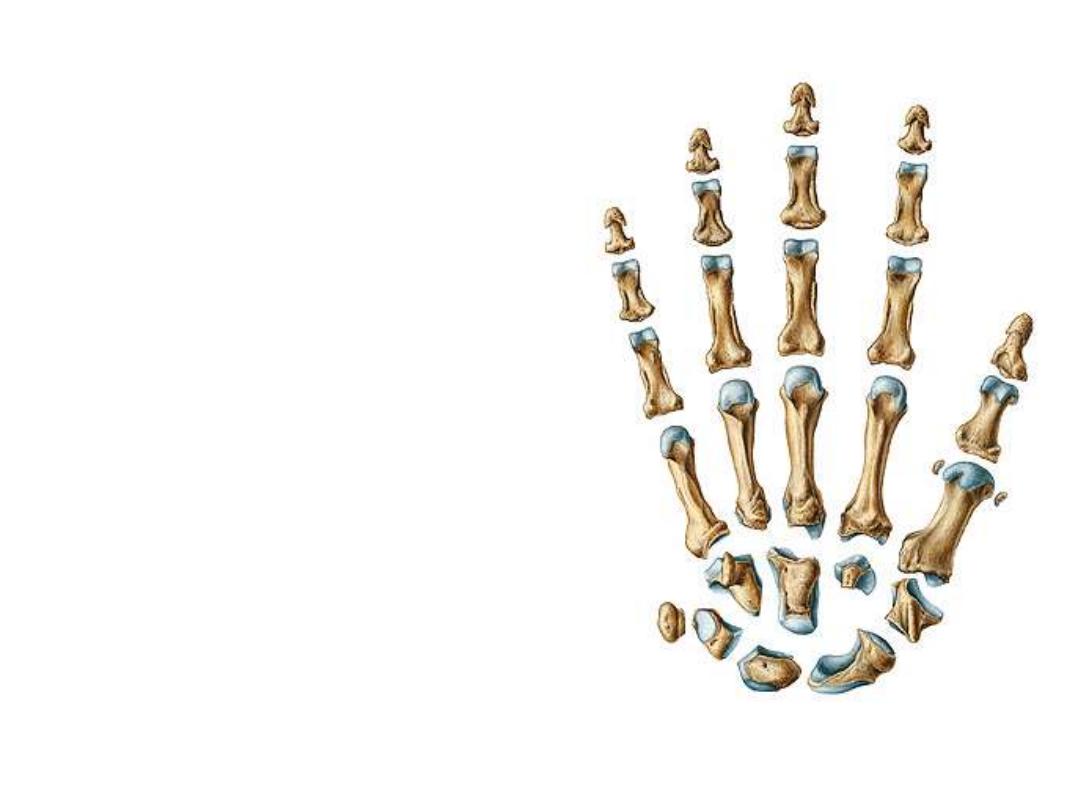
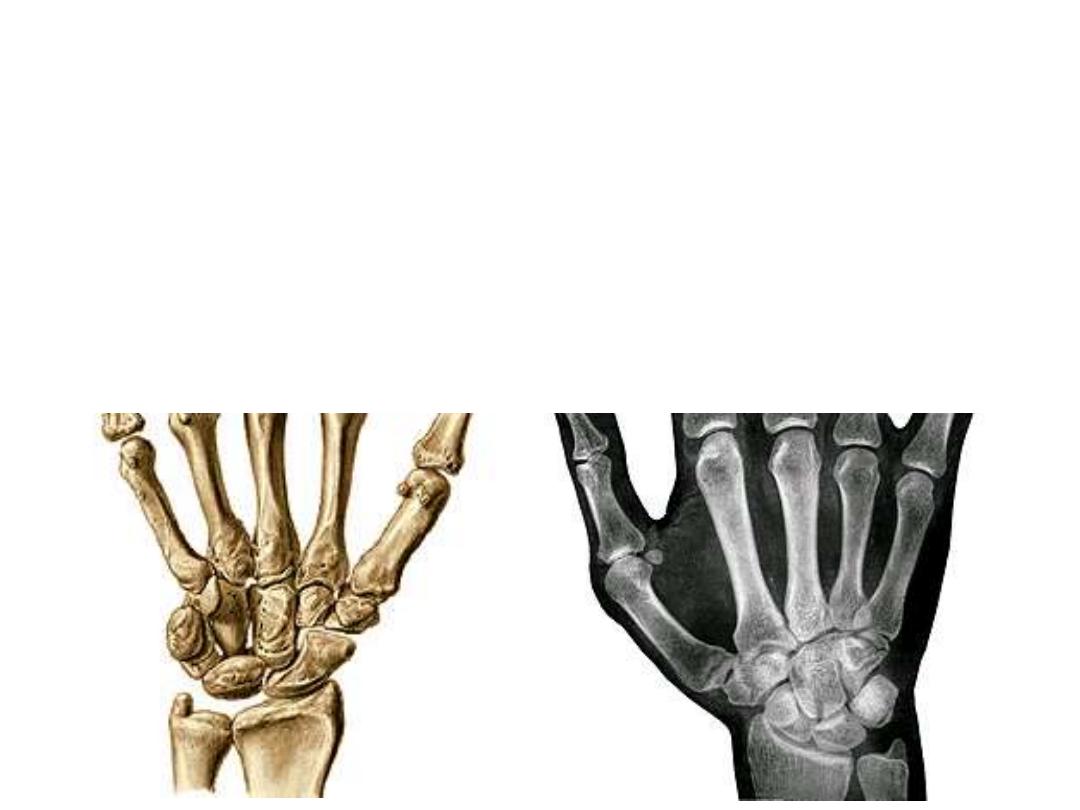
The metacarpals:
-Five small bones which simulate long
ones in having head, neck, shaft & base
-Their bases articulate with the distal
row of the carpal bones in the carpo-
metacarpal joints
-Their heads end distally as the
knuckles of the hand & articulate with
the proximal phalanges of the fingers at
the metacarpo-phalangeal joints
-The articular surfaces of the heads is
more prolonges dorsopalmarward than
from side to side to give the chance for
full flexion of the fingers at the MPJ
The phalanges:
-Fourteen in number, two for the
thumb & three for each of the
other fingers
-They resemble long bones in
having head, neck, shaft & base
-They
articulate
with
the
metacarpal heads by the MPJ &
with each other by the proximal
& distal interphalangeal joints
(PIP & DIP joints)
