
The pectoral region
The breast

OBJECTIVES
…
To list the muscles of the pectoral region
To recognize main vessels & nerves in the region
To describe the anatomy of mammary gland
To relate to anatomical facts to clinical conditions like
breast cancer
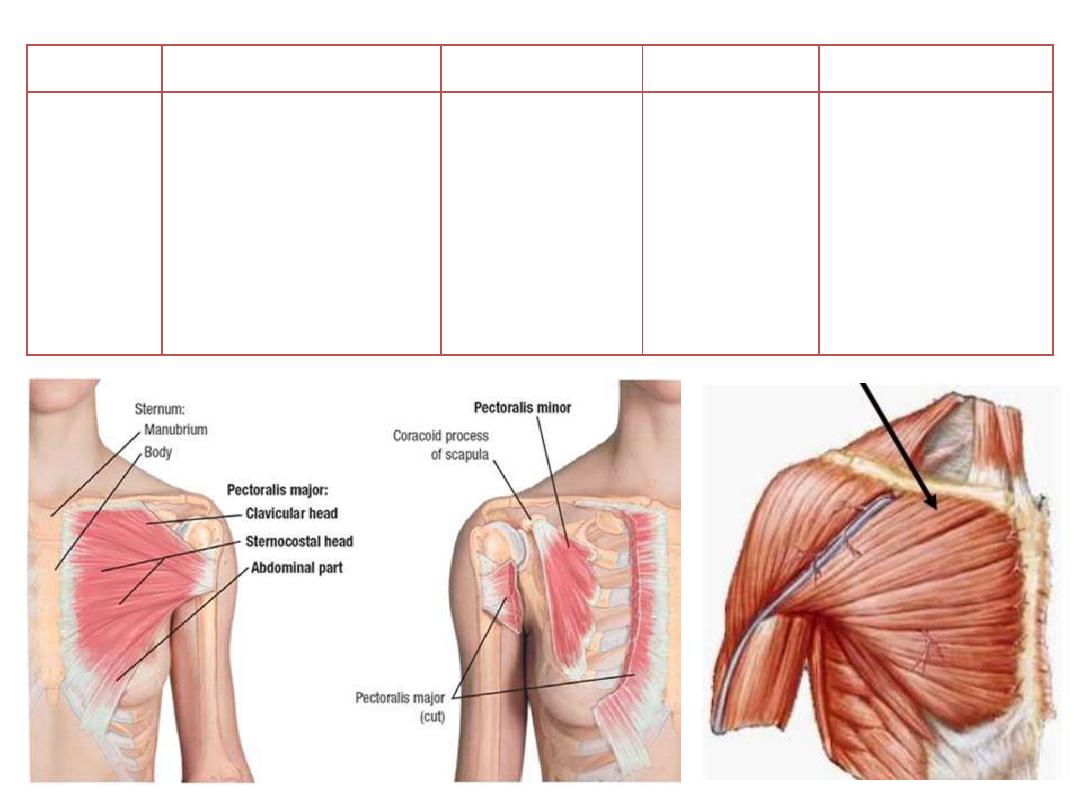
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Innervation
Function
Pectoralis
major
o Medial
half
of
clavicle
o Anterior surface of
sternum
o Upper
six
costal
cartilages
Lateral lip of
intertubercular
groove
Medial and
lateral pectoral
nerves
o Adduction
o Medial rotation
o Flexion
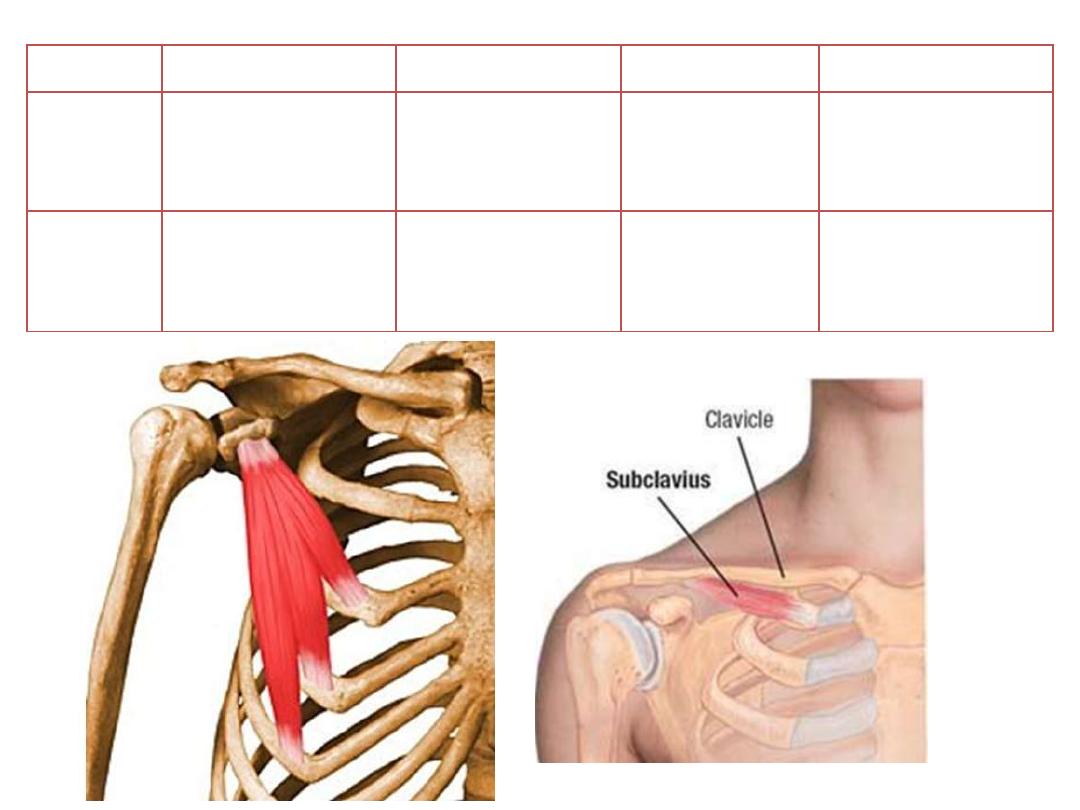
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Innervation
Function
Pectoralis
minor
Anterior surface of
ribs 3,4,5
Coracoid process
of scapula
Medial pectoral
nerve
o Depress
the
shoulder
o Protracts
the
scapula
Subclavius
First rib
Subclavius groove
of the clavicle
Nerve to
subclavius
Stabilization of SCJ
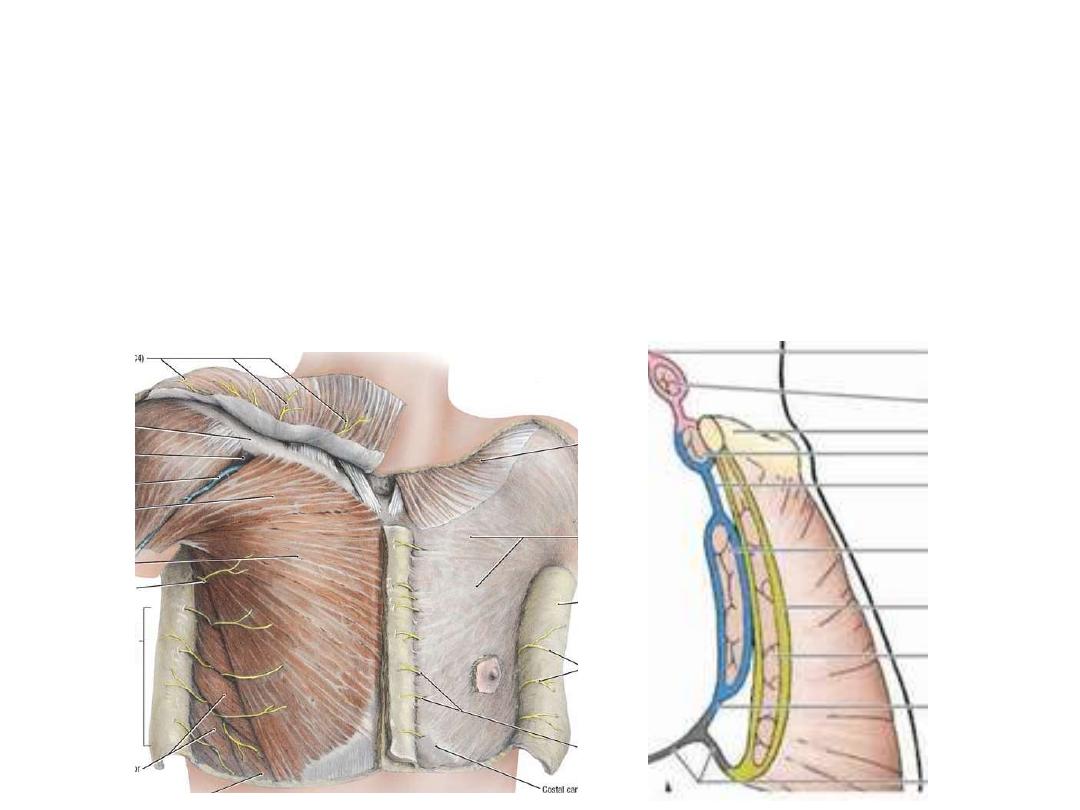
Pectoral fascia:
A thin lamina covering the surface of the pectoralis major & is attached to:
• Above: clavicle
• Medial: sternum
• Lateral: continuous with axillary fascia
• Below: continuous with abdominal fascia
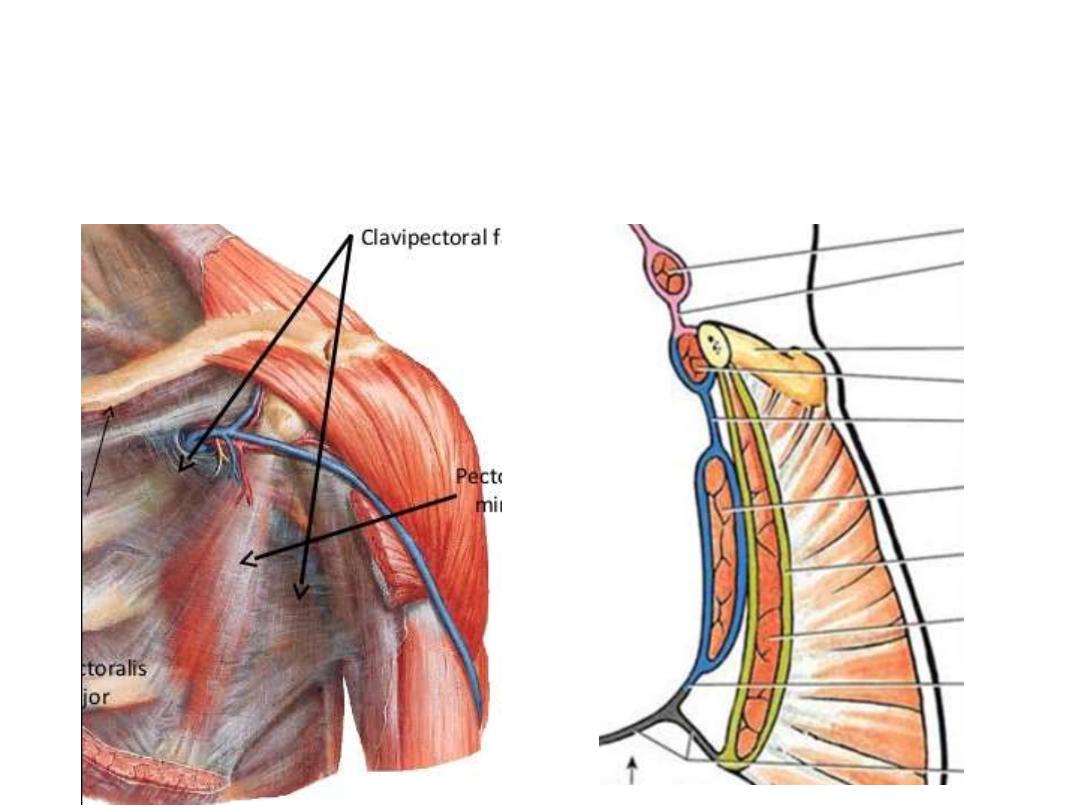
Clavipectoral fascia:
• Occupies the interval between the pectoralis minor and subclavius
• It splits to enclose subclavius, and its two layers are attached to the clavicle
• Laterally, it is very thick and dense, and is attached to the coracoid process.
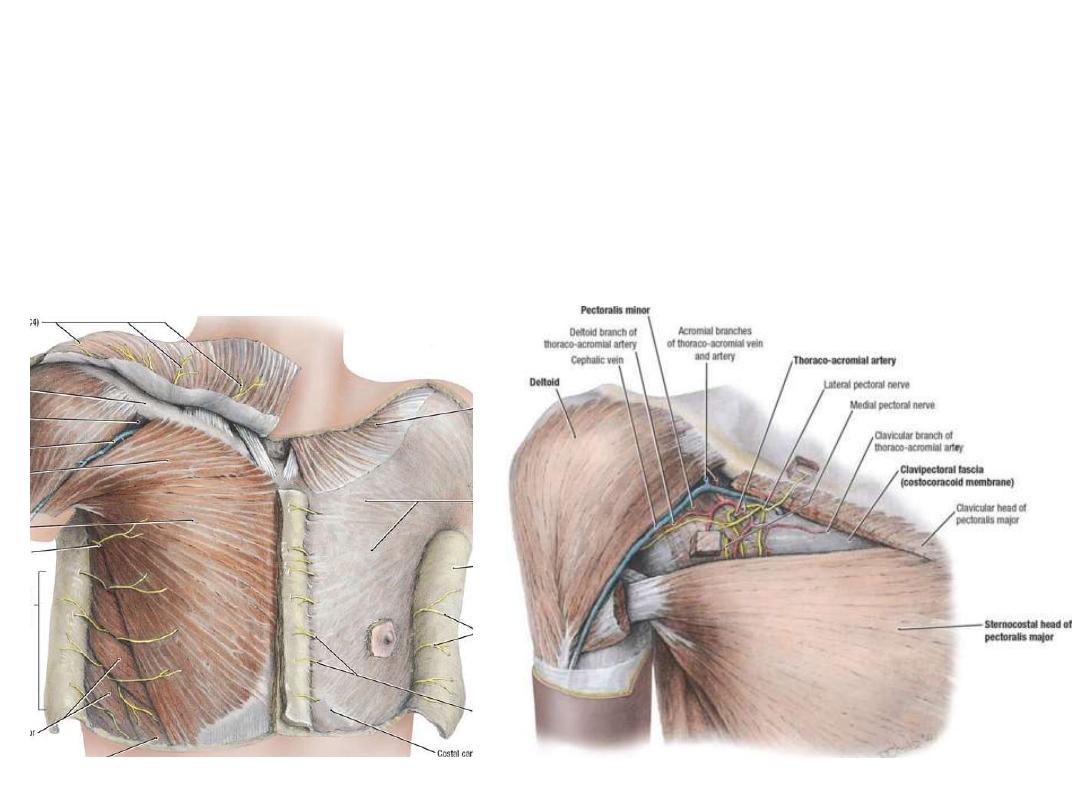
Detopectoral groove:
• Between pectoralis major & detoid
• Floored by the clavipectoral fascia
• Pierced by 4 structures:
1- Lateral pectoral nerve
2- Cephalic vein
3- Acromiothoracic trunk
4- Lymphatics
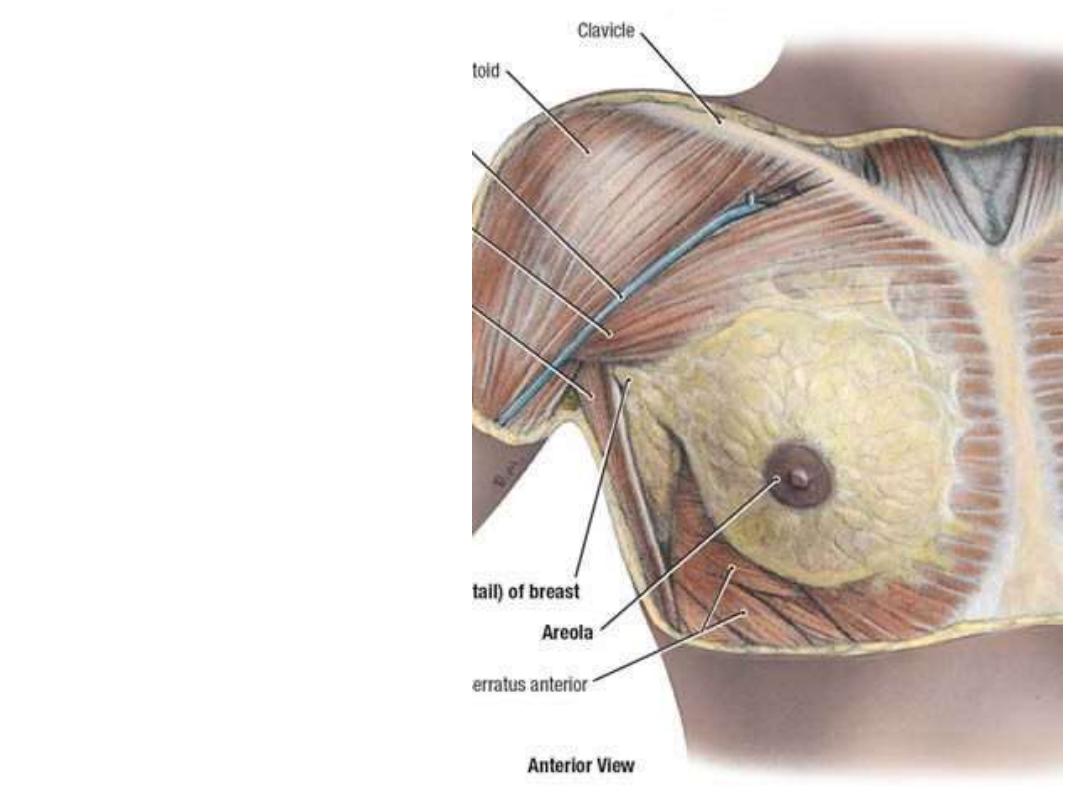
The mammary gland (Breast):
-A modified sweat gland which
functions for lactation in female
-The base of the breast is
almost fixed & extends from the
2
nd
to the 6
th
ribs & rests on the
pectoral fascia
-Laterally it occupies the area
between sternum & mid-axillary
line
-Breast size depends on the
amount
of
adipose
tissue
contents
Tissue types:
1- Glandular
2- Fatty (adipose)
3- Fibrous (connective)
The glandular system:
-Made of 15-20 pyramidal lobes of milk secreting tissue whose apices are directed to the
center of the breast
-Lobes are made of spherical lobules
-Lobular ducts open to the lactiferous ducts which open to the nipple
The areola:
-The circular pigmented area which
surrounds the nipple, its diameter &
color varies depends on many
factors
The nipple:
-On its top open the lactiferous ducts
-Contains smooth muscles which
erect under a hormonal control
Breast tail (axillary process):
Extension of breast tissue into the
anterior axillary fold
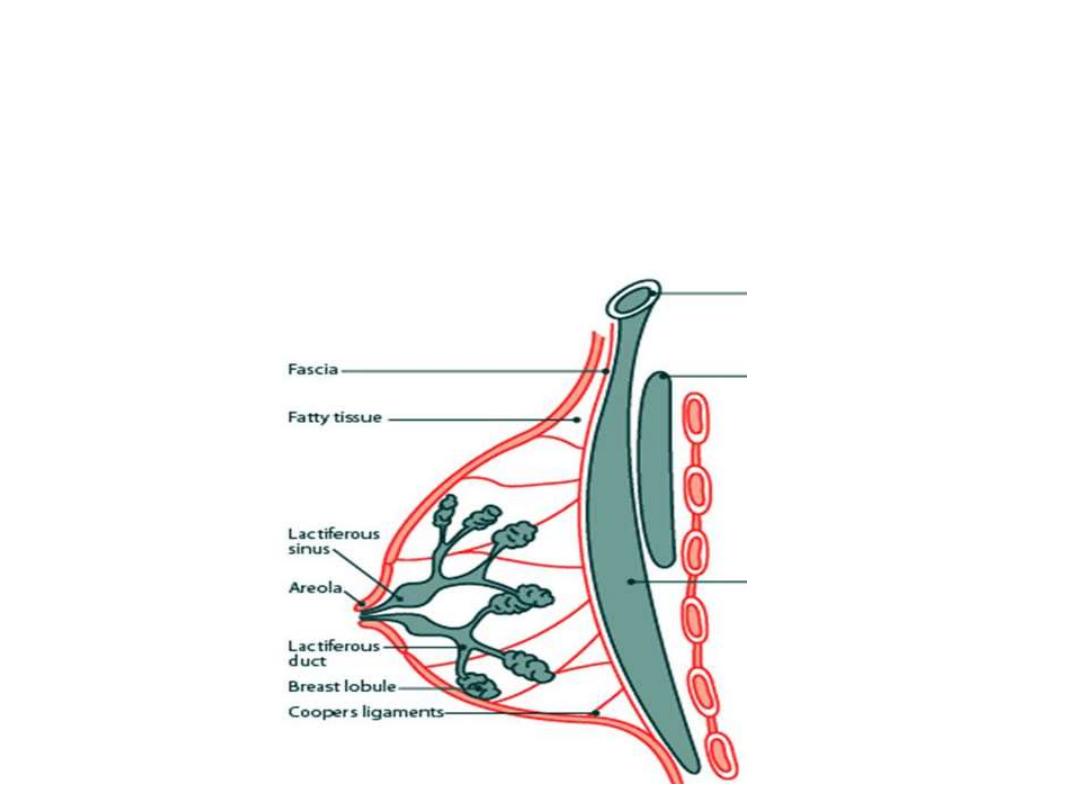
Suspensory ligament of Astley-Cooper:
-This conical ligament covers the breast underneath the skin & supports its
weight
-It is stronger at the lower than the upper half of the breast
-It is strong & tense in young age & becomes lax in multiparous women,
responsible for the change in appearance
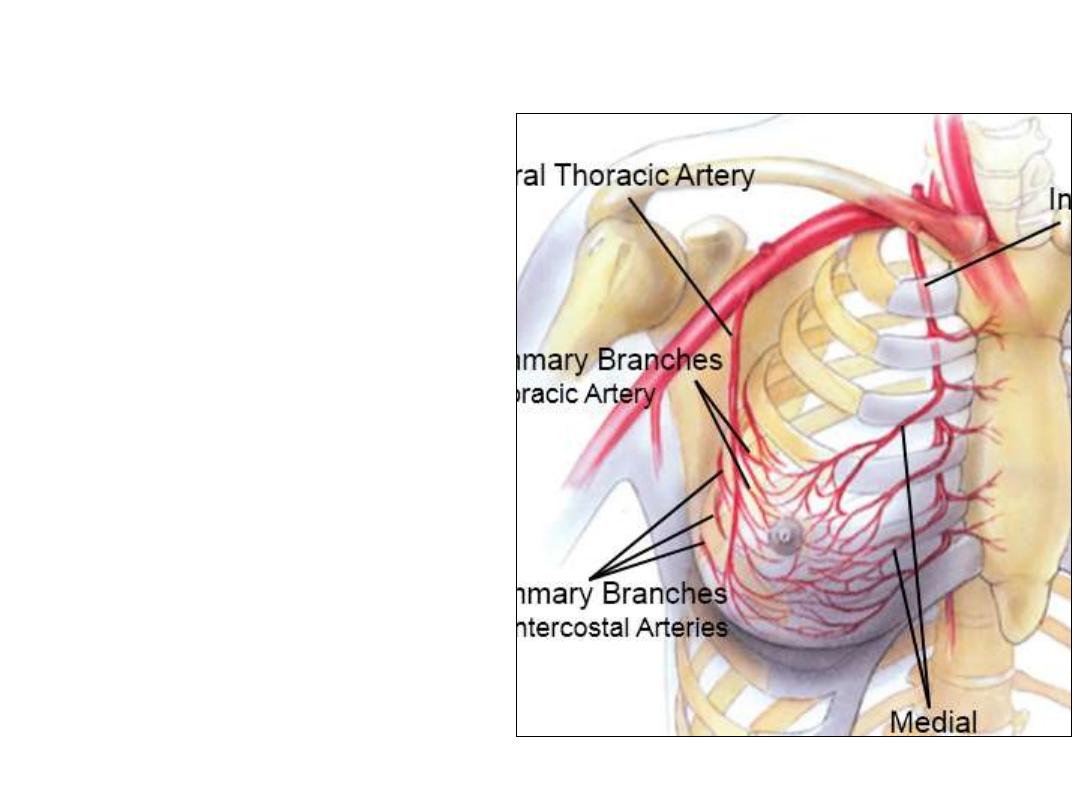
Arterial supply:
1- Perforating branches of anterior
intercostal & internal thoracic arteries
2- Lateral branches of intercostal
arteries
3-
Superior
&
lateral
thoracic
branches of the axillary artery
Venous drainage:
Similar to arteries but:
-They communicate with adjacent
veins of the neck above & of the
anterior abdominal wall below
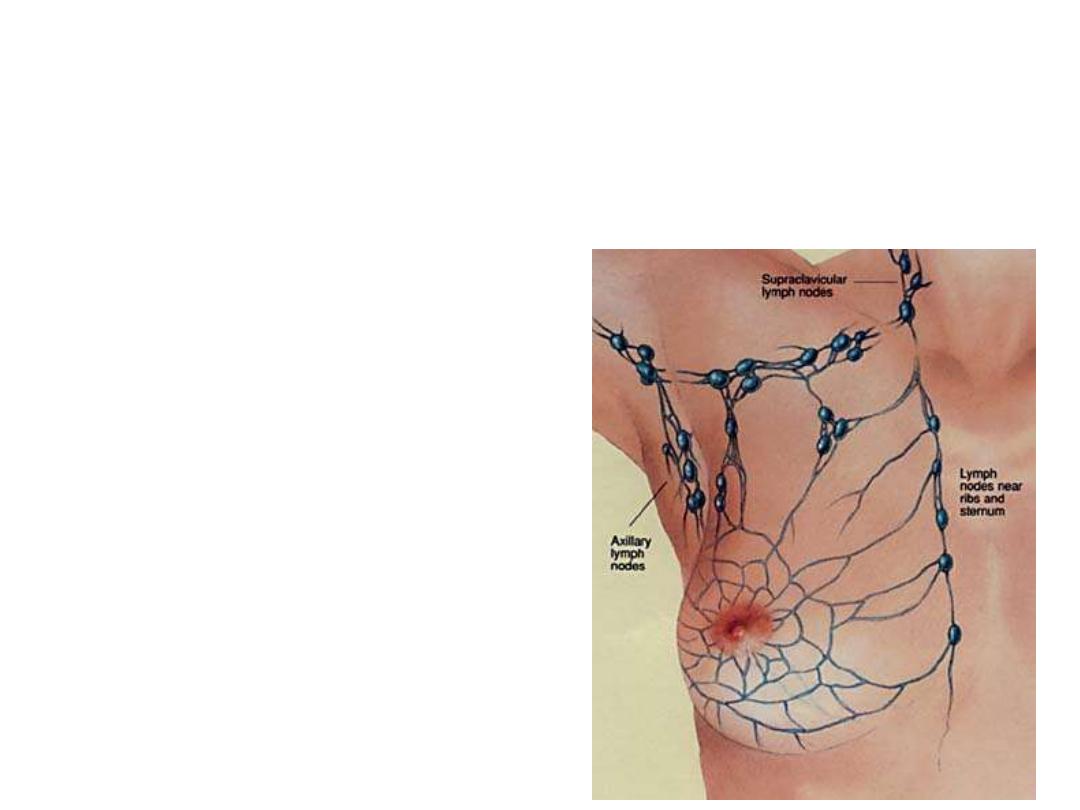
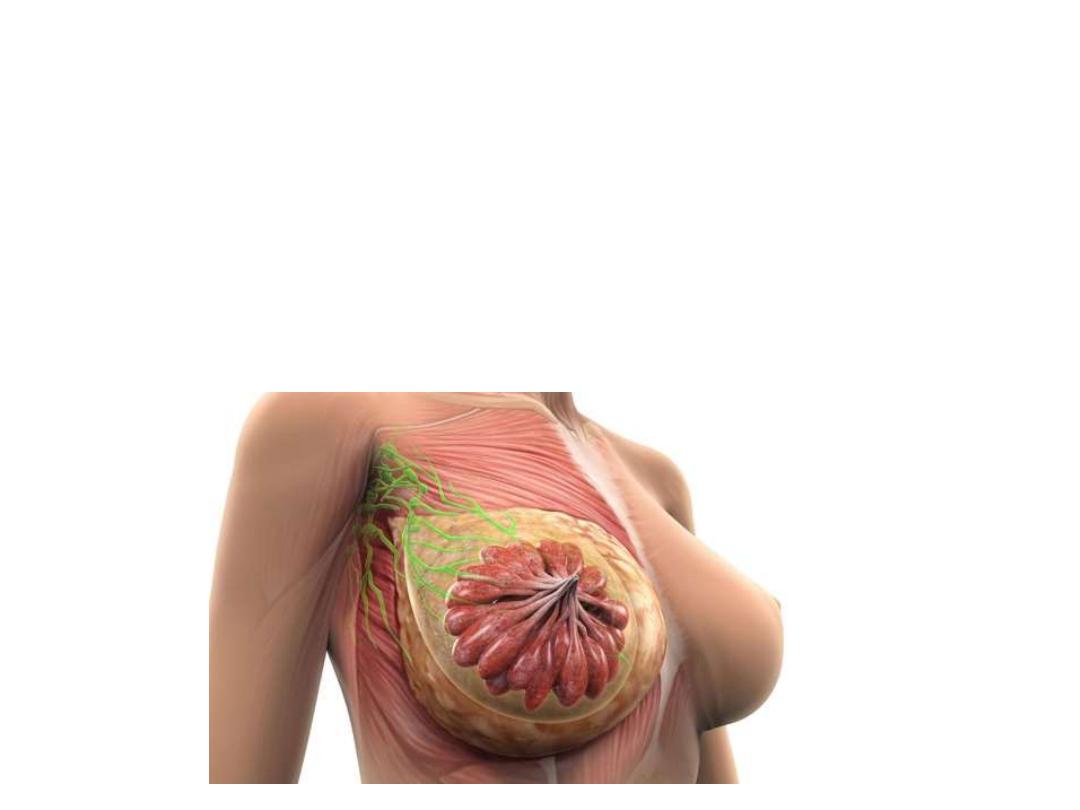
Lymphatic drainage:
1- Superficial lymphatics:
Drain the skin & subcutaneous tissue except the nipple & areola
2- Deep lymphatics:
Drains the rest of the breast tissue + the superficial lymphatics
Deep lymphatics drain to the lymph nodes
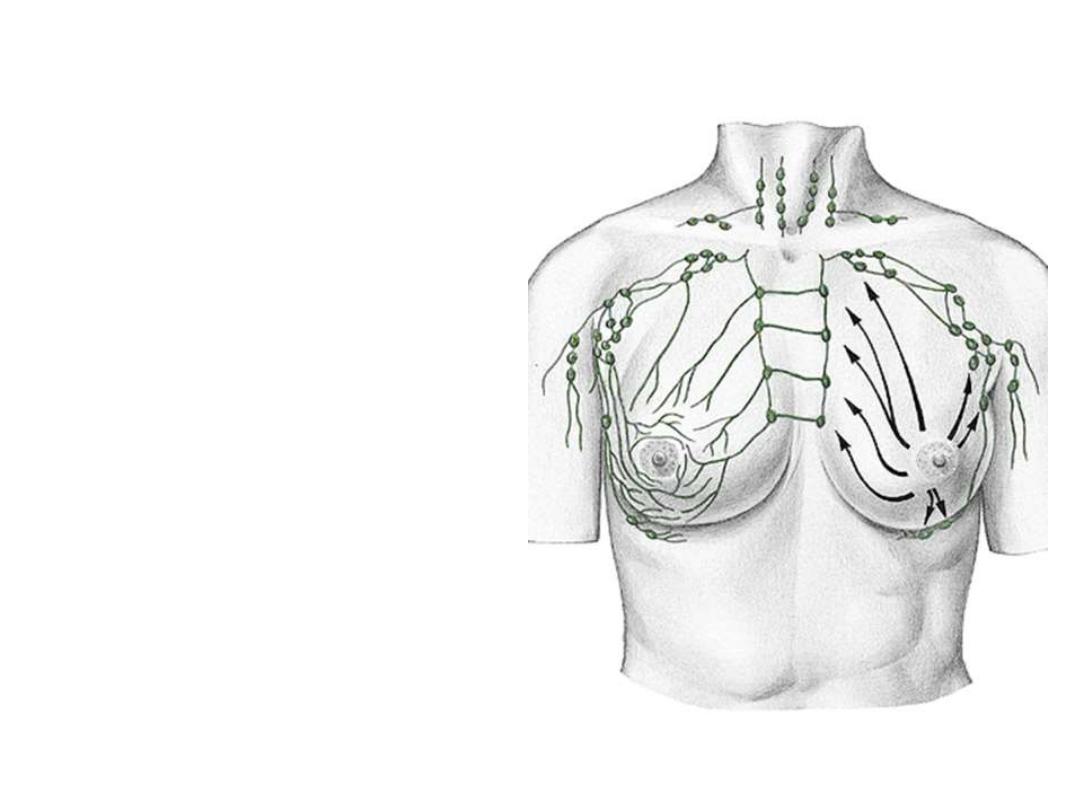
- 75% of breast lymph drains to the
axillary nodes (central & lateral
part)
- 20% to the internal thoracic LN
(medial part)
- The rest drains to:
• Intercostal LN
• Subdiaphragmatic LN
• Supraclavicular LN
• Infraclavicular (cephalic) LN
• Opposite breast LN
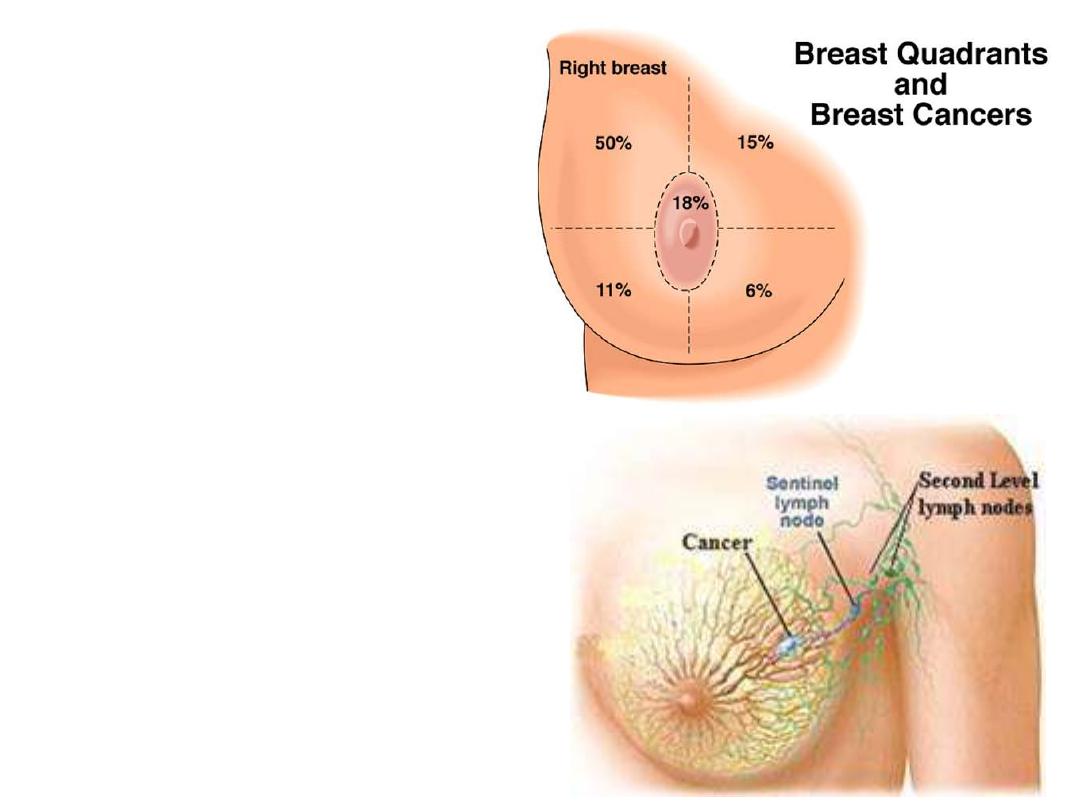
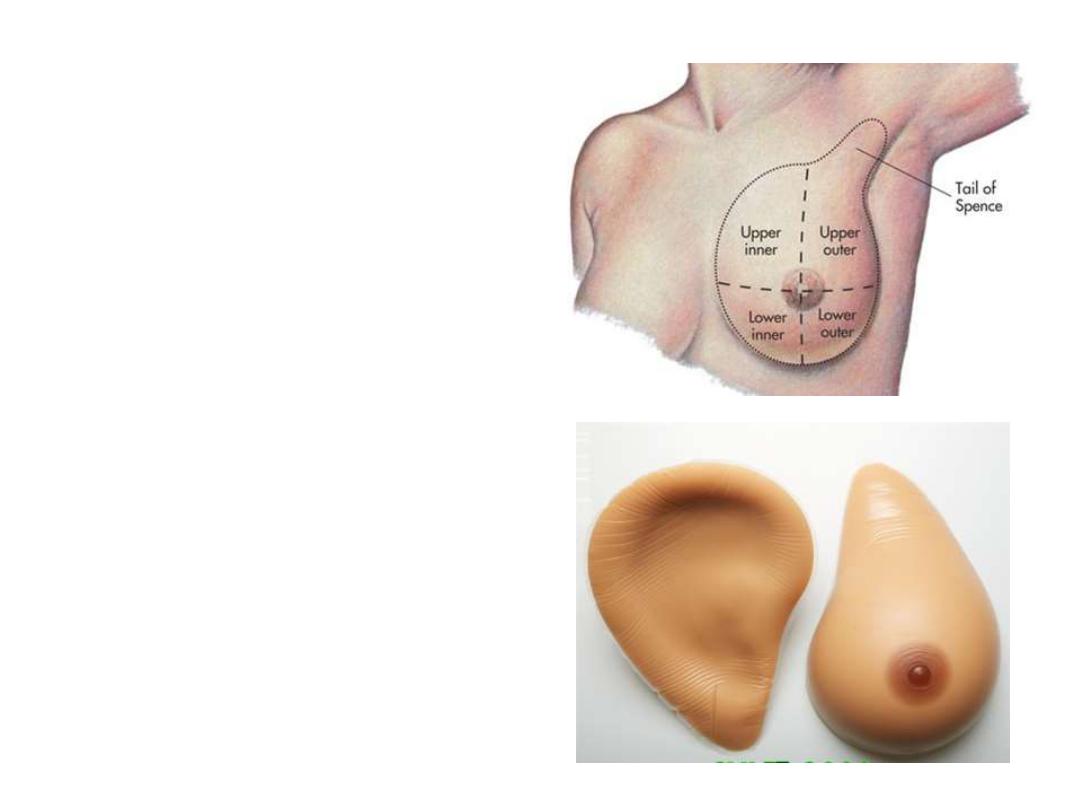
Cancer of the breast:
- Mainly affects the superolateral
quadrant
- Spreads:
1- Locally
2- By lymphatics to LN
3- By blood to distant organs
