
The axilla
(The armpit)

OBJECTIVES
…
To define the axilla
To describe axillary inlet
To recognize axillary walls
To define the axillary vessels & their main branches
To list the groups of axillary lymph nodes
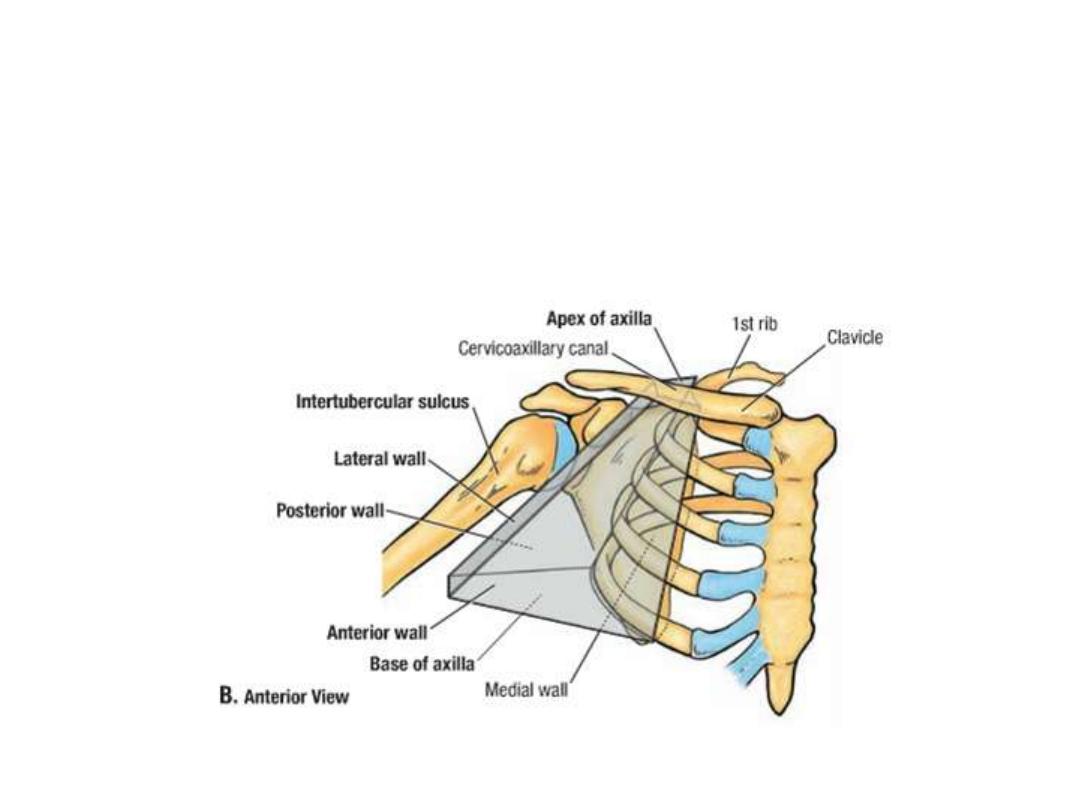
is a pyramid-shaped space between the upper Part of the arm and
the side of the chest.
It forms an important passage for nerves, blood, and lymph
vessels as they travel from the root of the neck to the upper limb.
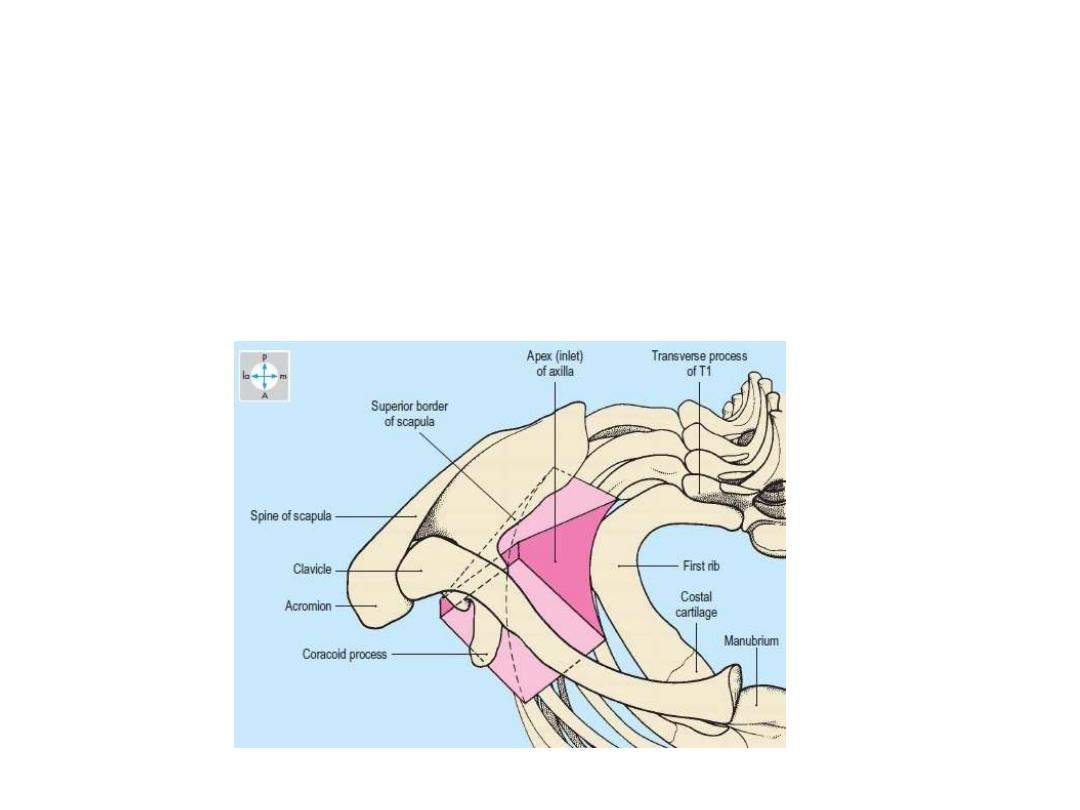
Axillary inlet (the apex):
The apex is bounded by the clavicle, upper border of the scapula and
the outer border of the first rib
It is the channel of communication between axilla and the neck
Through this opening the vessels, nerves
… reach the axilla from the
body
Walls of the axilla:
Anterior wall:
Pectoralis major
Pectoralis minor
Subclavius
Posterior wall:
Subscapularis
Latissimus dorsi
Teres major
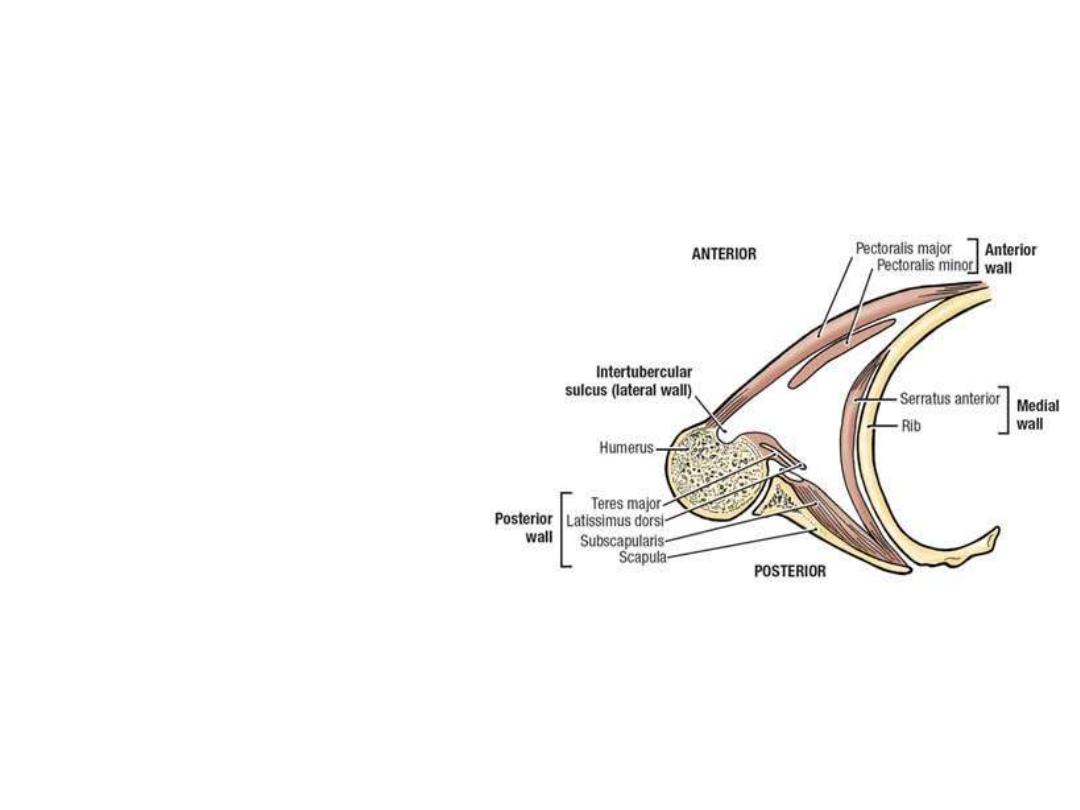
Medial wall:
Serratus anterior covering the
upper 5 ribs
Lateral wall:
Bicipital groove of the humerus
containing coracobrachialis and
biceps
The base:
skin
stretching
between
the
anterior and posterior walls.
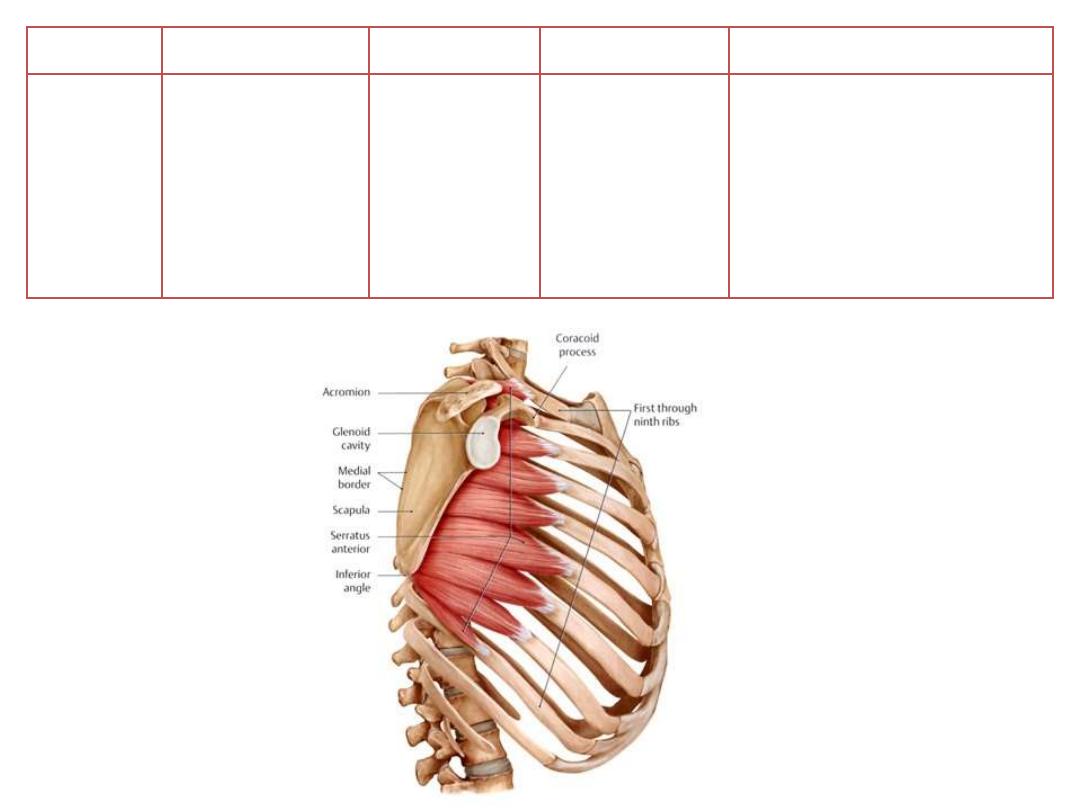
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Innervation
Function
Serratus
anterior
Lateral surfaces
of upper 8-9 ribs
Medial border
of scapula
Long thoracic
nerve [C5,6,7]
• Protraction and upward
rotation of the scapula
• Keeps medial border of
scapula
opposed
to
thoracic wall
Contents of the axilla:
1- Axillary artery
2- Axillary vein
3- Axillary lymph nodes
4- Brachial plexus
5- Axillary fat
The axillary artery:
-
The continuation of subclavian artery at the outer border of the 1
st
rib
-
Becomes the brachial artery at the lower border of teres major
-
Surrounded by fascial prolongation from the neck called the axillary sheath
-
Throughout its course, the artery is closely related to the cords of the
brachial plexus and their branches
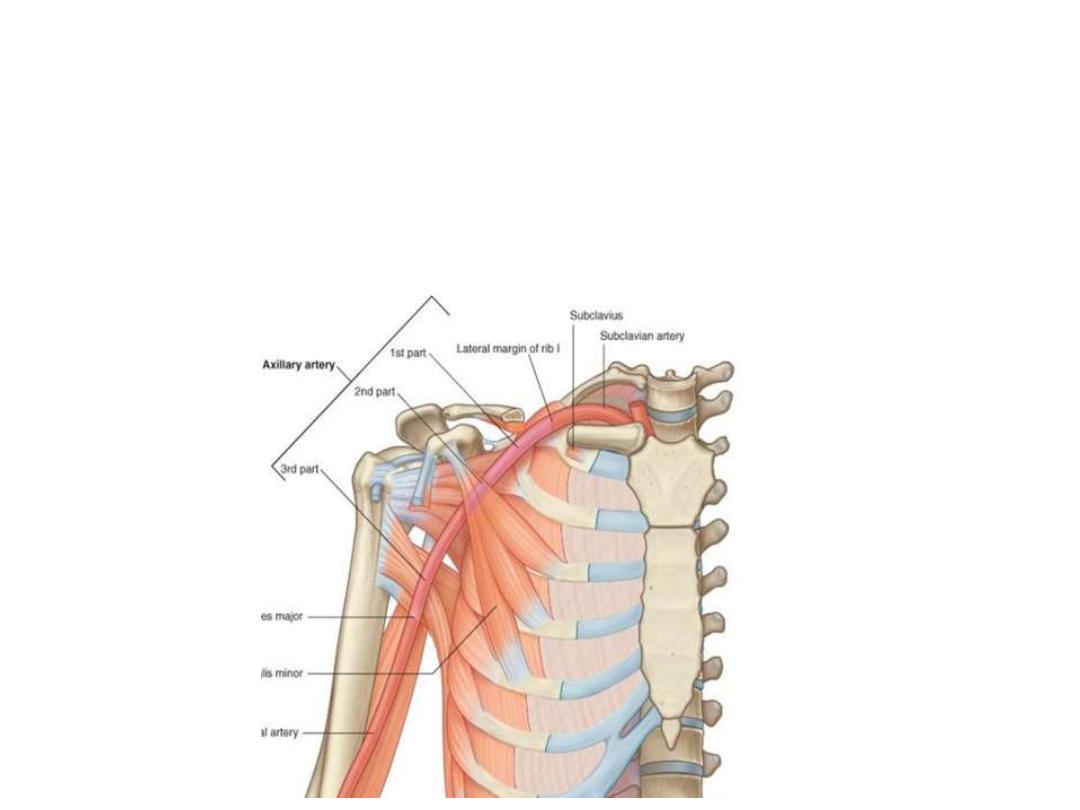
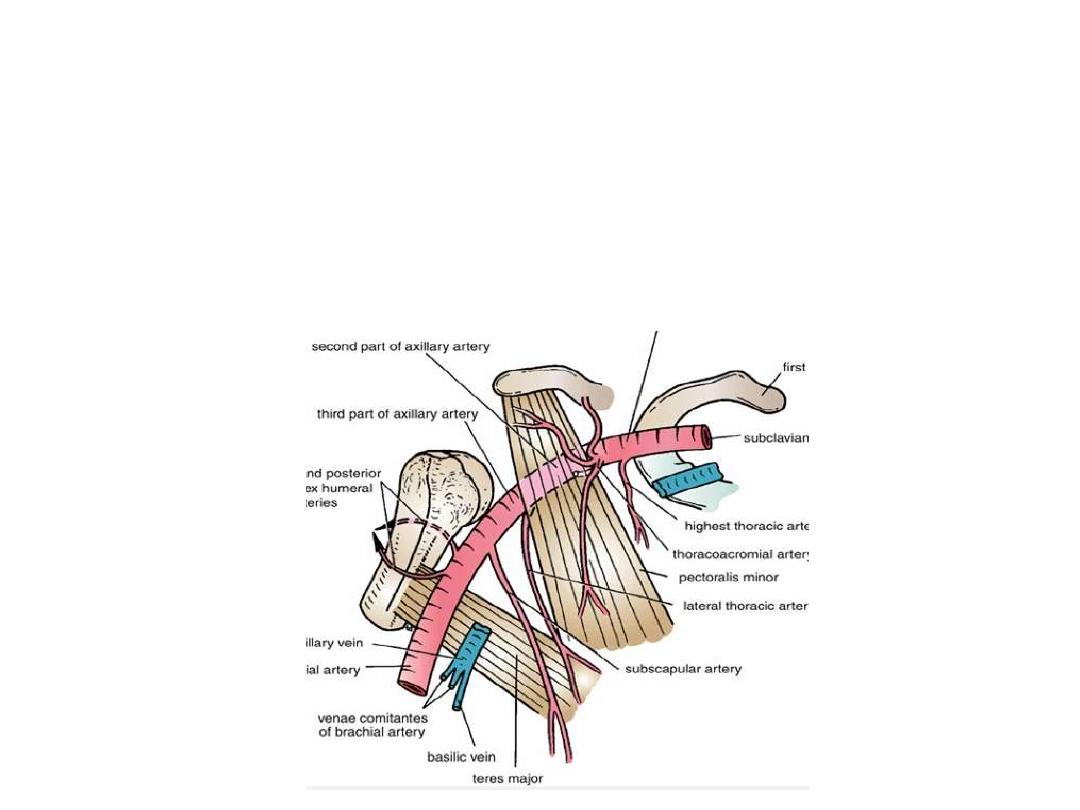
The artery passes behind pectoralis minor according to which it is divided into:
1st part:
proximal to pectoralis minor (1
st
rib
– PM); gives ONE branch
2nd part:
posterior to pectoralis minorl gives TWO branches
3rd part:
distal to pectoralis minor (PM
– TM); gives THREE branches
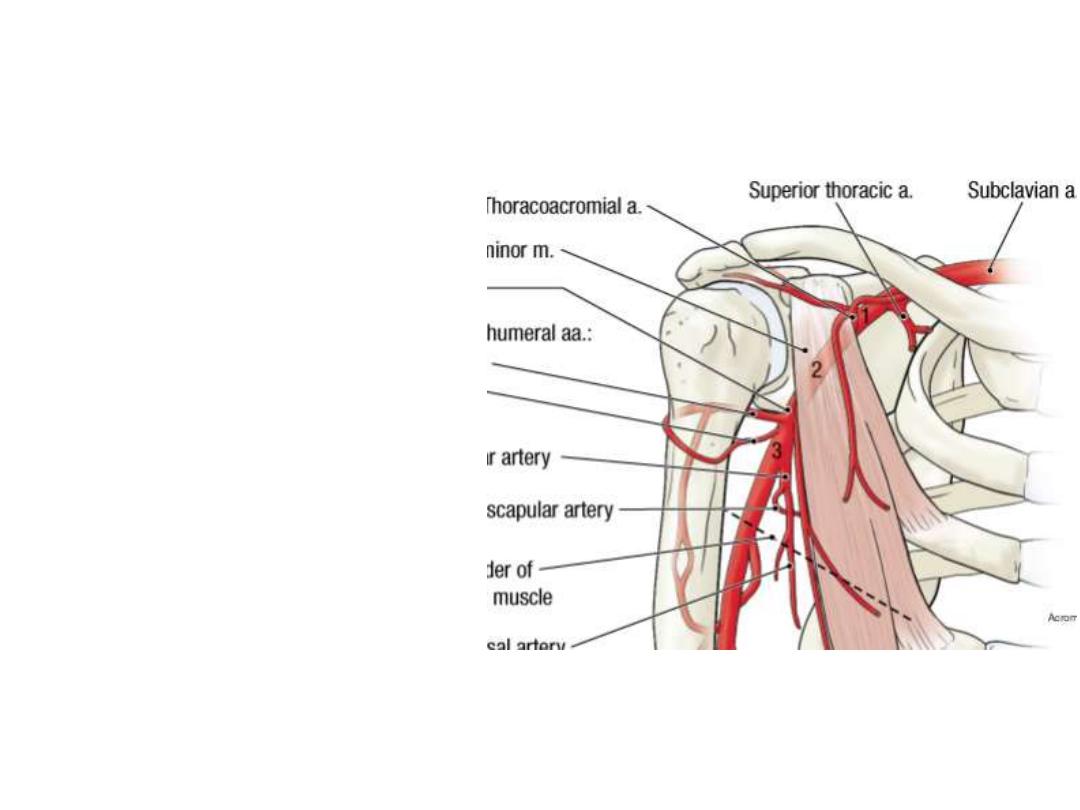
Branches:
1
st
part: Superior thoracic a:
- Small artery runs between
the two pectoral muscles
- Supplies the side of the chest
in the upper 2 intercostal
spaces
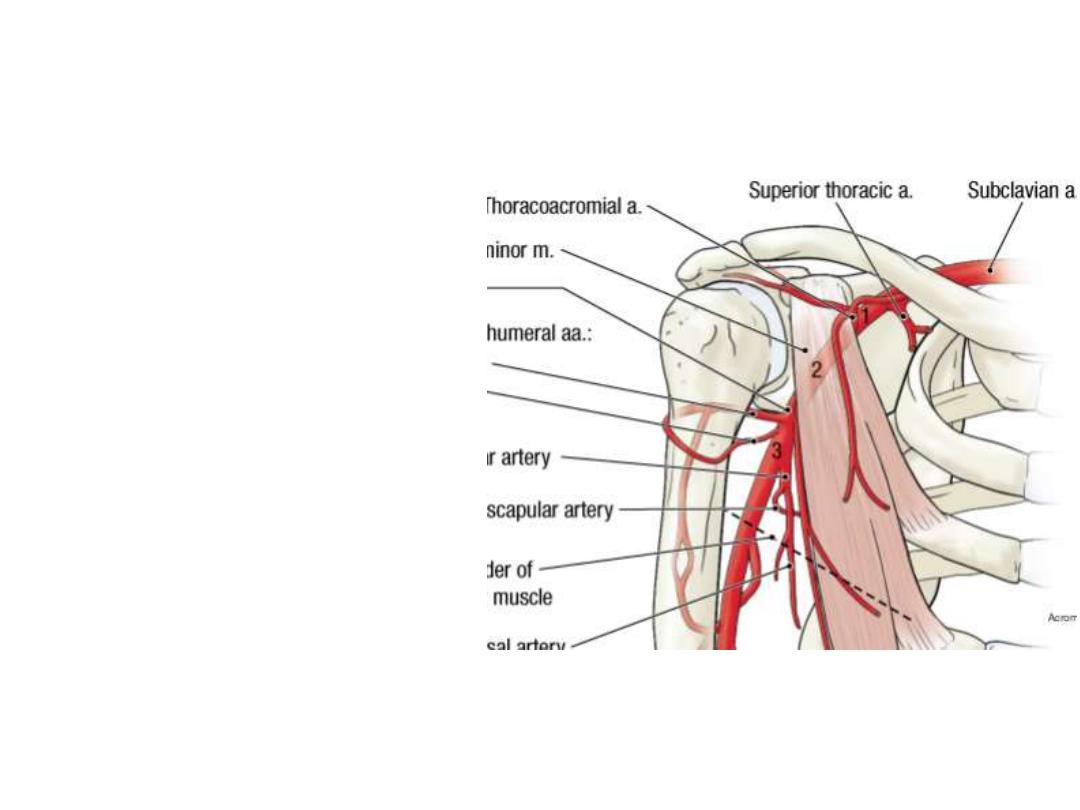
2
nd
part:
Lateral thoracic a:
- Passes
along
the
lower
border of P minor
- Supplies pectoral muscles,
serratus anterior & the breast
Thoracoacromial a:
- Passes
along
the
upper
border of P minor
- Pierces
the
clavipectoral
fascia
- Divides
into
4
branches
(pectoral, acromial, clavicular
& deltoid)
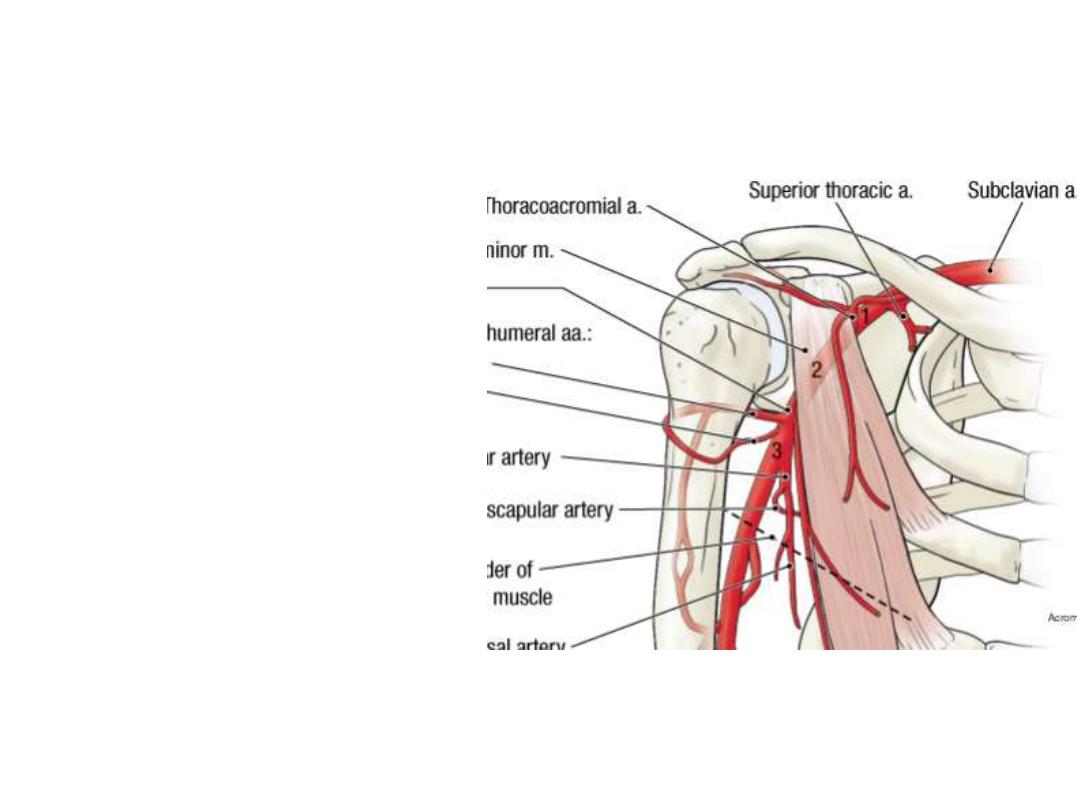
3
rd
part:
Subscapular a:
- Largest branch
- Passes towards the inferior
angle of scapula
- Accompanied by thoracodorsal
n
- Gives the circumflex scapular
branch
- Both
share
in
scapular
anastomosis
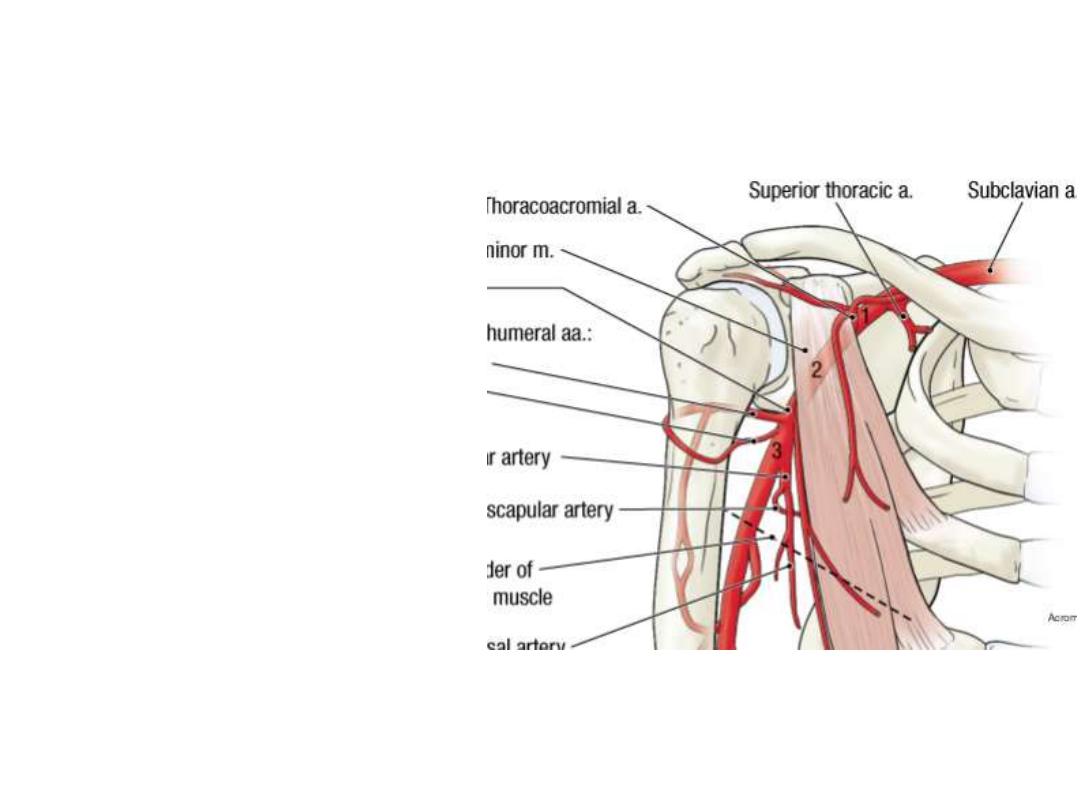
3
rd
part:
Anterior circumflex humeral a:
- Surrounds the surgical neck
of humerus anteriorly
Posterior circumflex humeral a:
- Leaves the axilla through the
quadrangular space
- Surrounds the surgical neck
posteriorly
Both
circumflex
arteries
anastomose with each other &
are important for the supply of
the shoulder joint
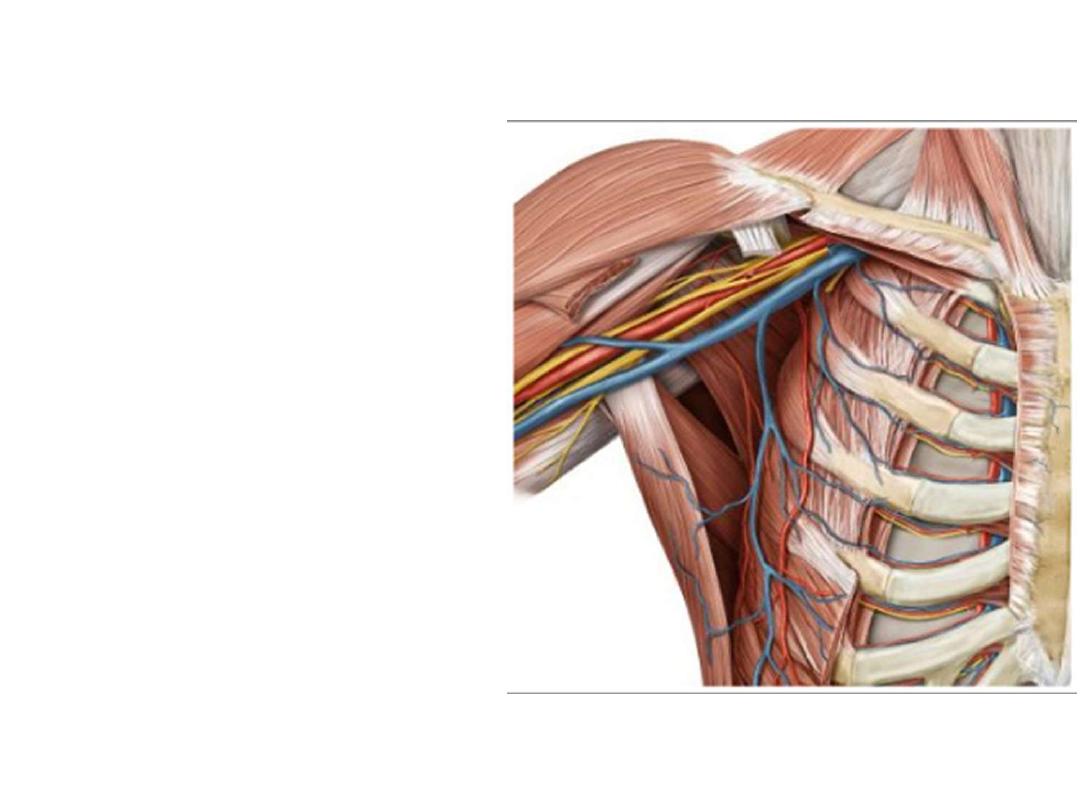
The axillary vein:
-
This
large
vein
is
the
continuation of the brachial vein
at the lower margin of the teres
major
-
It becomes the subclavian vein at
the outer border of the 1
st
rib
-
Has similar tributaries to the
branches of axillary artery
-
Lies on the medial side of the
artery

Superficial veins of the upper limb:
1- Cephalic (antecubital) vein:
- Begins from the lateral side of the
dorsal venous network of the hand
- Passes in the superficial fascia
along the pre-axial border of the UL
- Empties in the axillay vein in the
deltopectoral groove
- Communicates with the basilic vein
by the median cubital v in the cubital
fossa
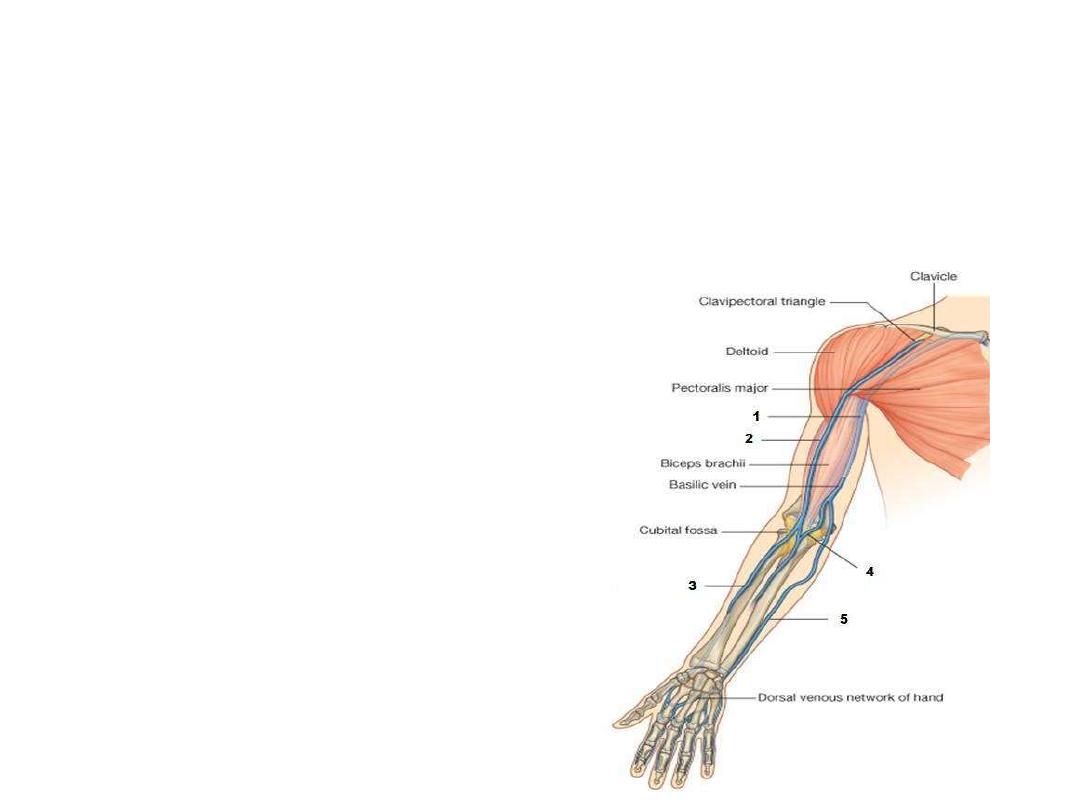
2- Basilic (antecubital) vein:
- Begins from the medial side of the dorsal venous network of the hand
- Passes in the superficial fascia along the post-axial border of the UL
- Meets the brachial artery in the midarm
- Communicates with the cephalic vein by the median cubital v in the cubital
fossa
- Uncommonly used for cannulation
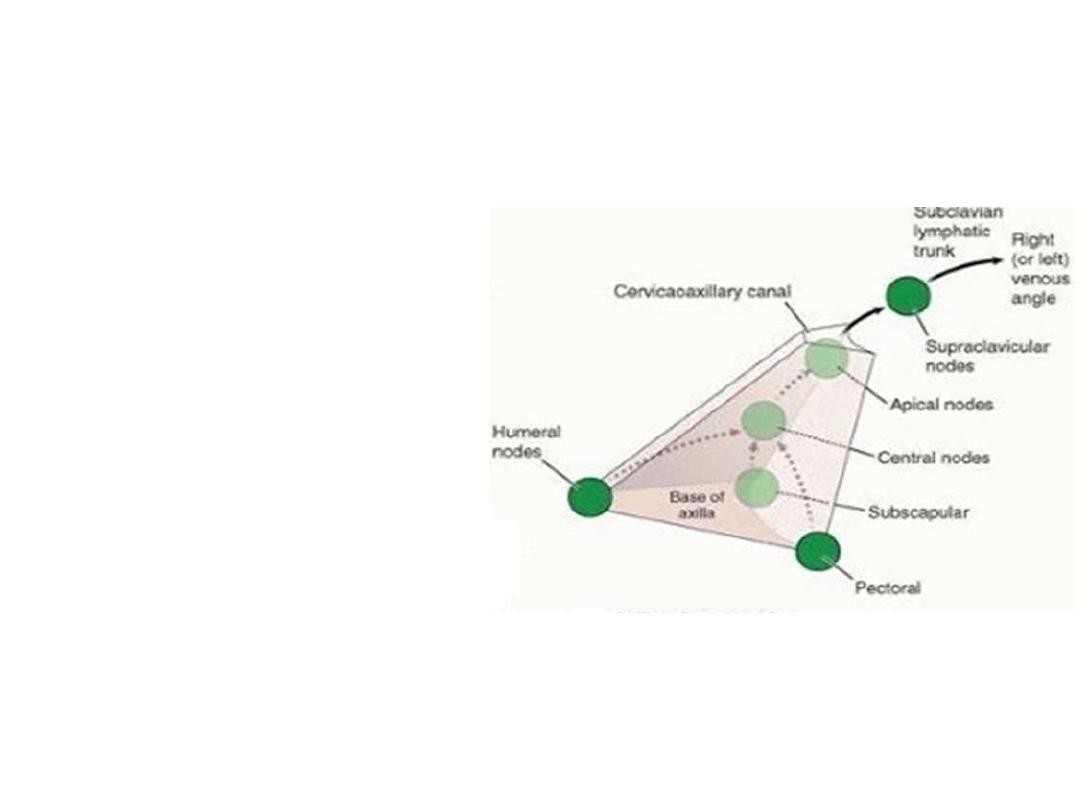
Axillary lymph nodes:
Around 20-30 LN
Embedded in the axillary fat
around the branches of axillary
artery
They drain an extensive area of
the UL & trunk
They are arranged in 5 groups
The arrangement reflects the
pyramidal shape of the axillary
space
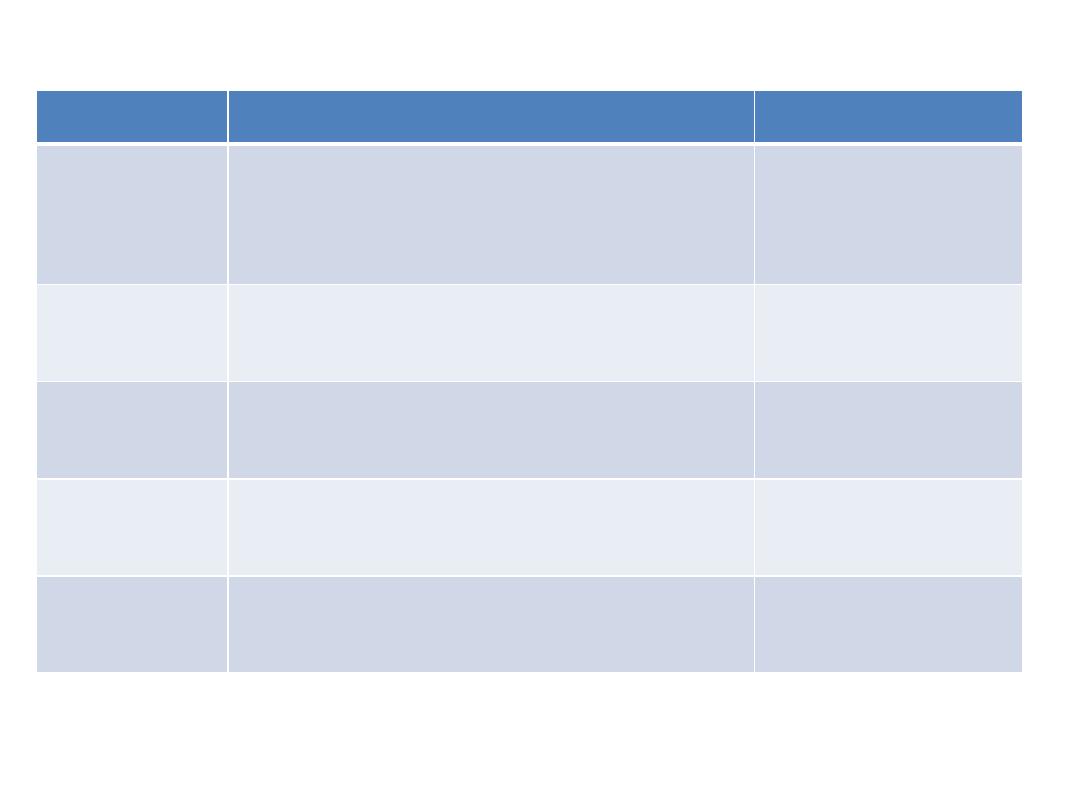
Efferent
Afferent
Group
Central
Breast
Anterior chest wall
Pectoral region
Pectoral
Central
Cubital nodes
Deep lymphatics of UL
Humeral
Central
Back of trunk to the waist
Scapular region
Scapular
Apical
Pectoral, scapular & humeral
groups +
breast
Central
Subclavian
lymph trunk
Central +
breast
Apical
