
Objectives
• Name the major parts and function of the respiratory
system.
• Define combining forms used in building words that
relate to the respiratory system and its parts.
• Comprehension of English language
• Describe the symptoms, disorders, treatments, and
surgical procedures related to the respiratory system

Student Duties
Read the lecture before attending
Print out the Formative assessment of this lecture and
hand it to the lecturer ‘solved’. It is your homework.
You should write on it your name, the date, your group
and the name of your lecturer.
A piece of advice: Take a look at the exercises of the
lecture before your actual reading, it will help you
design your strategy of studying.

NOTES
The methodology of the exercises in your formative
assessment in this lecture and in the other lectures
of the terminology module are similar to your
Summative exam.
If you encounter new terms not available in your
lecture, look it up using a dictionary or invest your
e-learning skills to look it up in the website .
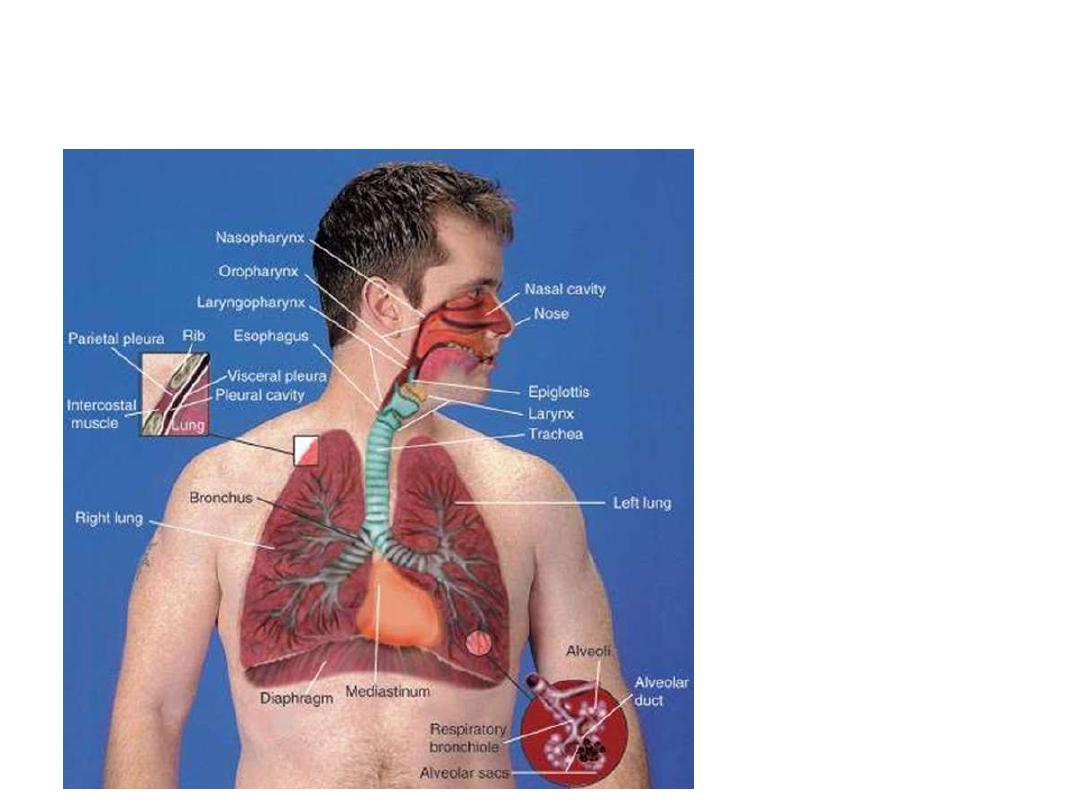
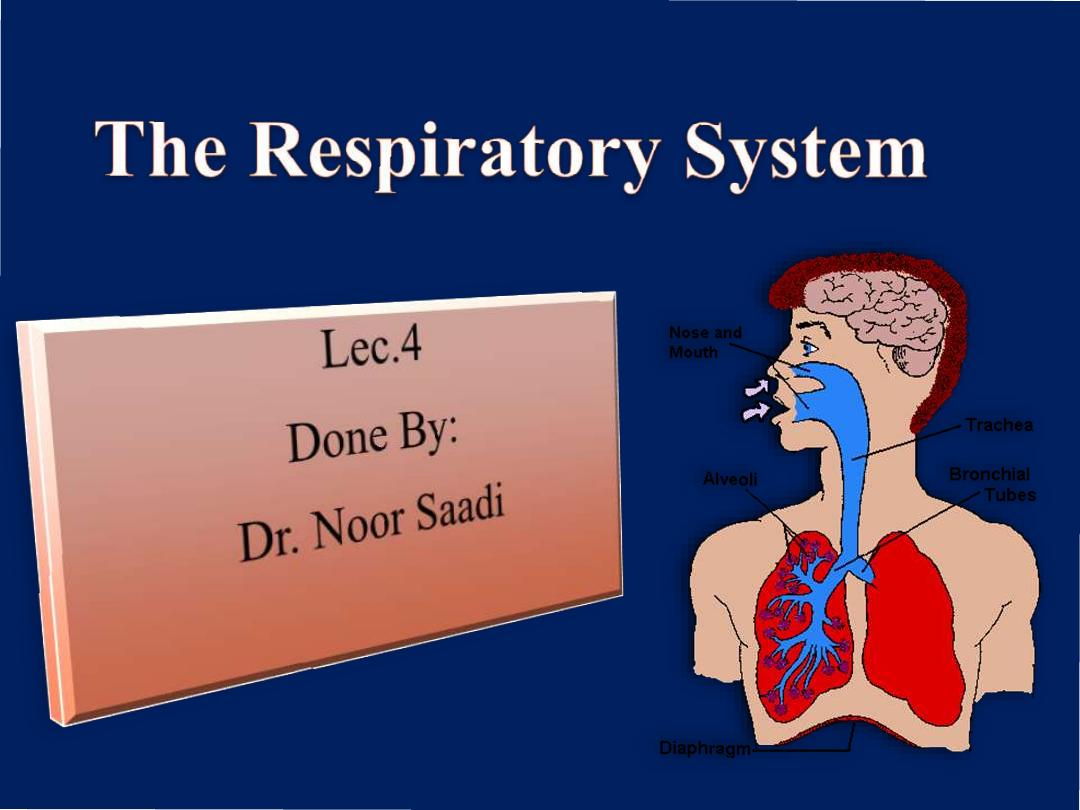
The Respiratory
System
The respiratory system performs
two
major tasks:
1-
• Exchanging air between
the body and the outside
environment
known
as
external respiration
2-
• Bringing oxygen to the
cells and removing carbon
dioxide from them referred
to as internal respiration
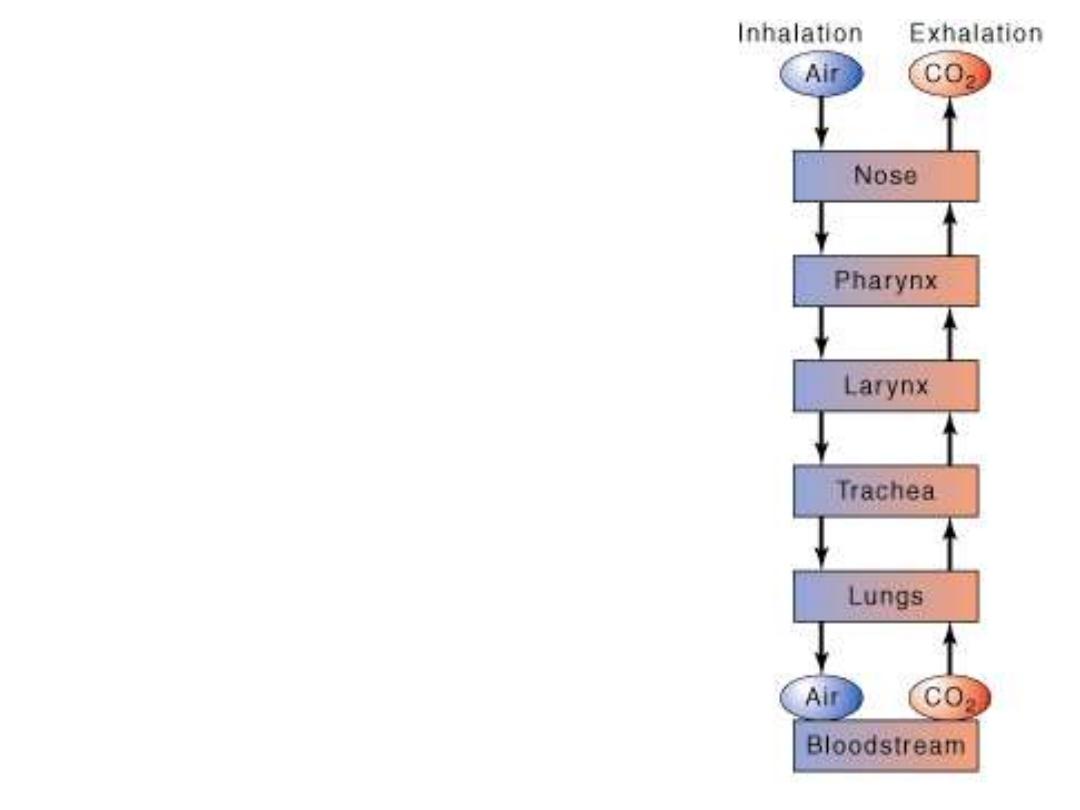
The
passage
of
air
from
the
external
environment
to
the
lung
capillaries,
bloodstream
and
out
consists
of
one
inhalation
and
one
exhalation.
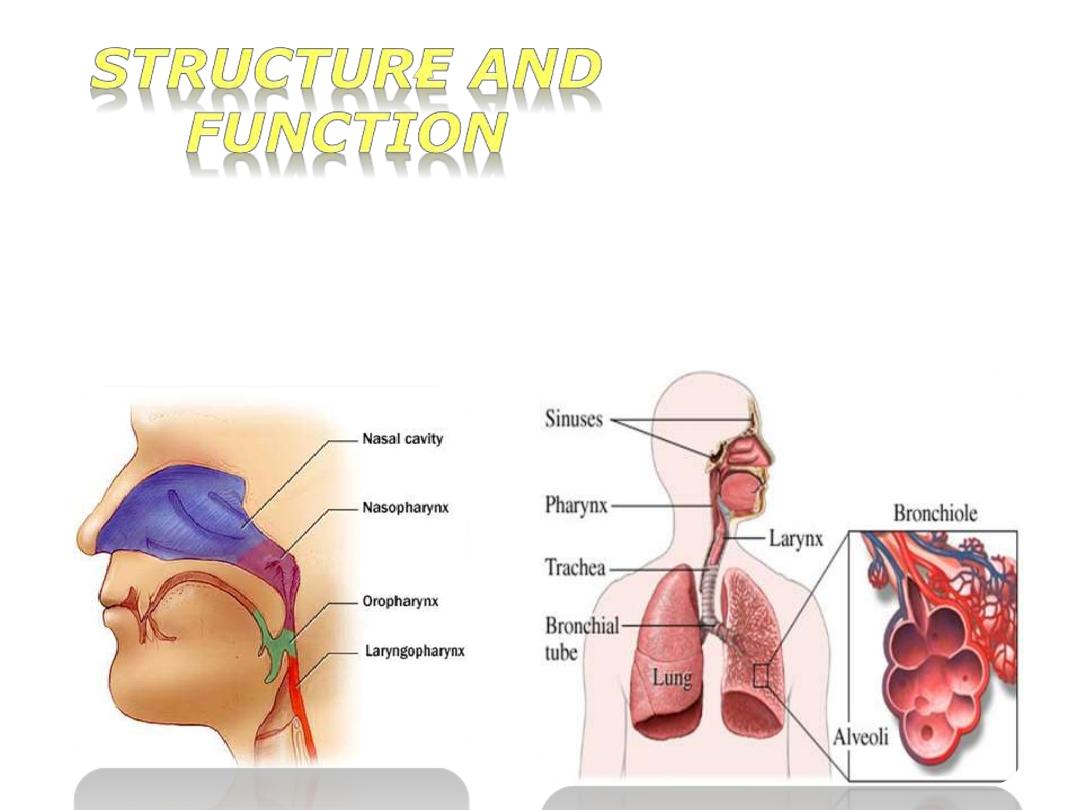
The
passage
of
air
from
the
external
environment
to
the
lung
capillaries,
bloodstream
and
out
consists
of
one
inhalation
and
one
exhalation.
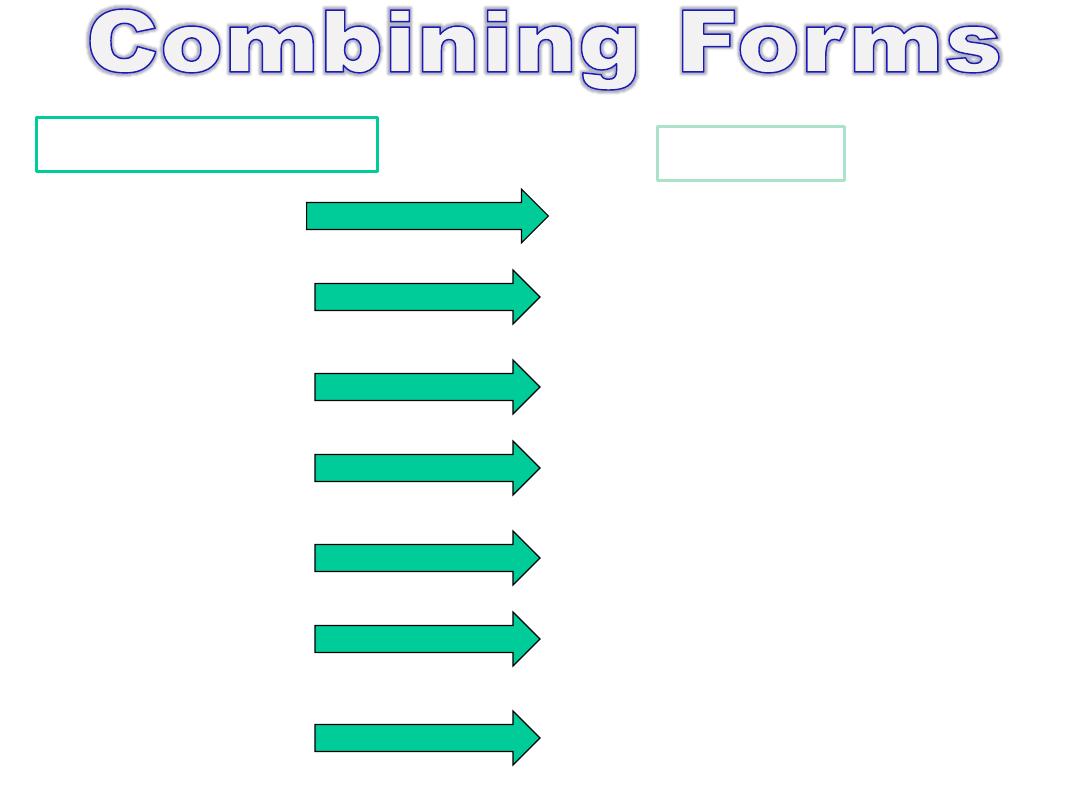
Combining Form
Meaning
adenoid (o)
alveol (o)
bronch (o)
bronchiol (o)
capn (o)
epiglott (o)
laryng (o)
adenoid; gland
alveolus
bronchus
carbon dioxide
larynx
epiglottis
bronchiole
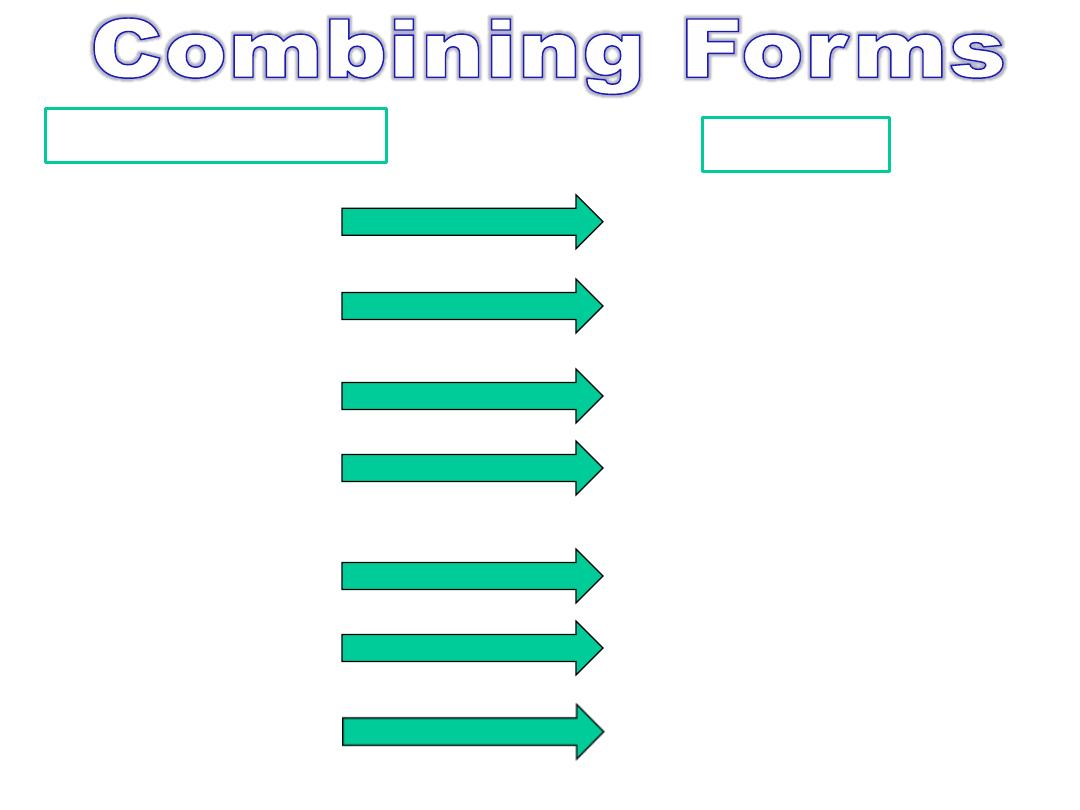
Combining Form
Meaning
lob (o)
mediastin (o)
nas (o)
or (o)
oxia (o)
pharyng (o)
phonia
lobe of the lung
mediastinum
nose
mouth
oxygen
pharynx
voice
,
sound
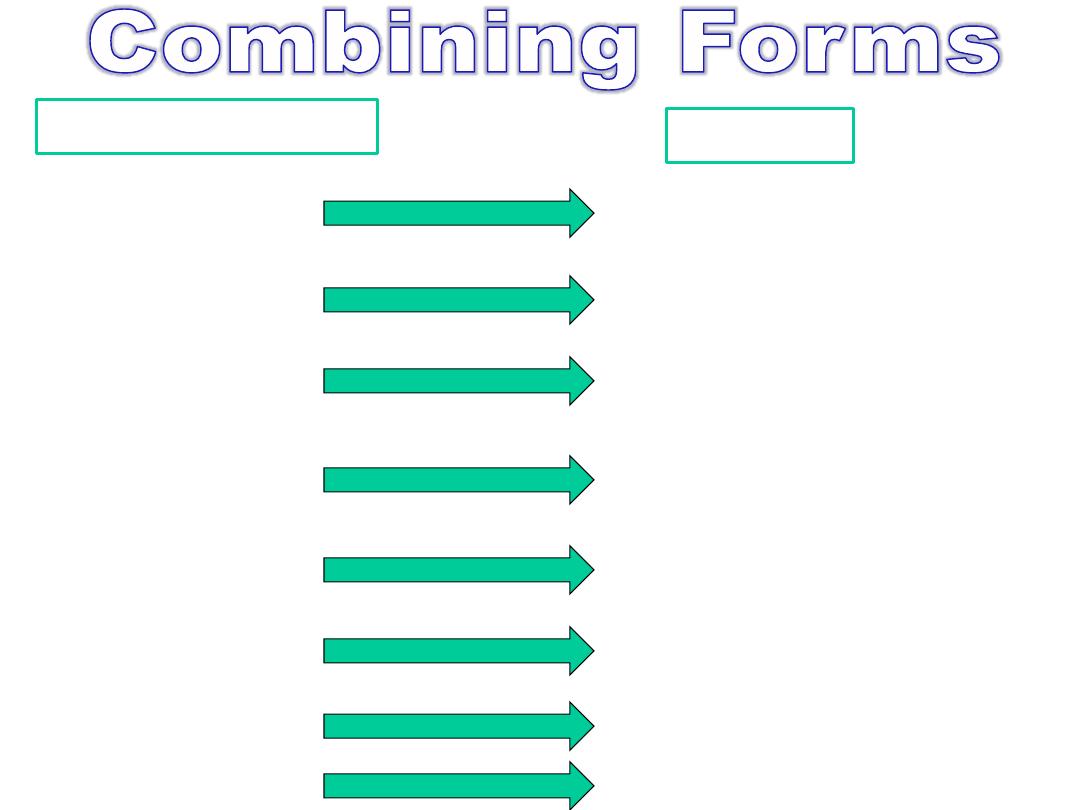
Combining Form
Meaning
phren(o)
pleur(o)
pneum (o)
rhin (o)
spir (o)
steth (o)
thorac (o)
trachea
diaphragm
pleura
air
nose
breathing
chest
thorax
windpipe
P
a
t
ho
l
og
y
a
d
e
n
o
i
d
i
ti
s
ep
i
g
l
l
o
tt
i
1
t
i
i
1
s
b
r
on
ch
i
t
i
s
I n
f
l
l
l
a m ma
t
o
r
y
C
o
n
d
i
1
t
i
o
ns
p aryng tis
rh
i
n
i
t
is
pne
un1
o
n
i
t
i
s
s
i
n
u
s
i
t
i
s
eu
p
n
e
a
I
Breathing Patterns
I
a
p
ne
a
hyp
o
pnea
o
r
t
hopnea
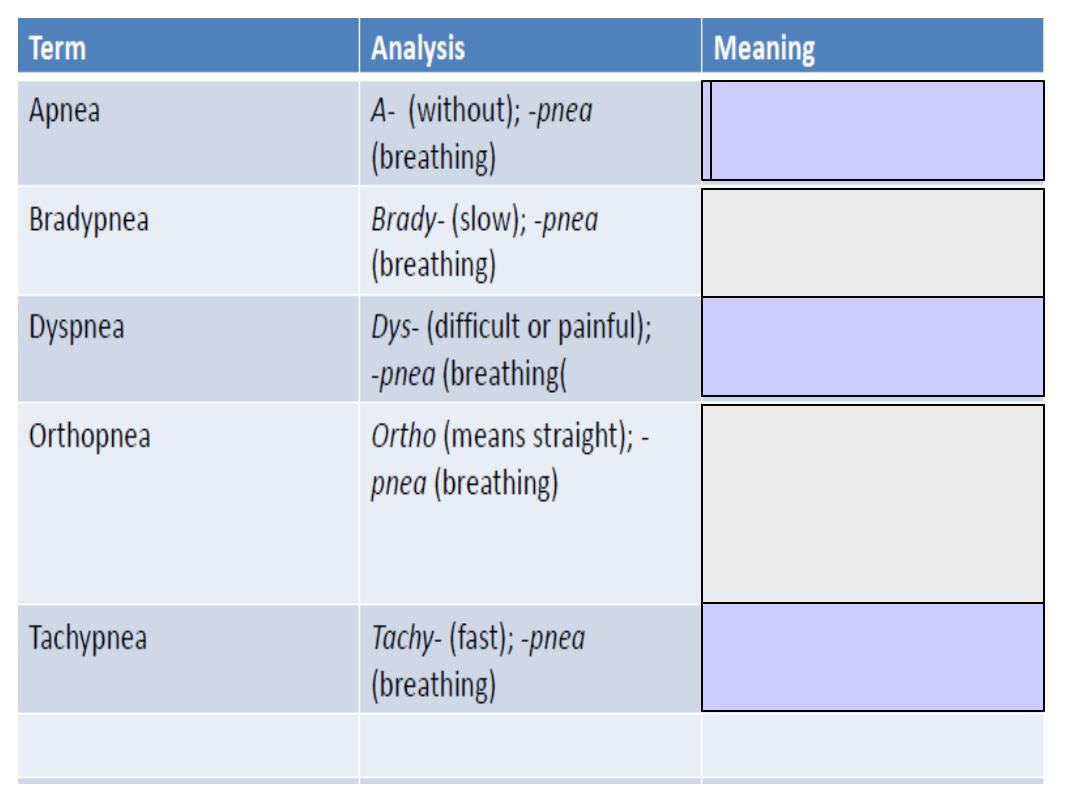
Abnormal slowness of
respiration
Without breathing
Painful or difficult
breathing
Discomfort or difficulty
in breathing while lying
flat ; difficulty is
relieved by sitting up
Abnormal fasting of
breathing
Dysphonea:
means difficult in speech

Pathology
Upper
respiratory
infection
is
a
term
that
covers
an
infection
of
some
or
all
of
the
respiratory
tract.
Such
as:-
-
Rhinitis: means inflammation of the
nasal cavity.
-
Sinusitis
; inflammation of the respiratory sinus.
-
Epiglottitis
-
Influenza
: viral infection that affect respiratory tracts
-
Laryngitis
-
Tuberculosis (TB)
: is an infectious disease
caused by bacteria.
-
Hemoptysis
-
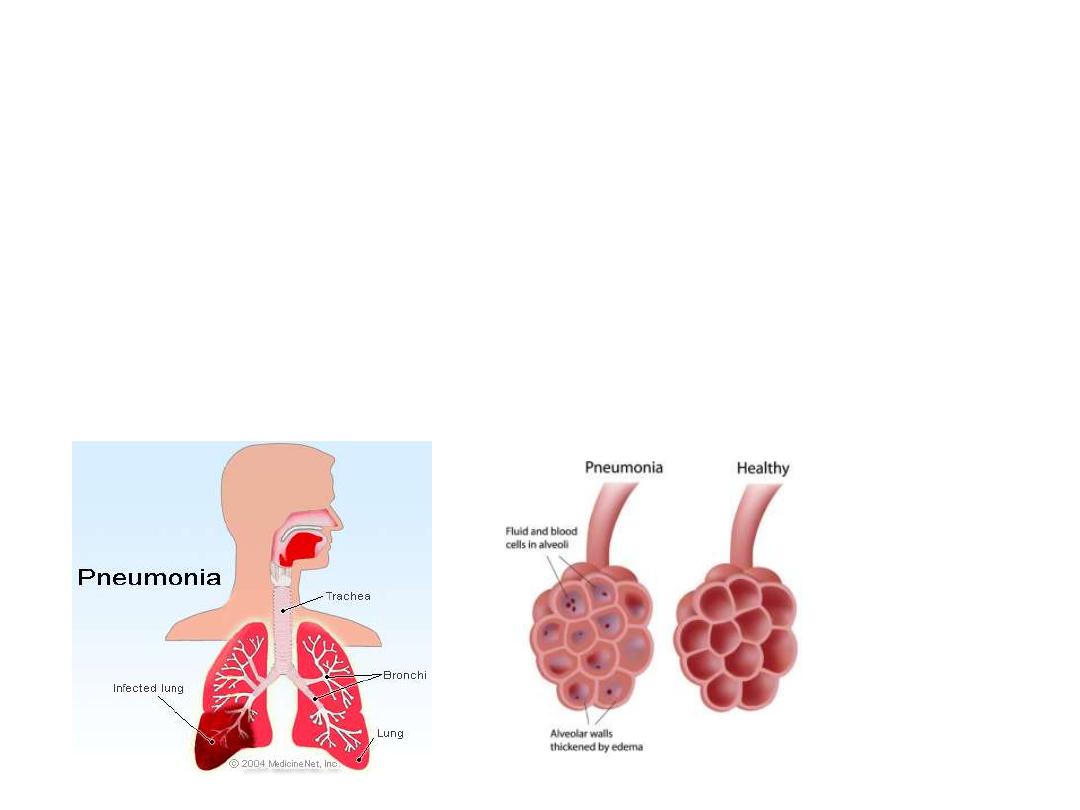
pneumonia
Hemoptysis
Hem/o
(blood);
-ptysis
(spitting).
Lung
or
bronchial
hemorrhage
that
results
in
the
spitting
of
blood.
Pneumonia
Pneumon/o (air, lung); ia
(condition). Inflammation of a
lung caused by
Infection, chemical inhalation or trauma

pathology
Chronic
Obstructive
Pulmonary
Disease
(COPD)
is
a
term
for
any
disease
with
chronic
obstruction
of
the
bronchial
tubes
and
lungs
that
may
be
due
to
increase
production
of
secretions
or
actual
destruction
of
lung
tissues
such
as:
Emphysema:
Asthma
Cystic
fibrosis
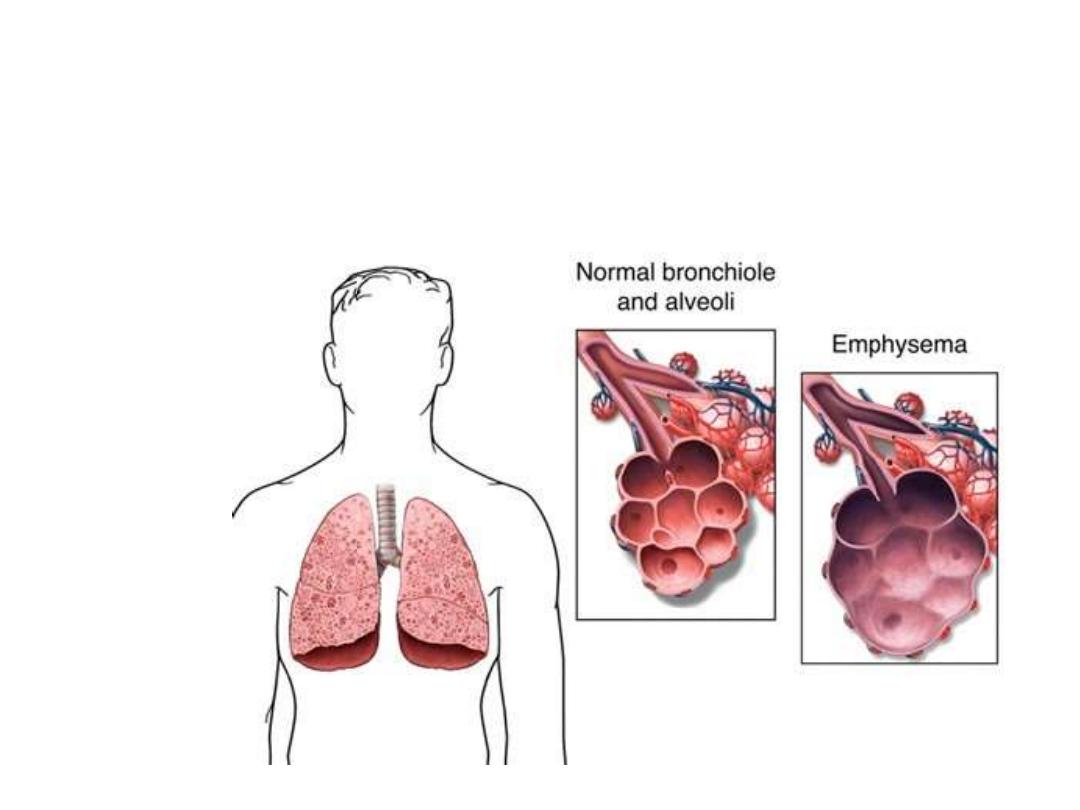
Emphysema:
in
which
alveoli
inefficient
because
of
distension
lead
to
permanently
alveolar
spaces.
The
alveolar
walls
become
thin
and
are
predisposed
to
rupture.
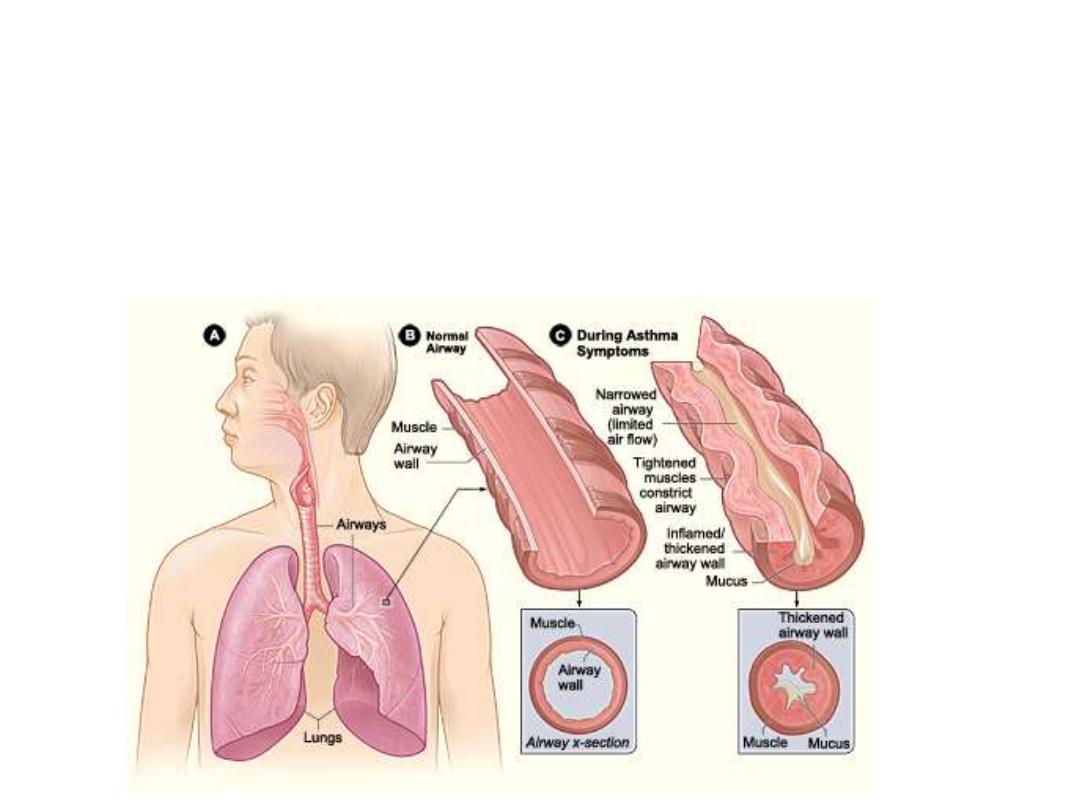
Asthma:
a
Greek
word
meaning
a
panting.
This
disease
has
narrowing
of
the
bronchi
leading
to
dyspnea,
wheezing
and
coughing.
•
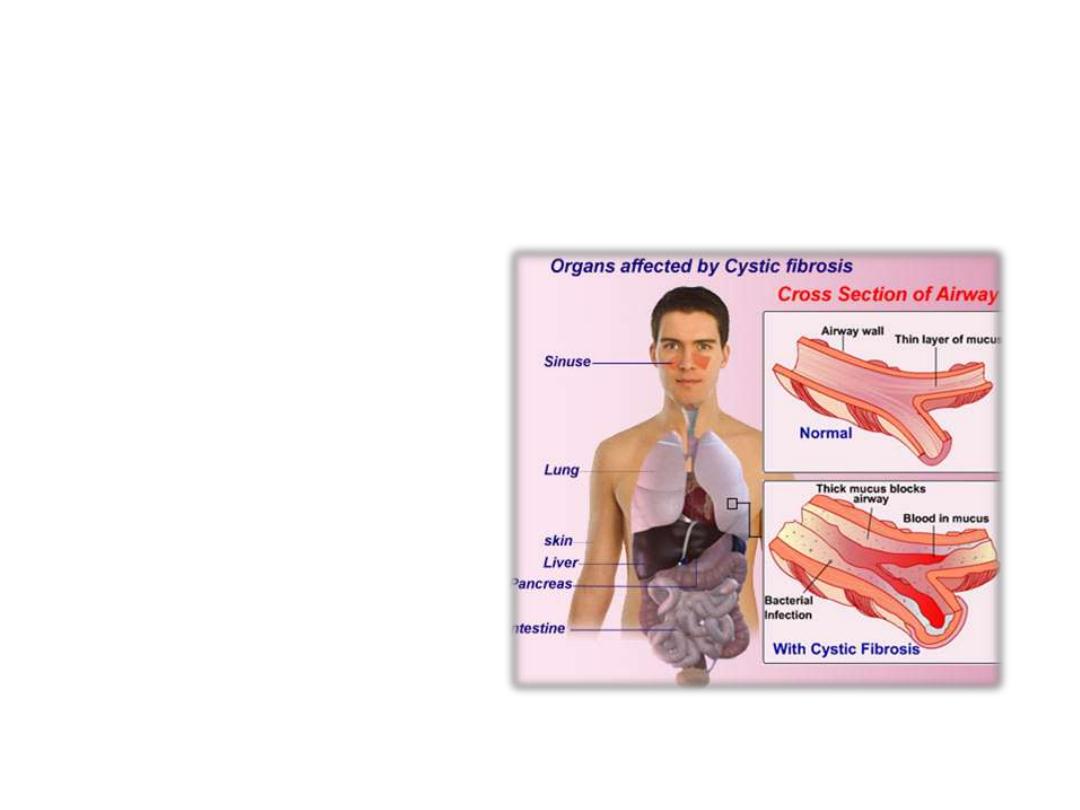
Cystic Fibrosis
From
the
Greek
word
kystis
(bladder,
pouch);
from
the
Latin
word
fibra
(fiber);
-osis
(abnormal
condition).
Disease
of
the
exocrine
glands
that
causes
secretion
of
abnormally
thick
mucus
which
leads
to
chronic
obstruction.
.
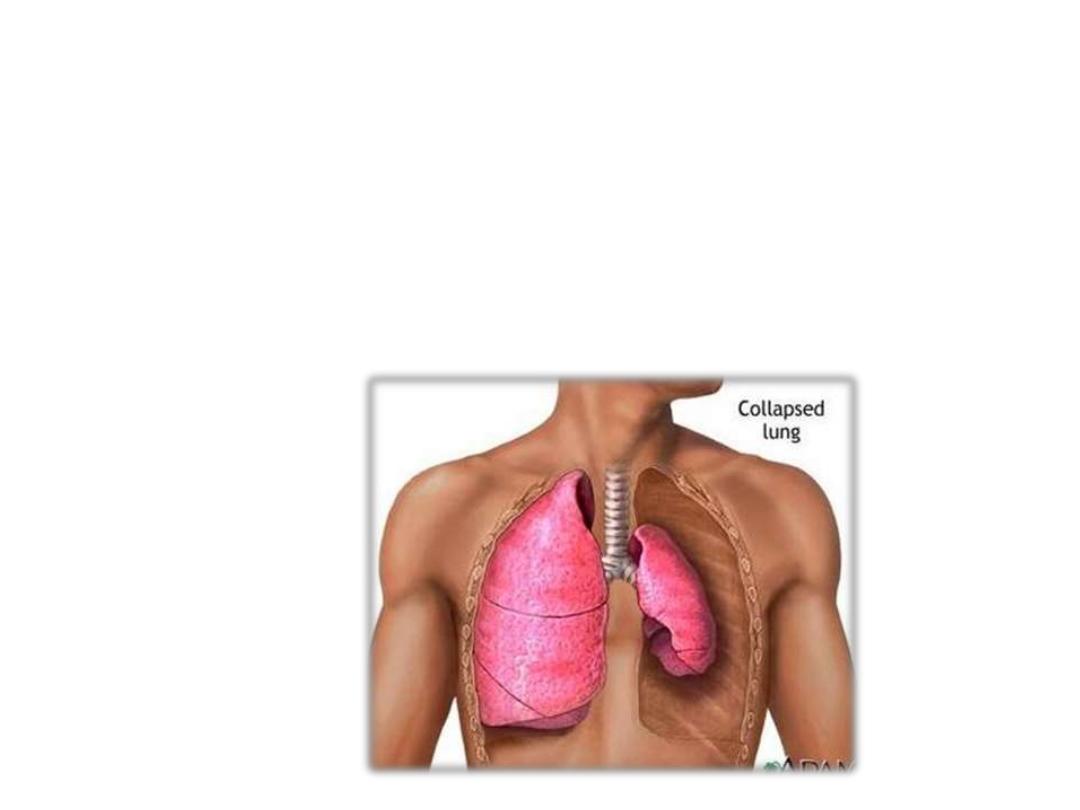
Expansion disorder:
-
Atelectasis
(ateles) is Greek meaning “incomplete”; -ectasis
means (expansion). Collapsed of a lung or part
of a
lung lead to decreased gas exchange.
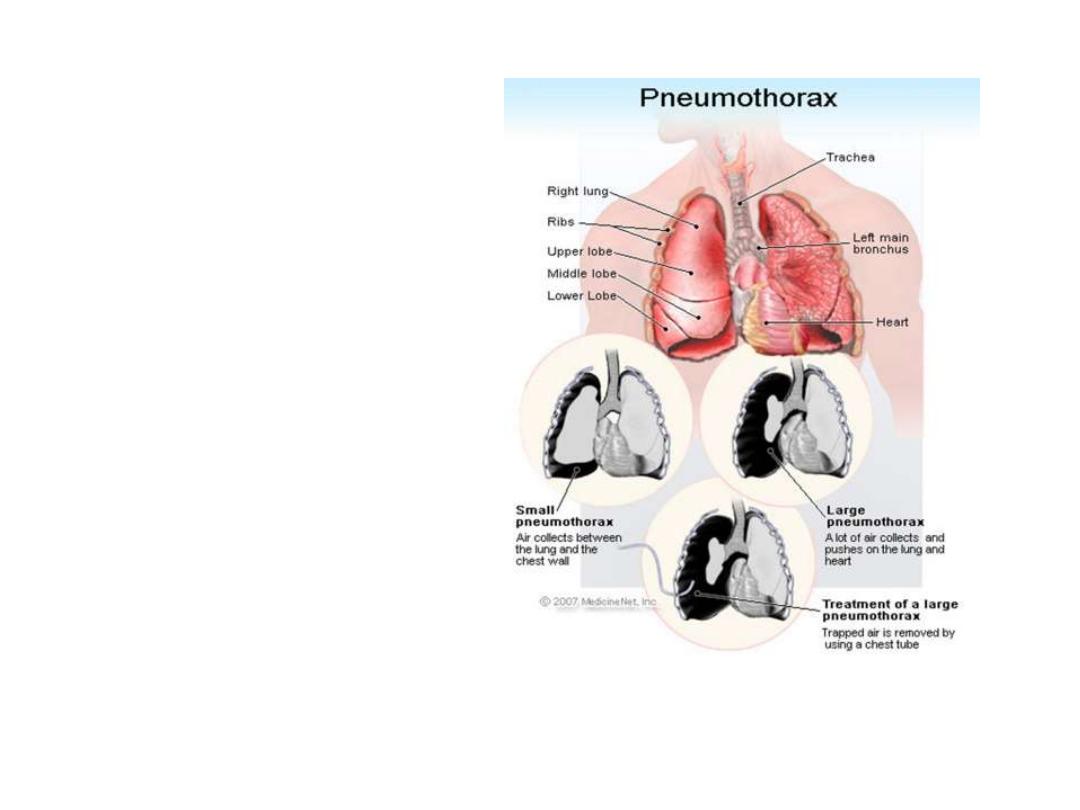
Pneumothorax
•Pneumon/o
(air, lung);
from
the Greek word
thorakos
(breastplate,
chest).
Accumulation of
air
or gas in the pleural
cavity.
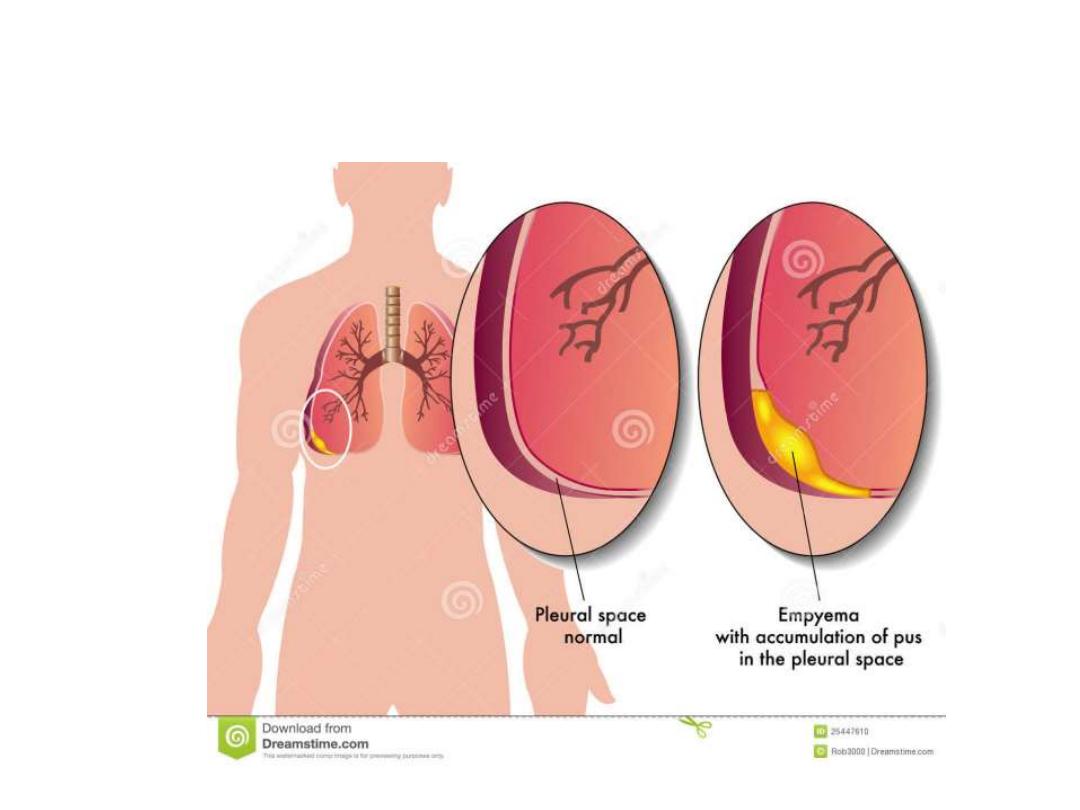
Empyema
•Pus
in the pleural cavity.

Other disorder
Bronchiectasis:
mean chronic dilation of bronchi.
Bronchiostenosis:
mean narrowing of bronchial tube.
Bronchospasm:
abnormal contraction of bronchi.
Dysphonia:
difficult or painful speech.

Surgical Terms
Otorhinolaryngologists
are physicians that specialize in
disorders of the
upper respiratory tract.
Surgical Removal Conditions:
Tonsillectomy
Laryngectomy
Lobectomy
Adenoidectomy
Pneumonectomy
Surgical Terms
Surgical Terms
Surgical Incisions
Tracheostomy tube
Laryngotracheotomy
Sinusotomy
Thoracotomy
Tracheotomy
•Endotracheal intubation is the insertion of a
tube through the nose or mouth, pharynx, larynx
and into the trachea to establish an airway.

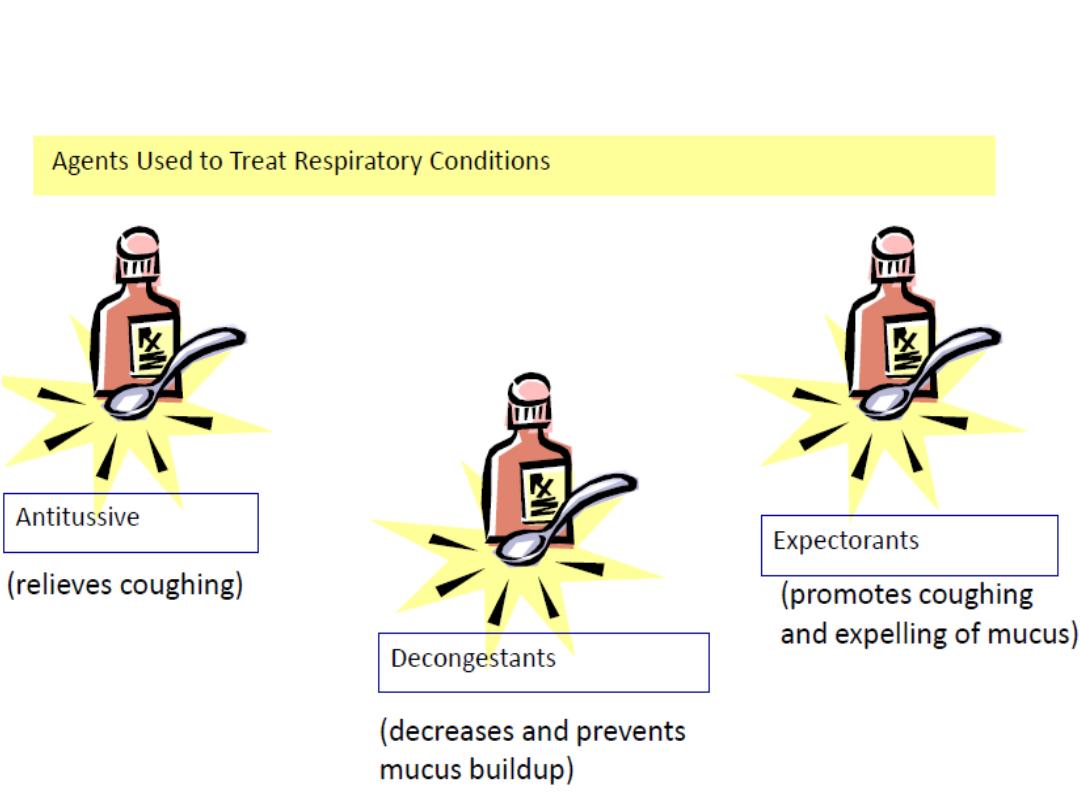
pharmacology
Antibiotics,
antihistamines, antipyretic and anticoagulants are
used
for respiratory disorders just as with other system
disorders.
Medications
specific to Respiratory Conditions:
1- Bronchodilators :
Dilate
the bronchial walls
2- Expectorants:
Promote
coughing and expulsion of
mucus

Pharmacology
Mechanical
Devices that aid in
Respiration
Ventilators
•Actually
serve as a breathing
substitute
for patients who
can
not breathe on their own.
•Deliver
medication through
the
mouth or nose to ease
breathing
problems .
Pharmacology

