Lec. 4
Done by:
the team work of ML

Name the parts of the cardiovascular system and the
medical terms associated with their function.
Analyse, define & pronounce the medical terms relate
to the cardiovascular system
Define selected terms associated with disorders,
procedures,
and
treatments
relating
to
the
cardiovascular system.
Comprehension of English language

Student Duties
1- Read the lecture before attending.
2- Print out the exercises of this lecture and hand it
to the lecturer ‘solved’. It is your homework. You
should write on it your name, the date, your group
and the name of your lecturer.
A piece of advice:
Take a look at the exercises of the
lecture before your actual reading, it will help you
design your strategy of studying.

Note (1):
The methodology of your exercises of
your formative assessment in this lecture and in
the other lectures of the terminology module are
similar to Summative exams.
Note (2):
If you encounter new terms, please use
your
e- learning skills or a dictionary to
identify them.
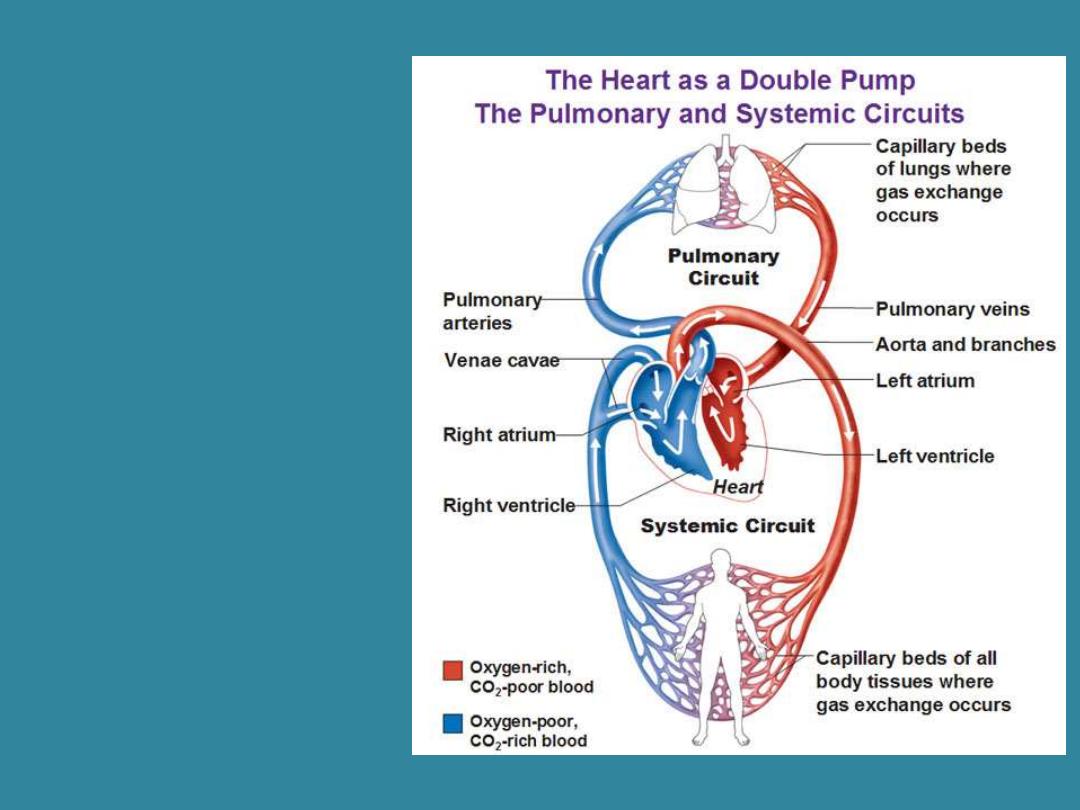
The heart act as a
double pump separate
by separated by a wall
or
septum
.
- The right side pumps
deoxygenated blood
to the
pulmonary
circuit (lungs)
where
it picked up oxygen.
- The left side of the
heart pumps the
oxygenated blood to
all other parts of the
body through
systemic circuit.
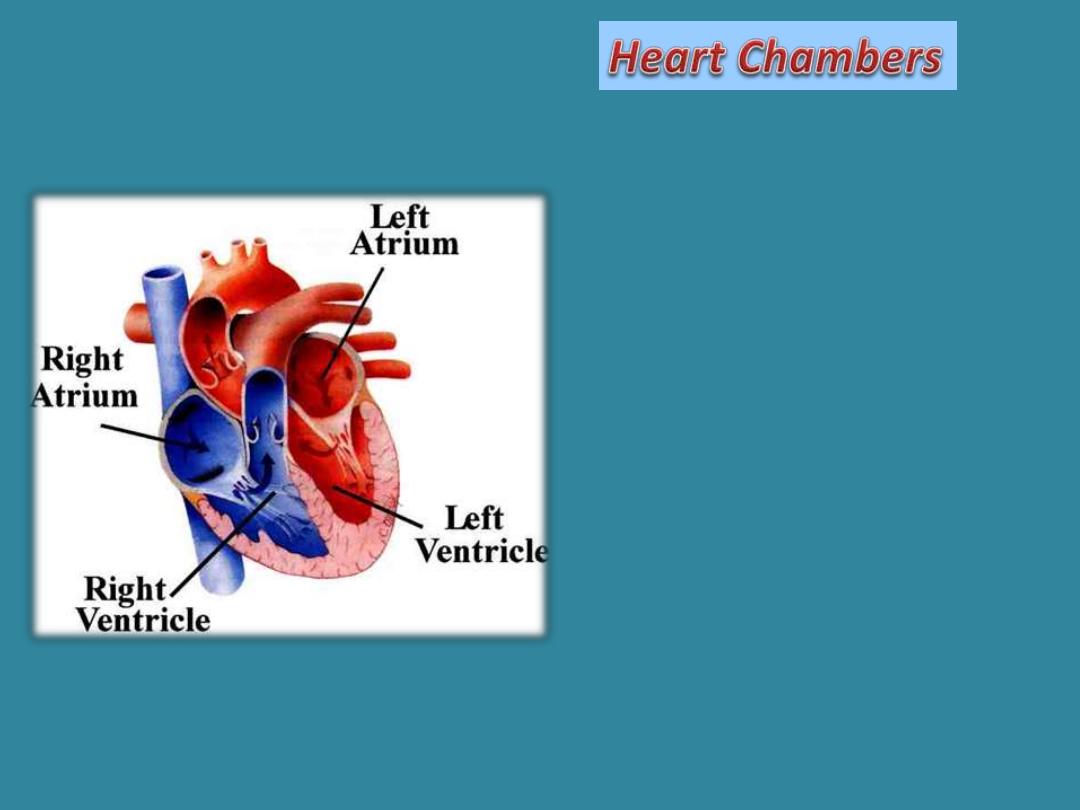
•Atria
(singular atrium). A
Latin word meaning entry
hall. Right and left atria
Upper chambers.
•Ventricles
, from the Latin
Venter (little belly) Right and
left ventricles are the lower
chambers of the heart.
•Fibers in the ventricles
(Purkinje fibers) cause the
ventricles to contract.
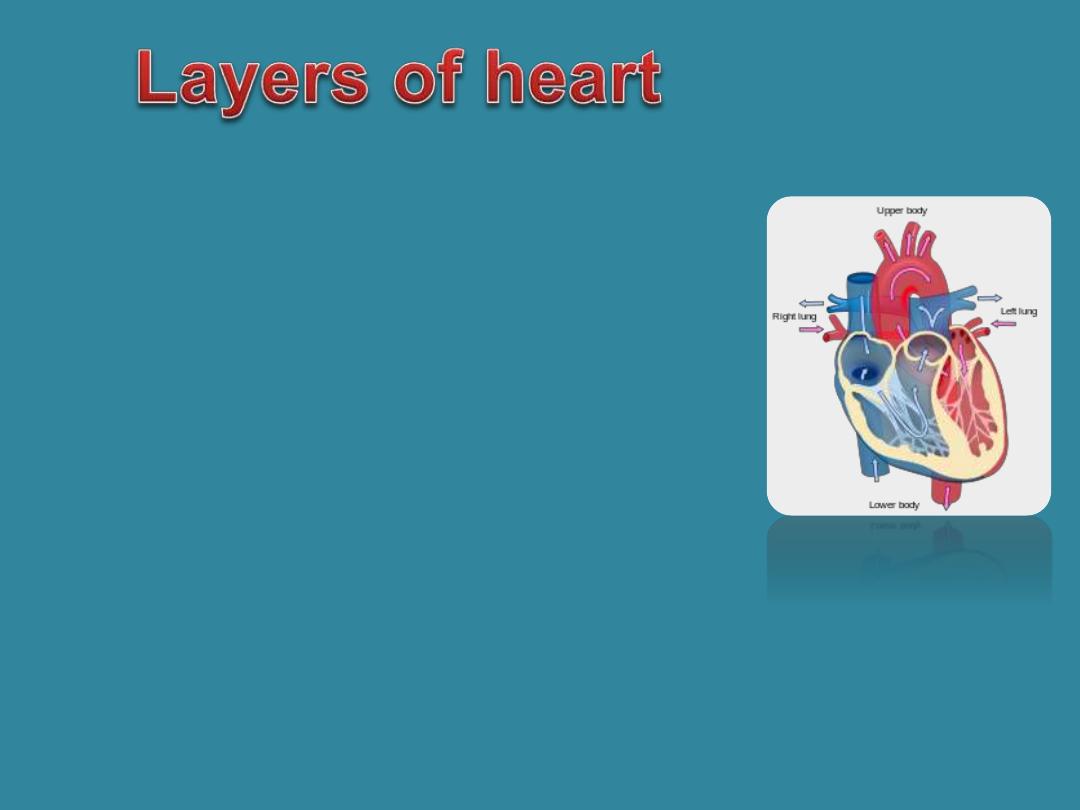
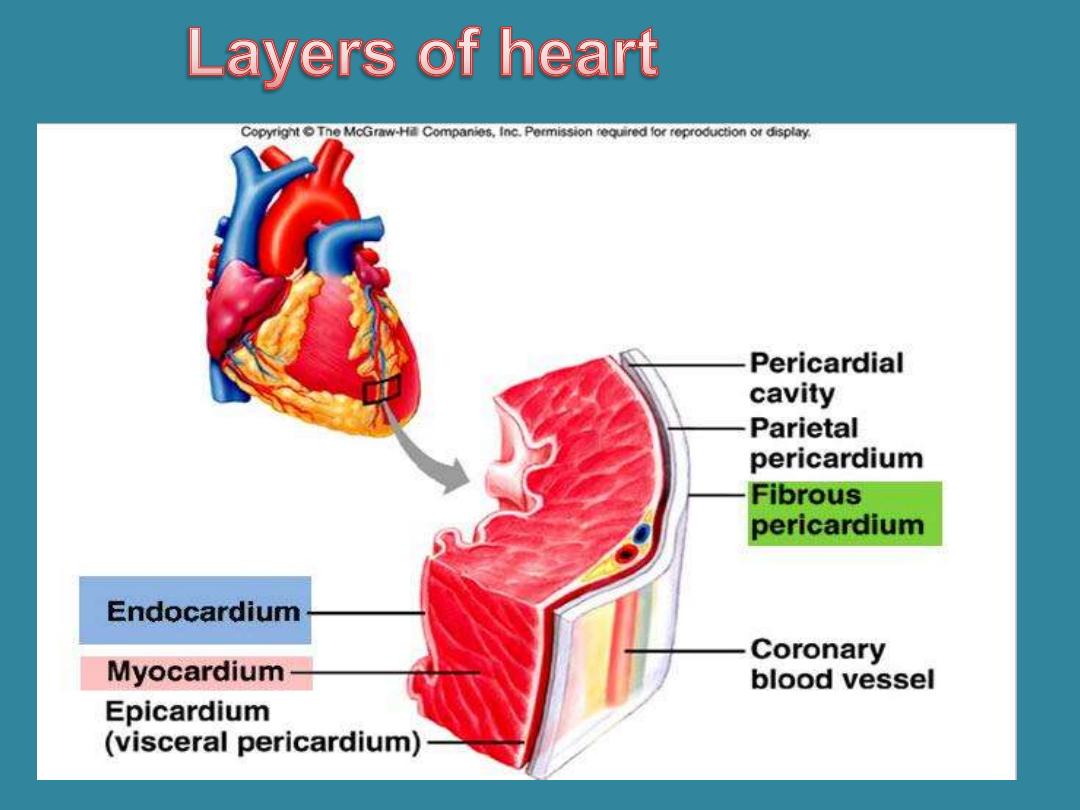
•Myocardium :
(middle layer of the heart that is
muscular tissue) , is the thickest of the three
layerss
my/o (muscle); cardi/o (heart) .
•Endocardium:
Inner most layer. endo (within);
cardi/o (heart).
•Epicardium:
The outer layer of the heart
(epi- (on,
upon); cardi/o (heart).
, which is acually the inner layer of the pericardium
(
peri-mean arround)
; the sac that surrounds the heart
Arteries and Veins
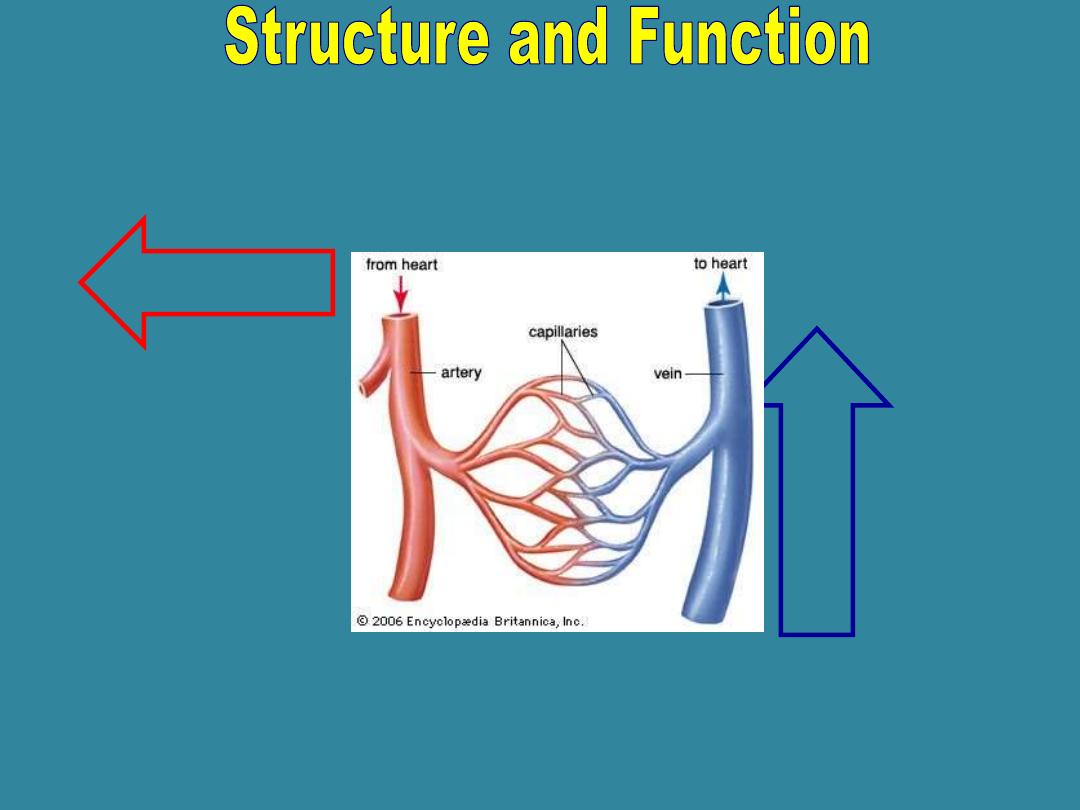
Arteries
•From the Greek
word arteria
(windpipe) Carry
blood
away
from
the heart.
•From the Latin word Vena. It
Carries blood from tissue
toward
the heart.
V
e
i
n
s
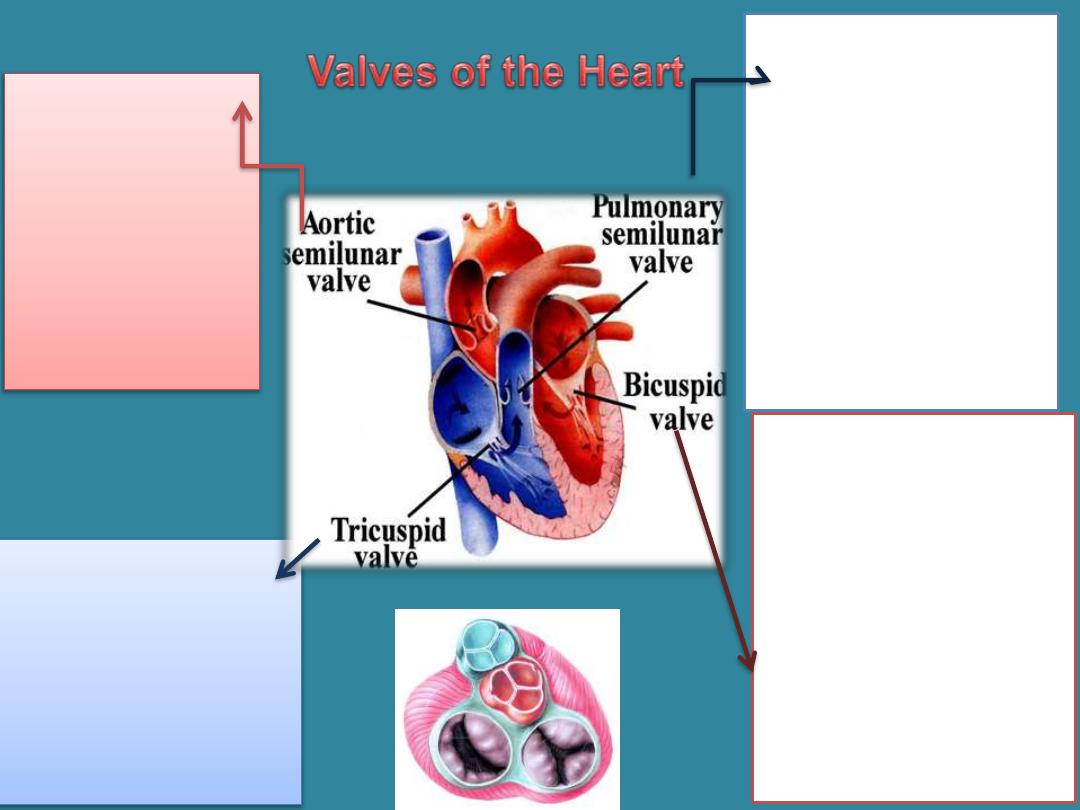
•Bicuspid valve
(mitral):
•From the Latin word
mitra
(turban); from the
Latin word
valva
(that
which turns); bi- (two);
from the Latin
cuspiderm
(cusp or point) .
•
Located between
the left atrium & left
ventricle
•Tricuspid valve
:
•
tri-
(three); from the
Latin
cuspiderm
(cusp or point) .
Located between
the right atrium &
right ventricle
•
Pulmonary
semilunar valve
:
pulmon/o (lung); from
the Latin word valva
(that which turns) semi
mean (half), lunar mean
(moon)
:
• located
between
the
right
ventricle
and the pulmonary
artery.
Aortic
semilunar
valve:
is located
between the
left ventricle
and the aorta
Blood Pressure (BP)
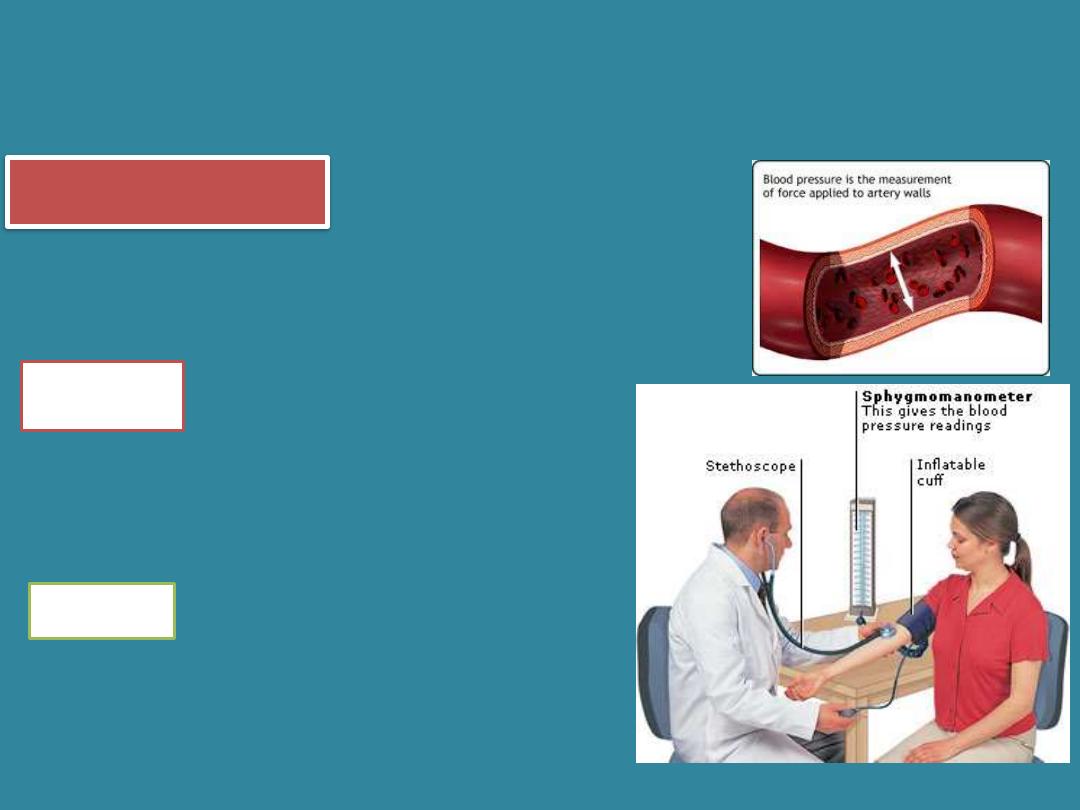
Blood Pressure
•Measures the force of the blood against
the walls of the arteries.
Systole
A Greek word means Contraction. It is the
Contraction phase of the heart
Diastole
From the Greek word diastole.
It is the Relaxation phase of the
heart
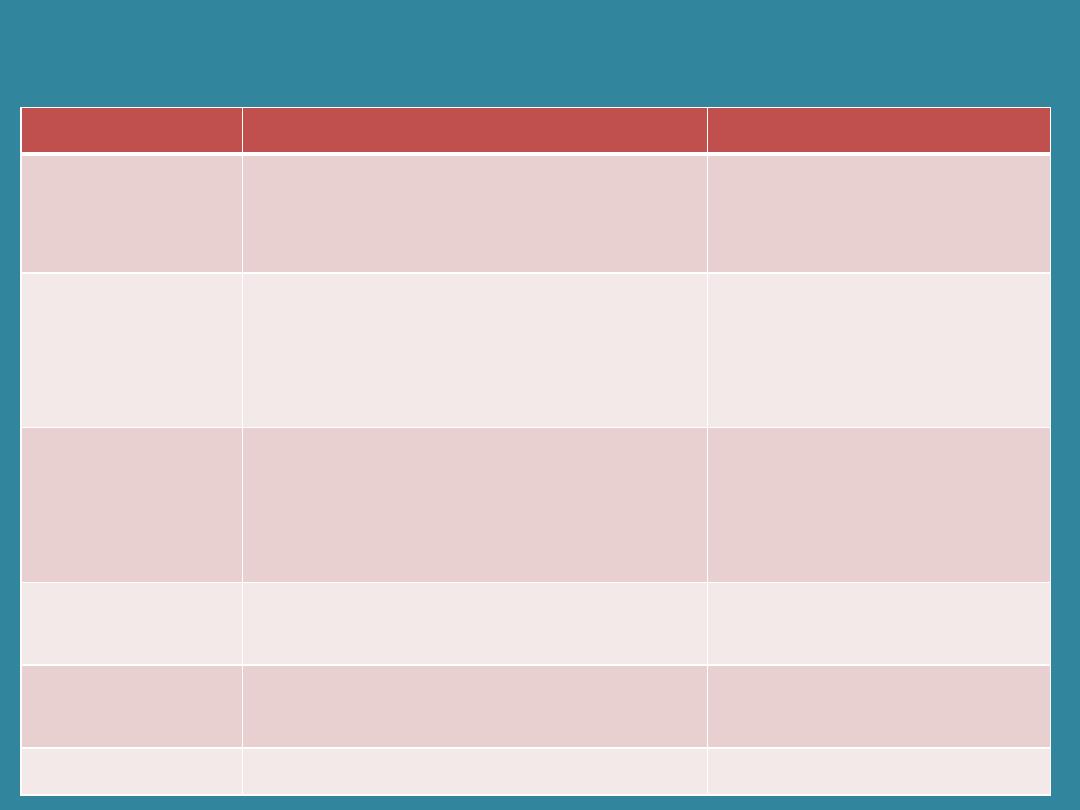
Combining Form
Meaning
angi (o)
aort (o)
arteri (o)
ather (o)
atri (o)
cardi (o)
hemangi (o)
blood vessel
artery
fatty matter
atrium
heart
blood vessel
aorta
Combining Forms

Combining Forms
Combining Form
Meaning
pericardi (o)
phleb (o) /ven (o)
sphygm (o)
thromb (o)
vas (o)
pericardium
vein
pulse
blood clot
blood vessel

Cardiology
is the science dealing with the cardiovascular
system and diseases , the physician who specializes in heart
conditions is called a
cardiologist.
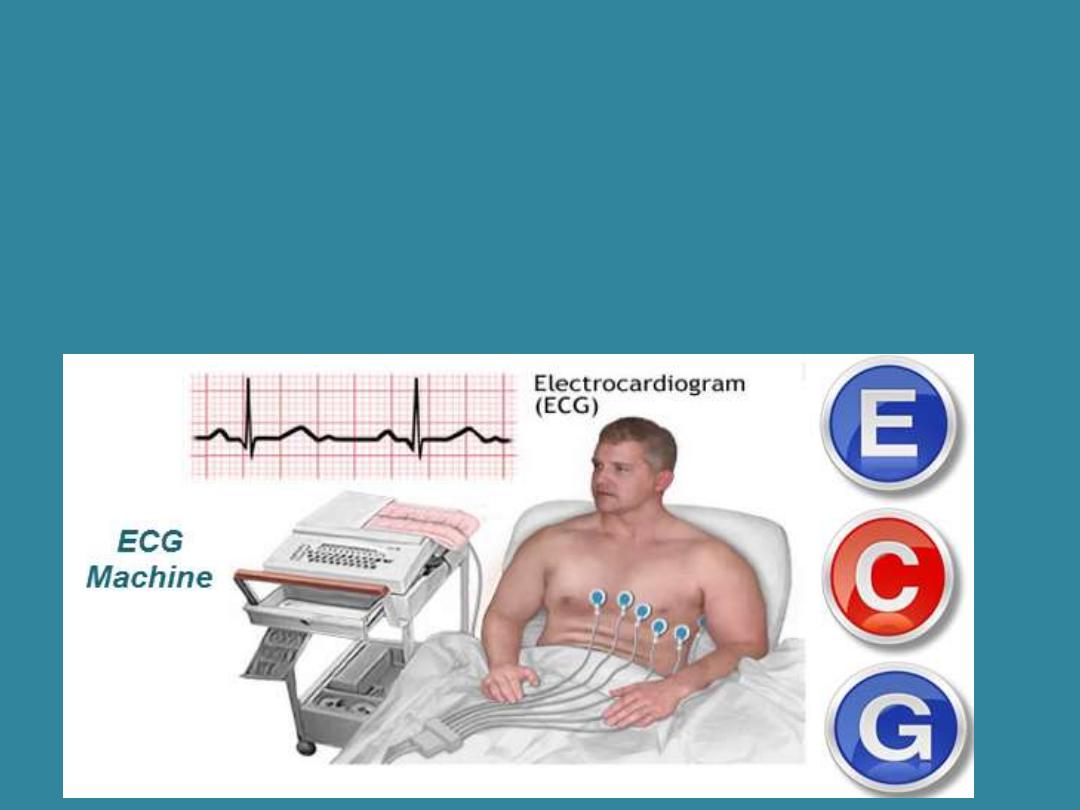
Electrocardiography (ECG)
in Diagnostic Tests
•Electr/o (electricity); cardi/o (heart); -gram (record or
picture). Produces an electrocardiogram which measures the
amount of electricity that flows through the heart.

Blood Pressure
Blood Pressure abnormalities can damage the
heart and other body systems.
•Hypertension hyper- (high); -tens- (pressure) ……….(too
high)
•Hypotension hypo- (low); -tens- (pressure) …………(too
low)

•endocarditis
•myocarditis
•bacterial endocarditis
•pericarditis
Different Inflammatory conditions of the heart
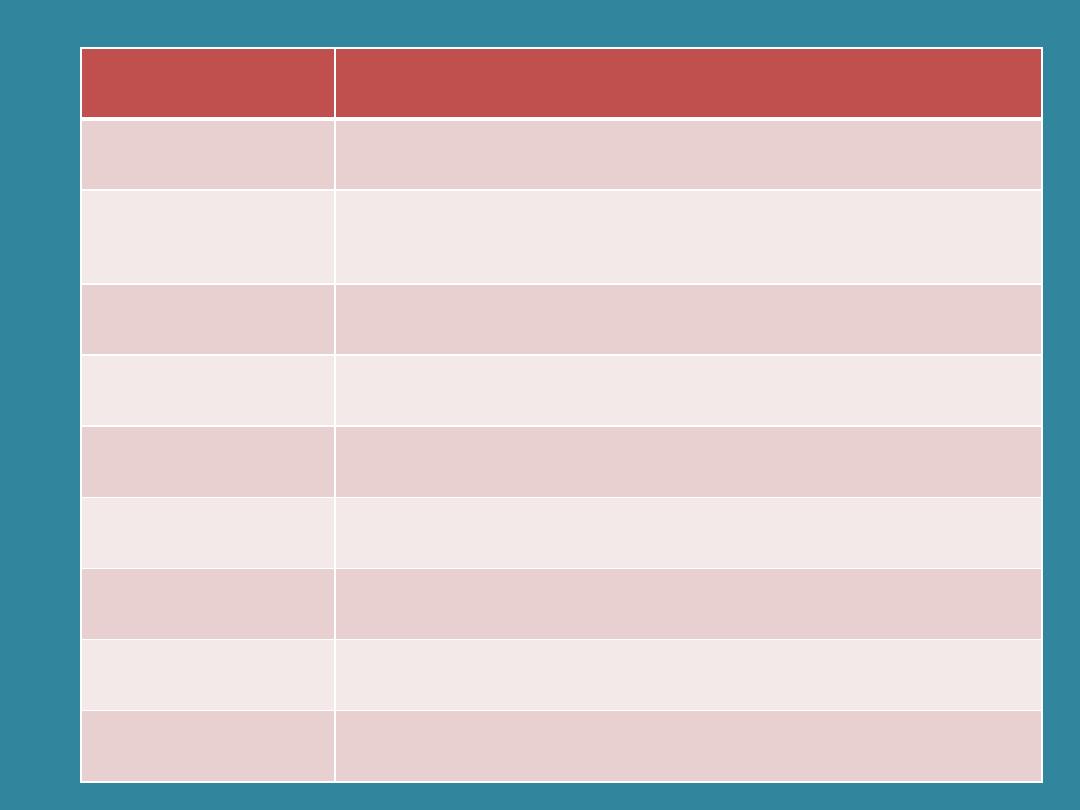
Common disorder
Term
Analysis
Meaning
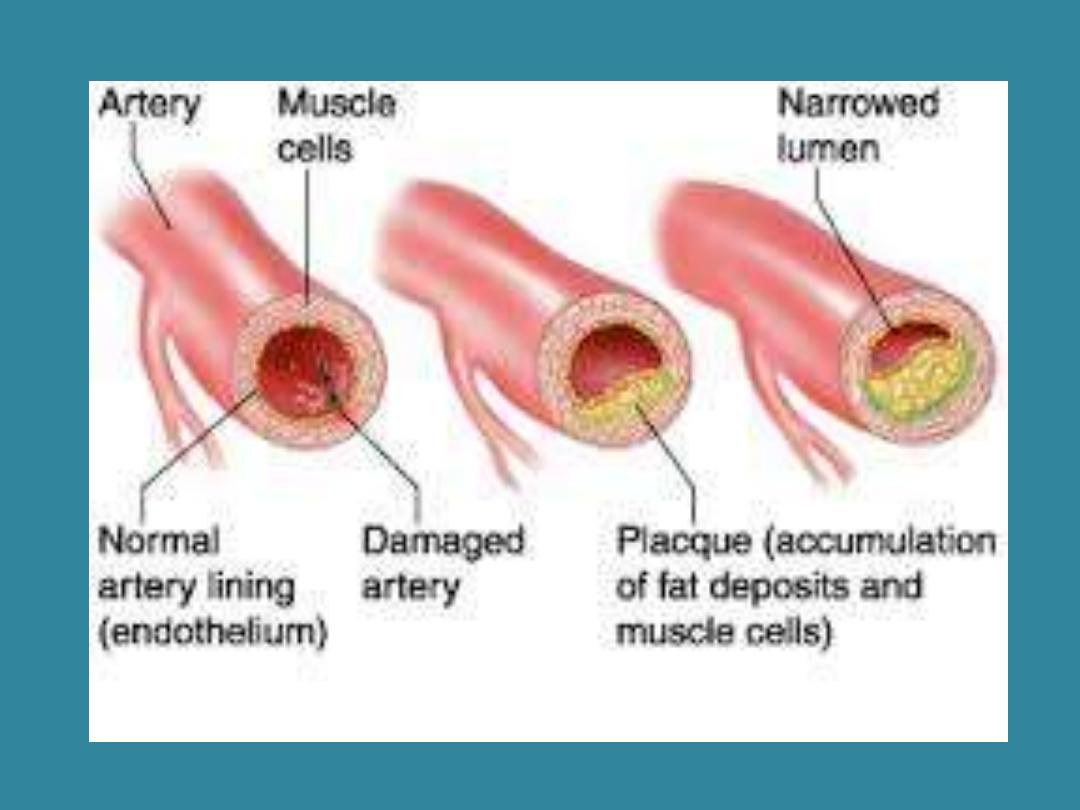
Arteriosclerosis
From the Greek word arteria
(windpipe); scler/o (hardness); -osis
(abnormal condition of)
Hardening of the arteries
Arteriostenosis
From the Greek word arteria
(windpipe); from the Greek word
spastikos (afflicted with spasm)
Narrowing of an artery
Atrial fibrillation From the Latin word atrium (entry
hall) -al (adjective suffix); from the
Latin word fibra (fiber, string,
thread)
Rapid, random, ineffective
contraction of the heart.
Cardiorrhexis
Cardi/o (heart); -rrhexis (rupture)
Rupture in the wall of the
heart
Dyscrasia
(dys-KRAY-sha)
Dys- (bad, difficult); from the Greek
word krasis (mingling)
General term for a blood
disorder)
mean
term
Abnormal low red blood cells
anemia
Localize dilation of an artery, cardiac chamber or other vessels
aneurysm
Chest pain (CP) due to ischemia
Angina pectoris
Spasm in blood vessels
angiospasm
Narrowing of blood vessels
angiostenosis
Abnormal rhythm; irregular heart beat
arrhythmia
Hardening and narrowing of the arteries
atherosclerosis
Rapid, random, ineffective contraction of atrium
Atrial fibrillation
Fatty deposit or plaque within the artery wall
atheroma
Term
Analysis
Meaning
Hemophilia
(Haemophilia)
Hem/o (blood); philia (abnormal
attraction)
Congenital disorder affecting
the coagulation process
Hemorrhage
(Haemorrhage)
Hem/o (blood); -rrhage (burst forth) Discharge of blood
Hyperlipidemia
(hyperlipidaemia)
Hyper (above normal); lip/o (fat);
demia (from the hema (blood)
Elevated cholesterol,
triglycerides, lipoproteins in
the blood
Ischemia
From the Greek word iskhaimos (a
stopping of the blood); ia
(condition)
Deficiency in blood supply
Myocardial
infarction (MI)
My/o (heart); cardi/o (heart) ; -al
(adjective suffix); from the Latin
word infractionem (a breaking)
Heart attack
Tachycardia
Tachy- (fast); cardi/o (heart) ; ia
(condition)
Abnormality rapid heart beat
cardiorrhexis
Cardi/o (heart); rrhesis (rupture)
Rupture in the heart wall
Common disorder
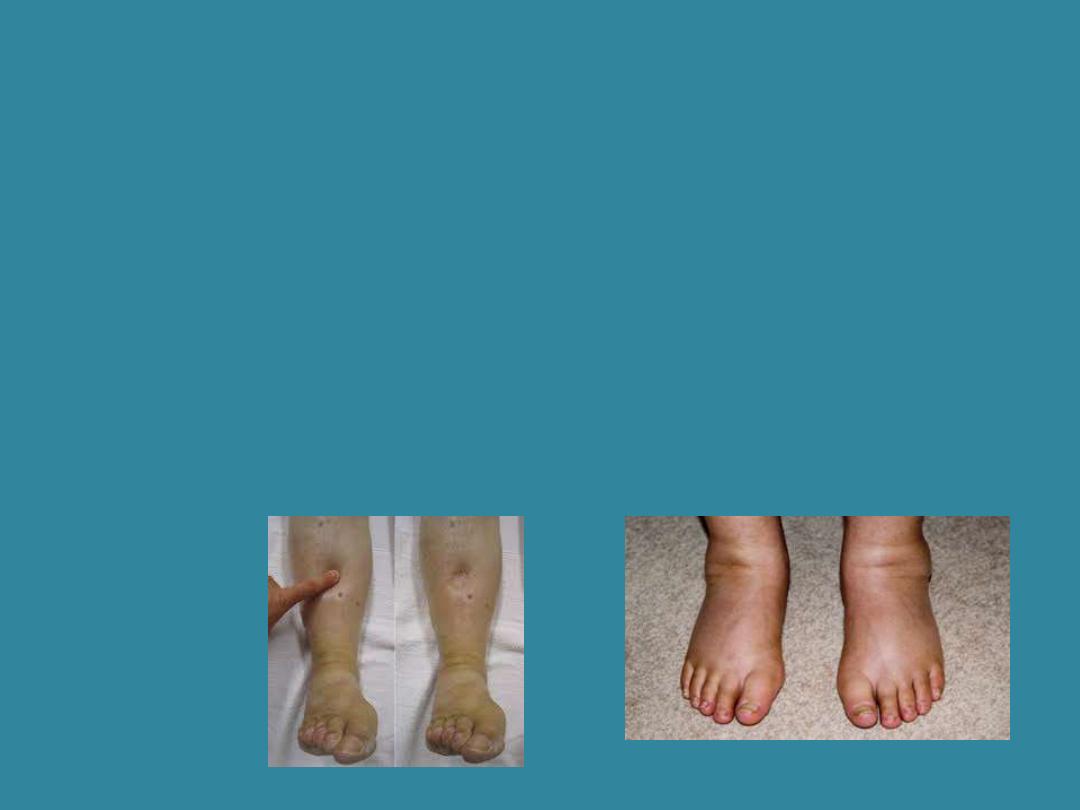
• Congestive heart failure:
• Syndrome where the heart is unable to pump
enough blood to meet the body needs for
oxygen and nutrients, as a result , fluid is
retained and accumulates in the ankles and
legs.
Diagnosis & treatment terms
Angiogram:
print record obtained through angiograph
Angiography:
radiography of a blood vessels after injection of contrast
media
Cardiac catheterization
: procedure where a catheter is inserted into the
artery and guided into the heart, may be used to diagnoses or treatment
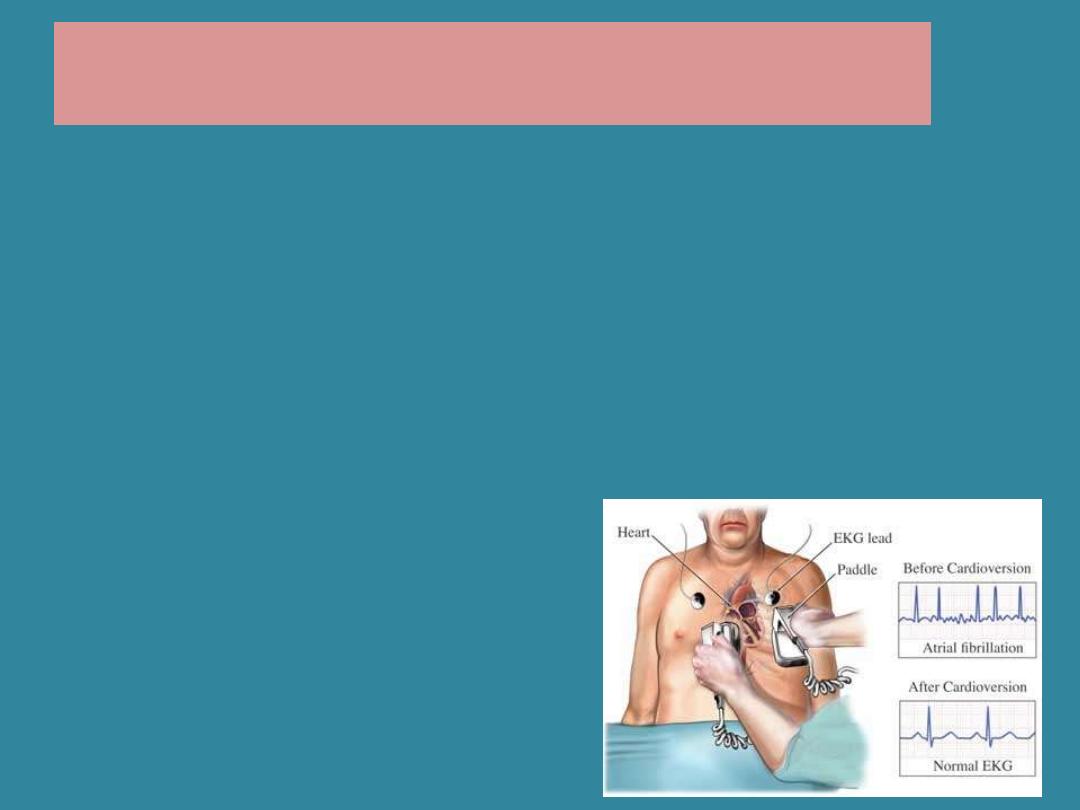
Cardioversion:
use of electrical shock to restore the heart’s
normal rhythm

Antianginals
Antianginals
Drugs used to
treat chest pain
and prevent
attacks of angina
Antianginals:
Anti- (against); angi/o
(blood vessel); -al
(adjective suffix).

Rhythm Disorders
Rhythm disorders
are treated with
medications that
normalize the heart
rate by affecting the
nervous system that
controls the heart
rate.
Medications for:
RHYTHM
DISORDERS
•Antiarrhythmics: anti-
(against); a (without)
rhythm: heart rhythm

Cardiac glycosides:
Drugs used to
improve heart output
by increasing the
muscular contraction
- Cardiac glycosides:

Statins:
A type of cholesterol
lowering drug
- statins:

Diuretic:
A drug used to
increase urine
production or
urination
- diuretic:

The goal of most cardiovascular surgery is to improve
blood flow to all body cells.
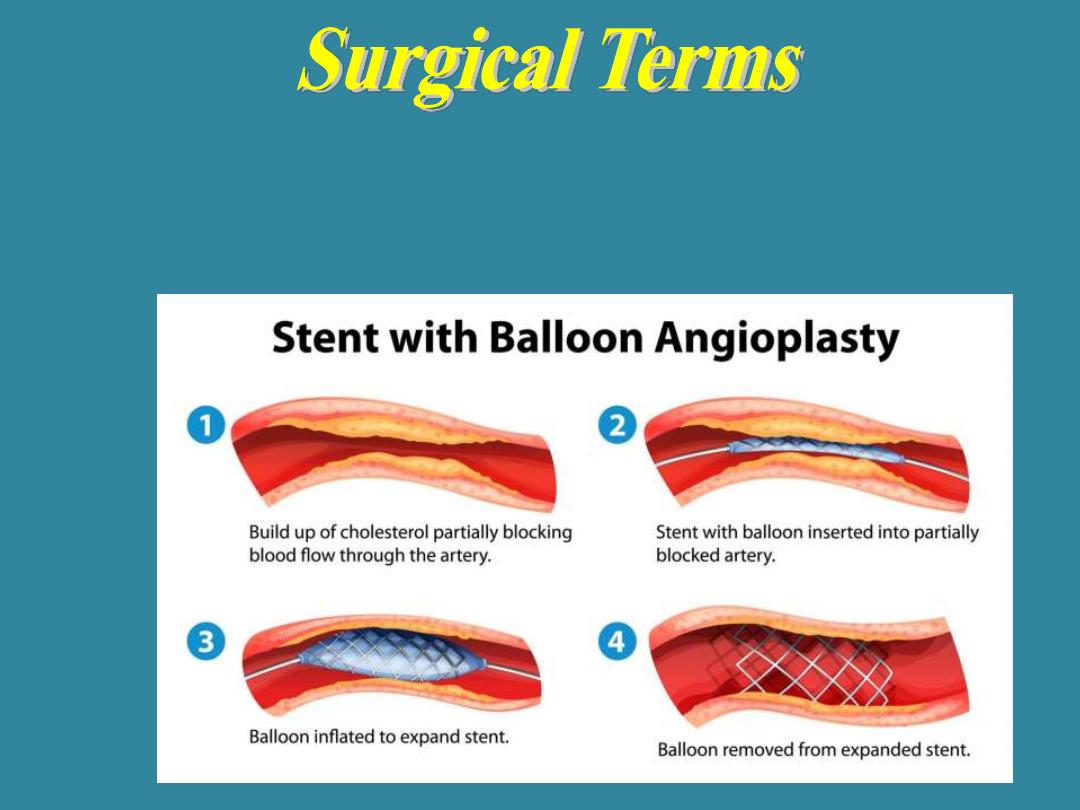
Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty
(PTCA)
is a
surgical procedure in which a balloon catheter is inserted into
a blocked blood vessel to increase the blood flow of that
vessel
.

valvuloplasty:
from the Latin word valva. (that which turns); -plasty
(surgical repair of the heart valve )
angioplasty
: angi/o (blood vessel); -plasty (surgical repair of blood
vessels).
Angioscopy
; angi/o (blood vessel); -scopy (to view)
•Uses a fiberoptic catheter to view the interior of a blood vessel
Endarterectomy
:
surgical removal of the lining of the artery
Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG
):
through an open chest, a
graft (piece of vein, or heart artery) is implanted on the heart to bypass the
blockage
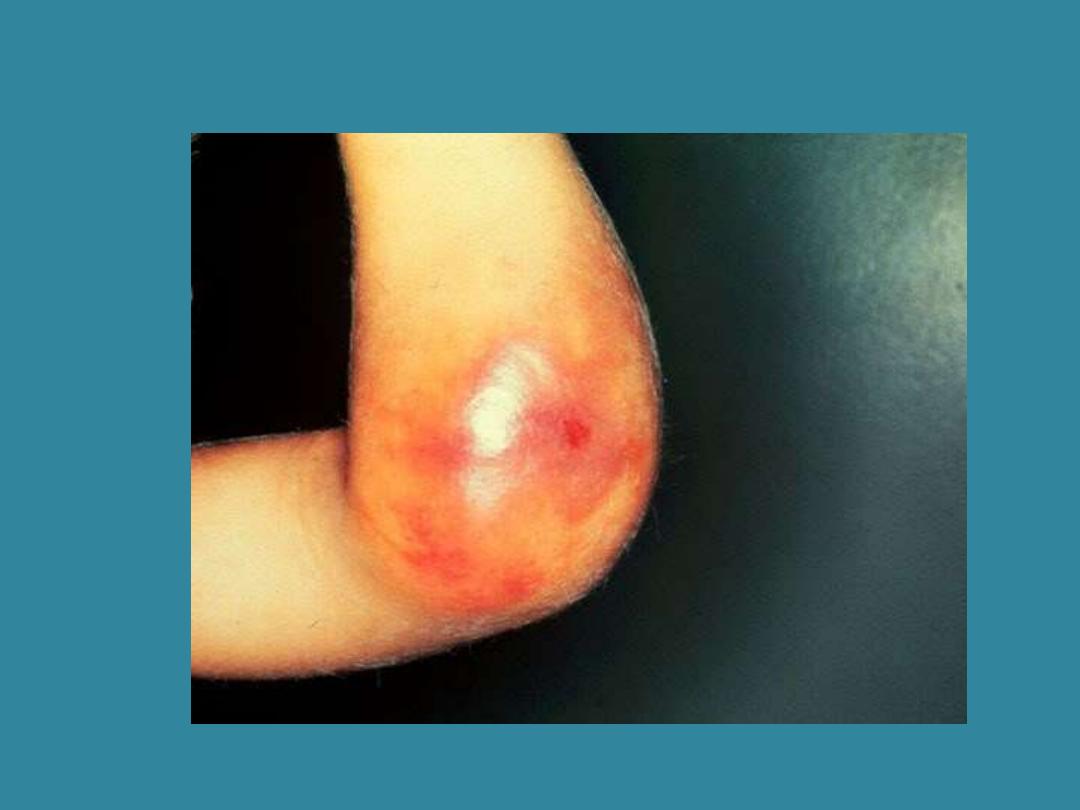
Hemophilia
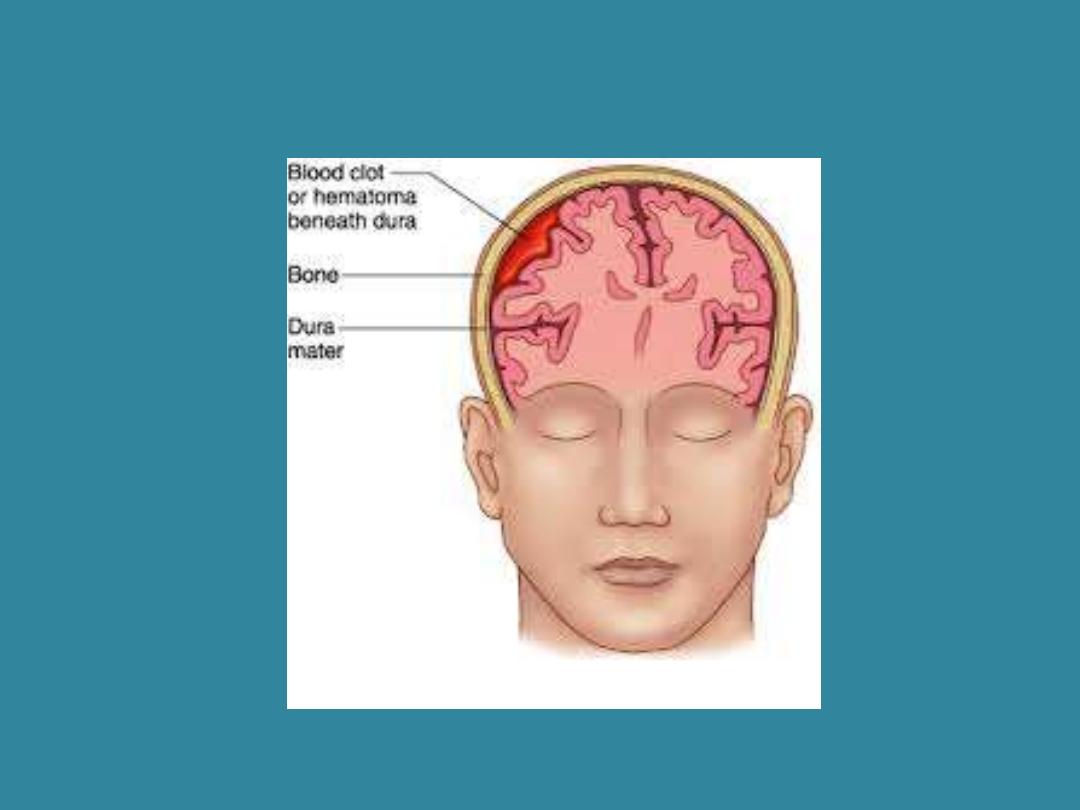
Haemorrhage
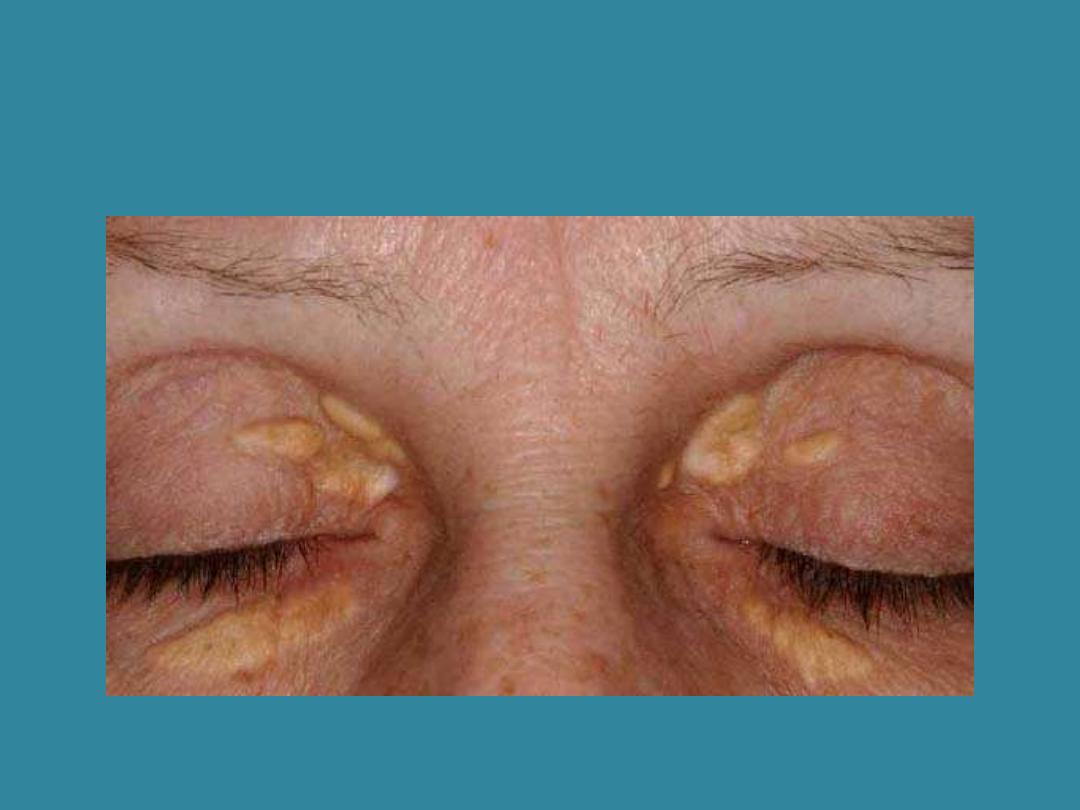
Xanthelasma (Hyperlipidemia)
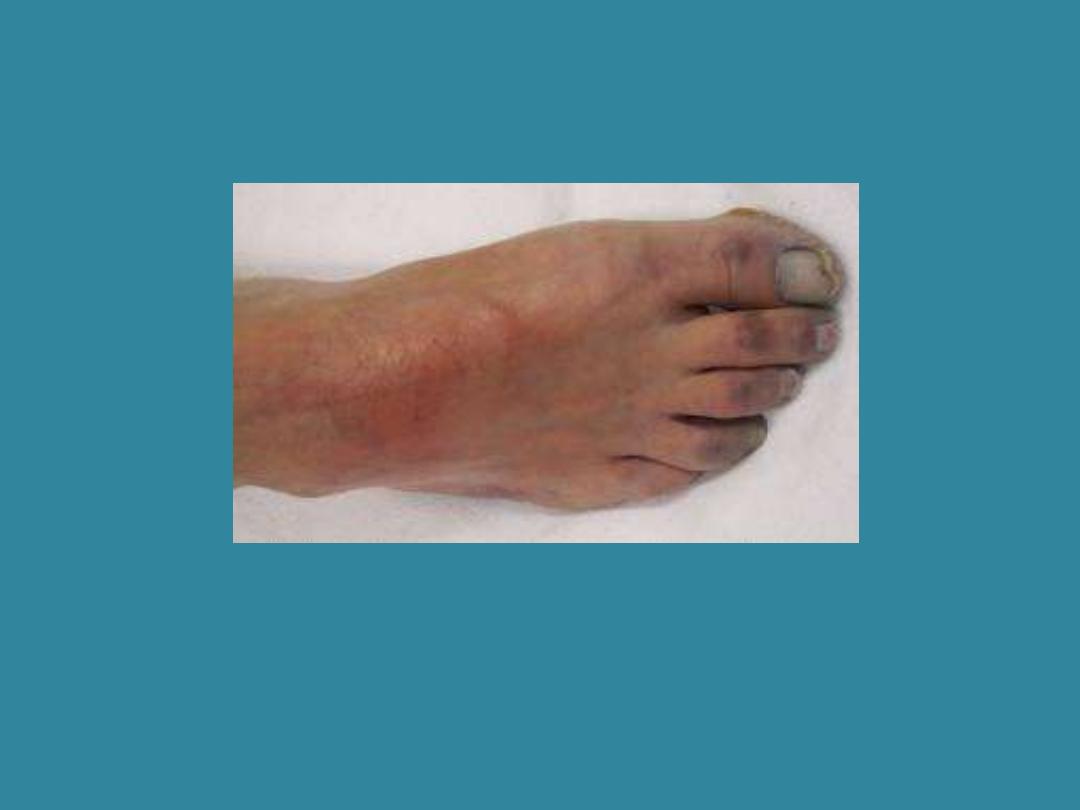
Ischemia

