Lec.6
Done by:
the team work of ML
The Digestive
System

Objectives
•
After studying this chapter, you will be able to:
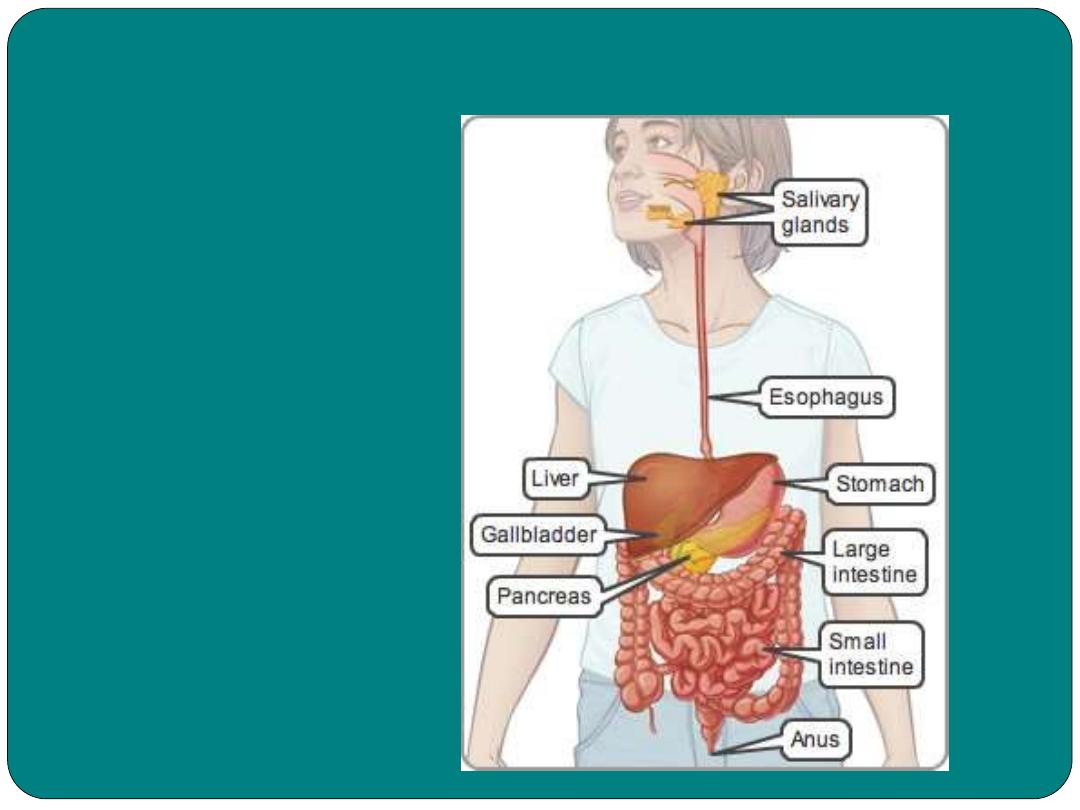
Parts of GIT
Upper GIT
Mouth
Pharynx
Esophagus
Stomach
Lower GIT
Small intestine
Large intestine
Anus
Accessary organs:
Salivary gland
Liver
Gallbladder
pancreas
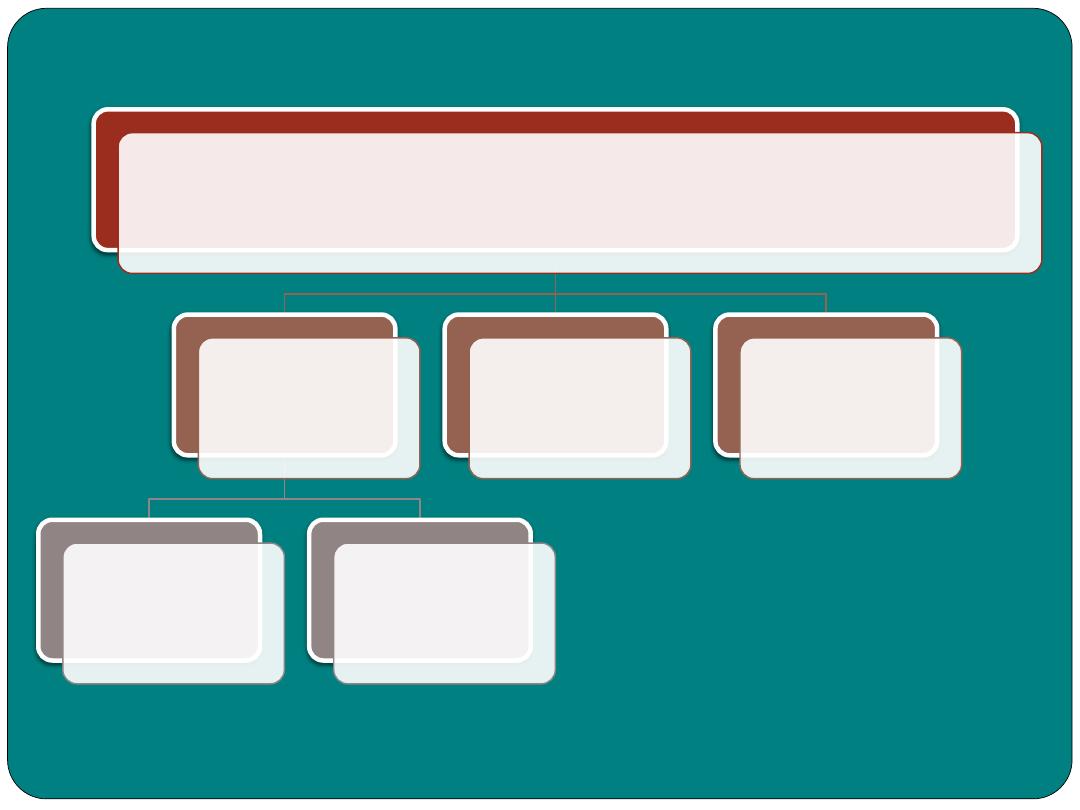
Functions of the digestive system
Digestion
mechanical
digestion
chemical
digestion
Absorption
Elimination
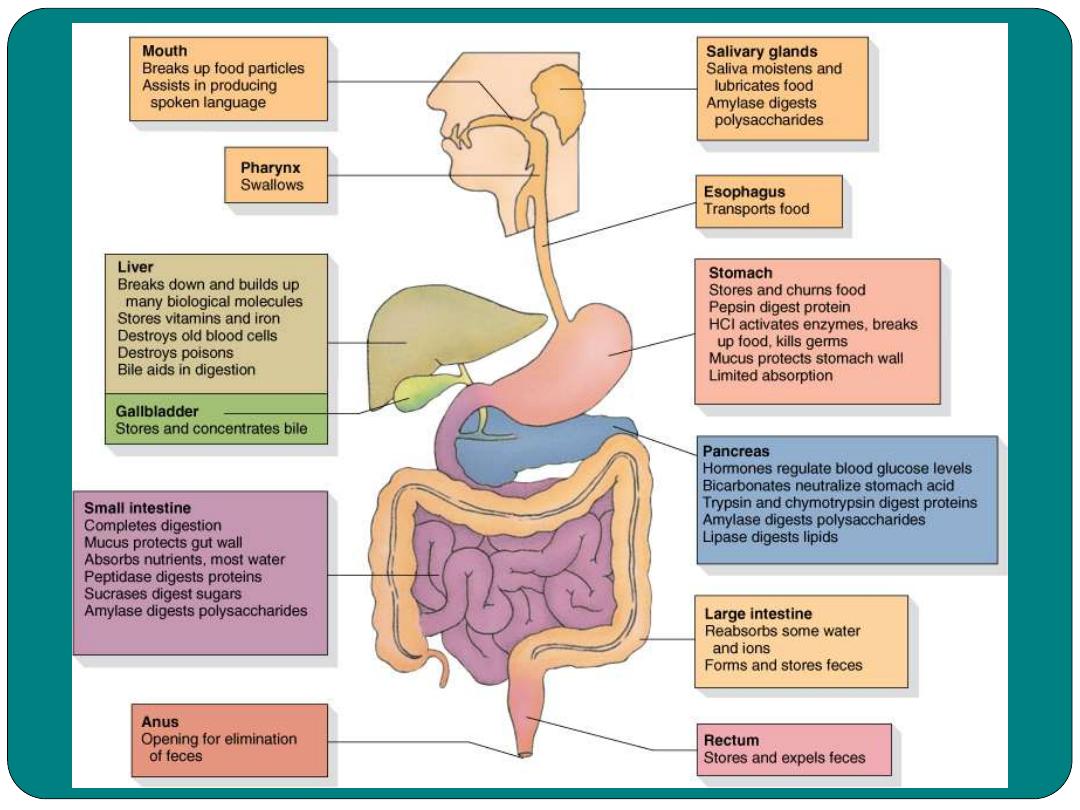
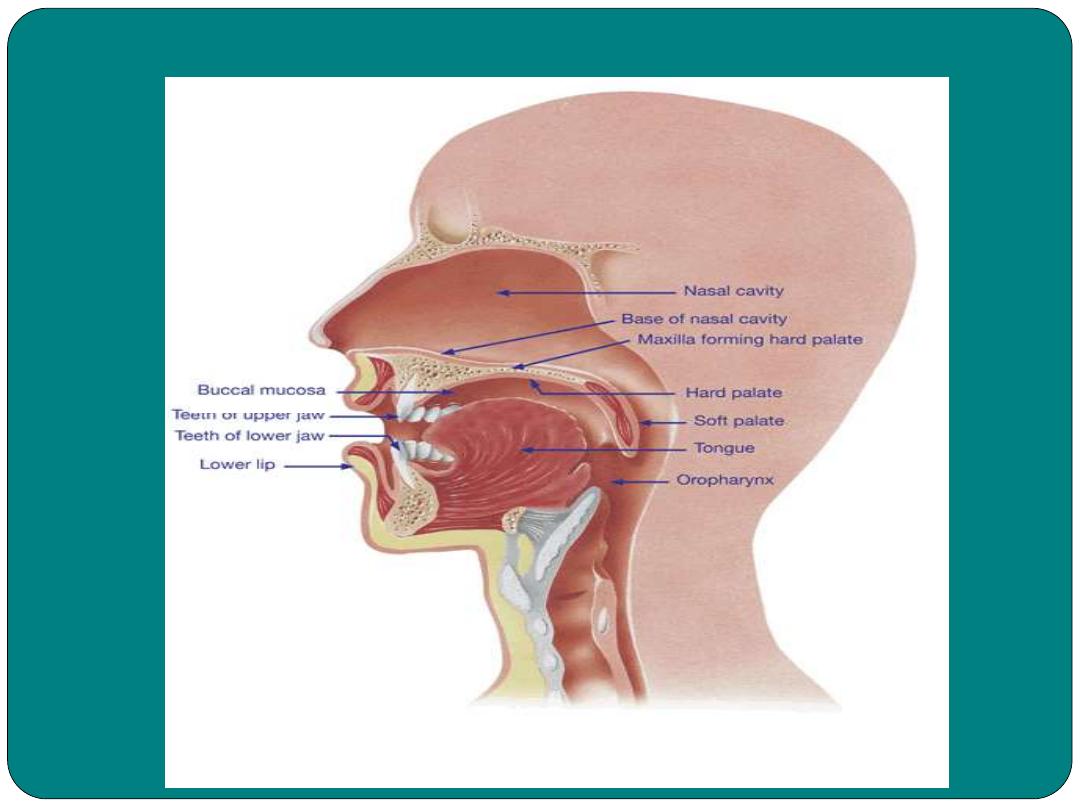
The mouth
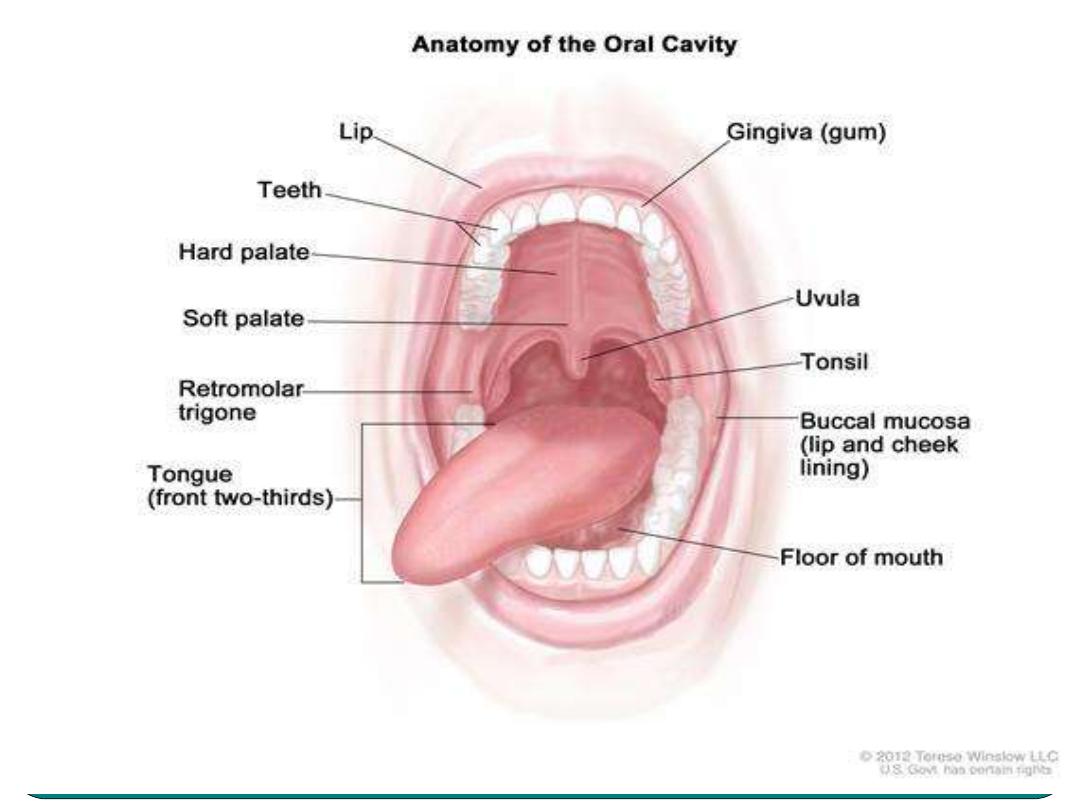

Sense the food ( sense the temperature
and the texture of the food)
(the wall of the oral cavity), important in
chewing of the food
muscle organ important in mastication and
chewing. The tongue has papillae.
soft and hard palate, uvula and palatine
tonsils.
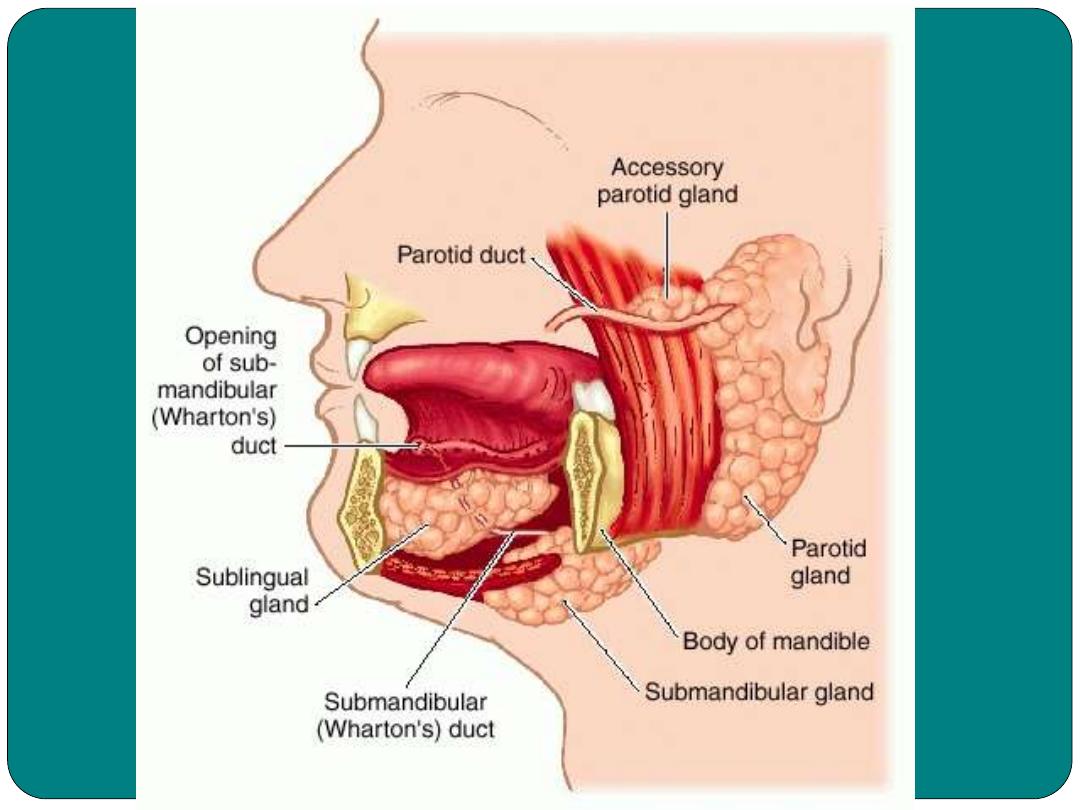
Secretes saliva contains amylase enzyme
digestion of Carbohydrates
•
Three major :
Parotid, sublingual and
submandibular.
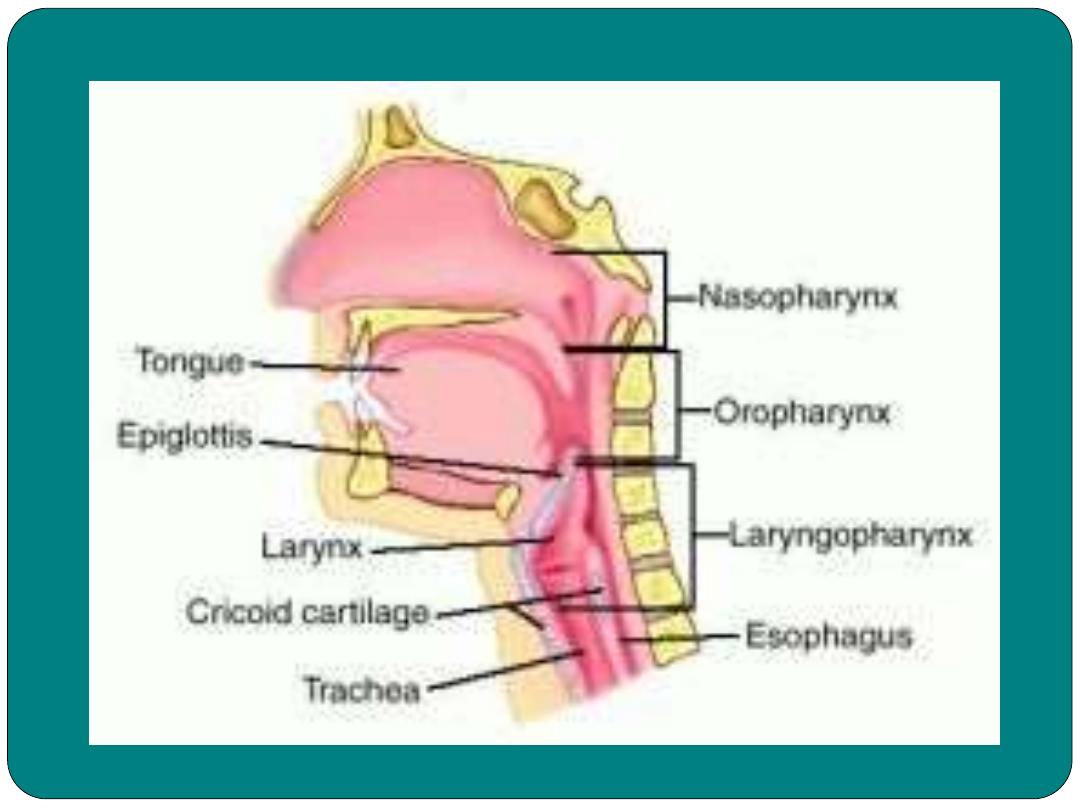
Pharynx
•
Muscular tube about 5 inches in length
Function:
Moves food to esophagus
Moves air through the trachea
Esophagus
•
Muscular tube about 9 to 10 inches in length
•
Contract rhythmatically to push food toward the
stomach
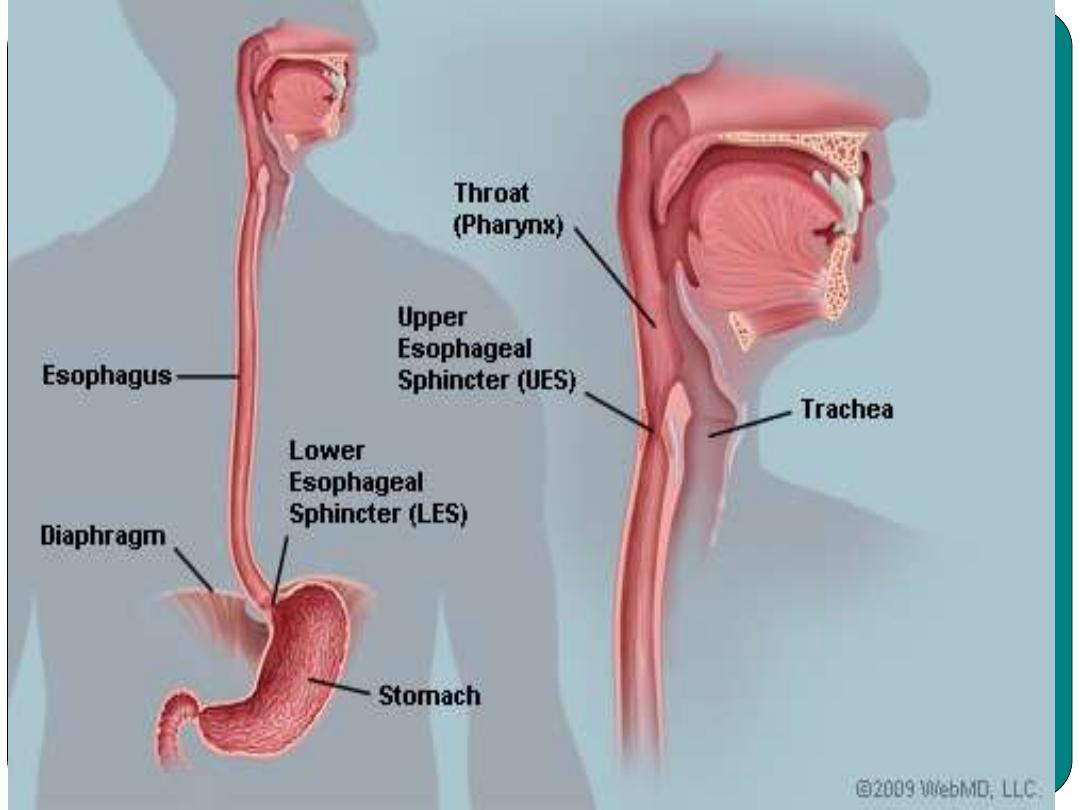
•
Reflux
backflow
•
Emesis: vomiting
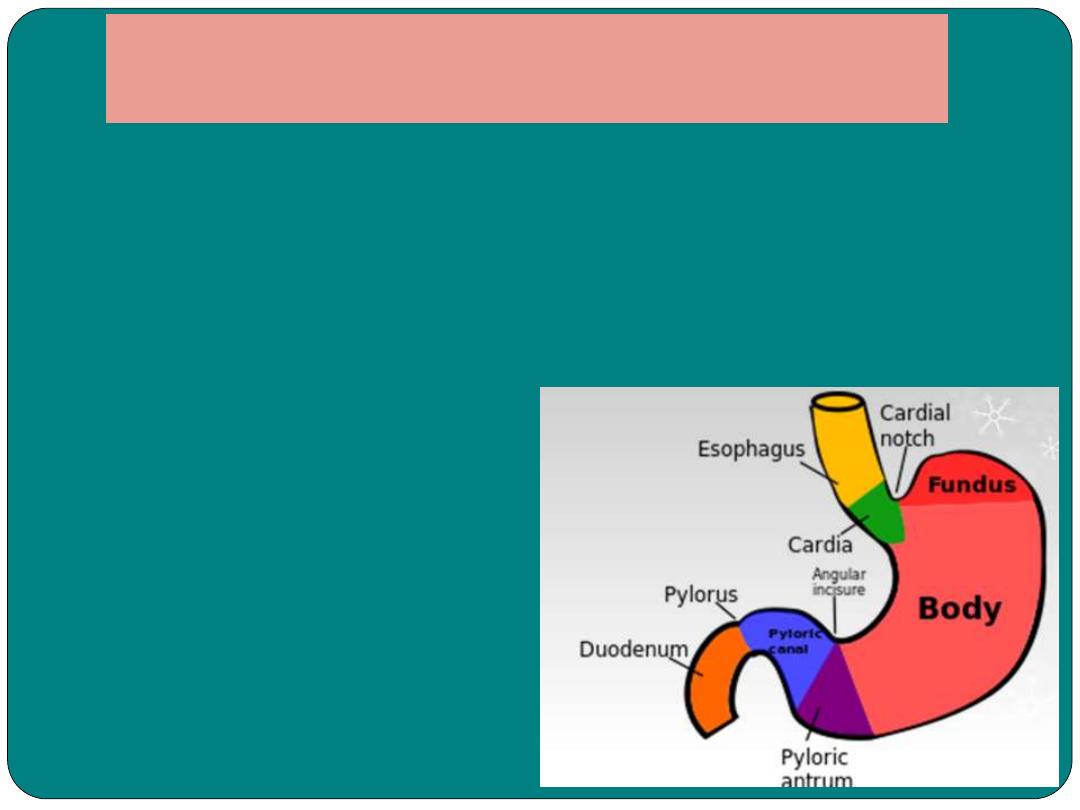
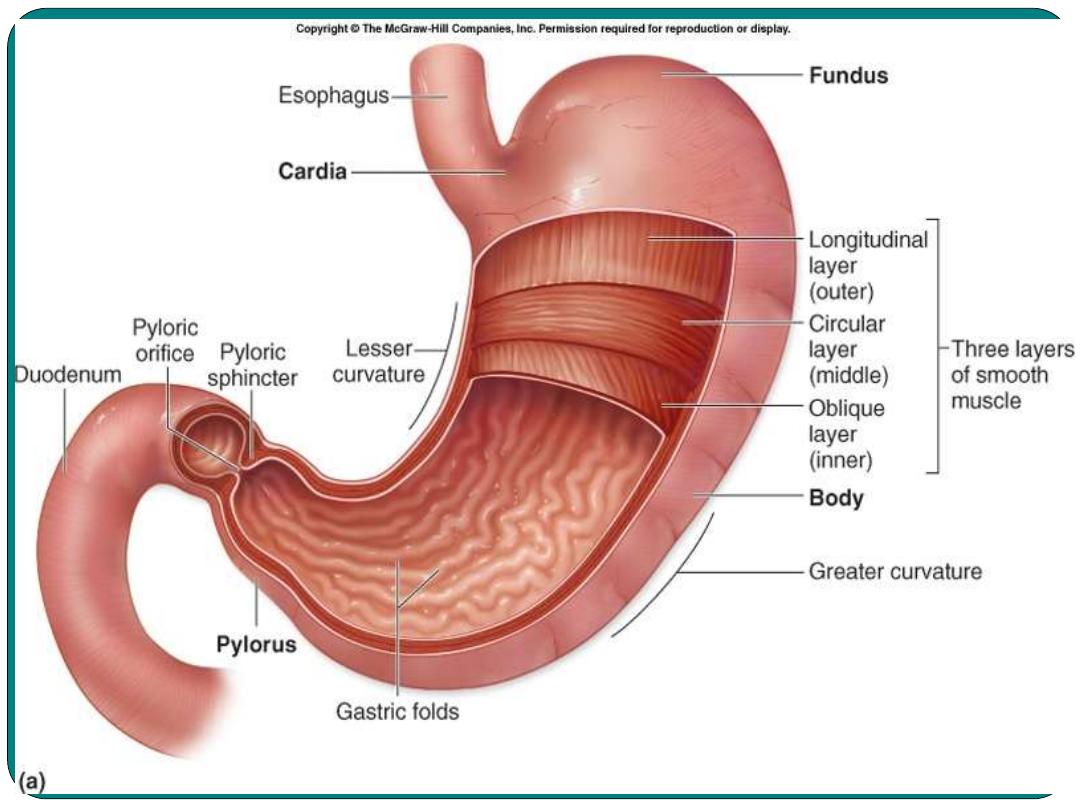
Stomach
•
Is pouch like organ in the left
hypochondrial region of the abdominal
cavity
•
Secretes the gastric juice
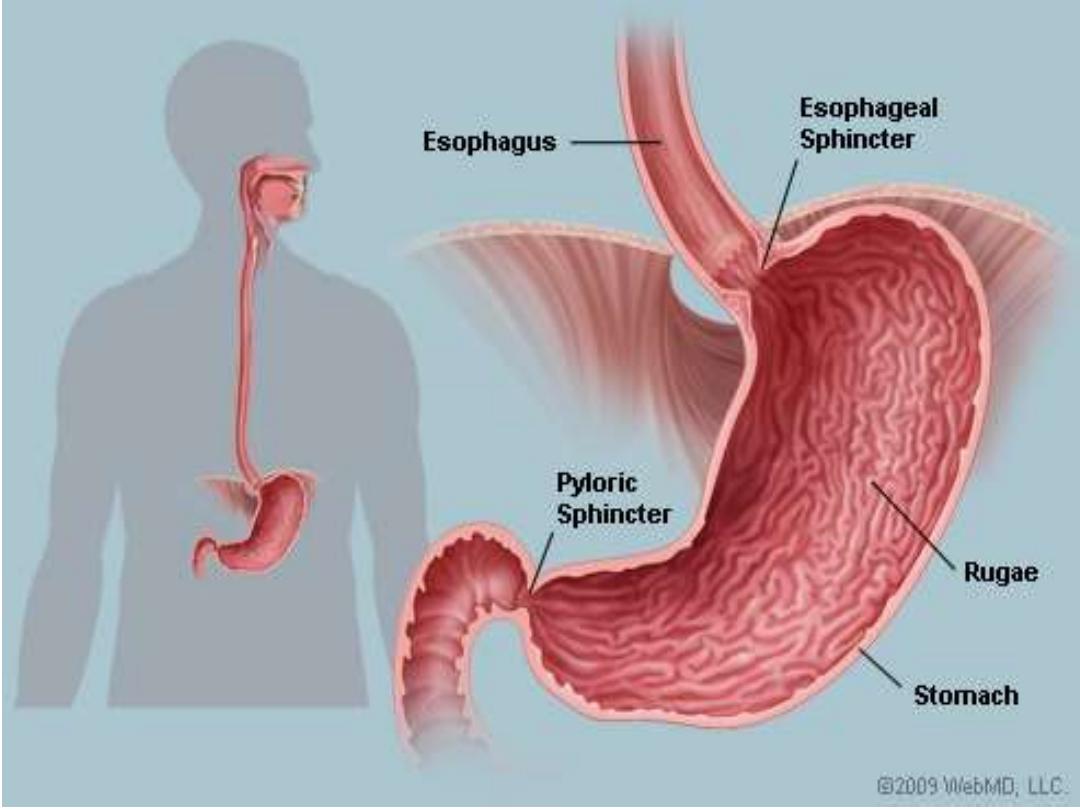

Major component of gastric juice
Digests almost all types of protein
pepsin
1
Provides acidic environments for the
action of pepsin
HCL
2
Provides alkaline protective layer on the
inside of the stomach wall
Mucus
3

Small Intestine
1- The Duodenum
:
12 inches in length
•
Chyme mixes with bile to aid in fat digestion
•
With pancreatic juice in digestion of starch, proteins
and fat.
•
With intestinal juice helps in digestion of sugars
•
The small intestine is lined with villi (singular villous)
2- Jejunum:
eight foot long
•
Digestive process continues
3- Ileum:
connects the small intestine to the large intes
tine
.
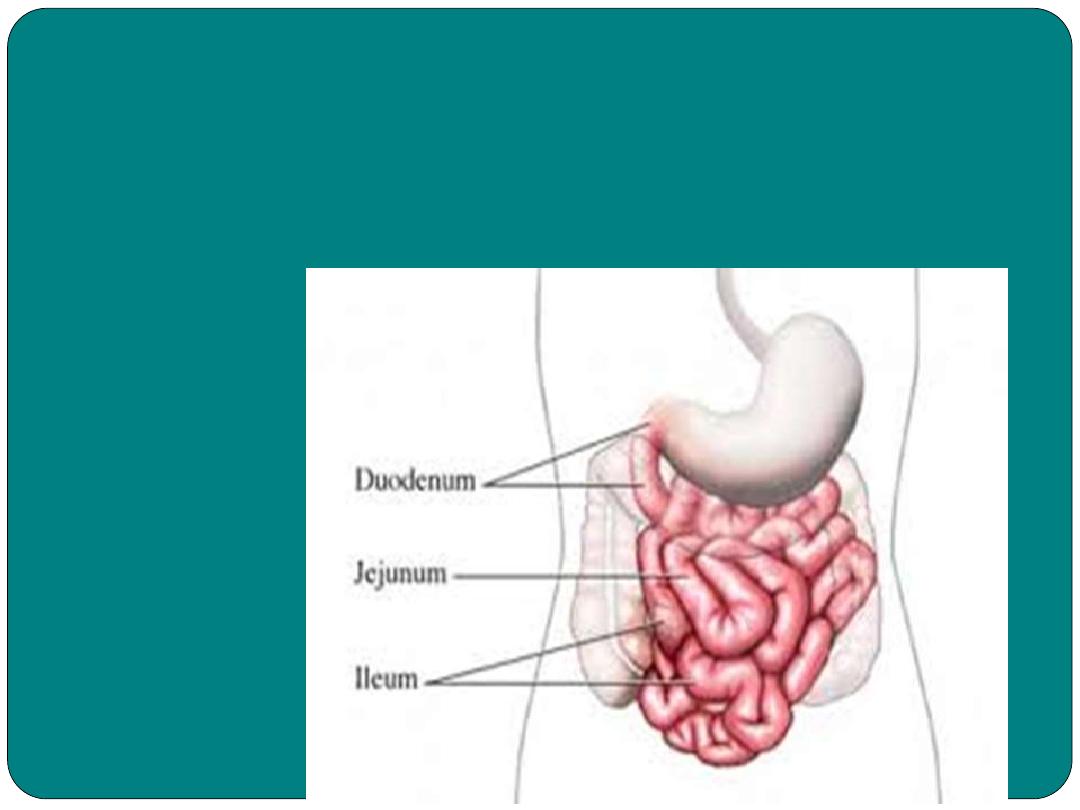
•
The small intestine leis within the abdominopelvic
cavity, where it held in place by
mesentery
(
membranous tissue that attached both the small
and large intestine to the muscle wall within the
abdomen).

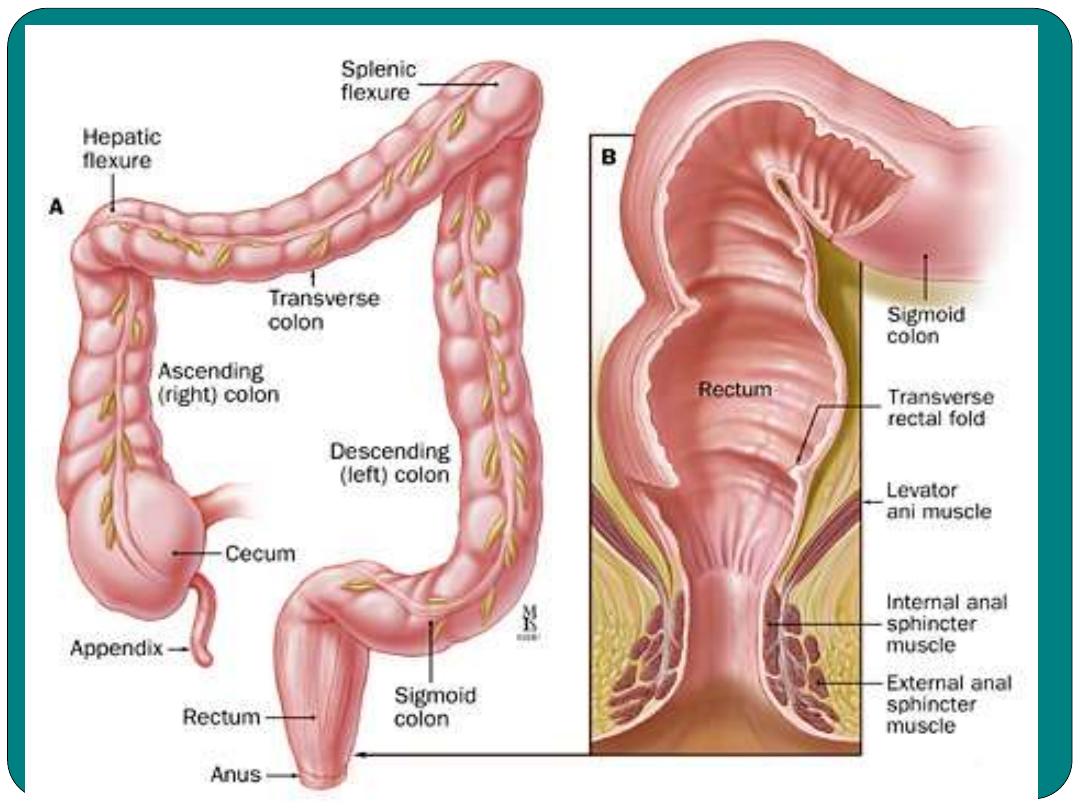
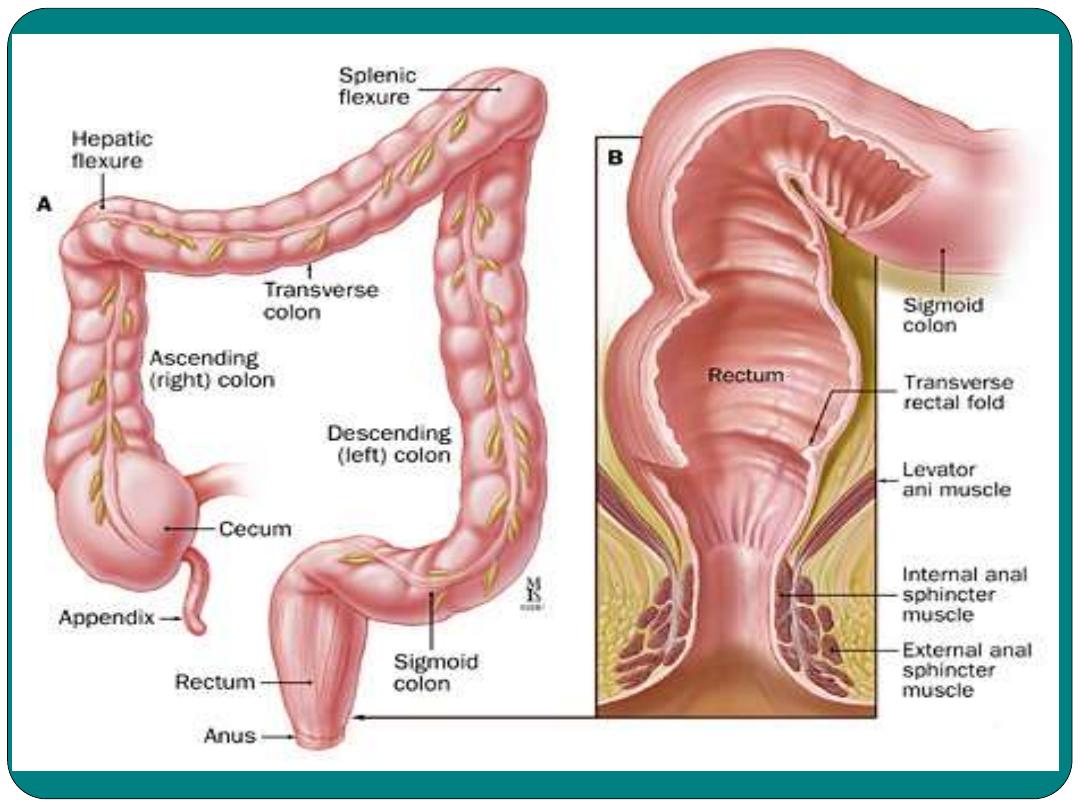
Large Intestine
1- The Cecum
: is a pouch attached to the bottom
of ileum.
•
Cecum
has three openings; one from ileum to
cecum, second from cecum into the colon and
the third from the cecum to the Appendix
2- The colon:
Three parts, ascending, transverse and
descending colon.
3- Sigmoid colon:
S shaped
4- Rectum:
attached to the anal canal

The Liver
•
Is an important digestive organ
•
Located on the right upper quadrant of the
abdominal cavity.
Its function:
1- changing food nutrient
2- Secretes Bile
( a yellow brown to greenish
fluid)
3- Secretes Bilirubin
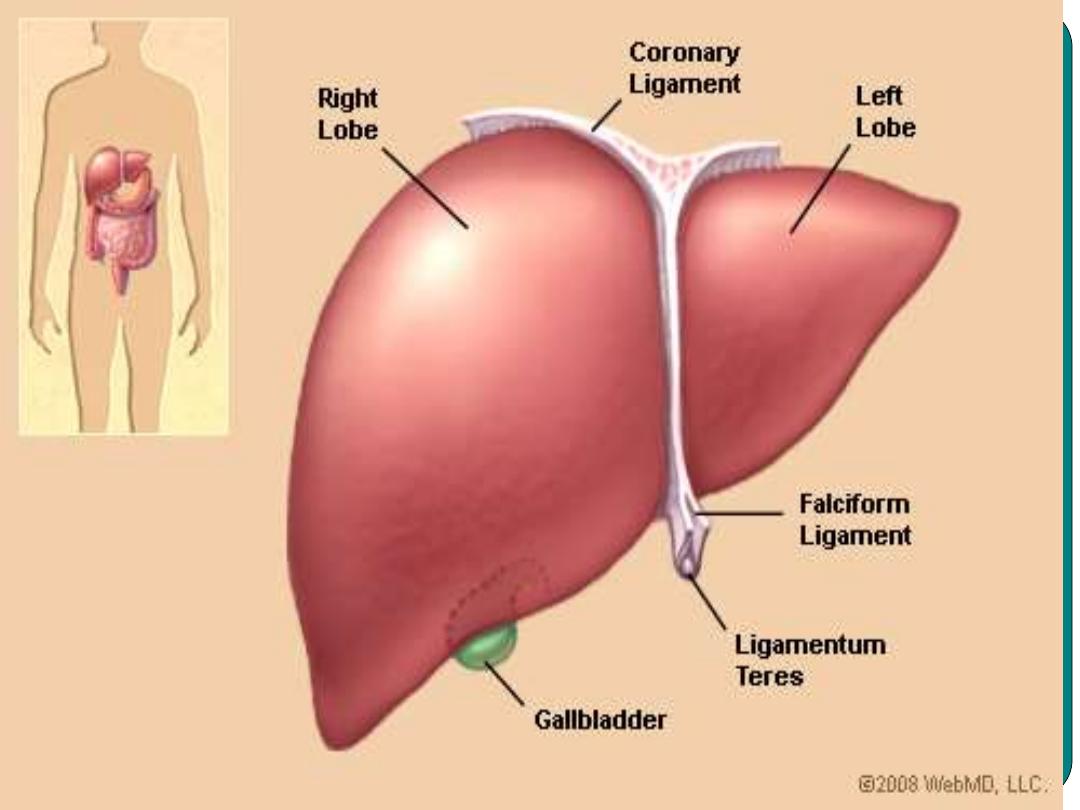
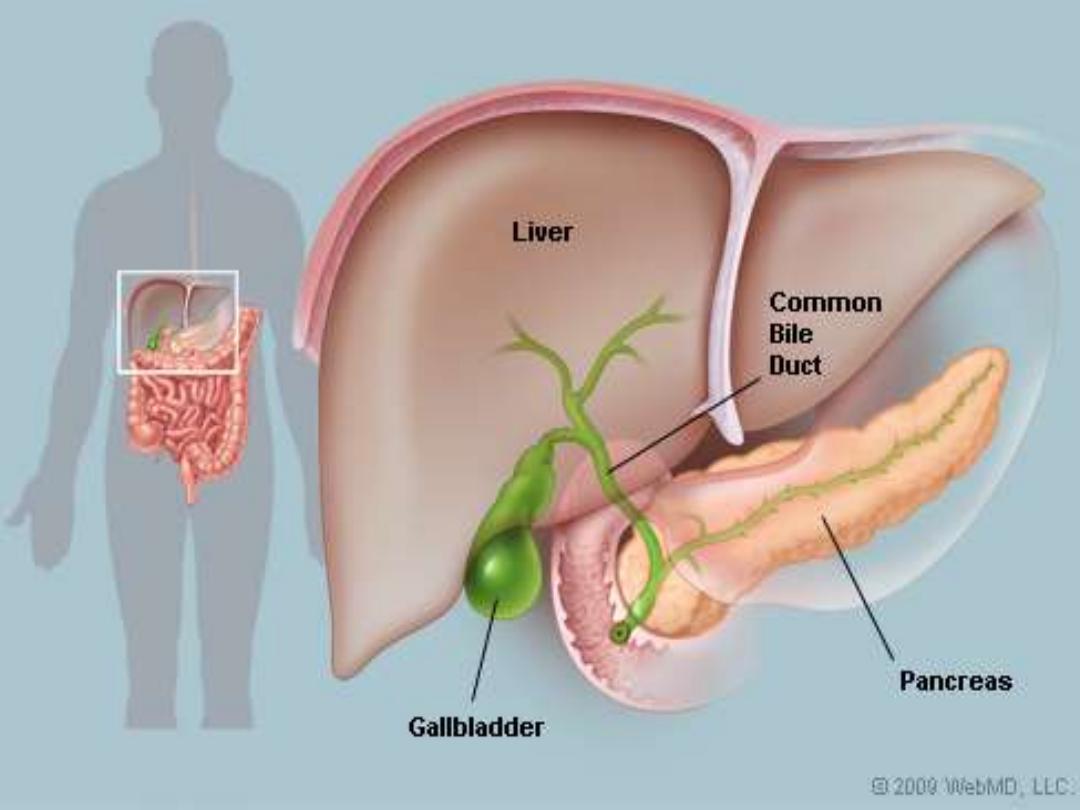
Gallbladder
•
Stores bile until it is needed for digestion
•
It concentrates bile by removing of some of the
water.

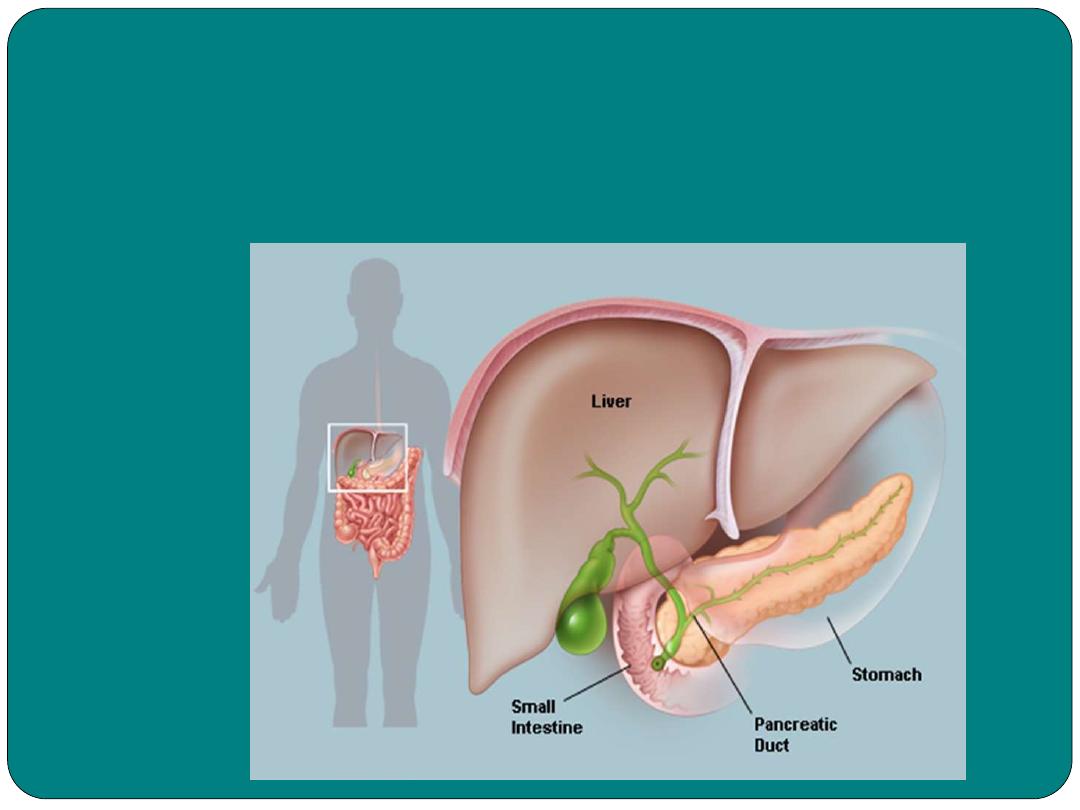
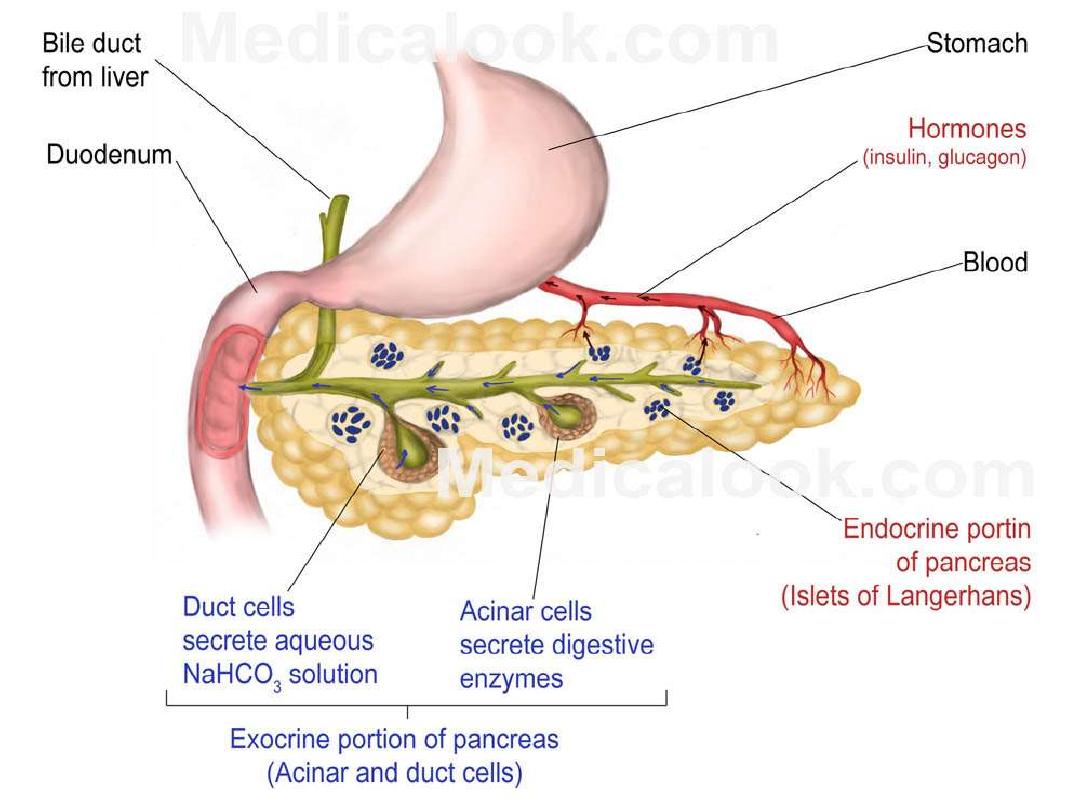
Pancreas
•
Five to six inches long
•
Lies across the posterior side of the stomach
•
It’s a digestive organ, secretes digestive fluid to
the small intestine. The digestive fluid is called
pancreatic juice, with include various enzymes
such as
amylase
and
lipase.
•
Pancreas
is also an endocrine organ secretes
insulin
that regulate blood sugar
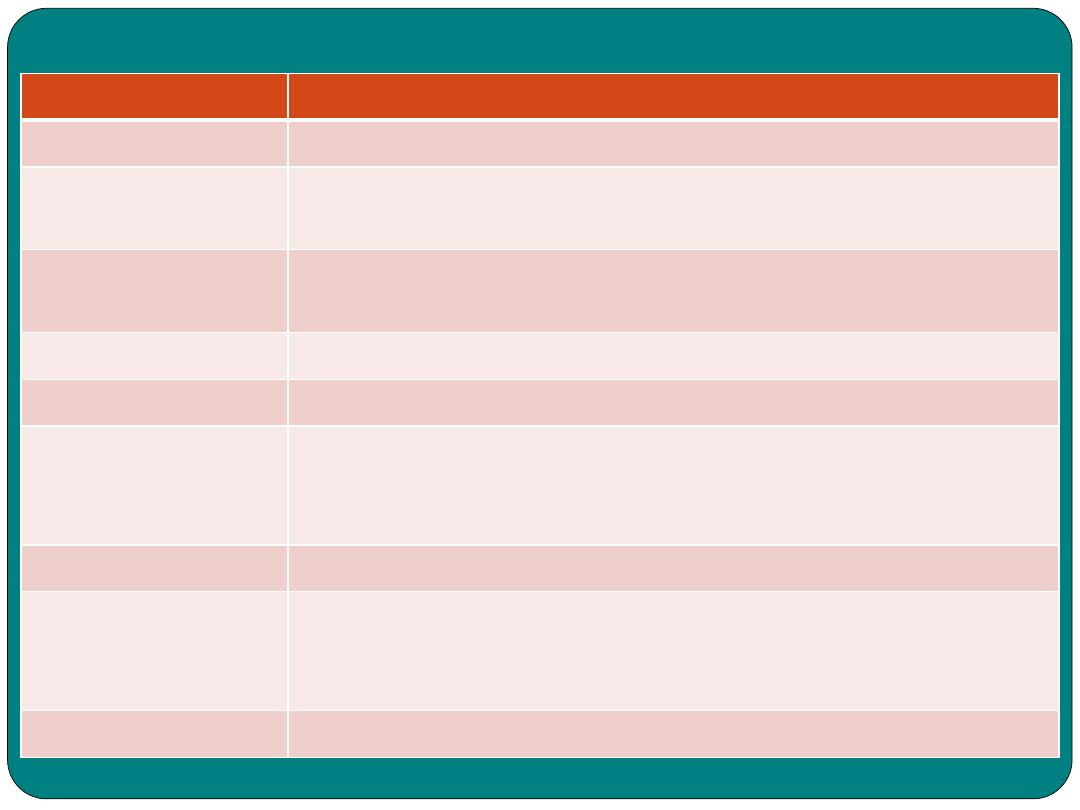
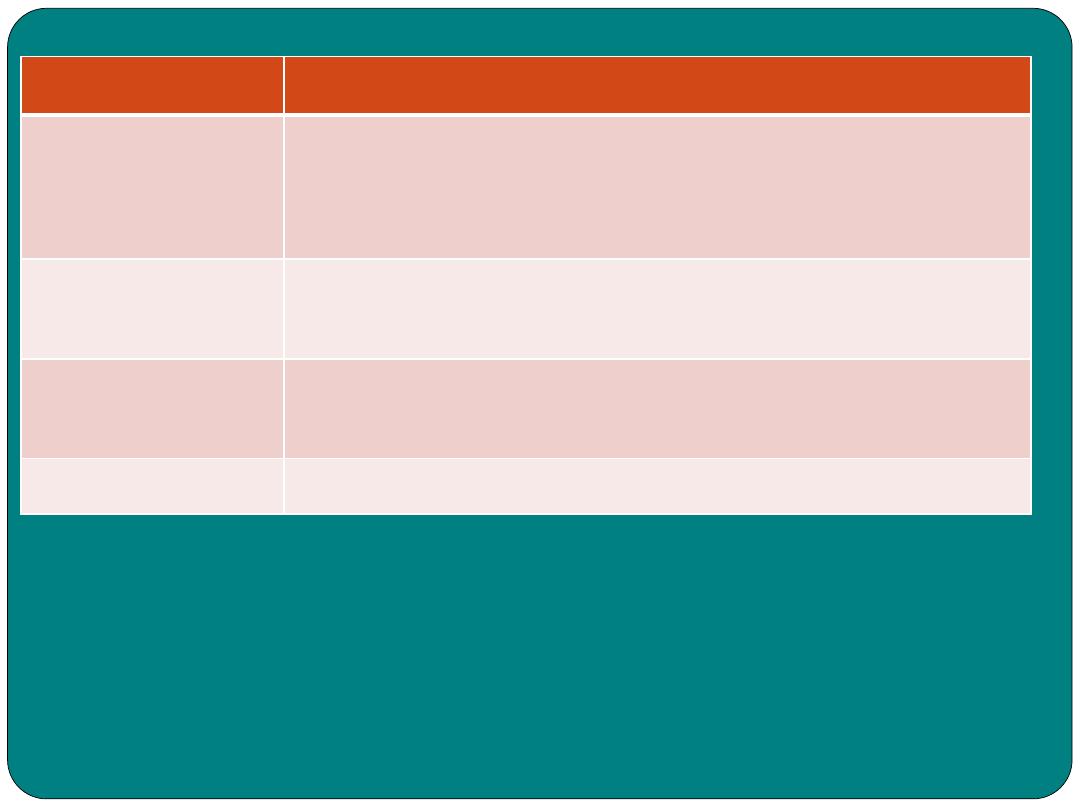
Study Table
TERM
MEANING
Absorption
Passing of nutrient to the blood stream
Amylase
Enzyme that is part of pancreatic juice and saliva
important in digestion of carbohydrates
Anal canal
Part of digestive tract extending from the rectum to the
anus
Anus
Place at which faeces exit to out side the body
Appendix
Wormlike appendage to the cecum
Bile
Yellowish-brown to greenish fluid secreted by the liver
and stored in the gallbladder, aids in fat digestion
Bilirubin
Pigment contained in bile.
Chyme
Semisolid mass or partially digested food and gastric
juice that passes from the stomach to the small intestine
Deglutition
Swallowing

TERM
MEANING
Glucose
Sugar that found in fruits and plants and
stored in various parts of the body
Glycogen
Starch that can be converted to glucose
Lips
Two muscular folds formed outside
boundaries of the mouth
mastication
Chewing
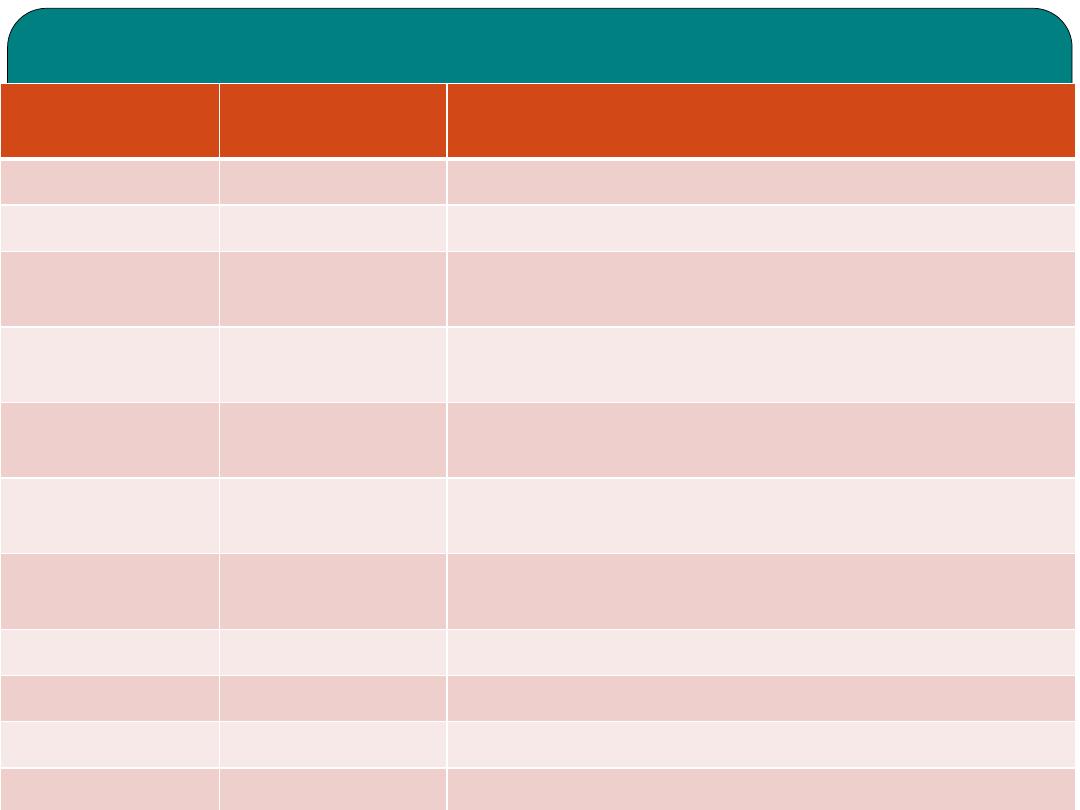
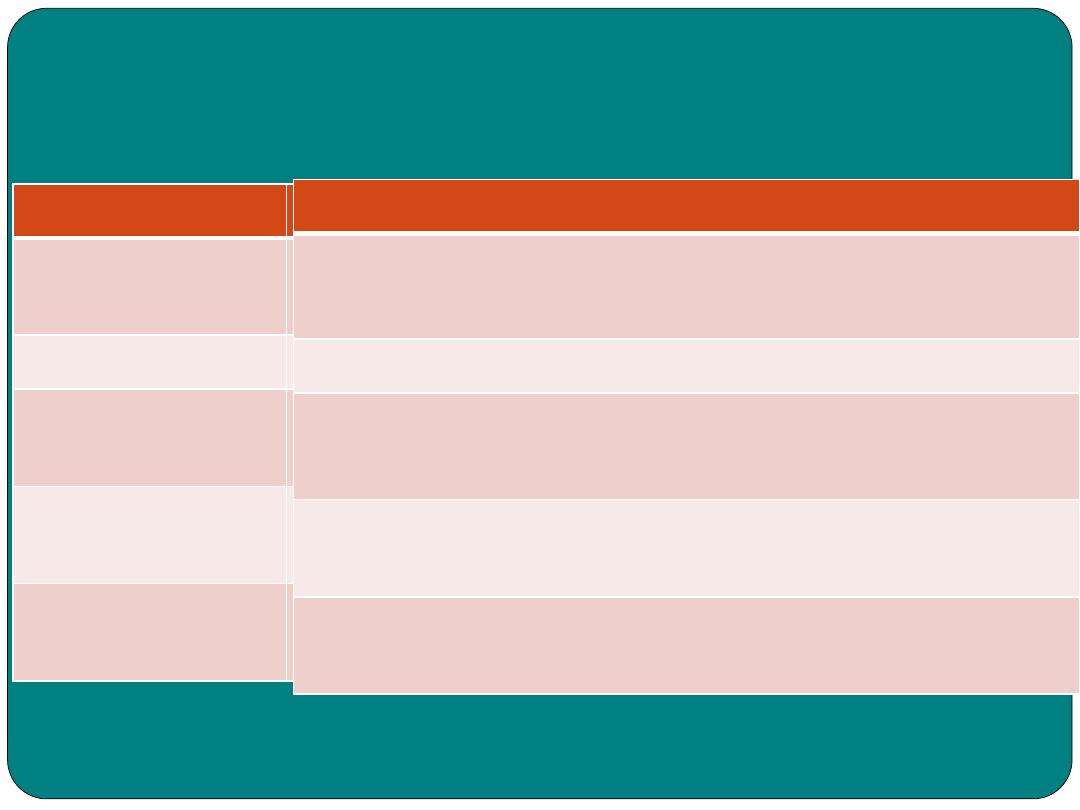
Combining forms
Combining
form
MEANING
EXAMPLE
an(o)
anus
Anoplasty, surgical repair of the anus
Append(o)
Appendix
Appendicitis: inflammation of the appendix
Bucc(o)
check
Buccogingival: related to the checks and gums
Cholangi(o)
Bile vessels
Cholangiogram: x-ray imaging of the bile vessels
Cholecyst(o)
Gall bladder
Cholecystectomy: removal of the gall bladder
Choledoch(o)
Common bile
duct
Choledochotomy: incision into the common bile
duct
Colo(o),
colon(o)
Colon
Colectomy: removal of all or part of the colon
Enter(o)
intestine
Enteropathy: any intestinal disease.
Gastr(o)
stomach
Gastritis: inflammation of the stomach
Gloss(o)
tongue
Glossopharangeal
Hepat(o)
liver
Hepatitis: inflammation of the liver
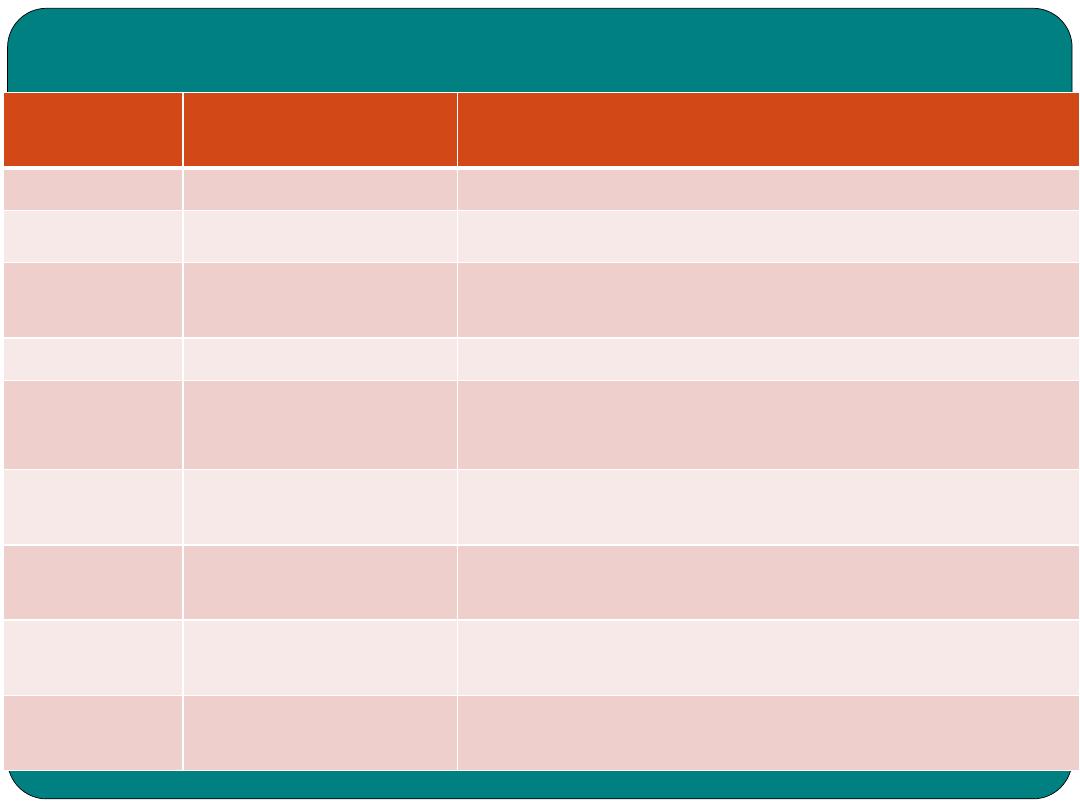
Combining forms
Combining
form
MEANING
EXAMPLE
Labi(o)
lips
Labioplasty: surgical repair of the lips
Lingu(o)
tongue
Linguodental: related to the tongue and teeth
Or(o)
mouth
Oropharynx: related to the mouth and pharynx
Proct(o)
rectum
Proctitis: inflammation of the rectum
sial(o)
Salivary glands,
saliva
Sialism: excessive excretion of saliva
Sialaden(o)
Salivary gland
Sialoadnitis: inflammation of the salivary glands
Steat(o)
fat
Steatorrhea : greater than normal amount of fat in
faeces
Stomat(o)
mouth
Stomatitis: inflammation of the lining of the mouth
stoma
An artificial opening

Diagnostic, procedural and
laboratory terms
term
Description
gastroscopy
Visualization of the stomach by gastroscope
Gastroscope
Instrument used to visualize the stomach
cholangiogram
An image of the bile vessels
Cholecytogram Image of the gall bladder
Peritoneoscopy Examination of the peritoneal cavity using the
peritoneoscope
Description
Visualization of the stomach by gastroscope
Instrument used to visualize the stomach
An image of the bile vessels
Image of the gall bladder
Examination of the peritoneal cavity using the
peritoneoscope
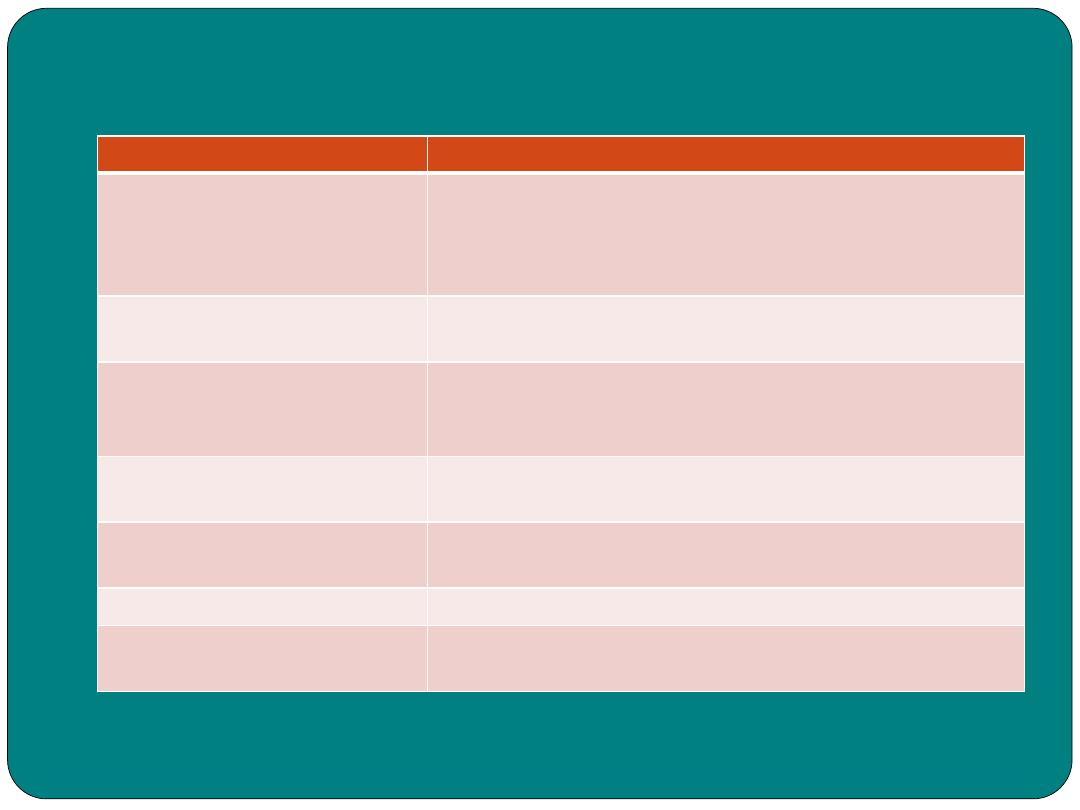
Pathological terms
Pathological term
Meaning
achalasia
Inability of the muscle of the cardiac sphincter to relax
Appendicitis
Inflammation of the appendix
ascites
Fluid build up in the abdominal and peritoneal cavity
chelitis
Inflammation of the lips
cholangitis
Inflammation of bile ducts
Cholecystitis
Inflammation of the gall bladder
cholelithiasis
Gall stone in the gall bladder
cirrhosis
Liver disease, often caused by alcoholism
constipation
Difficult or infrequent defecation
diarrhea
Loose or watery stool
diverticulae
Small pouch in the intestinal wall
dysphagia
Difficult in swallowing

Pathological disorder
Loss of appetite
Anorexia An (without),
orexia (appetite
Involuntary grinding of the teeth that usually occur
during sleep
Bruxism
Decrease in the frequency of bowel movements,
difficulty in passing stools, and/or hard dry stools
Constipation (to press)
Chronic inflammation of parts of intestinal tract
Crohn disease
Act of bleching or burping gas up from stomach
eructation
Erosion of the gastric mucosa
Gastric ulcer
Upword flow of stomach acid into the esophagus
Gastroesophageal reflux
disease (GERD)
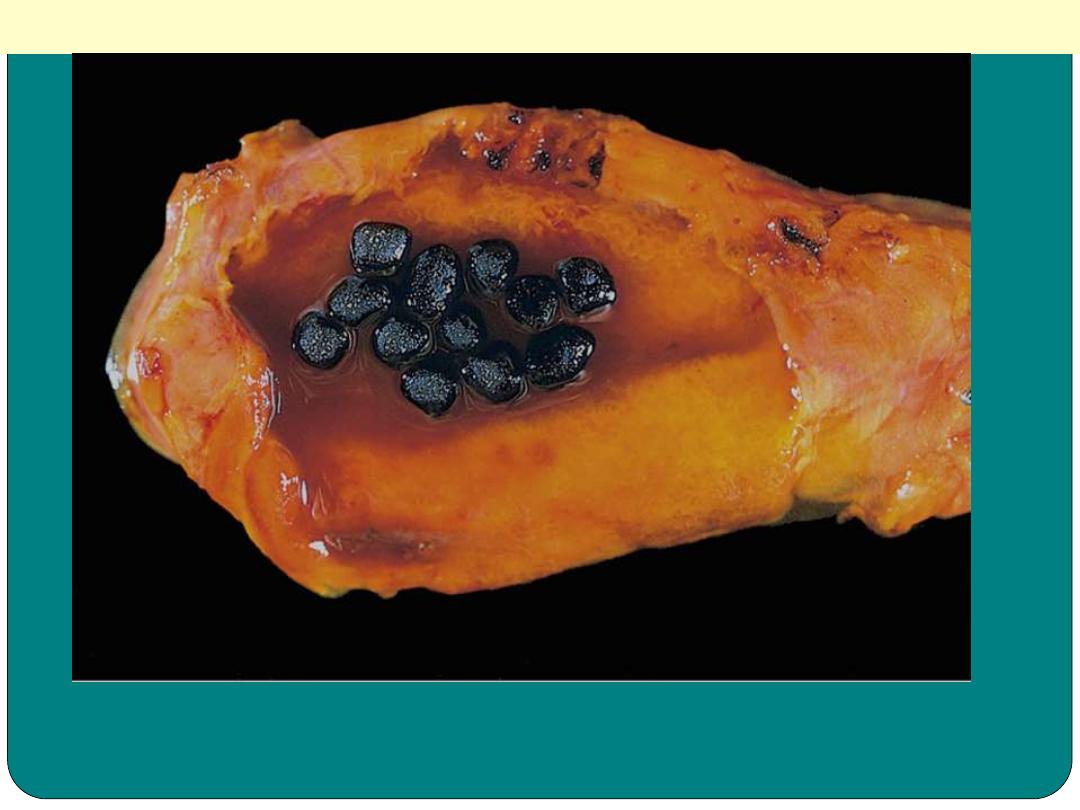
Pigmented gallstones
Several faceted black gallstones are present in the
gallbladder from a person with a mechanical mitral
valve prosthesis, leading to chronic intravascular
hemolysis.
Pathological terms
Pathological term
flatulence
flatus
glossitis
hematemesis
haemorrhoids
hepatitis
hepatomegaly
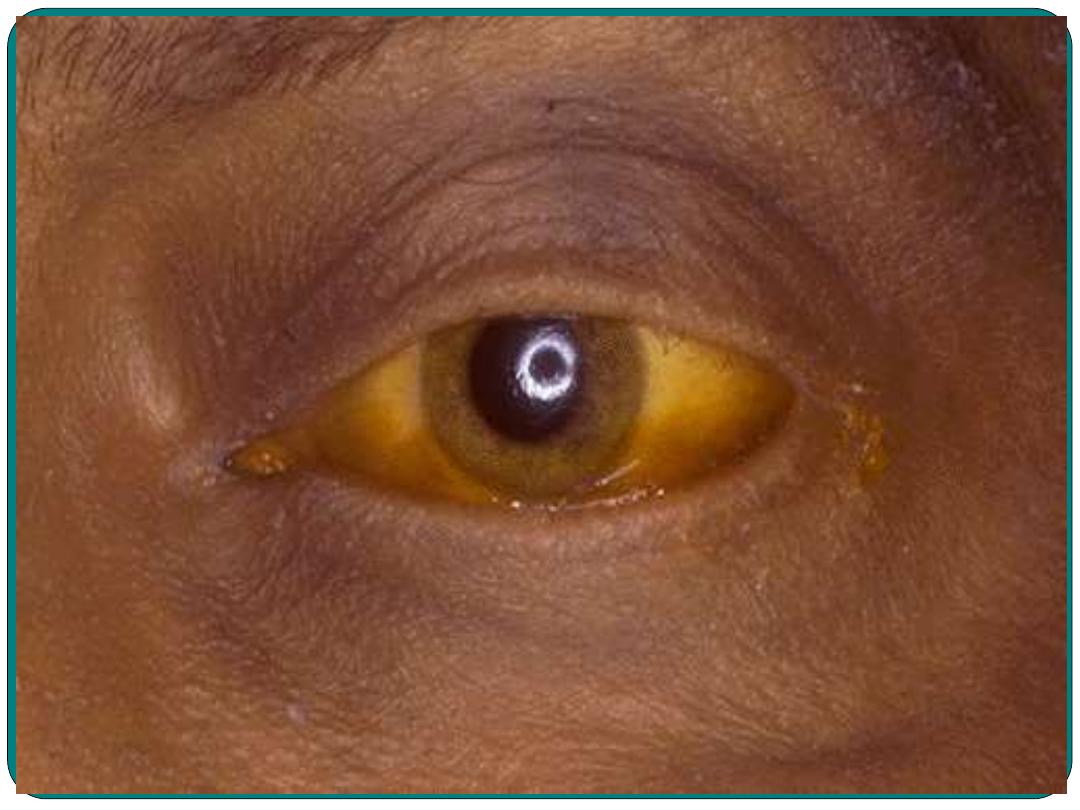
jaundice
melena
obesity
polyposis
Polyp
Meaning
Gas in stomach or intestine
Gas in the lower intestinal tract can be released through the anus
Inflammation of the tongue
Blood in vomit
Swollen twisted veins in the anus
Inflammation or disease of the liver
Enlarged liver
Excessive bilirubin in blood causing yellowing of the skin
Old blood in the stool
Abnormal accumulation of fat in the body
Presence of polyps in the intestine
A mass of a tissue that bulges outward from the skin’s surface on
a stem or stalk of mucous membrane

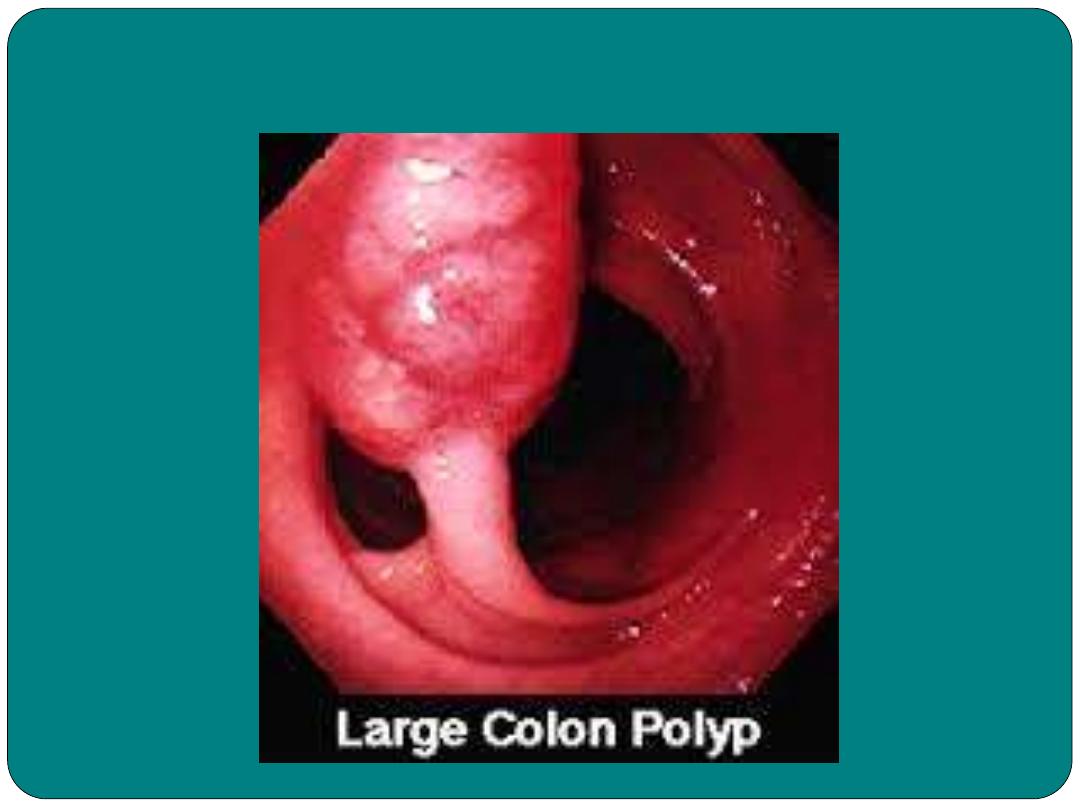
Polyp in Colon
Surgical terms
Surgical term
Meaning
appendectomy
Removal of the appendix
cholecystectomy Removal of gall bladder
Colostomy
Creating an opening from the colon to the
abdominal wall
Liver biopsy
Removal of small amount of liver tissue to
examine for disease.
Paracenthesis
Incision into the abdominal cavity to remove
fluid or to relieve pressure
Polypectomy
Removal of polyps
proctoplasty
Repair of the rectum and anus
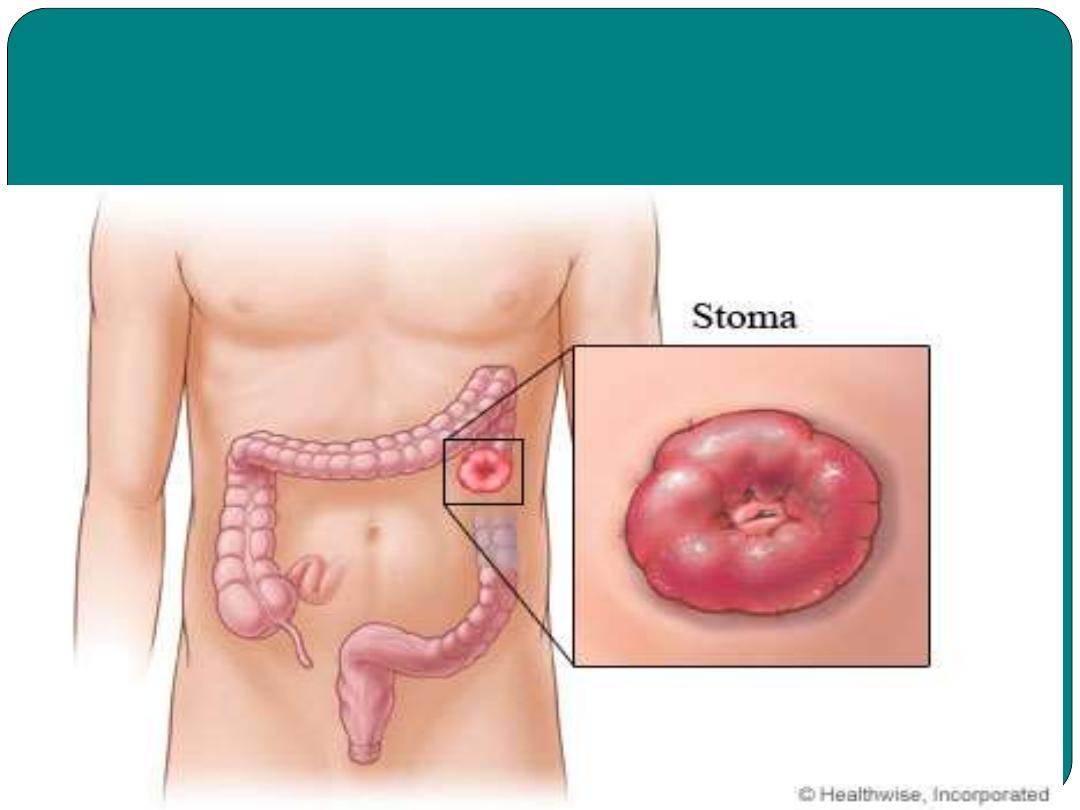
Colostomy procedure
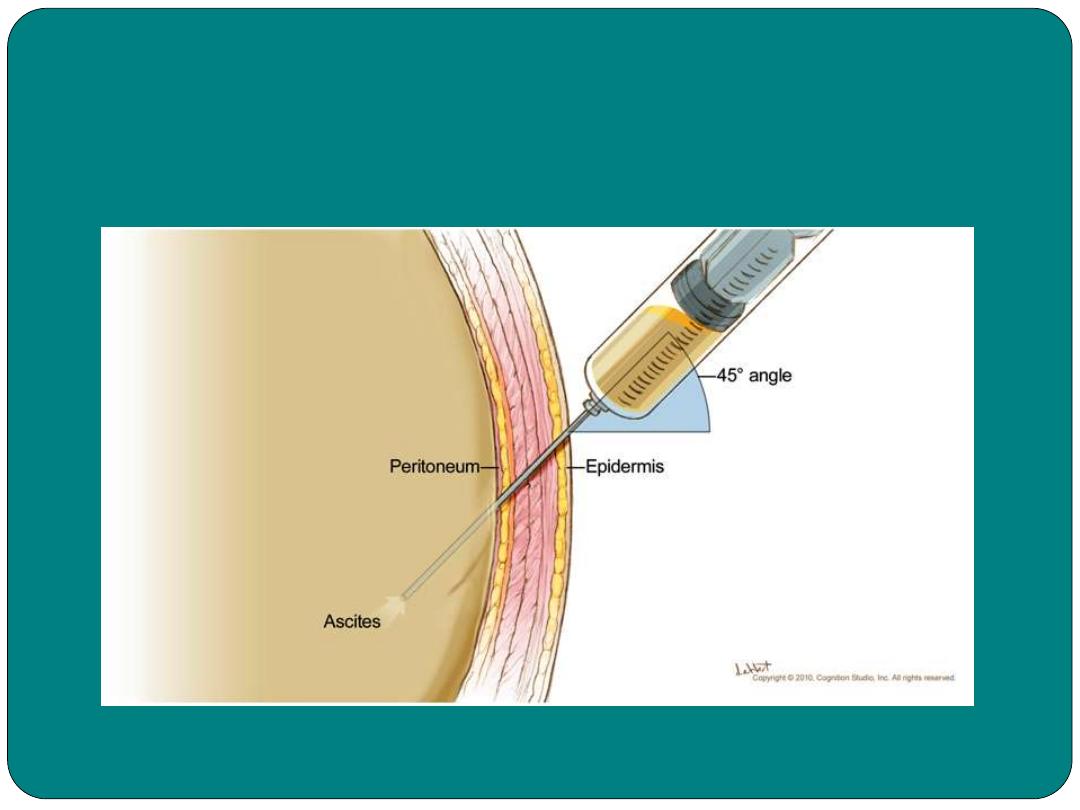
Paracenthesis

T
h
a
n
k
y
o
u
