
Epithelial Tissue
Lecturer: Dr.Firdous M. Jaafar
Department of Anatomy/Histology section
Lecture 1

Objectives
• 1- Define epithelial tissue, and describe its cell types.
• 2- Identify the intercellular adhesion and junctions, and
enumerate their types.
• 3- Enumerate the types of epithelial tissue.
• 4- Define basal lamina and basement membrane, and
recognize their functions.
• 5- Describe the specialization of epithelial cell surface;
• a- Define microvilli.
• b- Define stereocilia.

Introduction
• the human body is composed of only four basic types of
tissue
:
• Epithelial, connective, muscular, and nervous.
• These tissues, which are formed by cells and molecules of the
extracellular matrix, exist not as isolated units but rather in
association with one another and in variable proportions,
forming different organs and systems of the body.

Epithelial tissues
• are composed of closely aggregated
polyhedral cells
with very
little
extracellular substance
. These cells have strong
adhesions, membrane interdigitations, and intercellular
junctions. These features allow the cells to form cellular sheets
that cover the surface of the body and line its cavities or are
arranged as three-dimensional secretory units.
• They have
different shapes
; columnar, cuboidal, or squamous.
• They rest on
basal lamina
(
basement membrane
)
• The lateral membranes between adjacent cells exhibit
intercellular junctions
.

Epithelial tissues
• Epithelial cells are polyhedral in shape, ranging from
squamous, cuboidal, and columnar.
• Nuclear shape corresponds to the cell shape; ranging from flat,
cuboidal, to elongated, and their long axis is parallel to the
long axis of the cell.
• All epithelial cells rests on connective tissue layer to support
these cells.
• The lower part of epithelial cell is called
basal pole,
while the
upper part is called
apical pole or free surface.

Epithelial tissues
• The principal functions of epithelial tissues are
• 1- the covering and lining of surfaces (eg, skin,
intestines).
• 2-absorption (eg, intestines).
• 3- secretion (eg, glands),
• 4- sensation (eg, gustative and olfactory
neuroepithelium).
• 5- contractility (eg, myoepithelial cells).
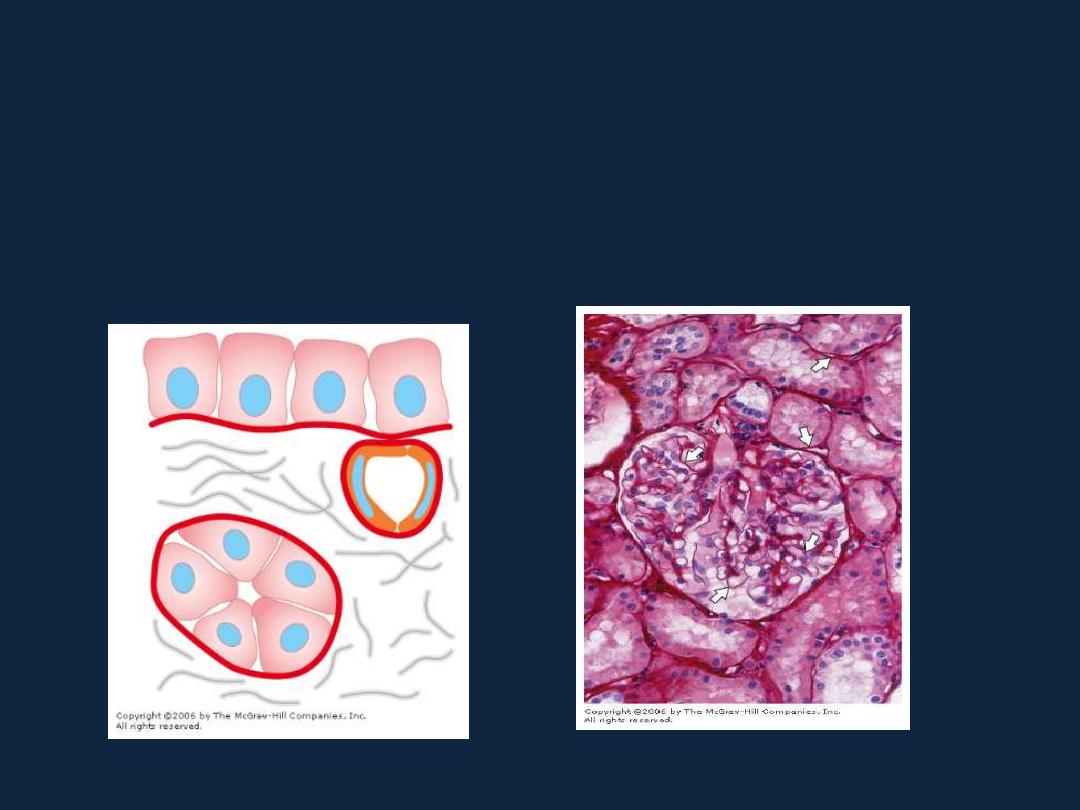
Basal Lamina & Basement
Membrane
•
Most epithelial cells are separated from the connective tissue by a sheet of
extracellular material called the
basal lamina
. This structure is visible only with the
electron microscope, and it is called
basement membrane
when seen by LM
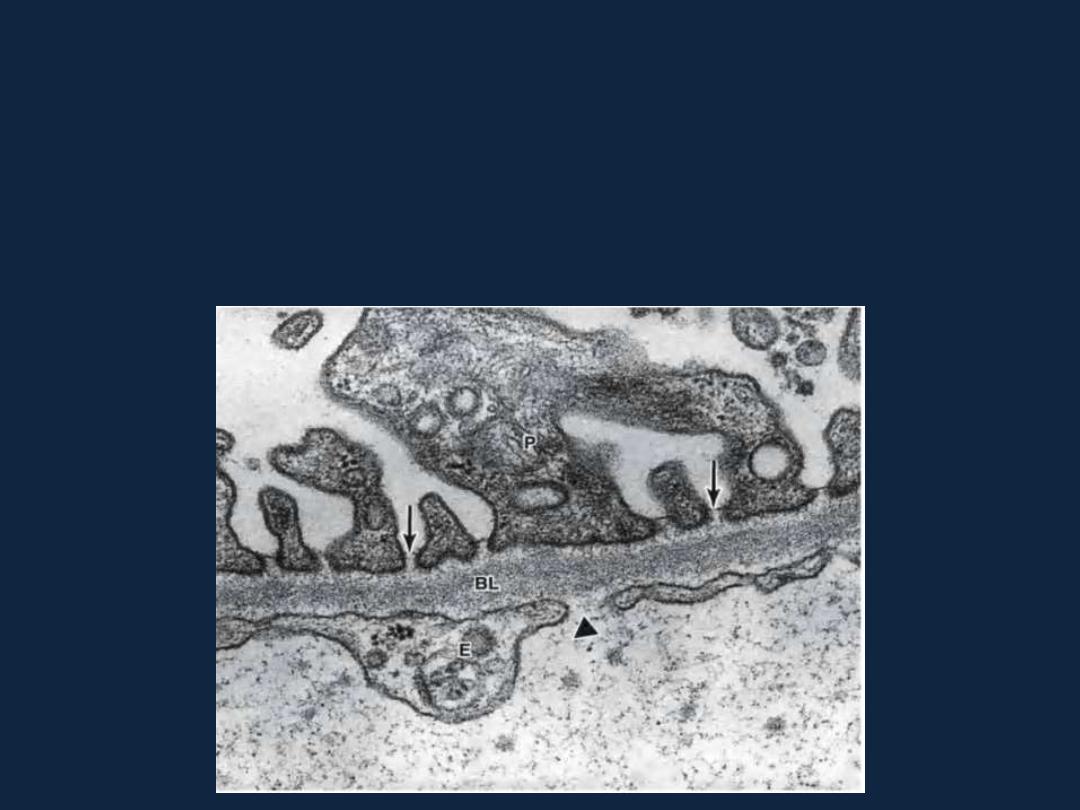
Structure of BM
• it appears as a dense layer, 20–100 nm thick, consisting of a delicate
network of very fine fibrils (
lamina densa
), and an electron-lucent layer on
one or both sides of the lamina densa, called
lamina rara
or
lamina lucida
.

Functions of basal lamina
• 1- structural functions as supporting the cells.
• 2- provide a barrier that limits or regulates the exchange of
macromolecules between connective tissue and cells of other
tissues.
• 3- influence cell polarity, regulate cell proliferation and
differentiation by binding with growth factors, influence cell
metabolism, and serve as pathways for cell migration.
• 4- contain the information necessary for certain cell-to-cell
interactions.
• 5-establishment of new neuromuscular junctions around
muscle cells.
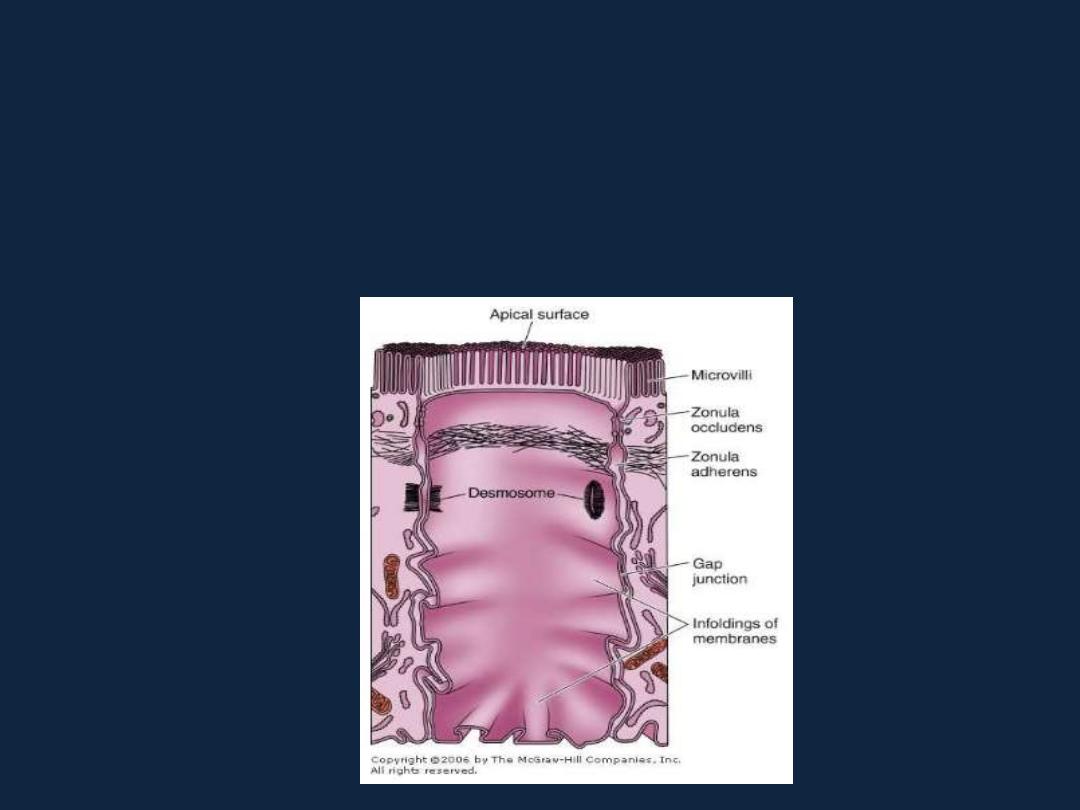
Intercellular Adhesion & Junctions
• Several membrane-associated structures contribute to cohesion
and communication between cells.
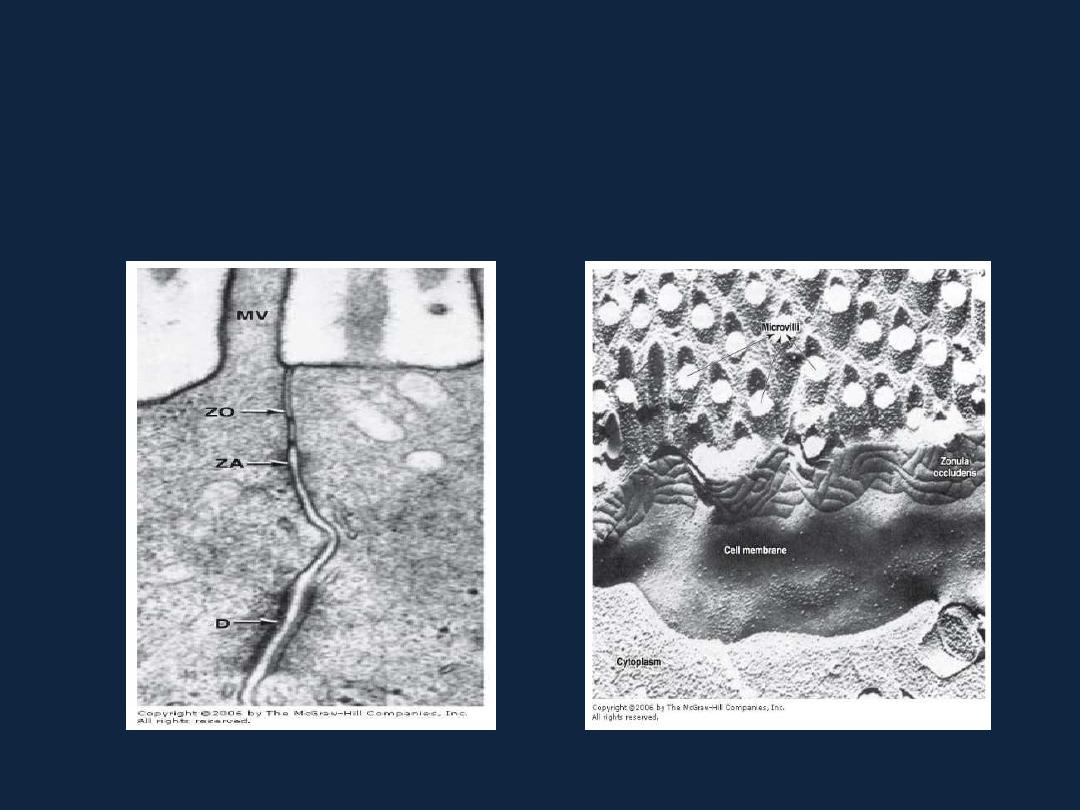
Types of intercellular junctions
• 1- Tight junctions, or zonulae occludens (singular, zonula occludens).
EM photo cryofracture
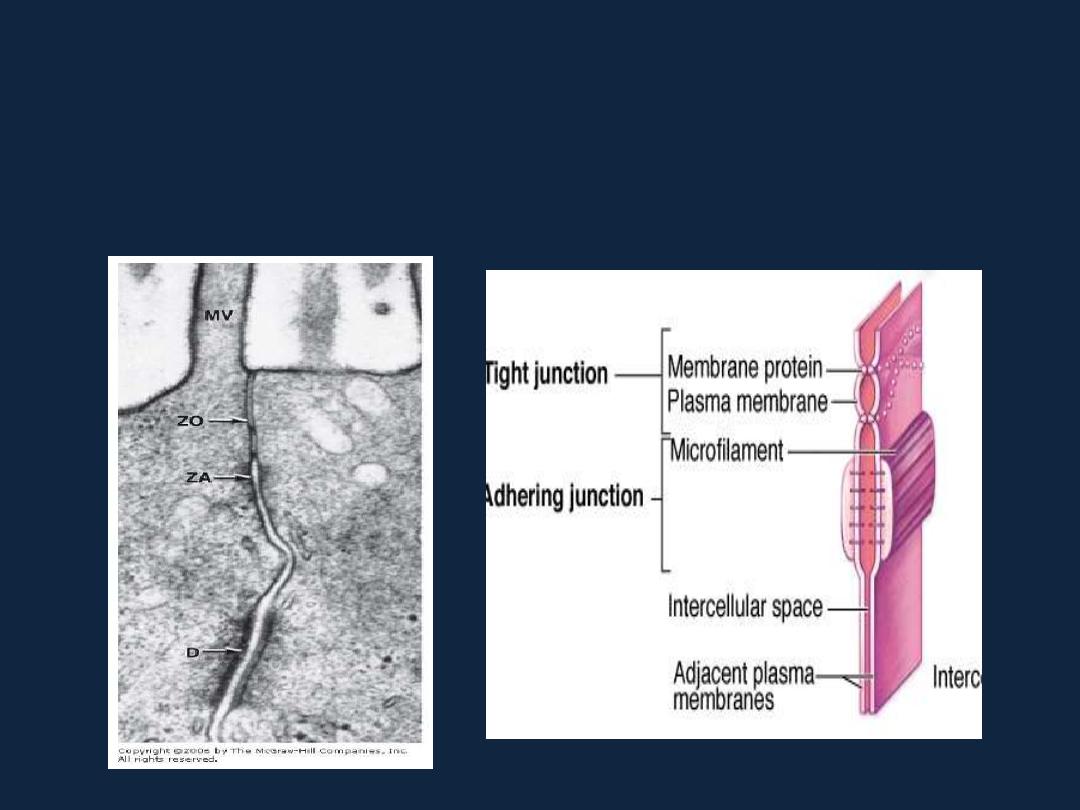
Types of intercellular junctions
• 2- zonula adherens.
Types of intercellular junctions
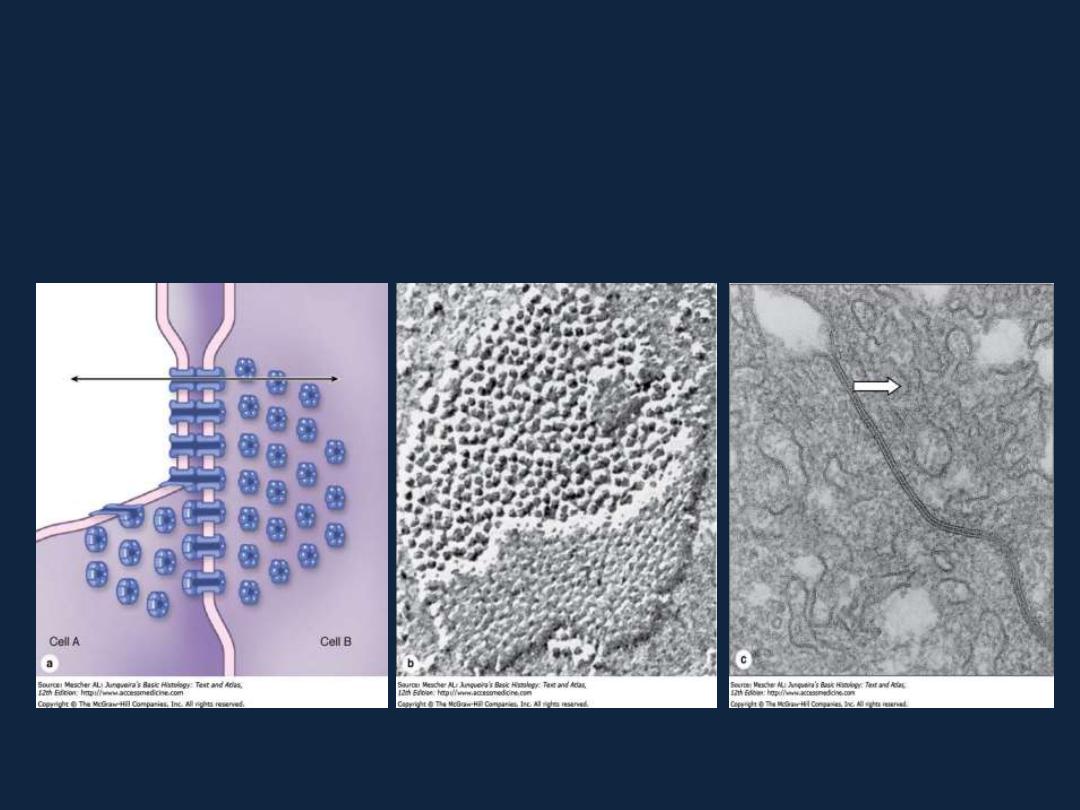
• 3- Gap or communicating junctions.
Types of intercellular junctions
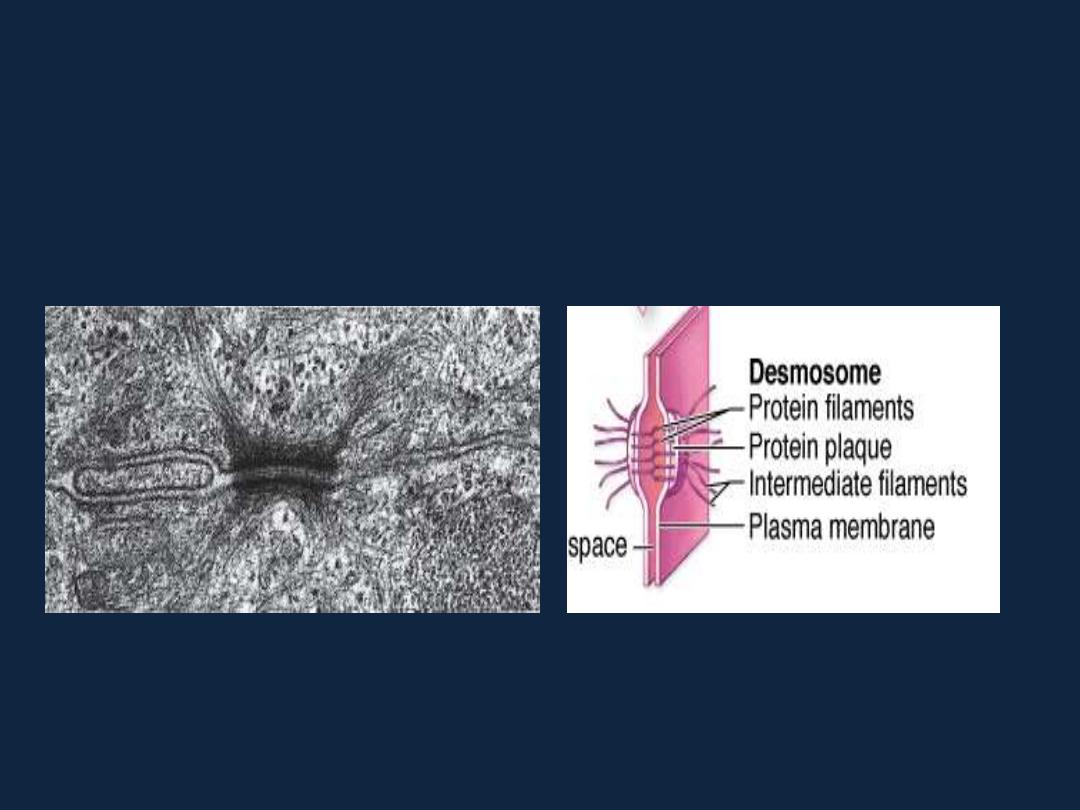
• 4- Desmosomes(macula adherens ).

Types of intercellular junctions
• 5- Hemidesmosomes.
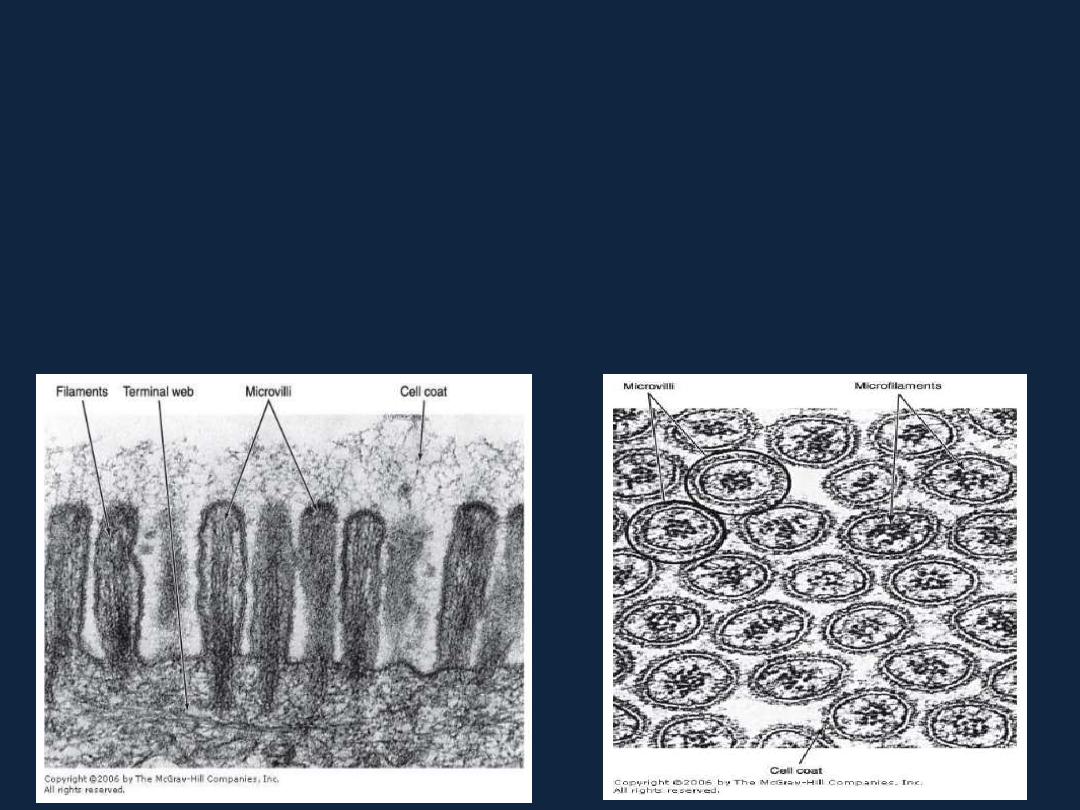
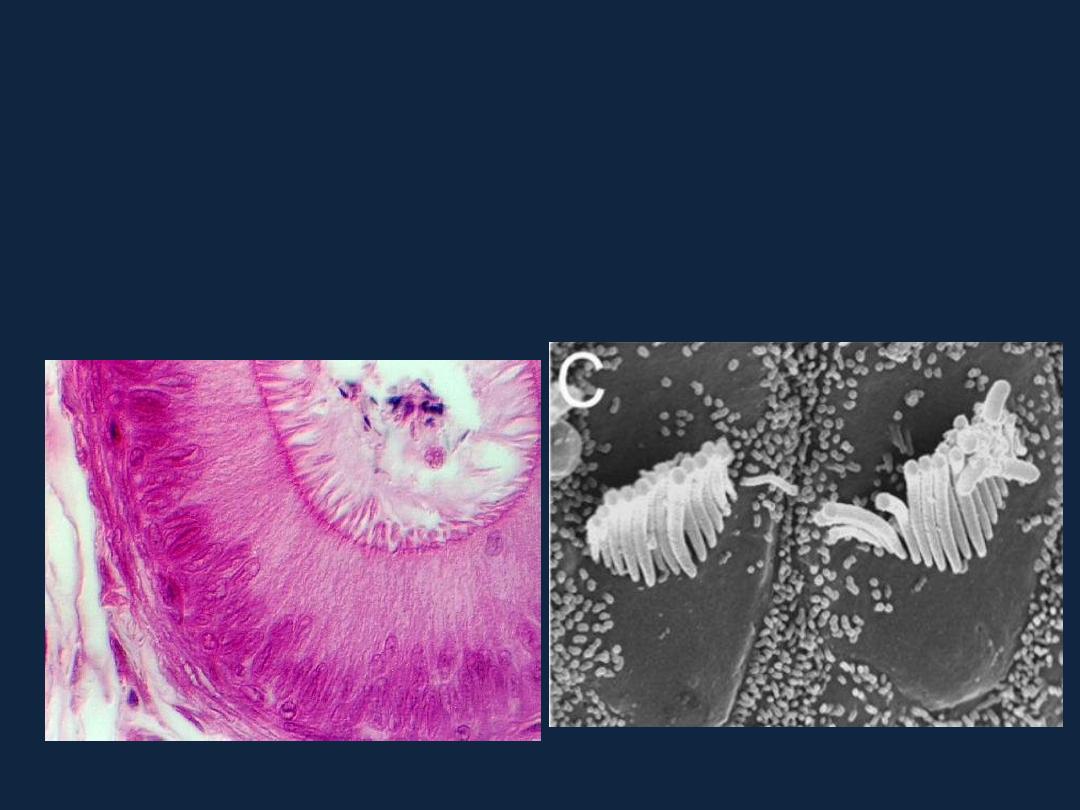
Specialization of cell surface
• 1- Microvilli.
are fingerlike cytoplasmic extensions measuring about 1μm high and 0.08 μm
wide. They are found mainly on the free cell surface of absorptive cells.
They are called
brush
or
striated border
when seen by light microscope.
Specialization of cell surface
• 2- Stereocilia.
• Stereocilia are long, nonmotile extensions of cells that are actually long
and branched microvilli.

Summery
• 1- there are four types of epithelia in the body
• 2- epithelial tissue is classified into covering
and glandular epithelia.
• 3- all epithelial cells rest on basal lamia.
• 4- there are four types of intercellular
junctions
• 4- apical surface of epithelial cells has certain
cell specializations
