
Epithelial Tissue
Lecturer: Dr.Firdous M. Jaafar
Department of Anatomy/Histology section
Lecture 2

Objectives
• 1- Describe the specialization of epithelial cell surface;
• a- Cilia & flagella.
• 2- Classify epithelial tissue into covering and glandular epithelium.
• 3- Classify covering epithelial tissue into simple and stratified epithelium.
• 4- Enumerate the types of simple epithelium.
• 5- Enumerate the types of stratified epithelium.
• 6- Identify some special types of epithelial cells;
• a- Neuroepithelial cells.
• b- Myoepithelial cells.

Specialization of cell surface
• 3- Cilia and flagella.
• cylindrical, motile structures on the surface of some epithelial cells, 5–10
μm long and 0.2 μm in diameter, contain a central pair of isolated
microtubules surrounded by nine pairs of microtubules, and inserted into
basal bodies.

Types of epithelia
• Epithelia are divided into two main groups according to their
structure
and
function
:
• 1- covering epithelia.
• 2- glandular epithelia.

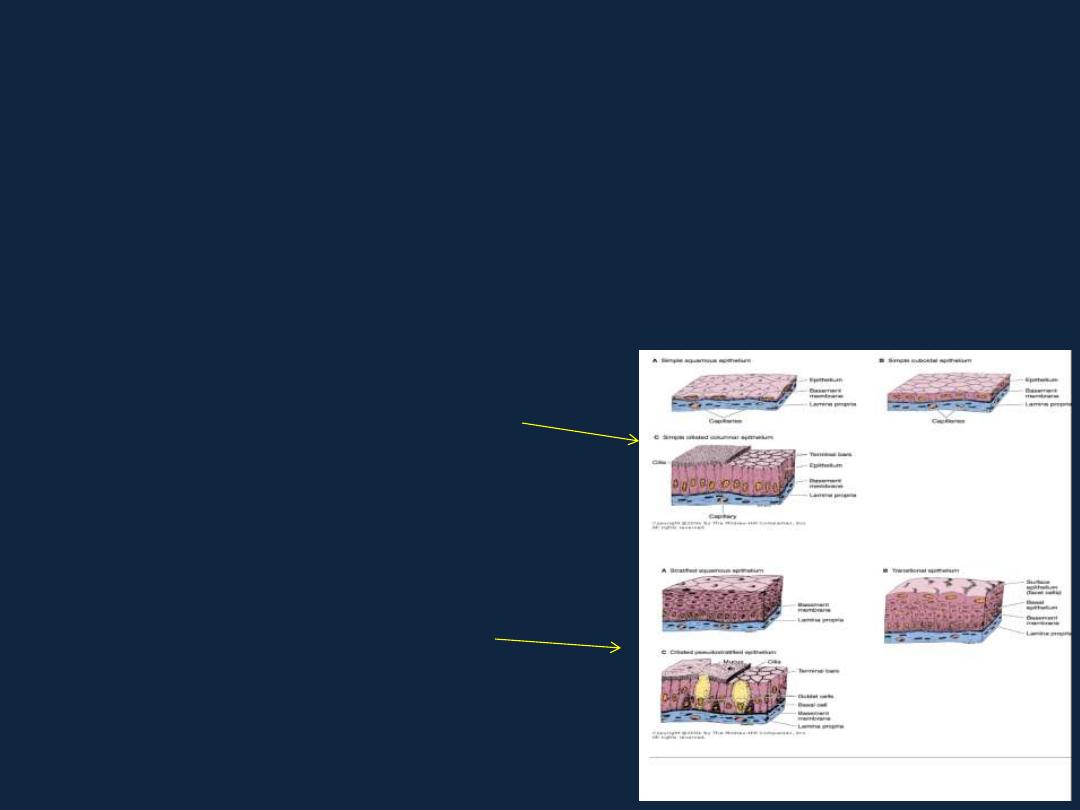
Covering Epithelia
• the cells are organized in layers that cover the external surface or line the
cavities of the body.
• They can be classified according to the number of cell layers and the
morphological features of the cells in the surface layer into:
• 1- Simple epithelium ;
contains only one layer of cells.
• 2- Stratified epithelium;
contains more than one layer.
Simple epithelium
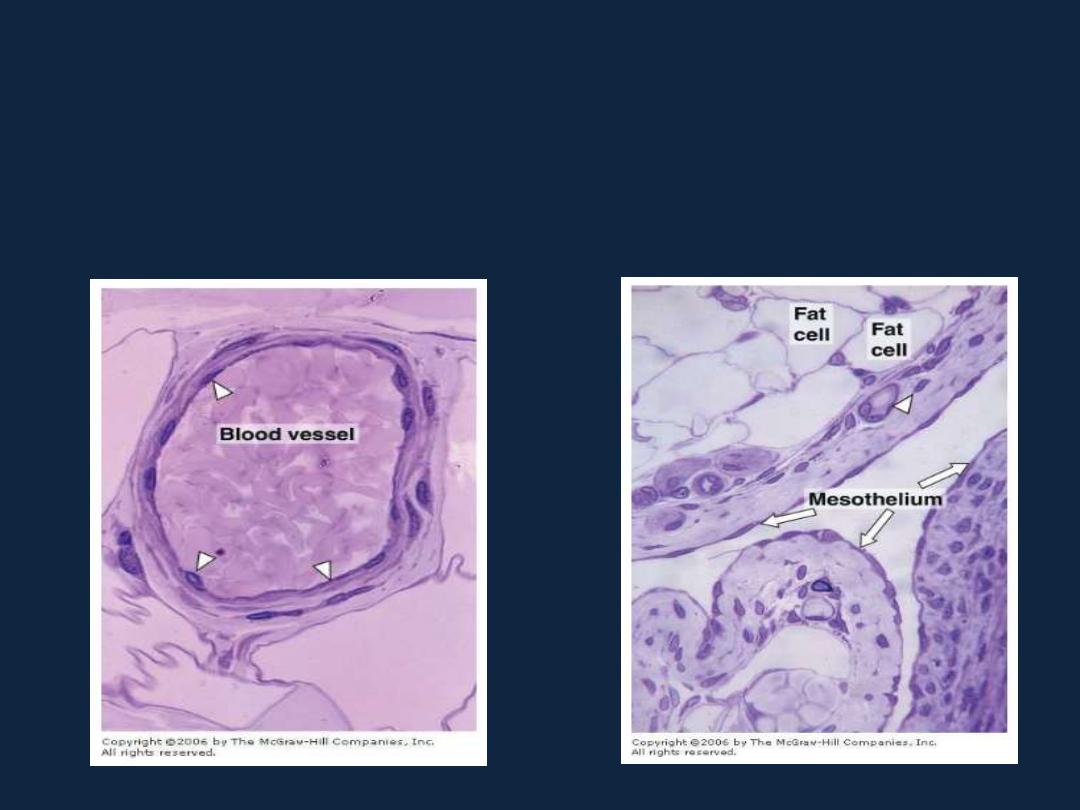
1- Simple squamous epithelium: as endothelial cells, and mesothelial cells.
Simple epithelium
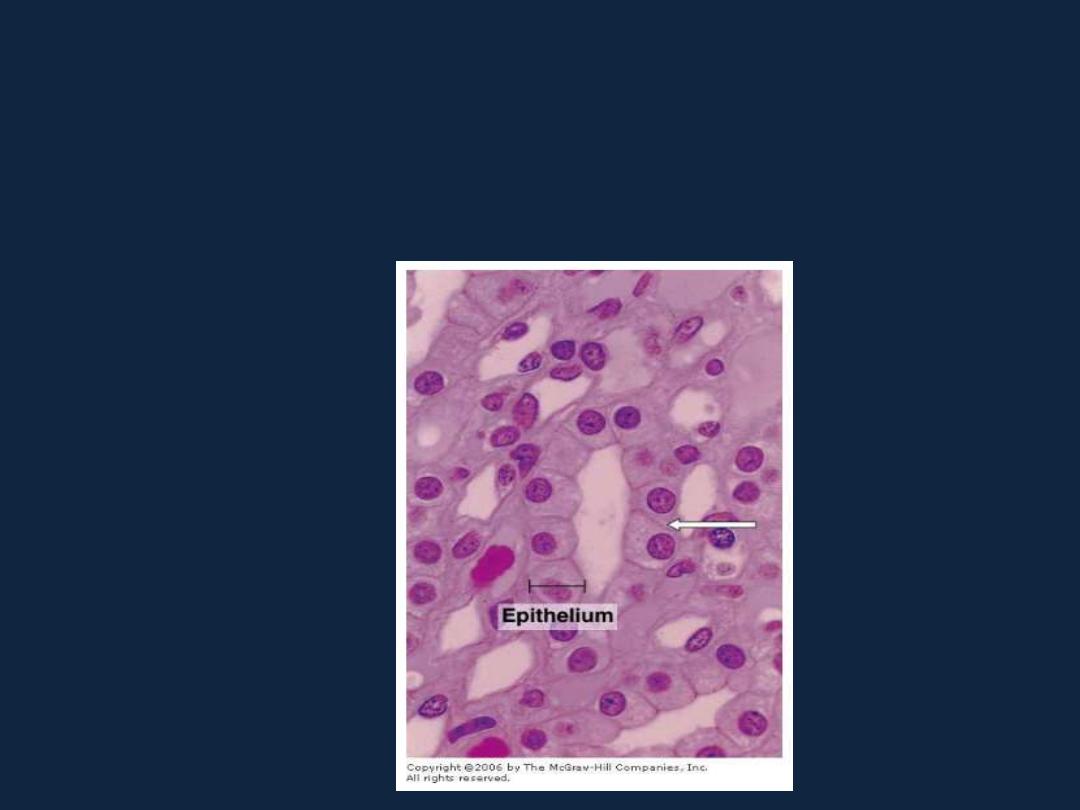
2- Simple cuboidal epithelium: as surface epithelium of the ovary, and
tubules of the kidney.

Simple epithelium
• 3- Simple columnar epithelium: as the lining of the intestines, uterus, and
other organs.
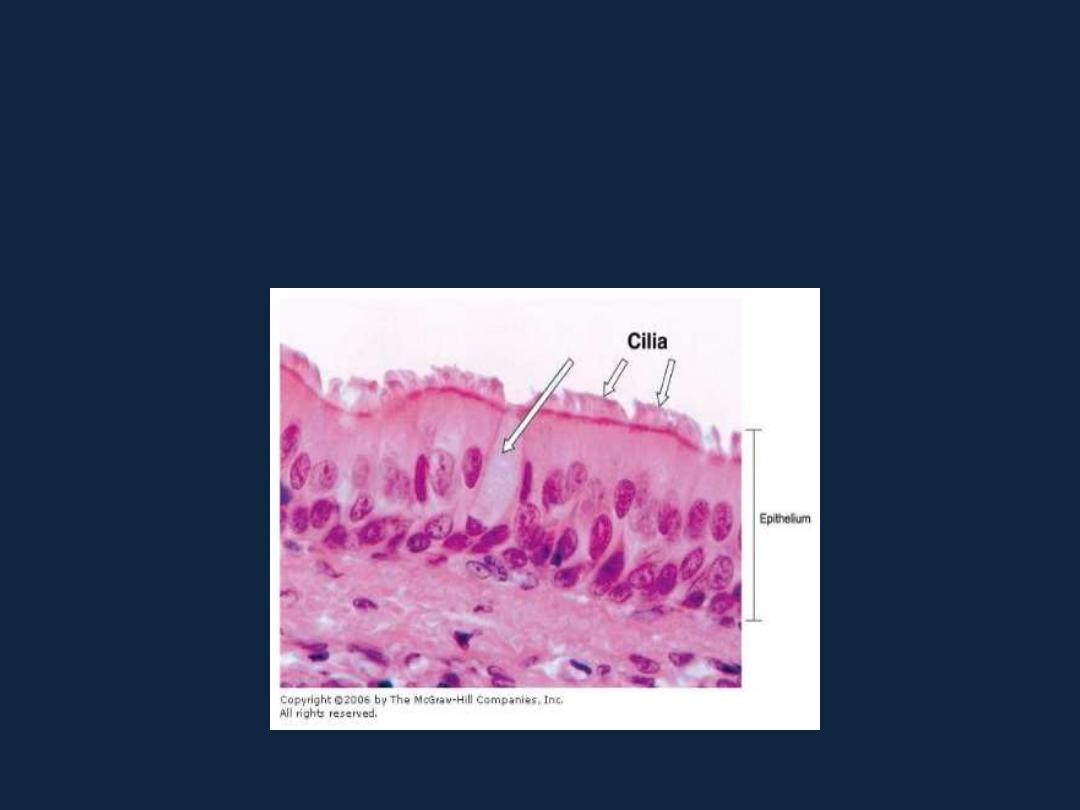
Simple epithelium
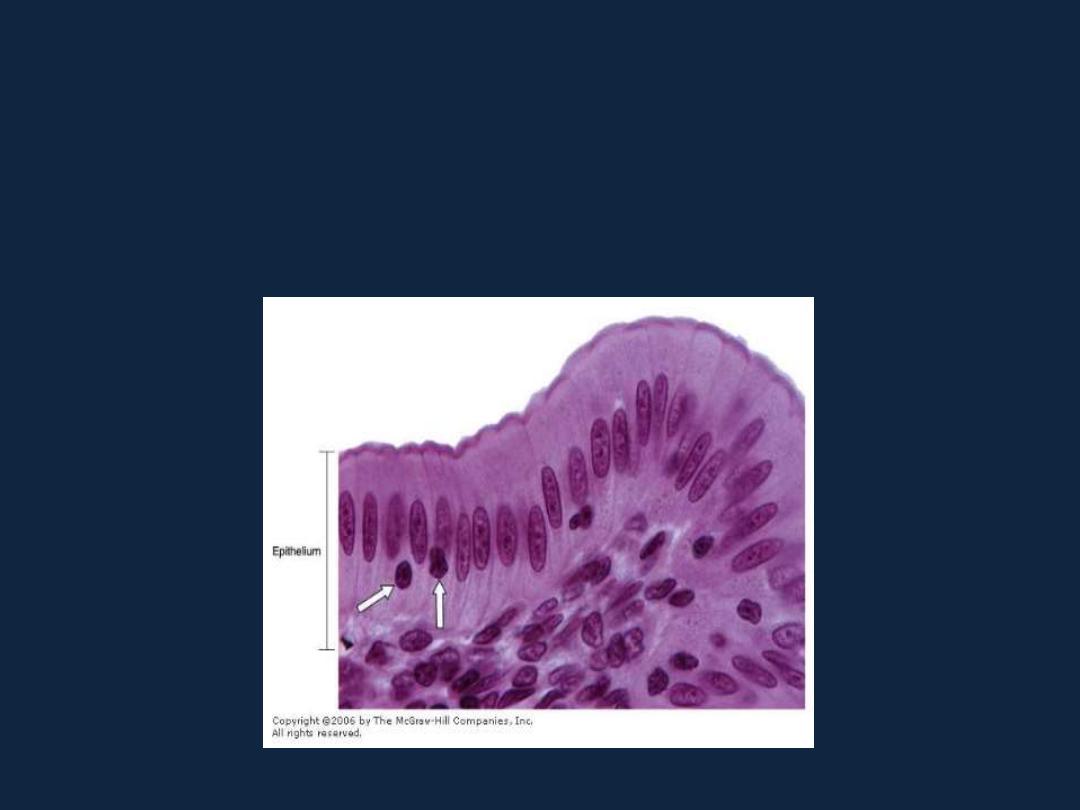
• 4- pseudostratified epithelium: as the respiratory epithelium.
(pseudostratified columnar ciliated)

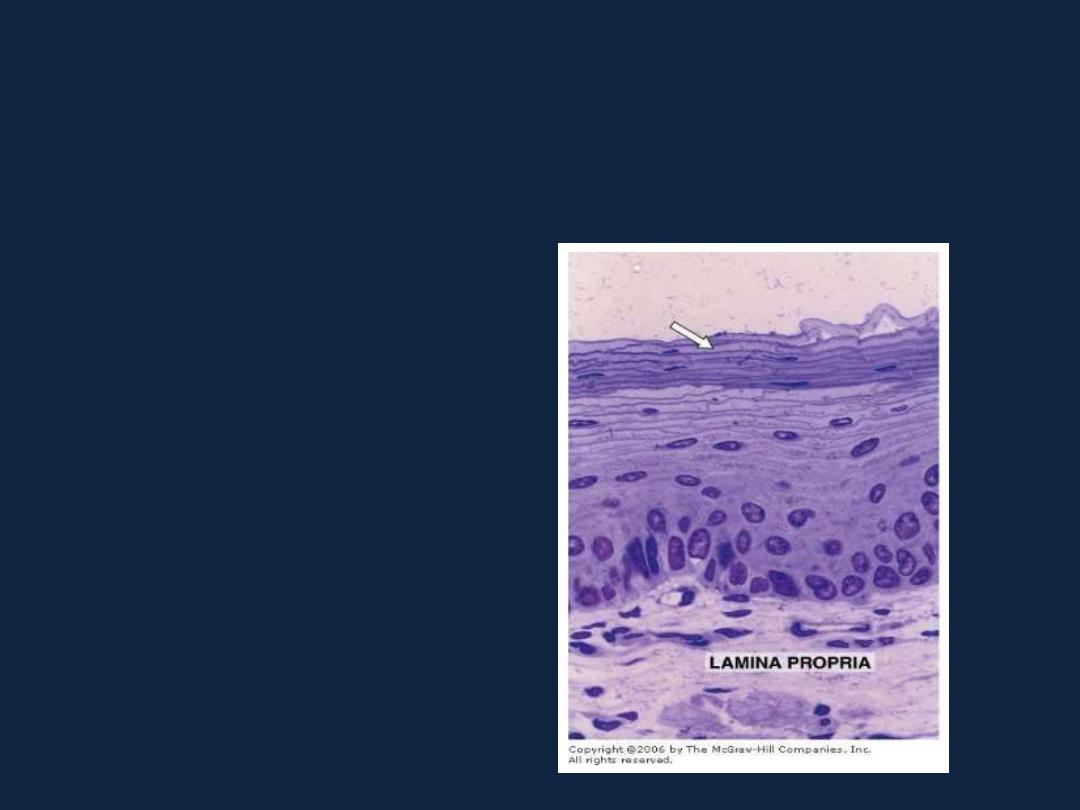
Stratified epithelium
1- Stratified squamous epithelium:
a- Keratinized: as in skin.
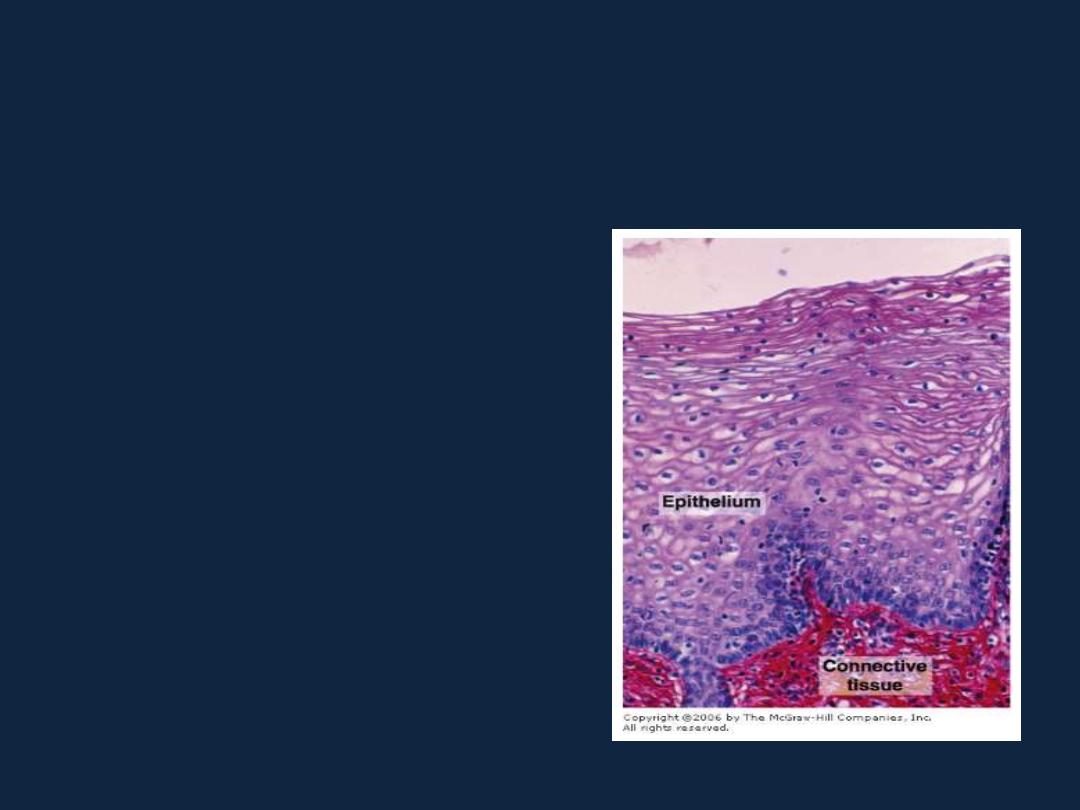
Stratified epithelium
1- Stratified squamous epithelium:
b- Non keratinized: as in esophagus,
vagina.
Stratified epithelium
• 2- Stratified cuboidal epithelium:
as in duct of sweat gland.
Stratified epithelium
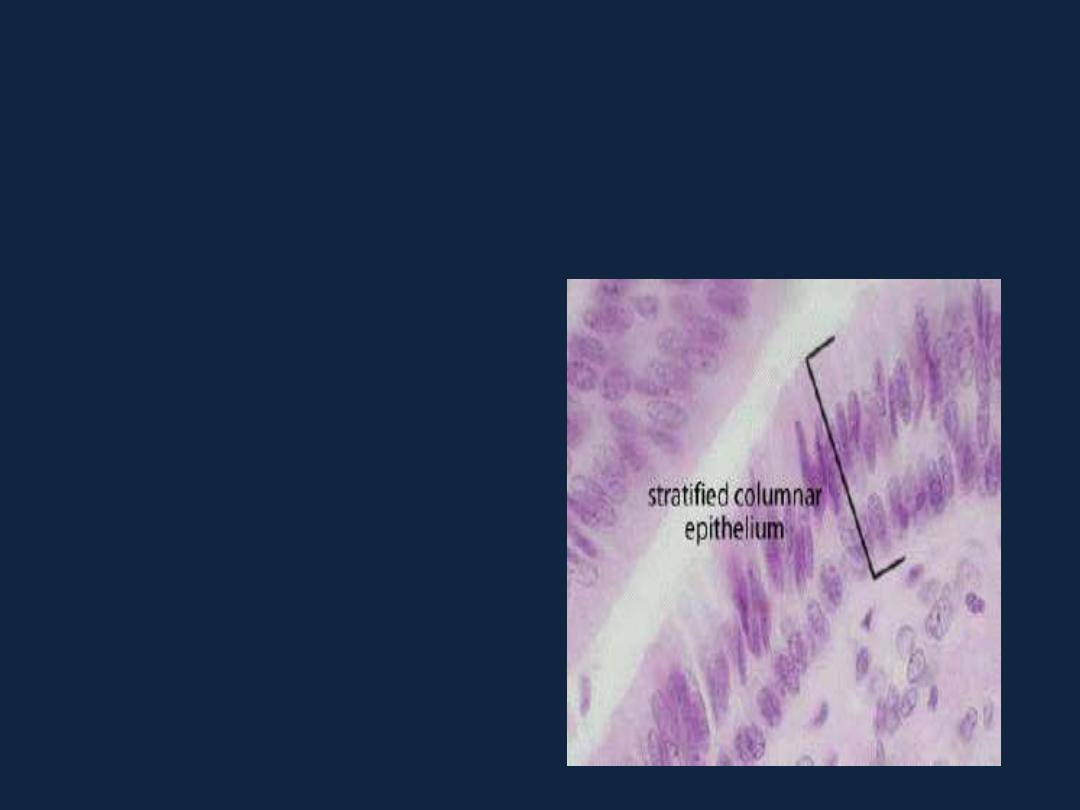
• 3- Stratified columnar epithelium:
as in conjunctiva, and large ducts
of salivary glands.
Stratified epithelium
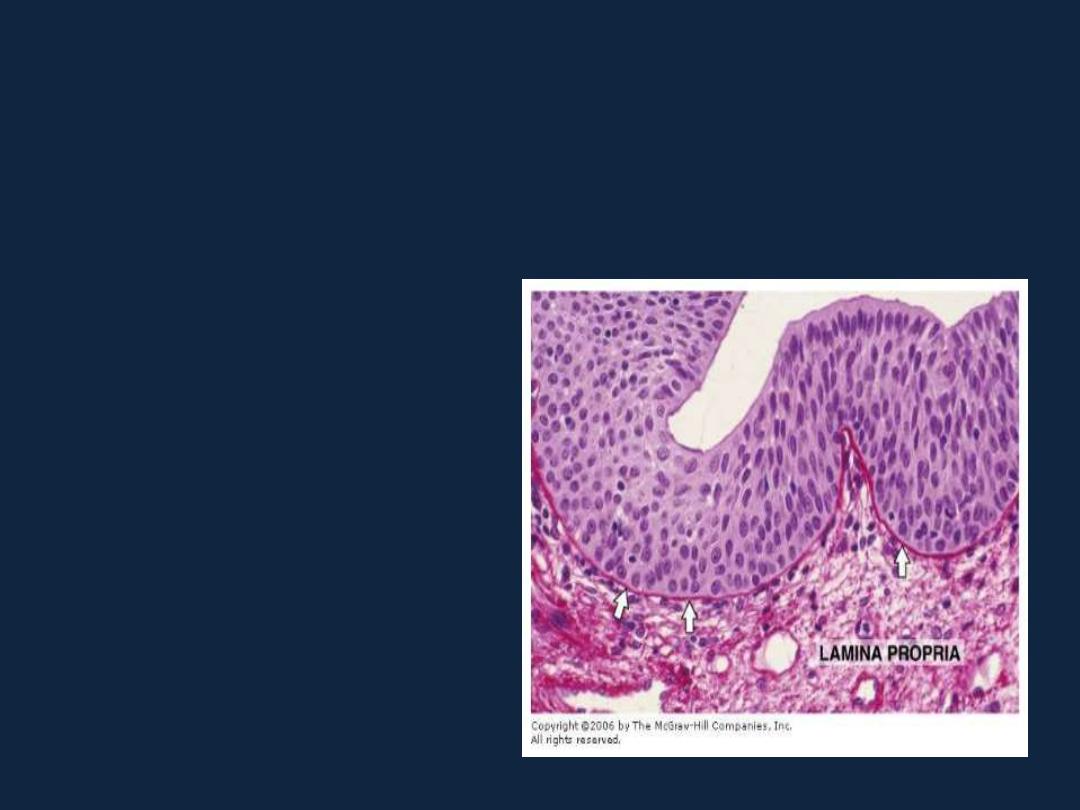
• 4- Transitional epithelium:
as in the urinary bladder, ureter.
Special type of epithelia
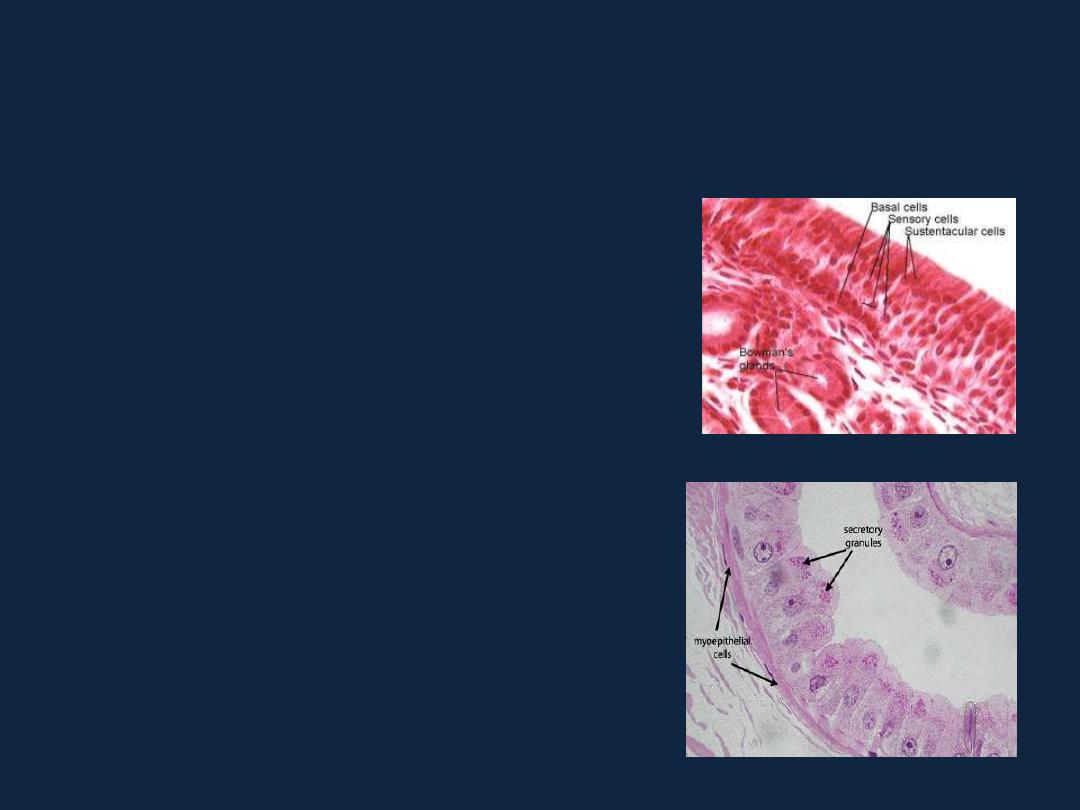
• Neuroepithelial cells : cells of epithelial origin
with specialized sensory functions
(eg, cells of taste buds and of
the olfactory mucosa).
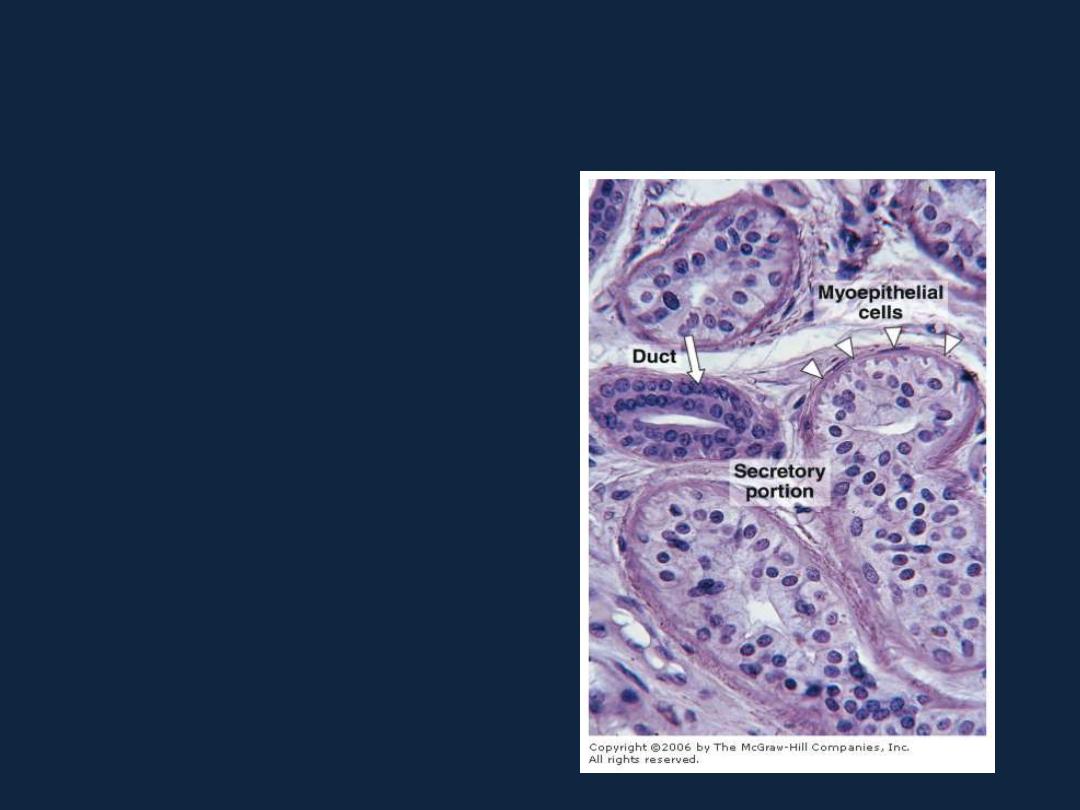
Myoepithelial cells are branched cells
that contain myosin and a large number
of actin filaments.
They are specialized for contraction,
mainly of the secretory units of the mammary,
sweat, and salivary glands.


Summary
• 1- apical surface of epithelial cells has certain cell
specializations(cilia and flagella)
• 2- epithelial tissue is classified into covering and glandular .
• 3- covering epithelia is classified into simple and stratified
epithelium.
• 4- simple epithelia is classified according to the shape of cell
into squamous, cuboidal, columnar, and pseudostratified.
• 5- stratified epithelium is classified into squamous; keratinized
or non keratinized, cuboidal, columnar, and transitional.
• 6- neuroepithelium and myoepithelium is a special type of
epithelium.
