
Cells physiology
إعداد
د.
رافع عاوي الفياض
كلية طب الفلوجة
6
1
Introduction
2
•
The basic organizational structure of the human body is the
cell.
•
There are
50-100 trillion
cells in the human body.
•
Differentiation is when cells specialize.
•
As a result of differentiation, cells vary in size and shape
according to their unique function.
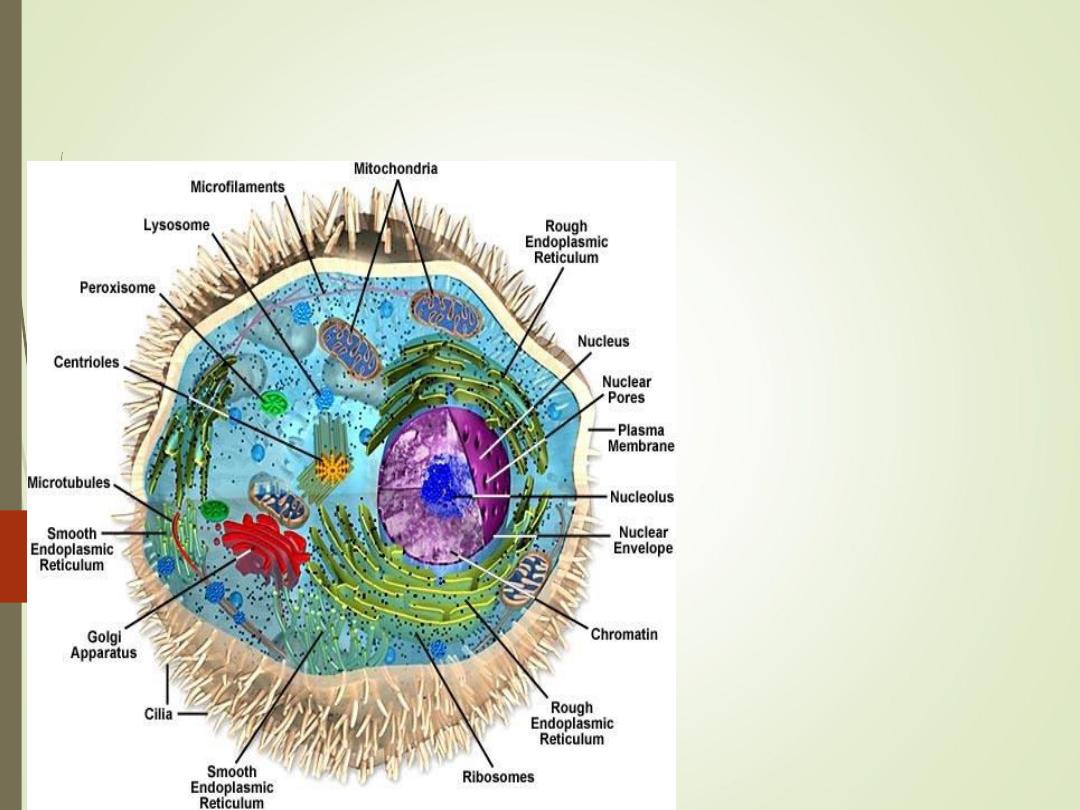
CELL PHYSIOLOGY
Cells are the
basic unit of
life

Cell physiology
There are
that make up all
living things on earth:
1)
, like bacteria, have no
'nucleus‘.
2)
, like those of the human
body.
5
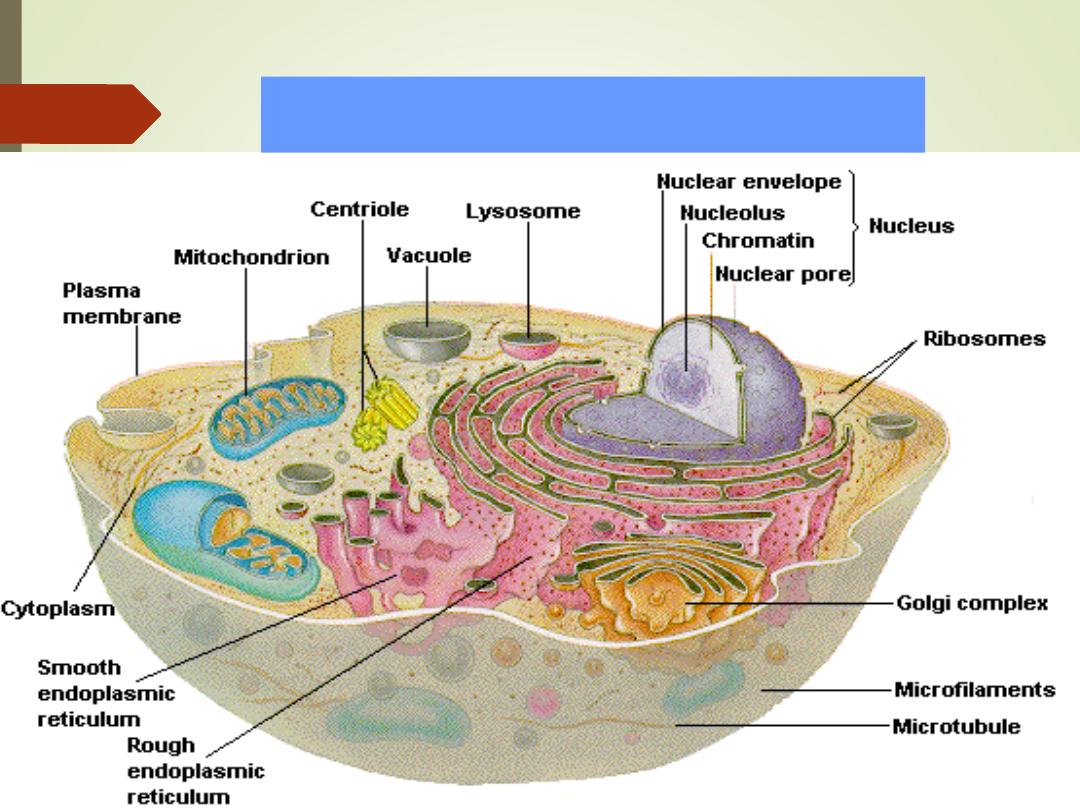
Cell structure and Functions
Cell structure and Functions
6
•
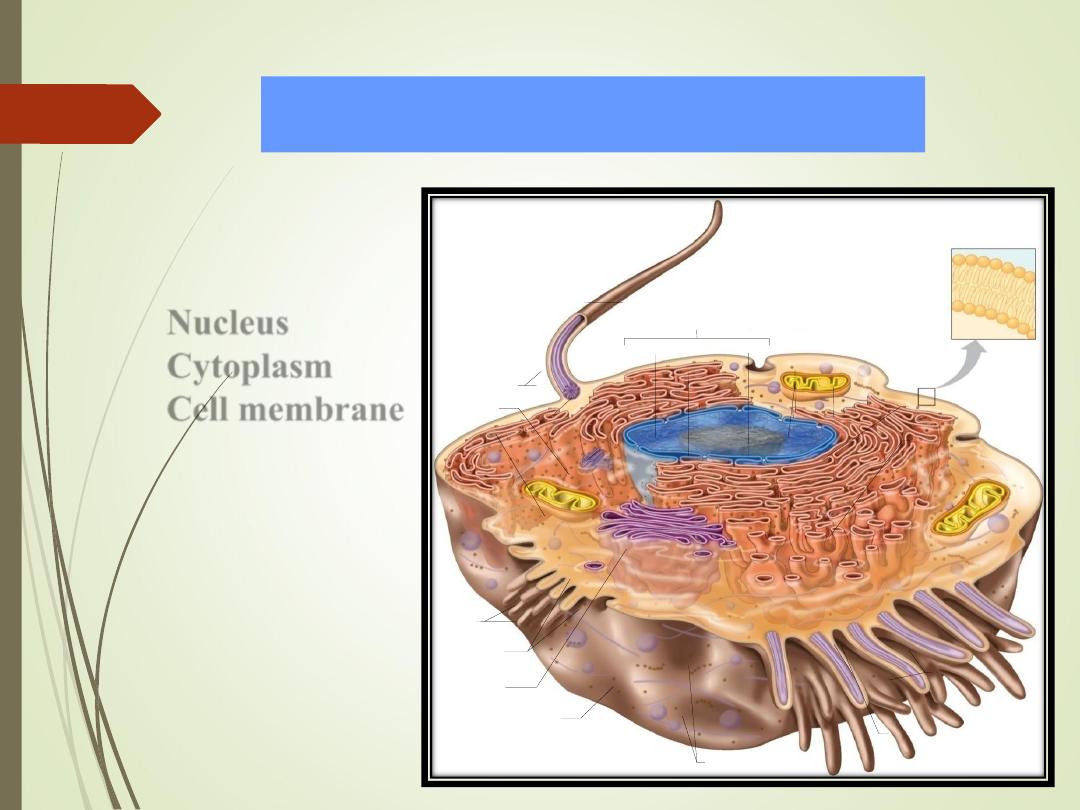
Typical cell has 3 major
parts include:
1)
Nucleus
2)
Cytoplasm
3)
Cell membrane
Microtubules
Flagellum
Nuclear envelope
Basal body
Chromatin
Ribosomes
Cell membrane
Mitochondrion
Cilia
Microtubules
Microtubule
Centrioles
Microvilli
L ysosomes
Nucleolus
Nucleus
Phospholipid bilayer
Smooth
Endoplasmic
reticulum
Rough
Endoplasmic
reticulum
Golgi
apparatus
Secretory
vesicles
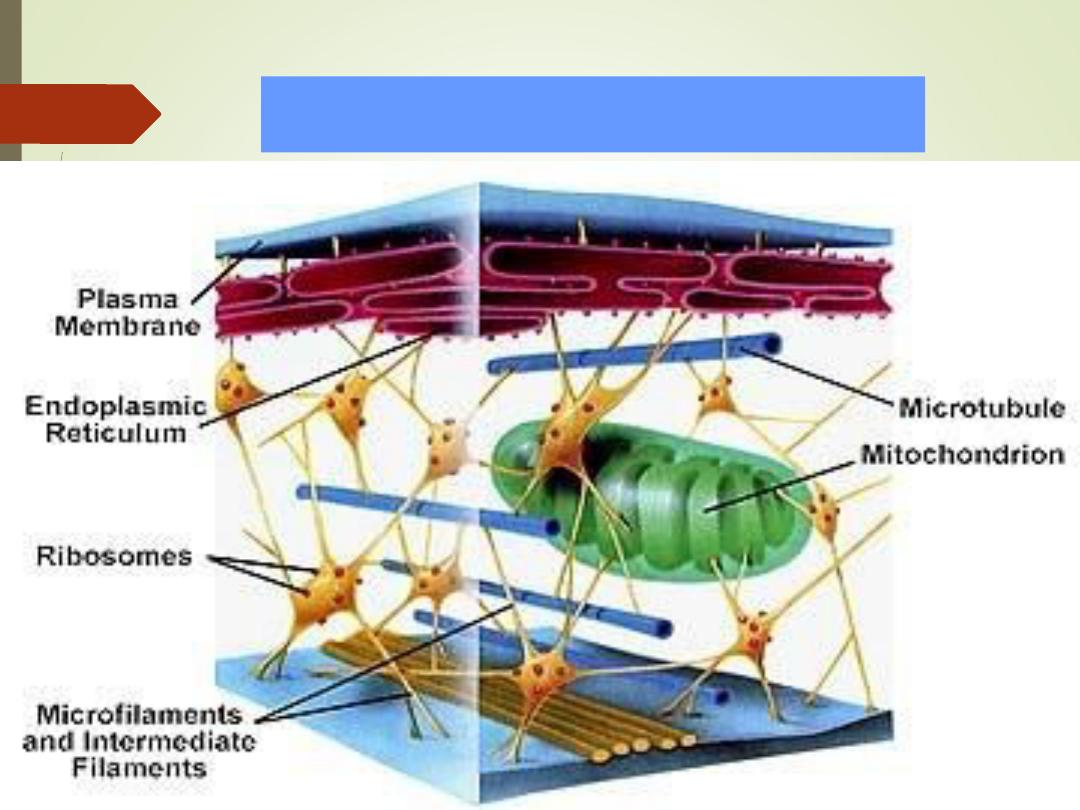
7
Cell structure and Functions

Cell/Plasma Membrane
8
•
Outer limit of the cell
•
Controls what moves in and out of the cell.
•
Selectively permeable
•
Phospholipid bilayer
•
Water-soluble
form surfaces (
hydrophilic
)
•
Water-insoluble
form interior (
hydrophobic
)
•
Permeable to lipid-soluble substances
•
Proteins:
•
Receptors
•
Pores, channels and carriers
•
Enzymes
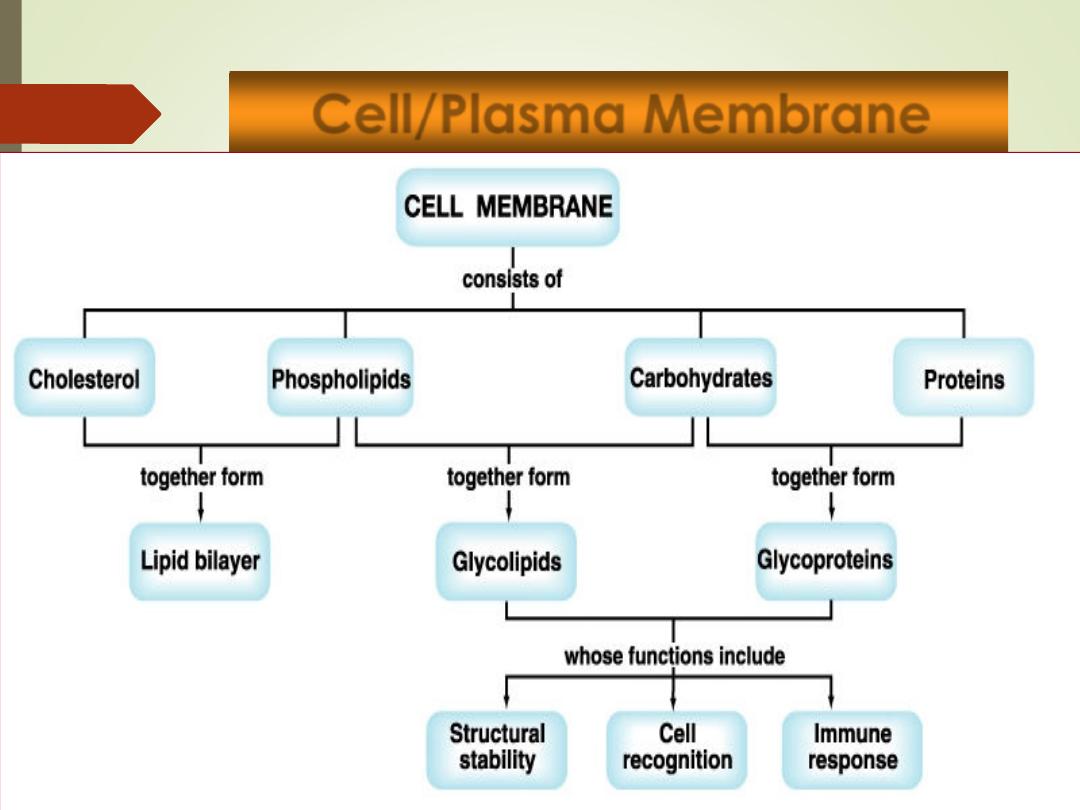
9
Cell/Plasma Membrane
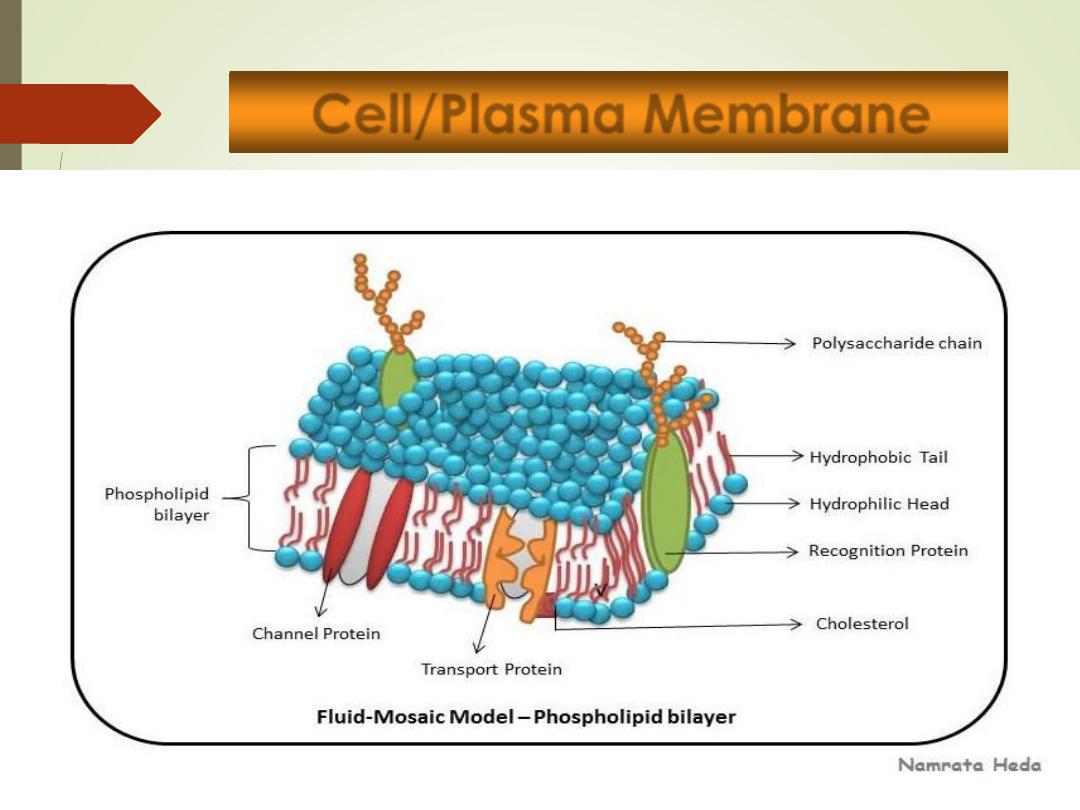
10
Cell/Plasma Membrane
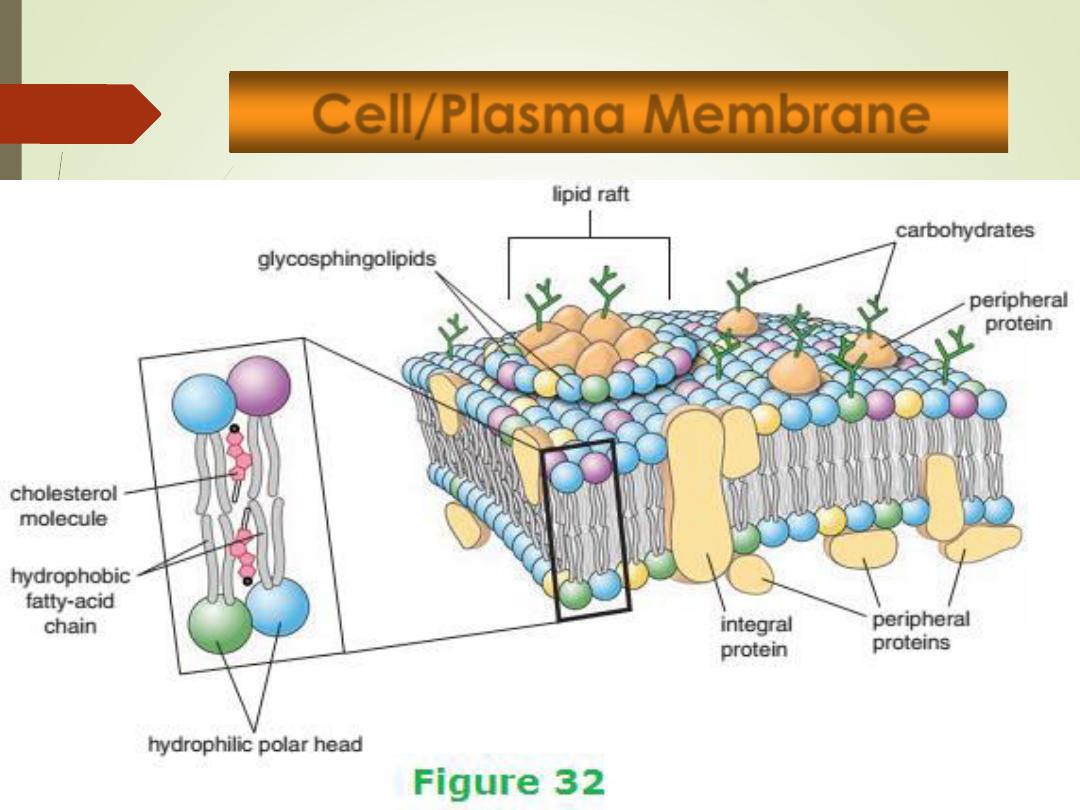
11
Cell/Plasma Membrane
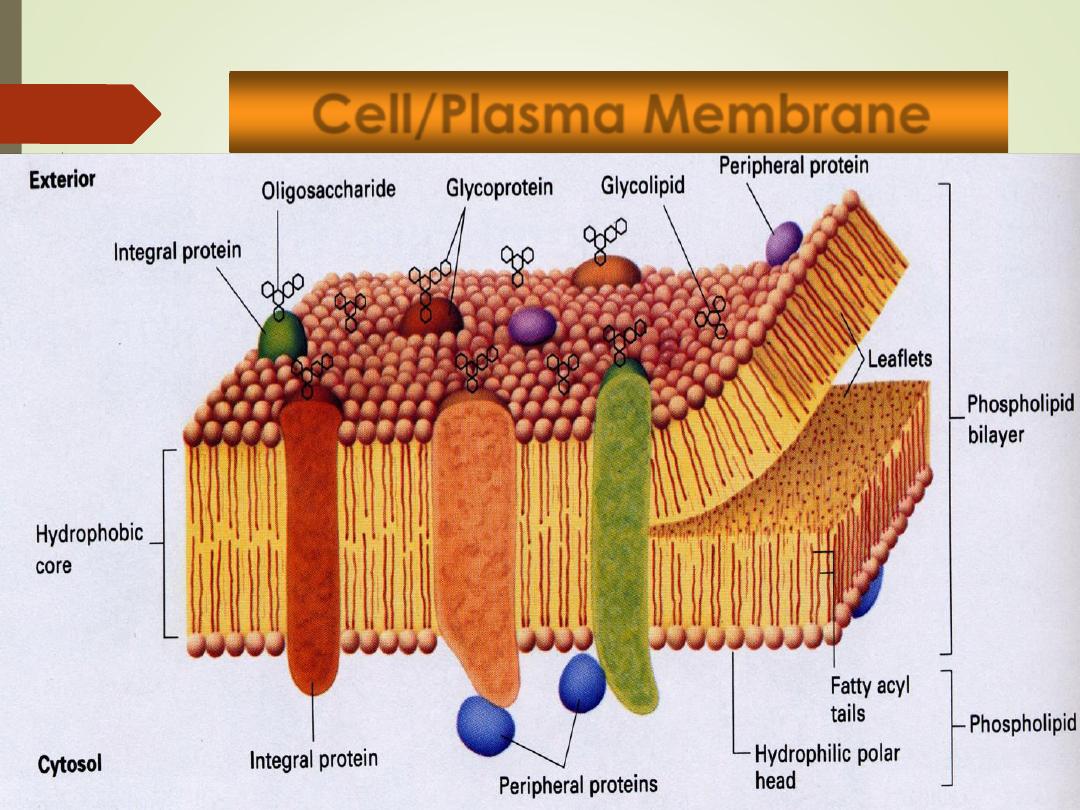
12
Cell/Plasma Membrane

Cytoplasm
13
•jelly-like fluid (
70% water
) that holds the cellular
organelles and occupies the space between the
nucleus and cell membrane.
• It contains abundant protein rods and tubules that
form a supportive framework (cytoskeleton)
•
Organelles
= solids
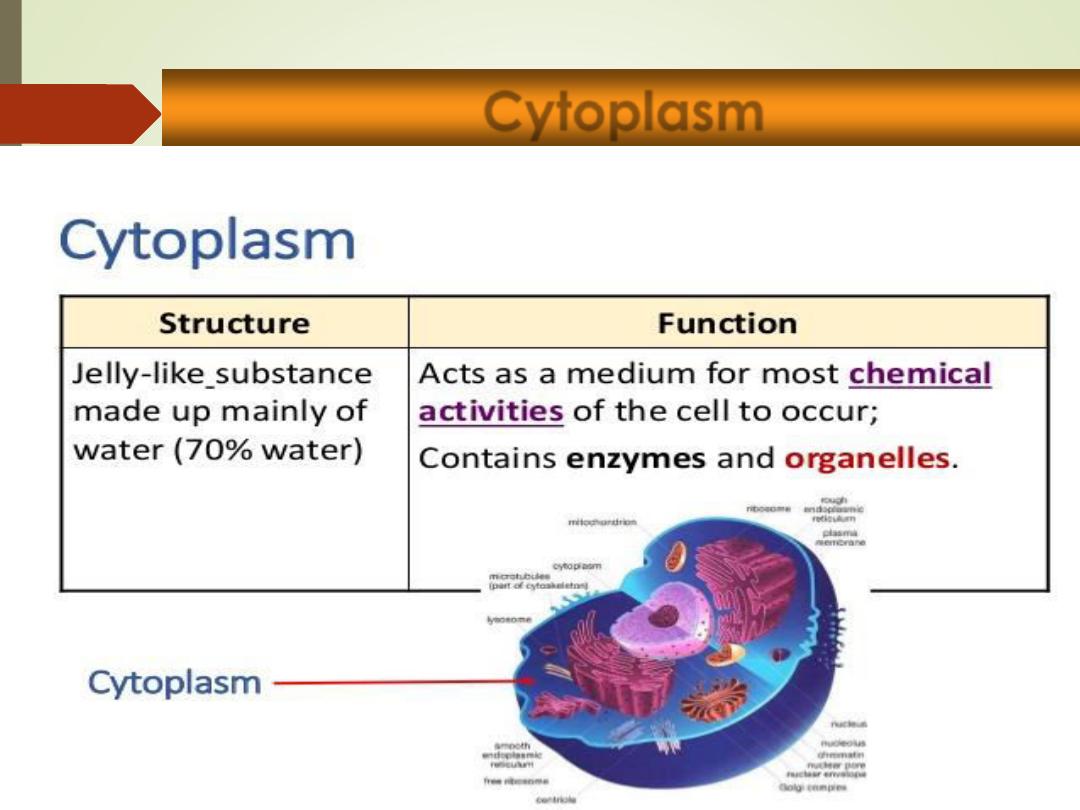
Cytoplasm
14

Organelles
15
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
•
A network of interconnected parallel membrane,
canals, vesicles and sacs, that is continuous with the
nuclear membrane;
•
It is transport system.
•
Rough ER (RER)
•
Studded with ribosomes
•
Function
–
Protein Synthesis
•
Smooth ER (SER)
•
lacks ribosomes
•
Function =
lipid & cholesterol synthesis
•
Stores calcium ions
•
Abundant in liver cells (hepatocytes)
•
Break down of drugs
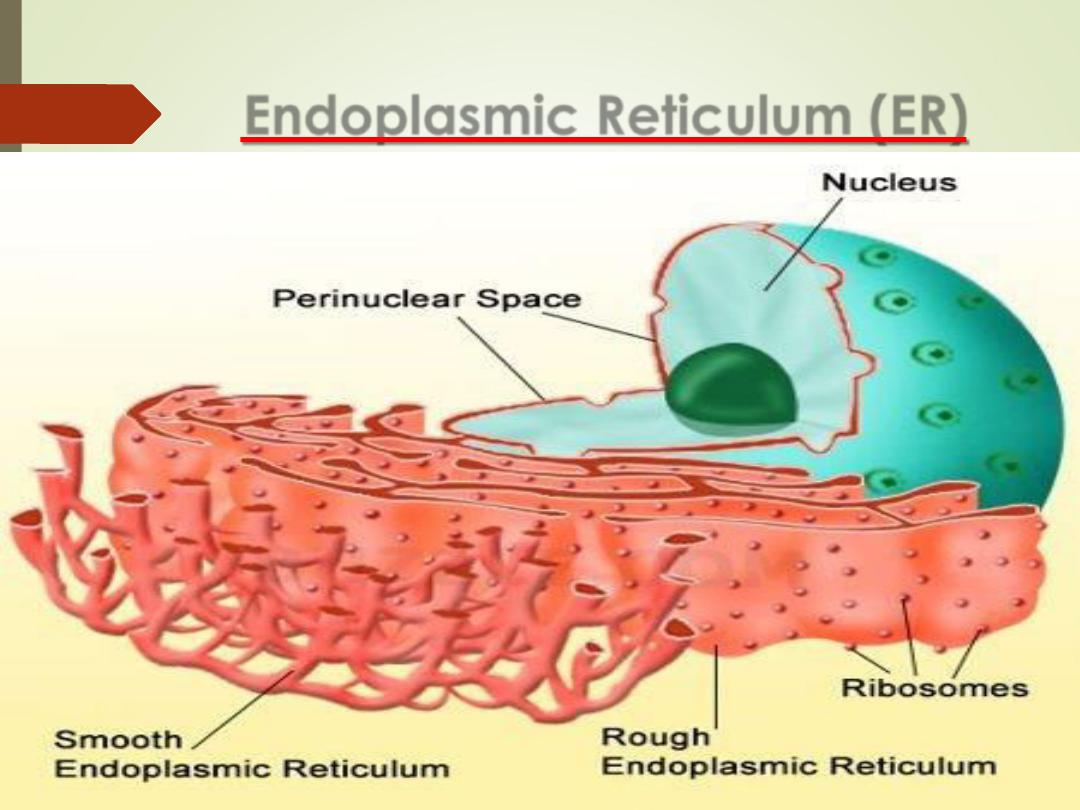
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
16
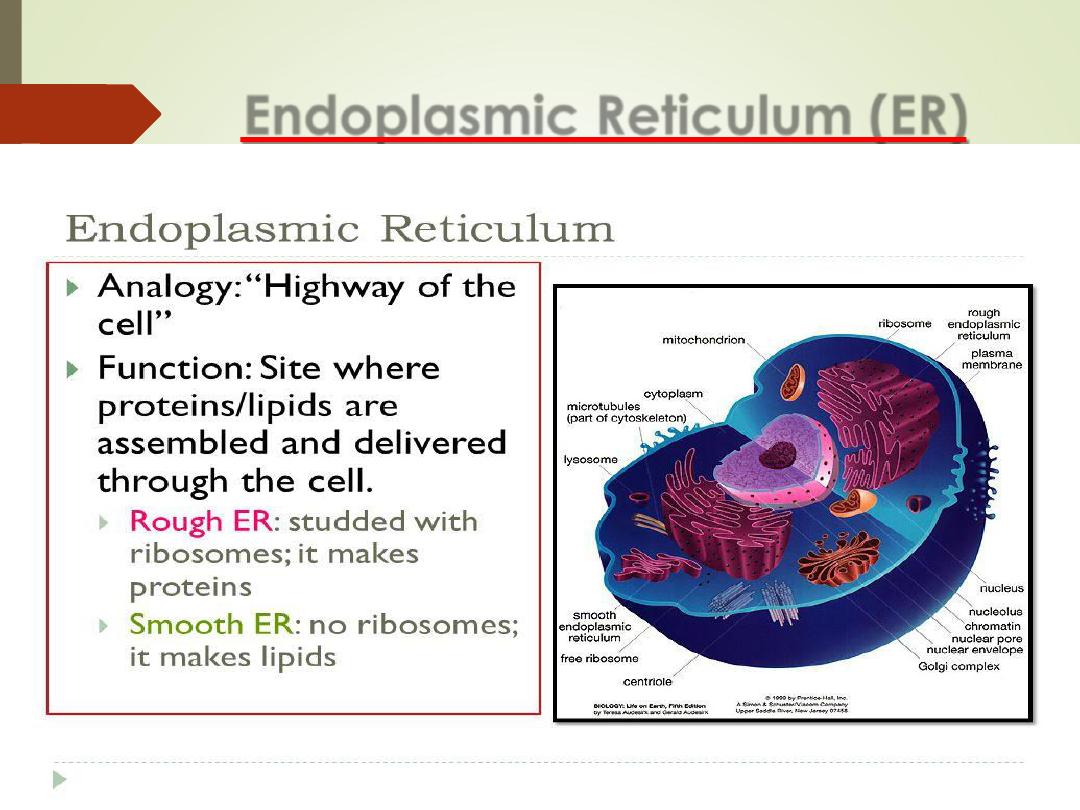
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
17

Organelles
18
Ribosomes:
1. Free
floating
small
granules
dispersed
throughout the cytoplasm and on the membranes
of
some
endoplasmic
reticulum
(rough
endoplasmic reticulum)
2. Composed of RNA and protein
3. Function =
protein synthesis
.
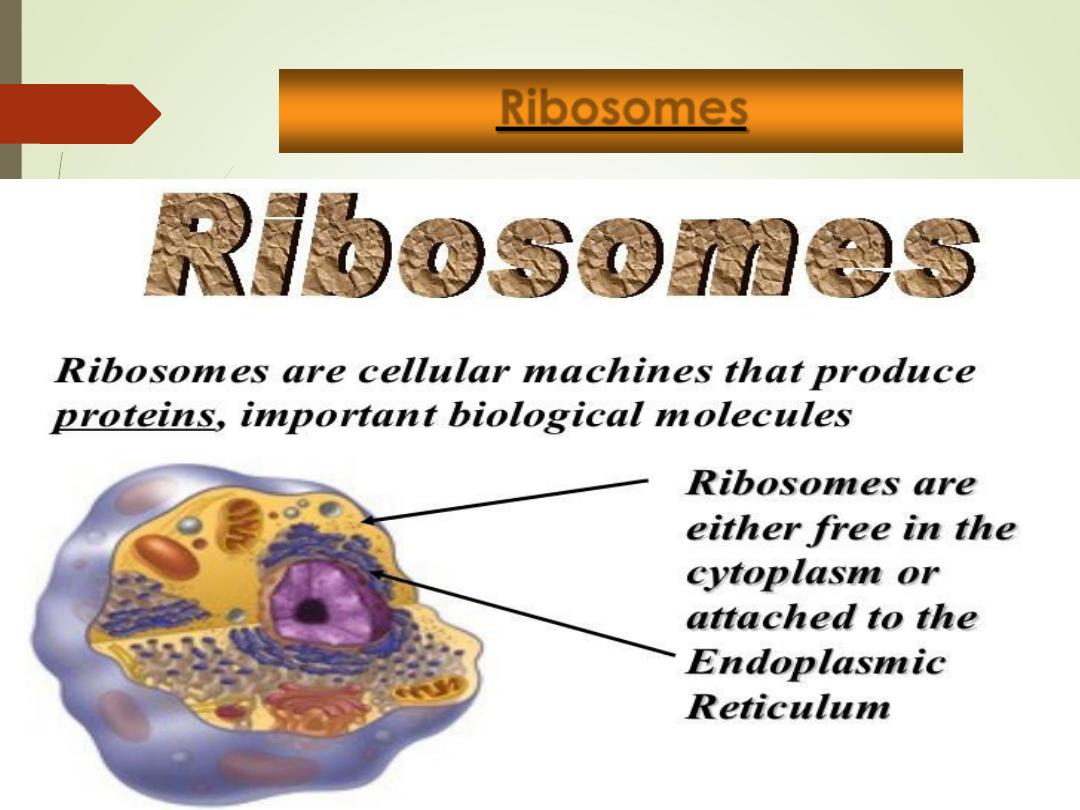
Ribosomes
19
Ribosomes:
1. Free
floating
small
granules
dispersed
throughout the cytoplasm and on the membranes
of
some
endoplasmic
reticulum
(rough
endoplasmic reticulum)
2. Composed of RNA and protein
3. Function =
protein synthesis
.
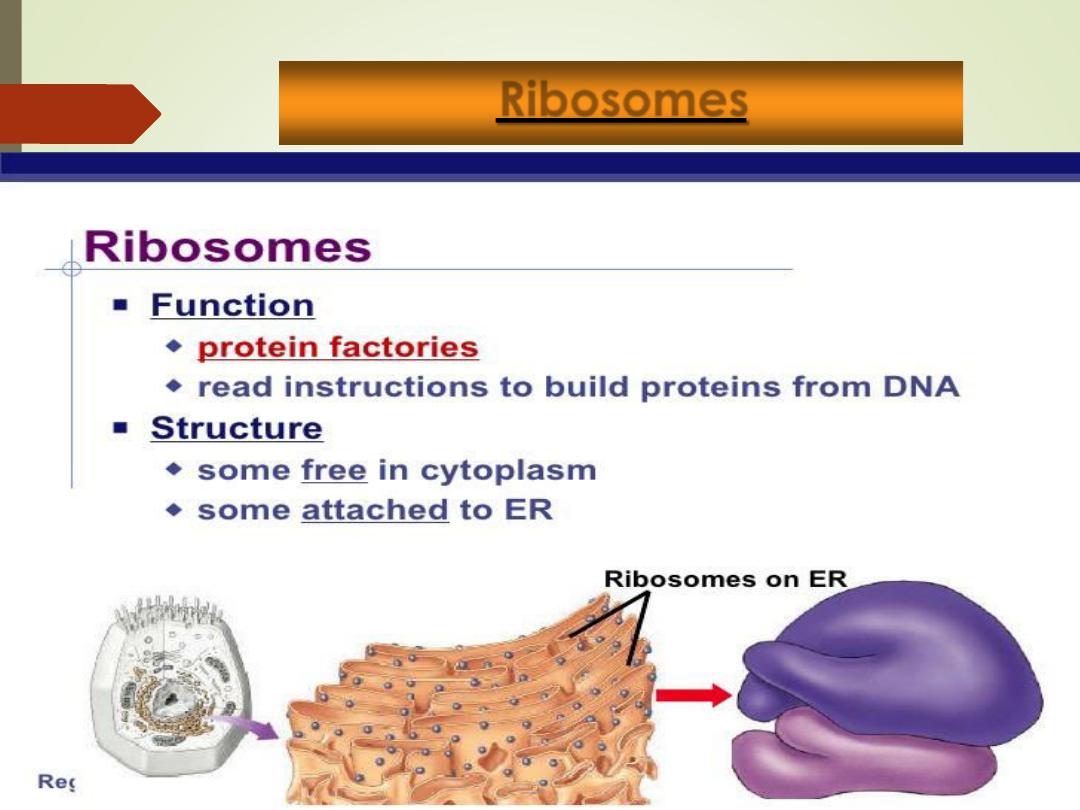
Ribosomes
20
Ribosomes:
1. Free
floating
small
granules
dispersed
throughout the cytoplasm and on the membranes
of
some
endoplasmic
reticulum
(rough
endoplasmic reticulum)
2. Composed of RNA and protein
3. Function =
protein synthesis
.
21
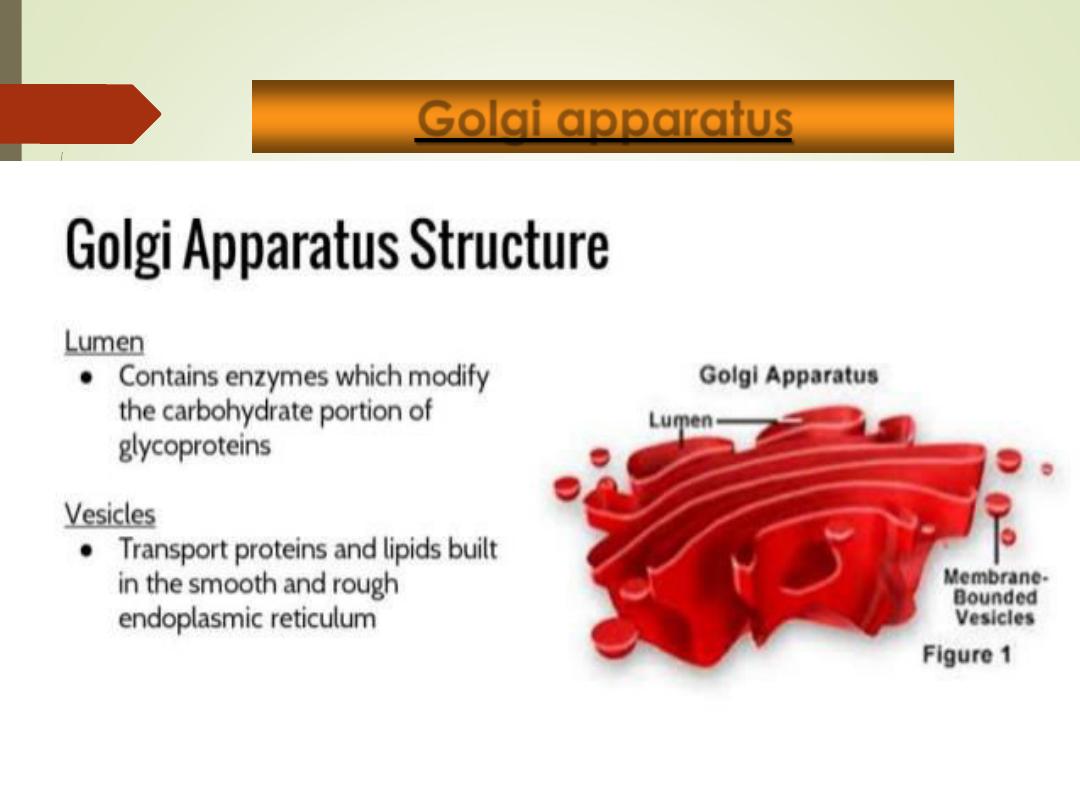
Golgi apparatus
•
Stack of flattened, membranous sacs (cisternae),
arranged in stacks.
•
Associated with many vesicles (membrane bound sacs
containing proteins)
•
Function =
modification, packaging, and transport of
proteins.
Organelles
22
Golgi apparatus

23
Golgi apparatus
Organelles
24
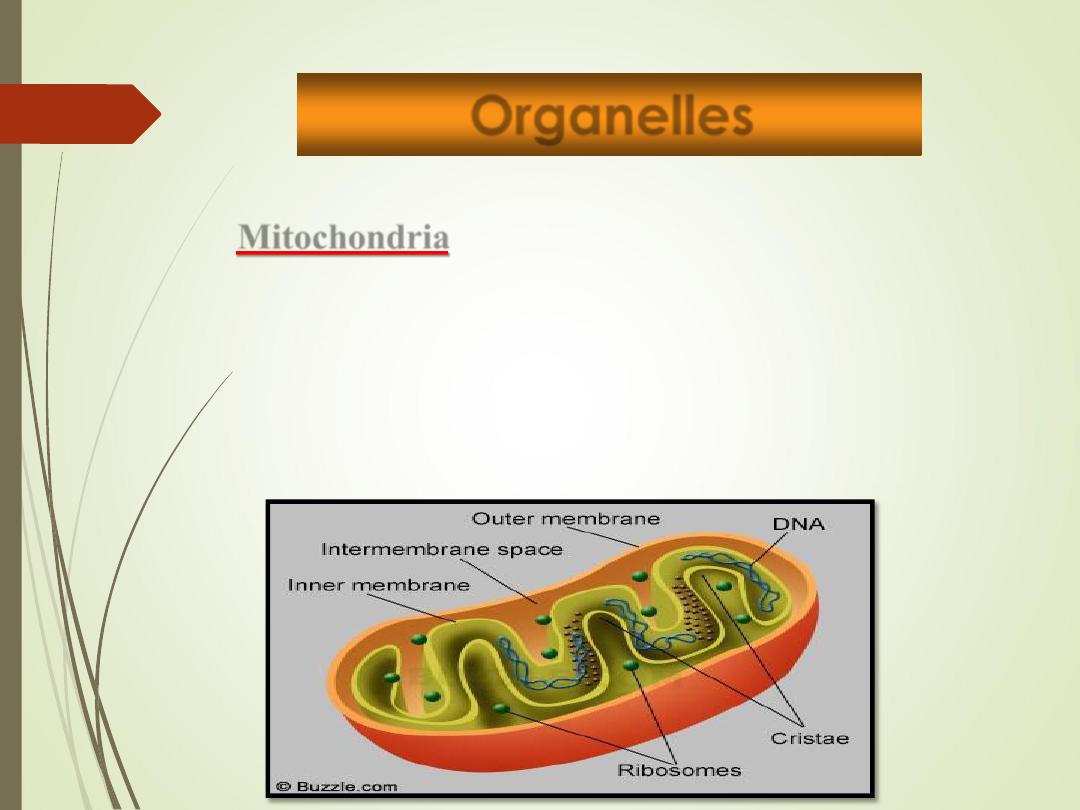
Mitochondria
•
Kidney-shaped organelle whose inner membrane is
folded into shelf-like partitions called
cristae
•
“
Powerhouse
” of the cell = site of cellular
respiration, where energy is released from glucose.
•
Contains their own
DNA & RNA
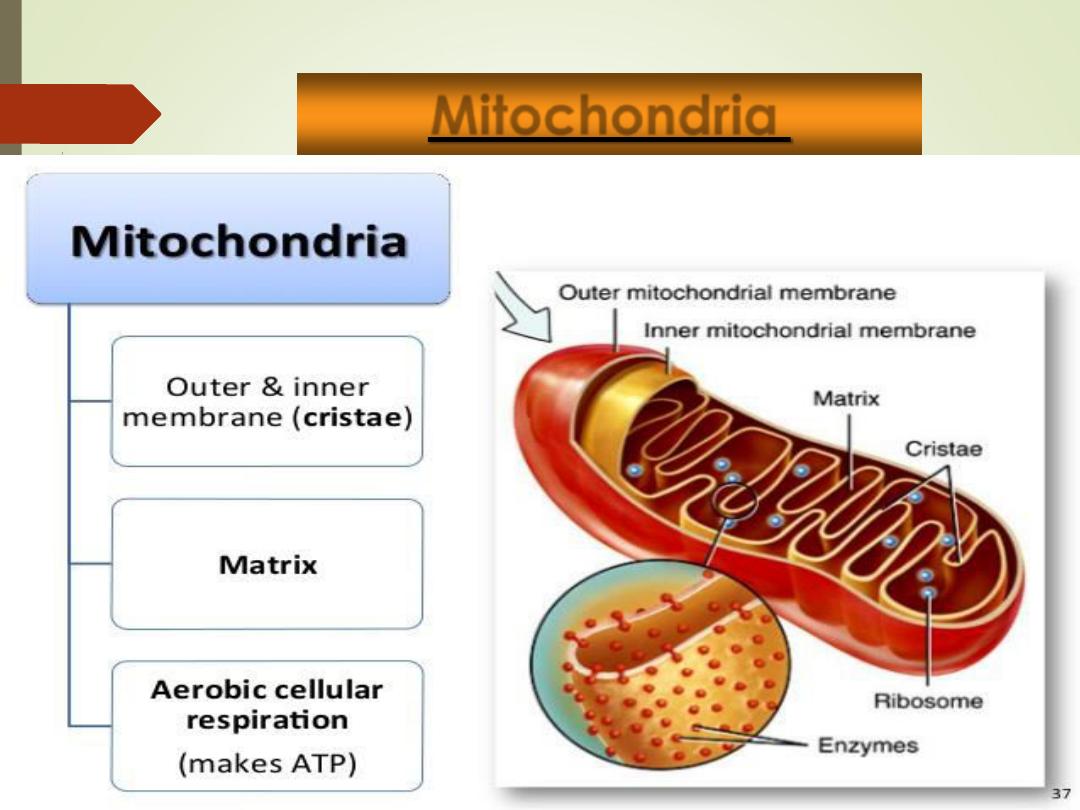
Mitochondria
25

Organelles
Lysosomes
•
Spherical membranous sacs containing digestive
enzymes (
acid hydrolases
).
•
“
Suicide sacs
” which destroy anything the cell
no longer wants or needs.
Function
:
1)
Digest ingested bacteria, viruses, and toxins
2)
Degrade nonfunctional organelles
3)
Break down and release glycogen
4)
Break down bone to release Ca
2+
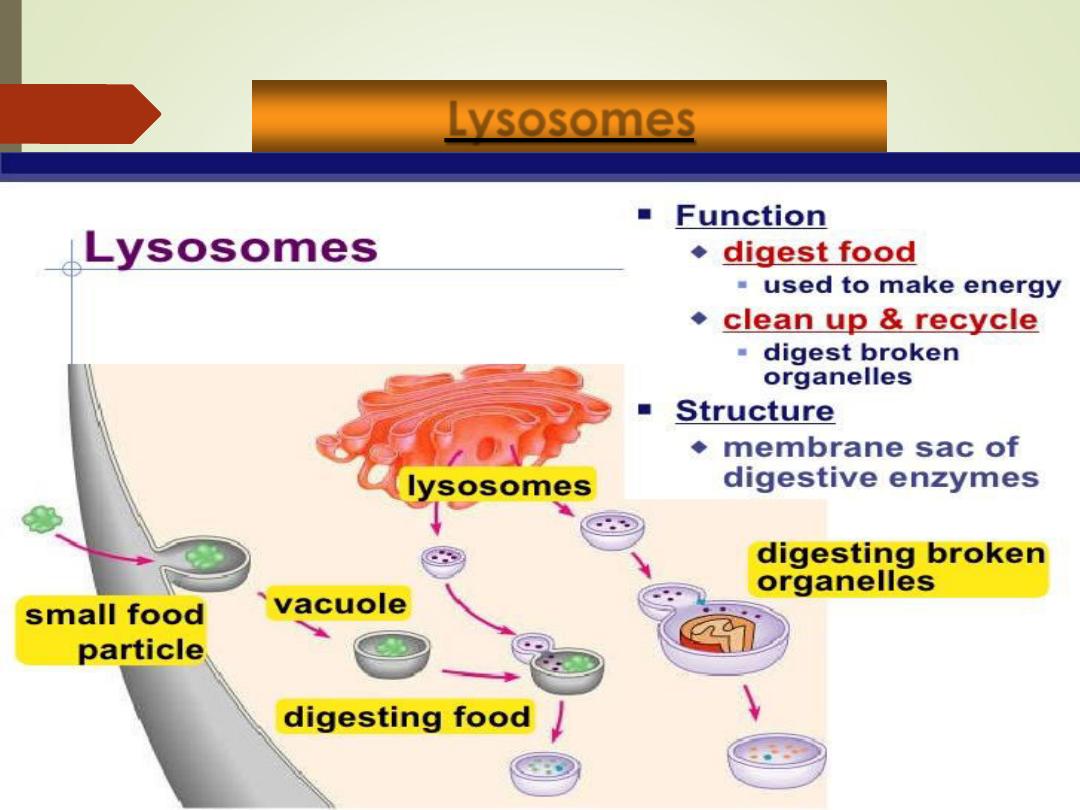
Lysosomes

Organelles
28
Peroxisomes
•
Membranous sacs containing oxidase enzymes.
•
Function
:
1)
detoxification of harmful or toxic substances
(i.e. alcohol, oxygen free radicals)
2)
Breaks down organic molecules.
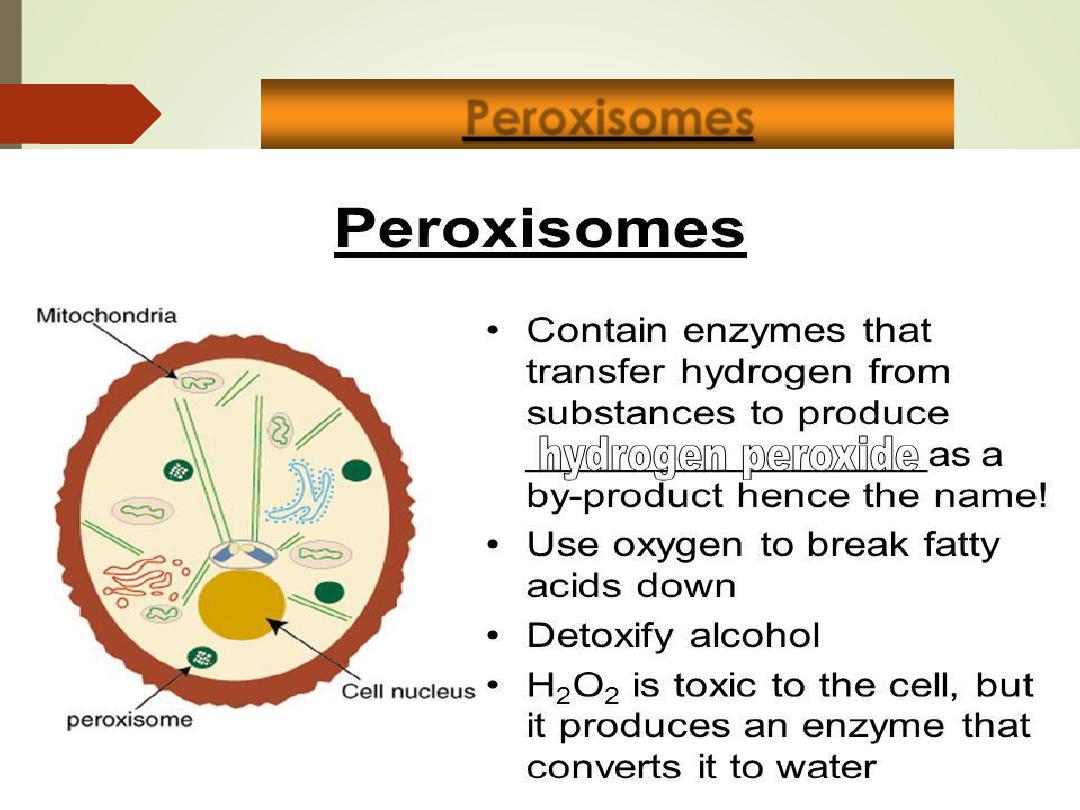
Peroxisomes
29
Organelles
30
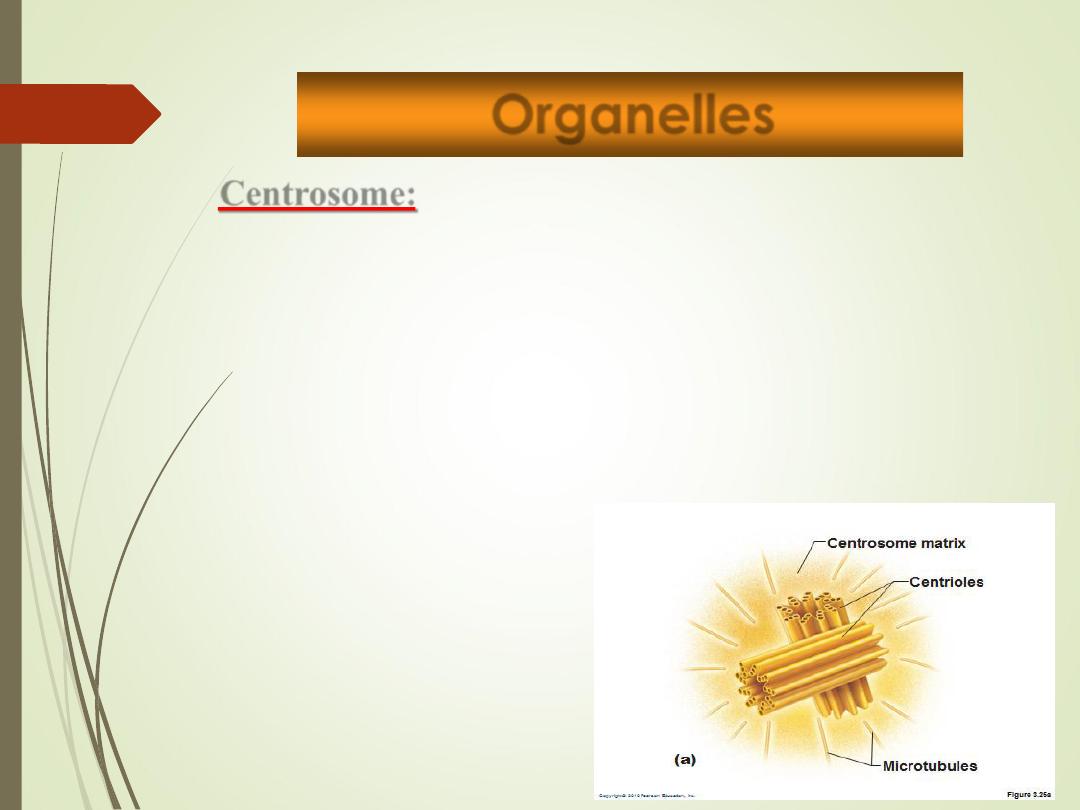
Centrosome:
•
Pair of microtubules located near the
nucleus
•
Two rod-like centrioles
•
Used to produce cilia and flagella
•
“Cell center” near nucleus
•
Generates microtubules.
•
organizes mitotic spindle

Centrosome
31

Organelles
32
Cilia
Short hair-like cellular projection
Propel substances through passage ways
and on cell surface.
Located in the lining of trachea and
fallopian tube.
Flagella
Long tail-like projection
Only one per cell in humans
Provides motility to sperm
Aids in cell locomotion
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Organelles
33
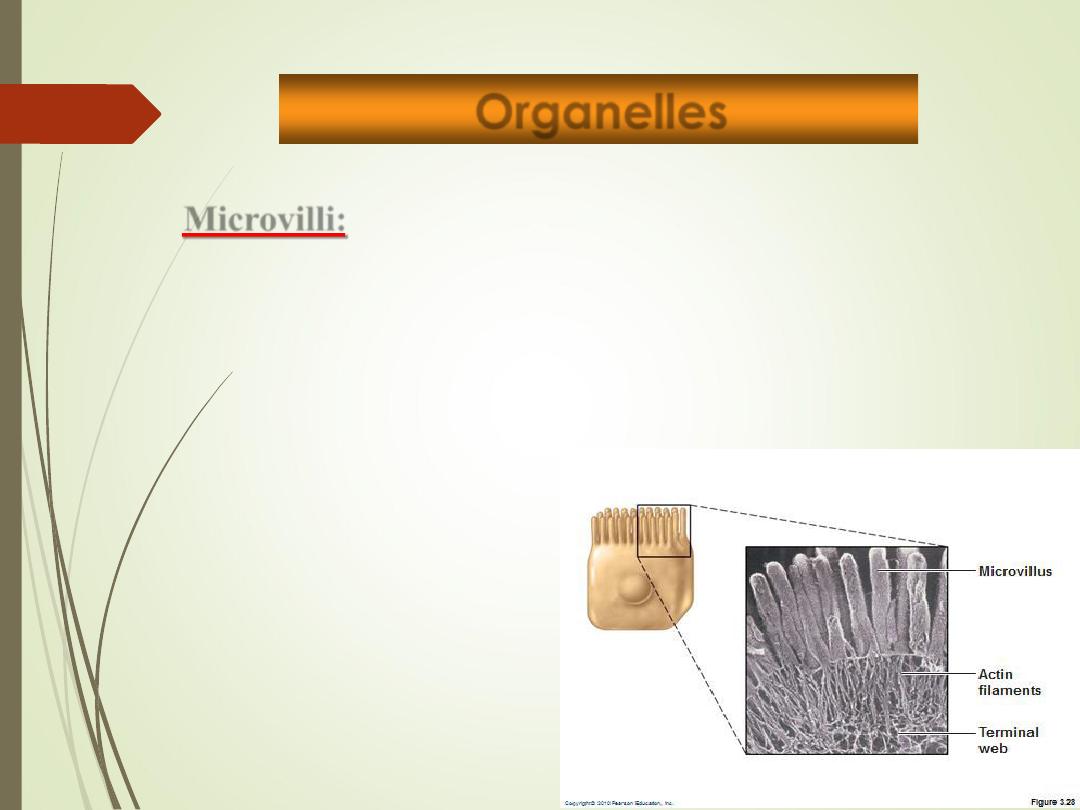
Microvilli:
Fingerlike extensions of plasma membrane/external surface
of the cell.
Function
:
increase surface area for absorption
Organelles
34
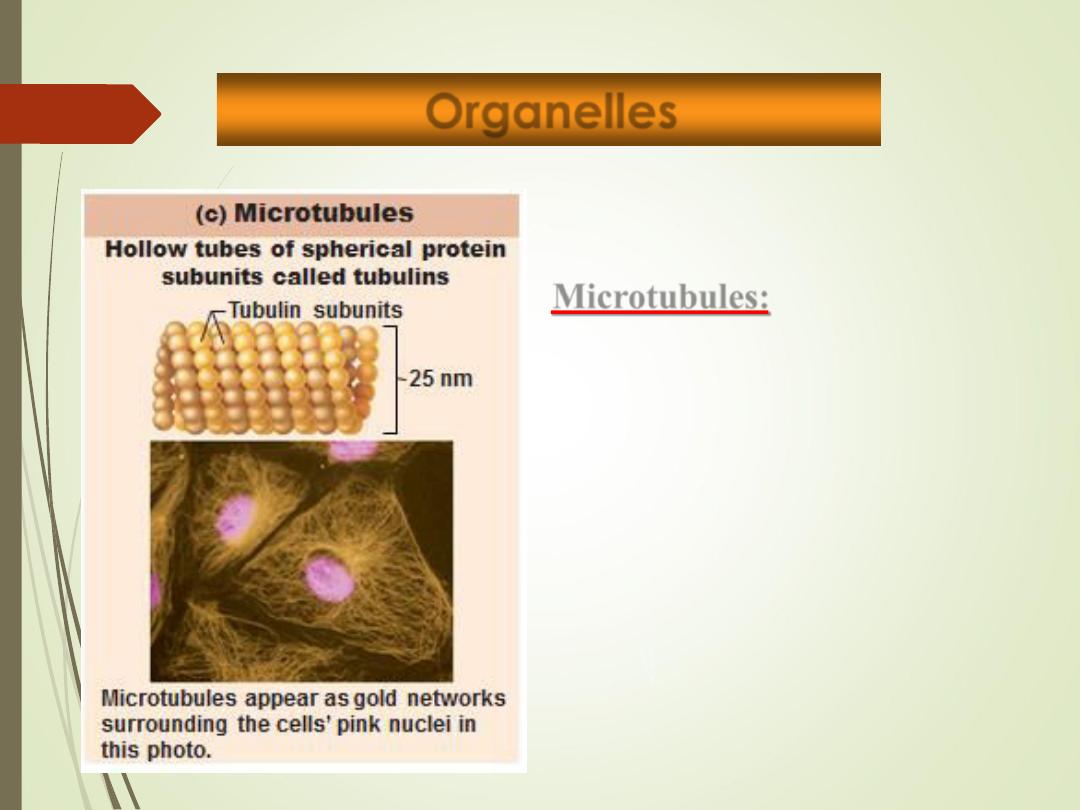
Microtubules:
• Dynamic hollow tubes
• Most radiate from centrosome
• Determine overall shape of cell and
distribution of organelles
Organelles
35
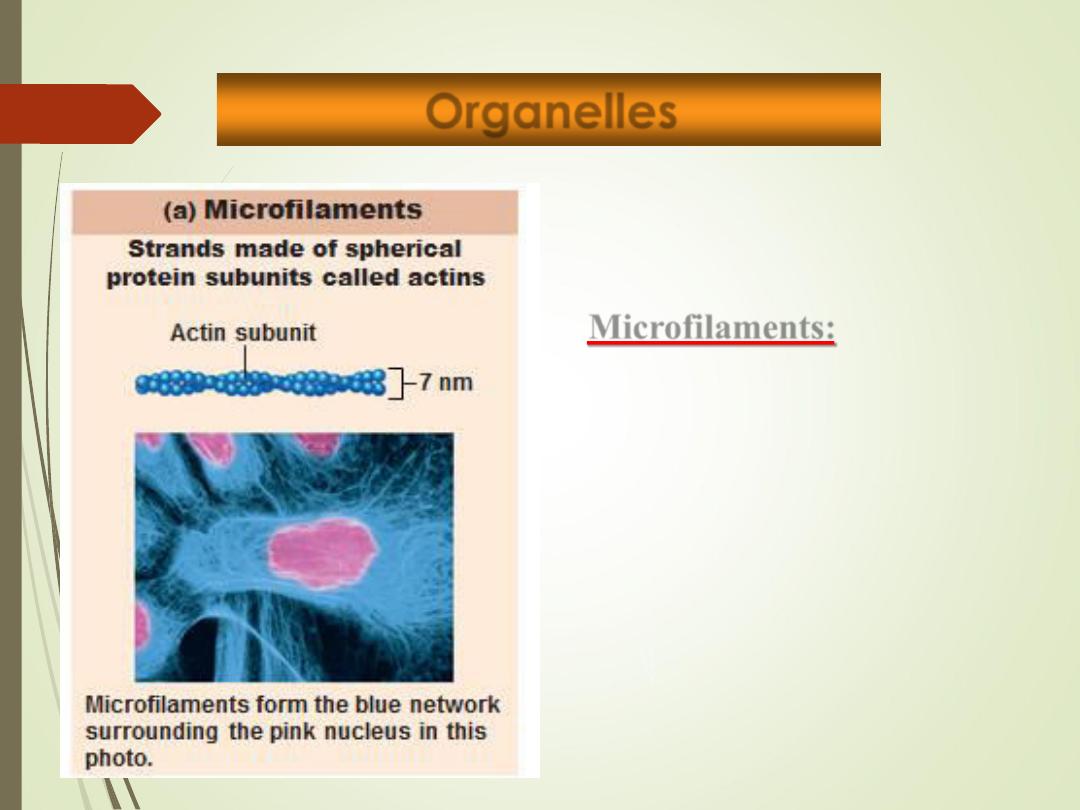
Microfilaments:
• Dynamic actin strands
attached to cytoplasmic
side of plasma membrane.
• Involved in cell motility,
change in shape,
endocytosis and exocytosis
Organelles
36
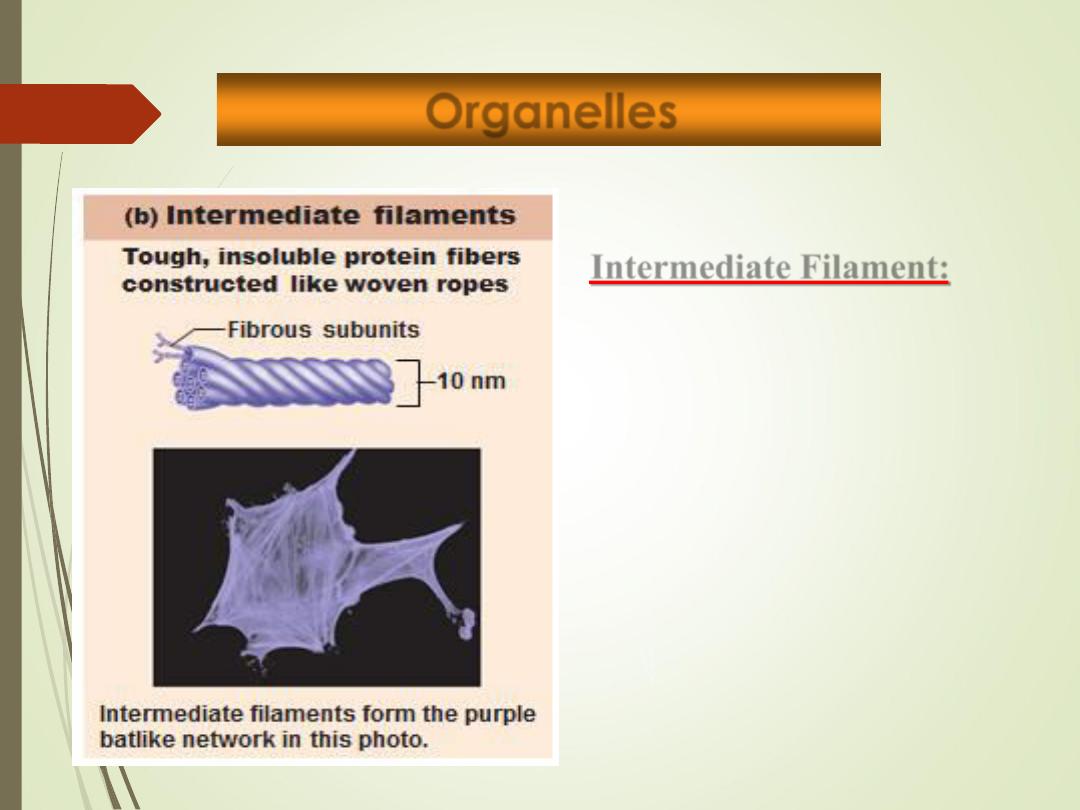
Intermediate Filament:
• Tough, insoluble protein fibers.
• Resist pulling forces on the cell
and attach to desmosomes.

Cell Nucleus
37
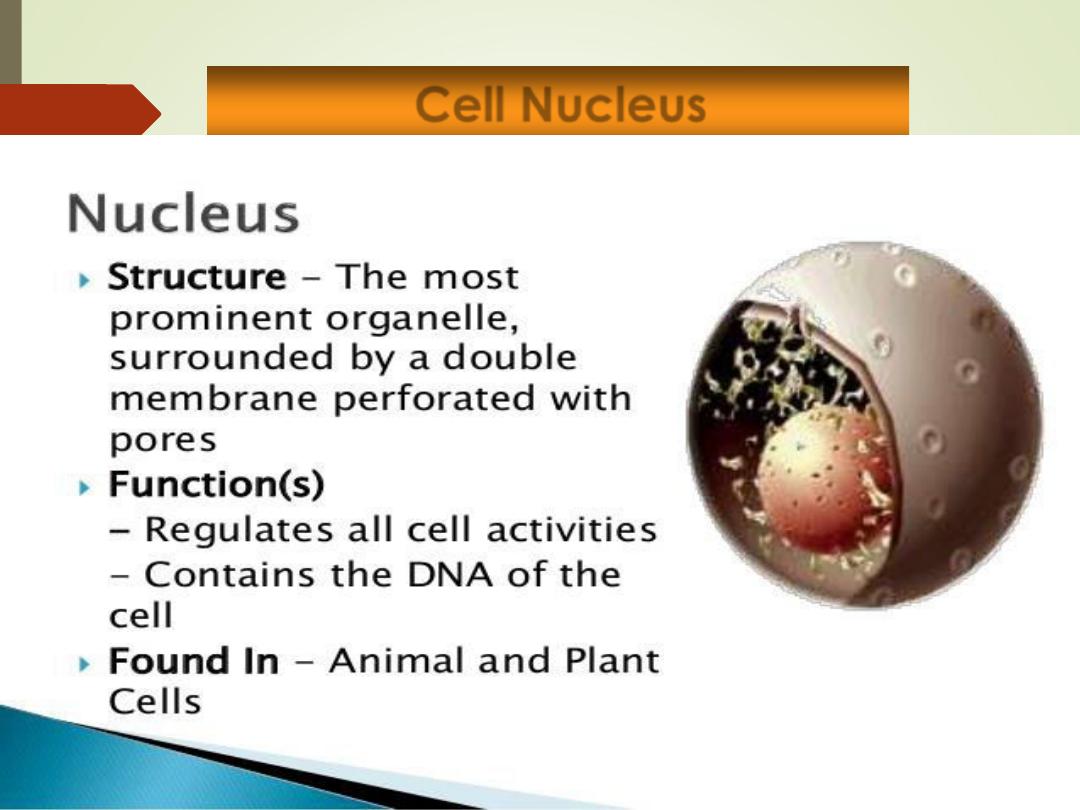
•
it is the control center of the cell.
•
The largest organelle of the cell.
•
Genetic library with blueprints for nearly all cellular proteins.
•
Responds to signals and dictates kinds and amounts of
proteins to be synthesized.
•
Most cells are uninucleate
.
•
Red blood cells are
anucleate
.
•
Skeletal muscle cells, bone destruction cells, and some liver
cells are
multinucleate
•
Contains 3 different regions:
•
Nuclear envelope
•
Nucleolus
•
Chromatin
Cell Nucleus
38
Cell Nucleus
39
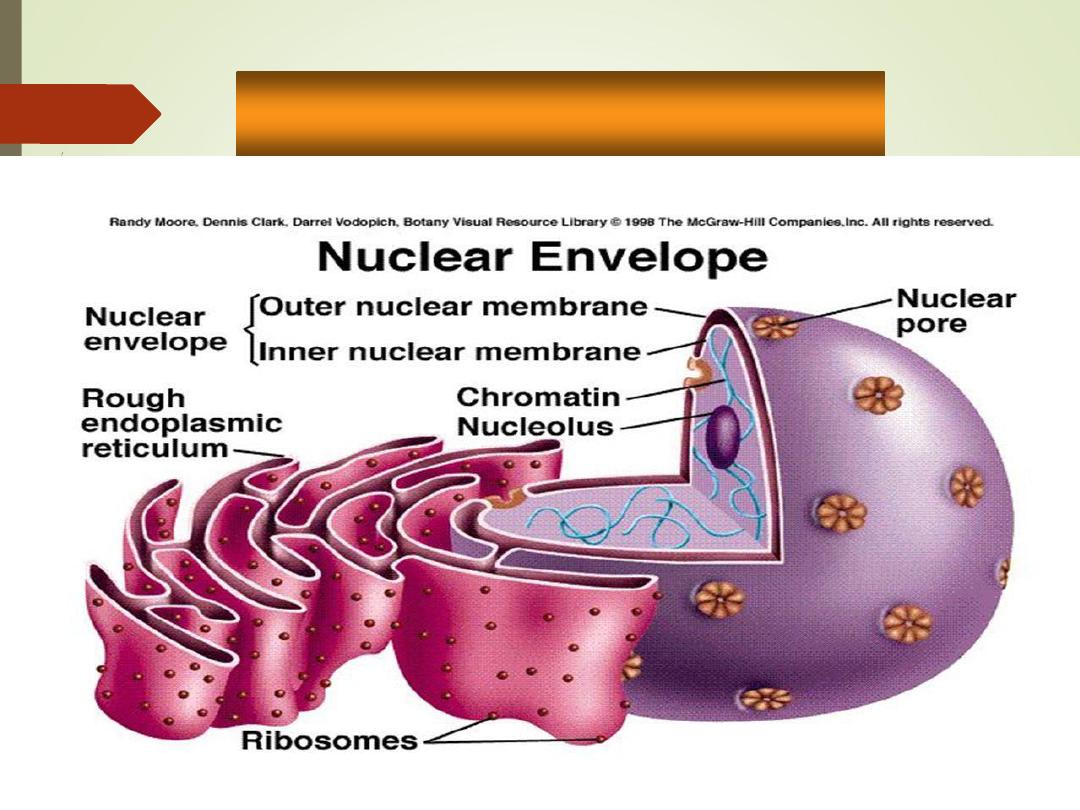
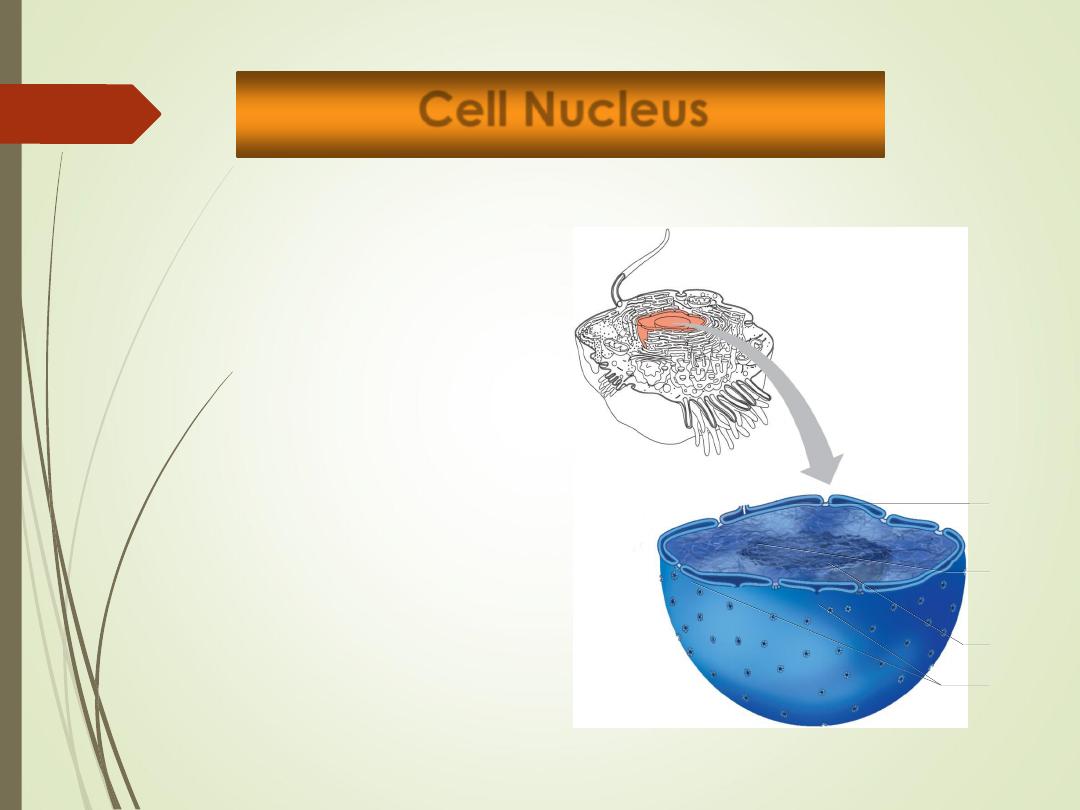
•
Nuclear envelope:
•
Porous double membrane
•
Separates nucleoplasm from
cytoplasm
•
Outer layer is continuous with
rough ER and bears ribosomes.
•
Inner lining (nuclear lamina)
maintains shape of nucleus.
•
Pore complex regulates transport
of large molecules into and out of
nucleus
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Chromatin
Nuclear
pores
Nuclear
envelope
•
Nuclear envelope
40
•
Nuclear envelope:
•
Porous double membrane
•
Separates nucleoplasm from
cytoplasm
•
Outer layer is continuous with
rough ER and bears ribosomes.
•
Inner lining (nuclear lamina)
maintains shape of nucleus.
•
Pore complex regulates transport
of large molecules into and out of
nucleus
Nucleus
Nucleolus
hromatin
Nuclear
pores
Nuclear
envelope
Cell Nucleus
41
Chromatin:
•
Threadlike strands of DNA (30%),
histone proteins (60%), and RNA
(10%)
• Arranged in fundamental units called
nucleosomes
• Condense into barlike bodies called
chromosomes when the cell starts to
divide
.
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Chromatin
Nuclear
pores
Nuclear
envelope
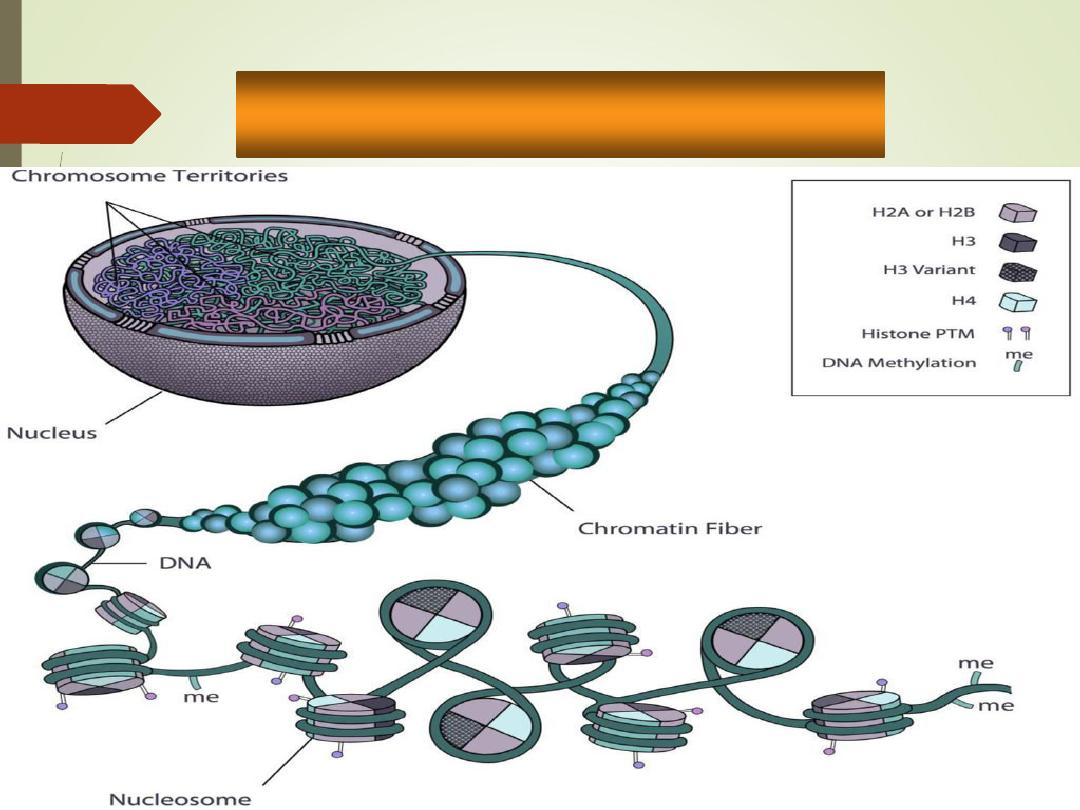
Chromatin
42
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Chromatin
Nuclear
pores
Nuclear
envelope
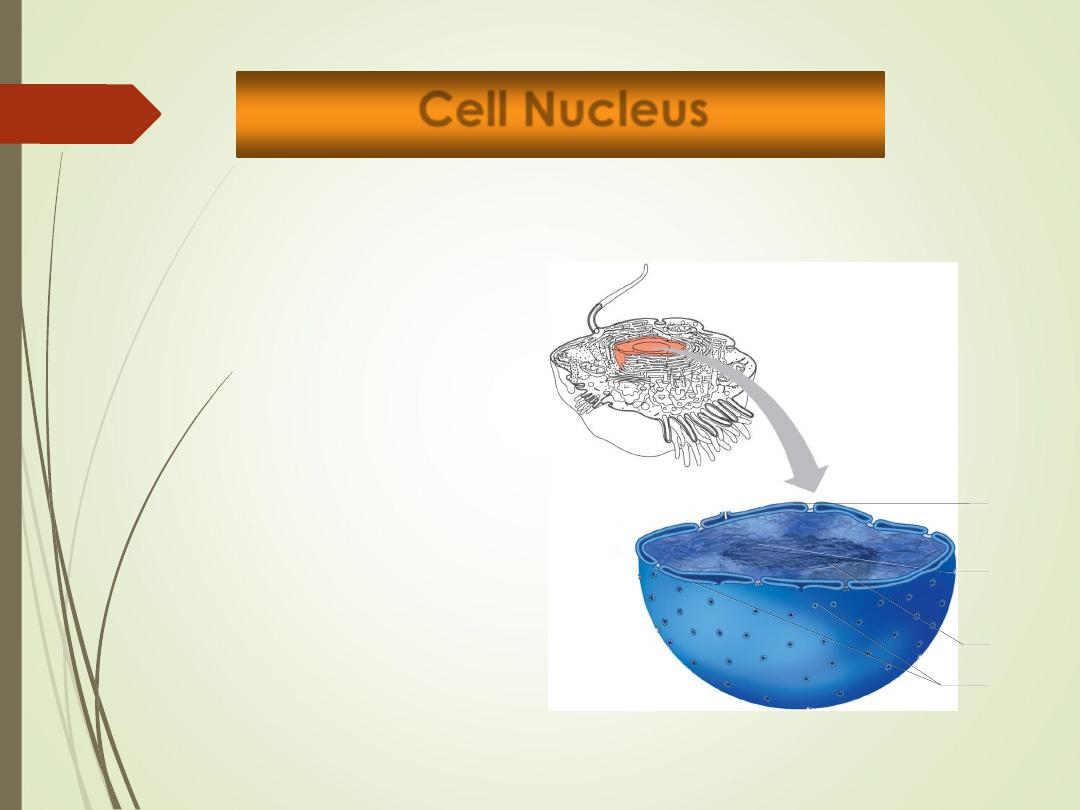
Cell Nucleus
43
Nucleolus
•
Dark-staining dense
spherical bodies within the
nucleus
•
Collection of RNA and
proteins
•
Function
:synthesis of
ribosomes.
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Chromatin
Nuclear
pores
Nuclear
envelope
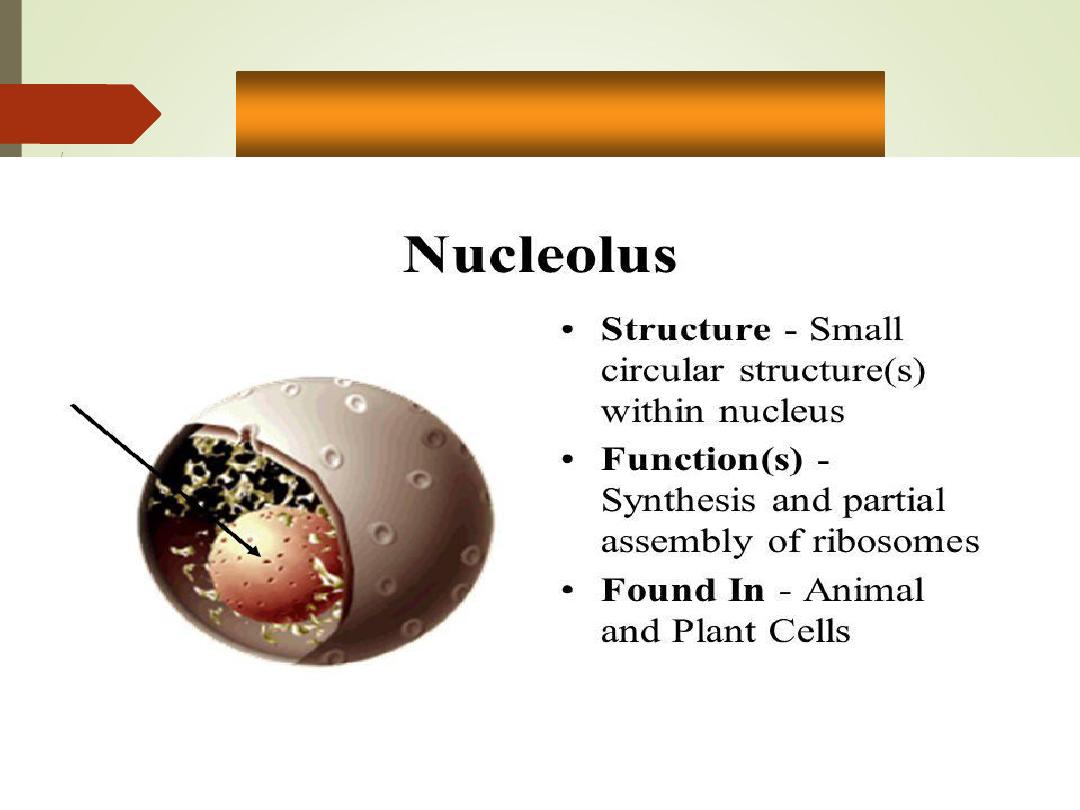
Nucleolus
44
Nucleolus
•
Dark-staining dense
spherical bodies within the
nucleus
•
Collection of RNA and
proteins
•
Function
:synthesis of
ribosomes.
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Chromatin
Nuclear
pores
Nuclear
envelope
Nucleolus
45
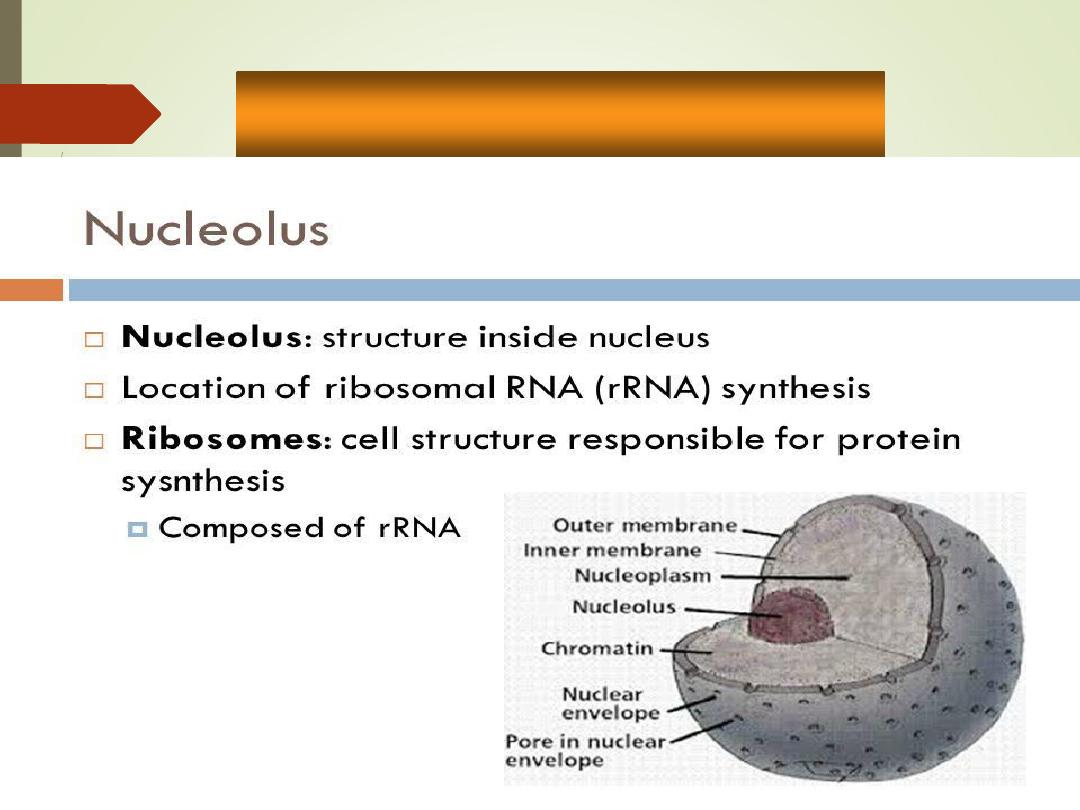
Nucleolus
•
Dark-staining dense
spherical bodies within the
nucleus
•
Collection of RNA and
proteins
•
Function
:synthesis of
ribosomes.
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Chromatin
Nuclear
pores
Nuclear
envelope
