Sterilization
Sterilization: is a process whereby all forms of microorganisms, including bacterial spores , vegetative cells , viruses are killed. Any material that has been subjected to this process is said to be sterile. The material is either sterile or not.Disinfection: is a process whereby pathogenic organisms, but not necessarily all microorganisms or spores, are destroyed
Heat
Moist heatAutoclave
Sterilization
Boiling water, Hot water, Pasteurization
Disinfection
Dry heat
Incineration
Sterilization
Dry oven
Sterilization
The mechanism of action of moist heat Coagulation and denaturation of proteins that cause cell death. moist heat in the form of saturated steam under 1 atmosphere of pressure causes irreversible denaturation of enzymes and structural proteins.
Moist heat: is used to sterilize biohazardous trash and heat-stable objects.
Methods of Moist heat
1-Autoclave (steam under pressure):
the most commonly used method of moist heat.
Autoclave Sterilization
Uses : heat-resistant materials such as gloves, clothes, surgical instruments, liquids, paper, some types of media.Instruments are usually autoclaved for 15 minutes a 121° C.
Infectious medical waste, on the other hand, is often sterilized at 132° C for 30 to 60 minutes to allow penetration of the steam throughout the waste and the displacement of air trapped inside the autoclave bag.
Autoclave Sterilization
Advantages: This method can kill all kind of microorganisms including vegetative forms and spore forming m.o. like Clostridium spp., Bacillus spp. and viruses.Disadvantage: cannot used to sterilize heat sensitive media, heat sensitive plastics and substance that repel moisture like waxes, oils, powders. Care is needed during this process in addition to experience and skill. Required special instrument for the sterilization.
Methods of Moist heat
2.Nonpressurized Steam: Intermittent sterilization on 3 days intervals passing a steam of hot air on the material for 30-60 min this cycle will repeated for 3 days.Uses: Substance that can't withstand the high temperature of the autoclave.
Advantages: only used for sensitive culture media, i.e. Those containing sera or eggs.
Disadvantages: this method can't kill the spores, long time is required for complete sterilization so it is not practical.
Methods of Moist heat
Boiling: A simple boiling water chamber is used.Uses: Used mostly for drinking water, food preparation and bedding.
Advantages: It is a relied process for disinfection not for sterilization because it will kill most m.o but not the spore-forming bacteria.
Disadvantage: can't kill heat resistant bacteria, sporforming microorganisms, the materials easily recontaminated when removed from the water.
Methods of Moist heat
Pasteurization: is a technique in which heat is applied to liquid to kill potential agent of infection and spoilage, while at the same time retaining the liquid's flavor and food value.
Uses: to prevent transmission of milk – borne bacteria from transmission from caw to human like Brucella .milk after regular Pasteurization is not sterile completely.
Advantages: It longing the storage time of milk, use to stop fermentation by some winners.
Disadvantage: not kill sporforming bacteria, or some heat resistant viruses.
Dry heat
Dry heat: it is not commonly used as moist heat; the temperature used mostly is higher than those used for moist sterilization.Mechanism of action: Kill by dehydration that cause irreversible denaturation of an essential enzymes.
1- Incineration: most commonly used to sterilize the inoculating loop and needles using Bunsen burner in microbiology labs.
Uses: in hospital and research labs for complete destruction and disposal of infectious materials such as syringes ---etc.
Advantage: help to get rid of large amount of contaminated materials at once. Fast and effective but also limited to metals and heat resistant glass materials.
Disadvantage: Toxic air emissions and the presence of heavy metals in ash have limited the use of incineration, this method represents hazards to operator (open flame) and to the environment (contaminants on needle or loop often spatter when placed in flame).
• There Are Two Main Kind Of dry heat
There are two main kind of dry heatHot air oven: another mean of dry sterilization.
Uses and Advantage: used in labs and clinics with heat resistant items that don't sterilize well in moist heat substances like glassware, metallic instruments, powders and oil (that do not penetrated by steam).
Disadvantages: this method is not suitable for plastic , cotton ,papers which will burn at high temperature, or for liquids which will evaporate ,also this method requires longer exposure times, and higher temperatures than moist heat.
Cold Sterilization
the principle effect of this method is to slow the growth of culture and microbes in food during storage. This method would kill some m.o. but not kill staphylococcus spp., Clostridium spp., Bacillus endospores. This method include: chilling, freezing, desiccation, all of which is not considered as sterilization method because it have erratic effect as well as their killing effect is uncertain.
Physical Sterilization
Radiation: omitted energy can be used as an antibiotic agent,Can be divided into ionized radiation and non-ionized radiation the most important used radiation is gamma rays, X-ray, Ultraviolet Ray (UV).
Radiation:
Mode of action:When a cell is bombarded by a certain waves its molecules absorb the energy leading to one of two consequences :
• Ionization radiation directly affect the microbe DNA which would undergo mutations which lead to chemical changes in the m.o. organelles and production of toxic substances. Gamma rays, X-ray are both ionization radiation.
• in case of non ionization radiation _UV_ high energy waves that effect the molecules without causing them to be ionized also leading to formation of abnormal bond in the DNA and thus become a source of mutations.
Radiation
Uses of ionizing radiation: food sterilization can penetrate liquids ,most of solid materials , sterilizing disposables such as plastic syringes, catheters, or gloves before use, the most commonly used are gamma radiation.Advantages: heat sensitive materials, can kill not only bacteria but also insects, worms, fast, high penetration power.
Disadvantages: potential dangers to radiation machine operators from exposure to radiation and possible damage to some materials.
Radiation
Uses of Nonionizing radiation (UV): the most common application of UV is by the UV light lamp called germicidal lamp it is disinfectant rather than steralint. Used to sterilize the air in surgery room, microbiological labs, slaughterhouses….etc. sterilization of drinking water, for sterilization of vaccins and plasma, walls, floors, meat, drugs, grafting tissue.Advantage: simple, not expensive, easy to operate, not need heat, can kill fungal cells, parasites, viruses, bacterial vegitativecells in addition to spores.
Disadvantages: poor penetrating power through solid such as glass, even paper.UVhas a damaging effect on human tissues, including sunburn, retinal damages, cancer …etc.
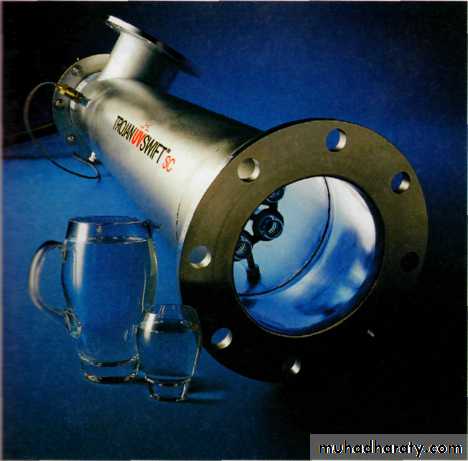
(UV) treatment system for the disinfection of water.
Mechanical Sterilization
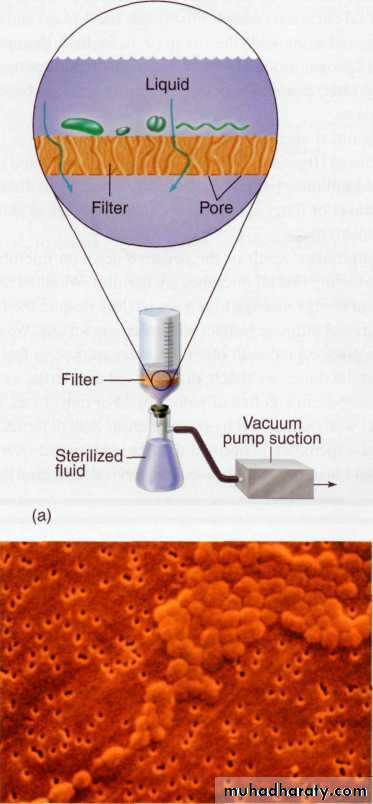
Filtrationit is an effective method to remove microbes from air and liquids.
Mechanism of Action: Filtration of liquids is accomplished by pulling the solution through a cellulose acetate or cellulose nitrate membrane with a vacuum. In practice, a fluid is strained through a filter' openings large enough for the fluid to pass through small for microorganisms to pass through. Most modern microbiological filters are thin membranes whose pore size can be carefully controlled and standardized.
Filtration
Filtration
Uses and application: is the method of choice for antibiotic solutions, toxic chemicals, radioisotopes, vaccines, IV fluids, water purification, milk…etc. which are all heat-sensitive. Even air sterilization in some closed environment (sterile room).Advantages: have no toxic effect on the material that sterilized , and not subjected to heat that might change its chemical nature, no harmful effect on the environment, no hazard to the operator.
Disadvantages: cannot remove soluble molecules (toxins) that can cause disease.
The Chemical methods
The Chemical methods of sterilization :
The use of chemical materials in sterilization, there are 10000 chemical that has been use in sterilization in homes, lab, hospitals …etc.
Uses: in every aspect of life like food preservations, labs, surgery floors walls, as detergents used for sterilizing heat-sensitive objects.
Advantages: The most common chemical sterilant is used for sterilizing heat-sensitive objects. Fast, easy to find , some of the chemicals can kill all kind of microorganisms.
Disadvantages: Wide range of side effect, some of them are toxic to humans, can be abused by people, there is no perfect chemical that fulfill all the requirements of a safe effective agent.
Microscopy and their kinds
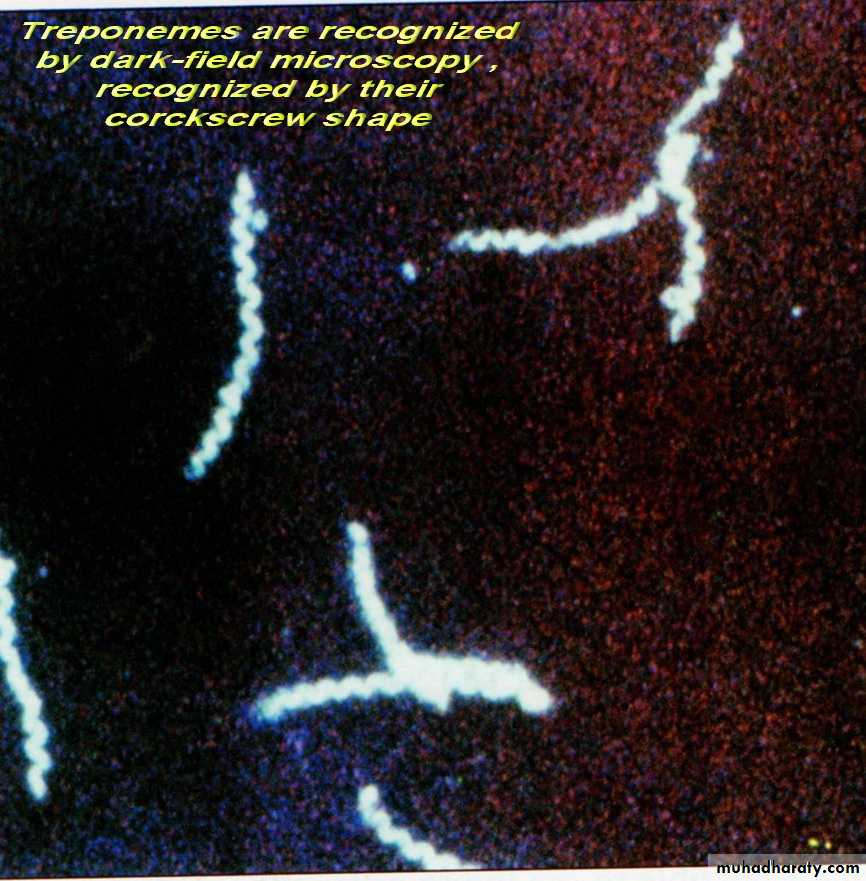
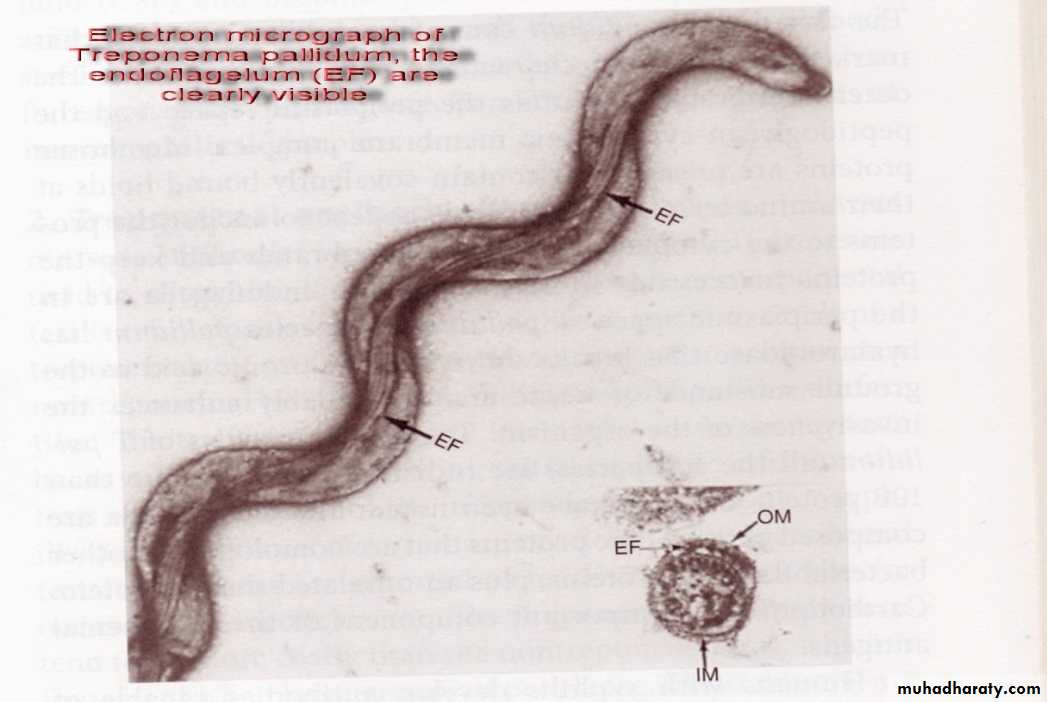
Microscopy: the most common used methods for both detection of microorganisms' directly in clinical specimens and for characterization of organisms grown in culture.There are four types of microscopy:
Types of Microscopy
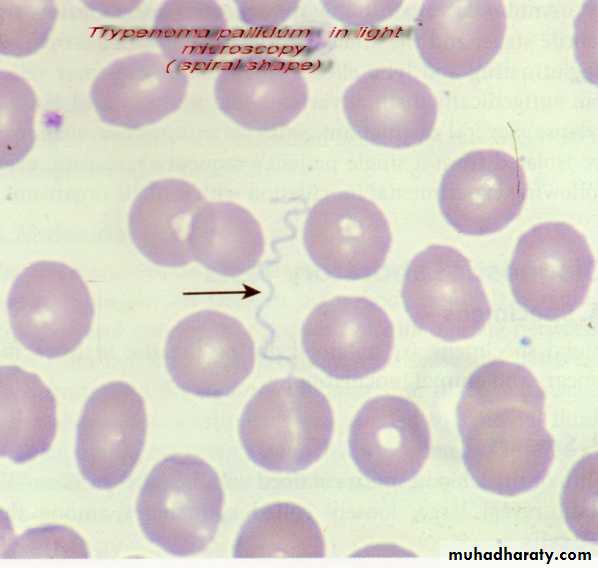
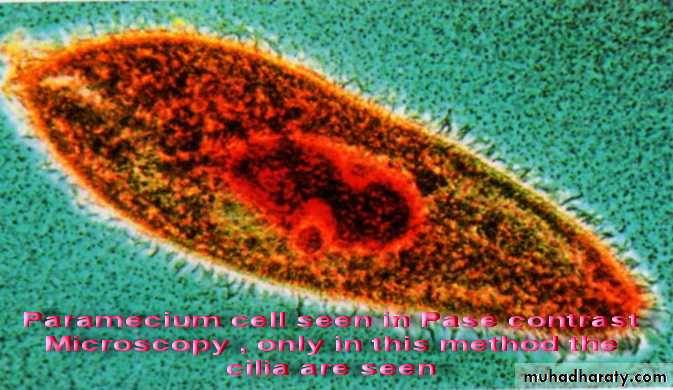
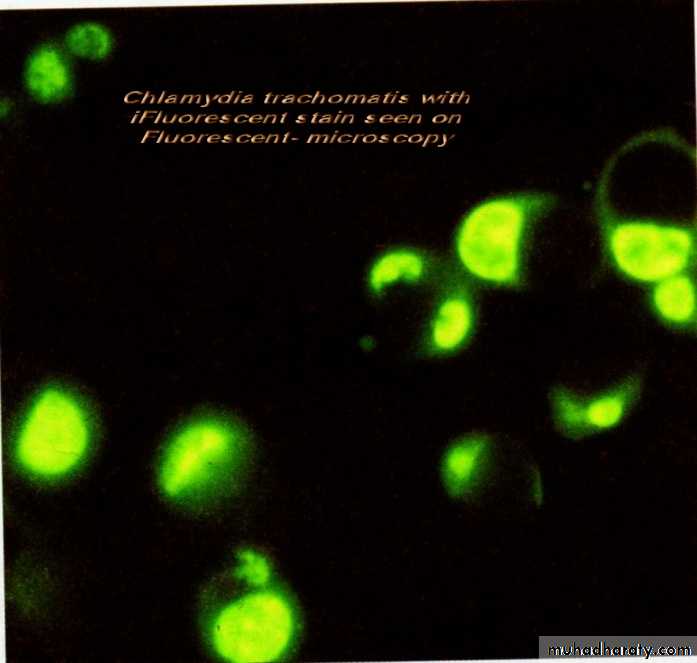
• Bright field microscopy (Light) microscopy: The most commonly used microscopy in ordinarily labs; allow observing the dead m.o. need many kind of stain like gram stain.