Identification of Bacteria
depend on:1 – Microscopic appearance :-under the compound light microscope which include
a . Reaction with gram stain .
b .Morphology and arrangement .
c . Capsulated or not .
d . Motile or not .
e . Spore forming or not .
2 – Macroscopic appearance :include
a . Culture appearance .
b . Biochemical tests .
c . Gene tests .
Culture Media
common ingredient of culture media : pepton , meat extract , NaCl , agar , water .Uses of culture media:
1-To obtain pure culture.
2-Identification and recognition of bacteria .
3-Some media use to study the bacteria.(to do biochemical tests).
Types of media:
According to
A- physical status there is : ● liquid media.
● solid media.
● semisolid media.
B_ use of the media:1 . simple (basal) media :It uses for cultivation of common m.o. but not for fastidious bacteria . e.g nutrient broth, nutrient agar.
2.Special purpose media
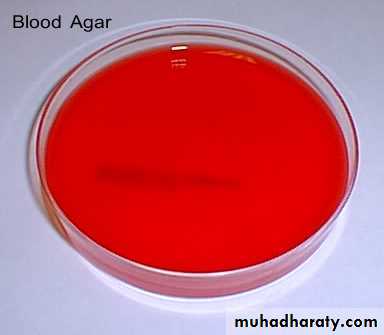
A/ enriched media :e.g (blood agar ,Chocolate agar).
It is simple media enriched with one of the following substance (blood, serum, glucose,…) it used to cultivate fastidious m.o. e.g. Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Haemophilus lnfluenzae.
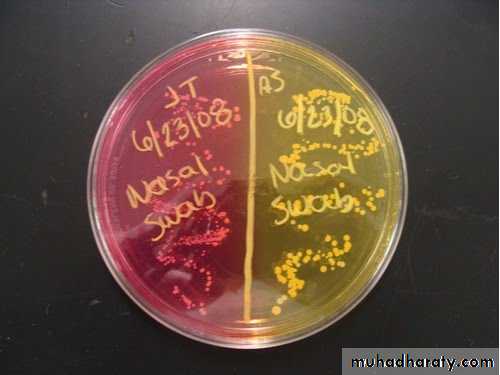
B/selective media favor the growth of certain bacteria and inhibit growth of other bacteria because it contain inhibitory substance e.g: Mannitol salt agar : contain high conc. of NaCl that most bacteria cannot grow in this conc. except Staphylococcus spp.
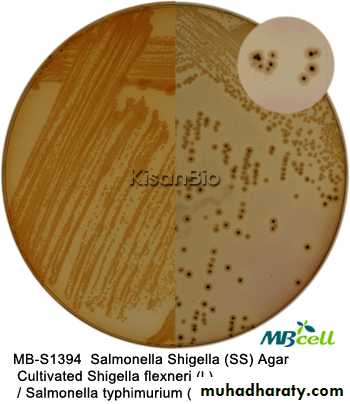
MacConky᾽s agar: contains bile salt that inhibit all kinds of bacteria except enterobacteriacea.Salmonella shigella agar (SS) is selective for Salmonella and shigella
Bismuth sulfate agar is selective for Salmonella spp.
C/differential media It is used to recognize certain spp . of bacteria either by :
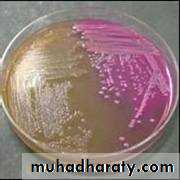
1 -certain characteristic colonies : such as fermentation or non fermentation of lactose on MacConkey᾽s agar (these media contain neutral red as indicator which change in color during fermentation , because the gas will be produced and decrease in the pH.left: no lactose fermentation
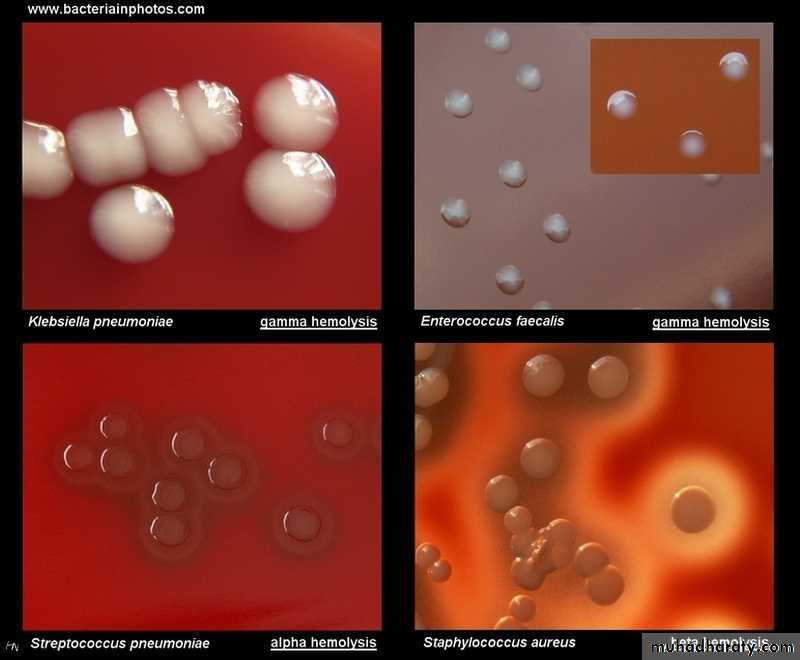
right: lactose fermentation2-certain effect on the media e.g hemolytic or non hemolytic on blood agar. Beta hemolytic β (complete hemolysis ) e.g Streptococcus pyogenes Alpha hemolytic α (incomplete hemolysis or partial hemolysis) e.g Streptococcus viridans Gamma hemolytic ϒ ( no hemolysis ) e.g Enterococcus faecalis
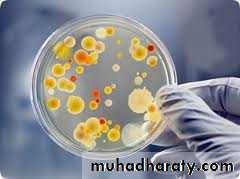
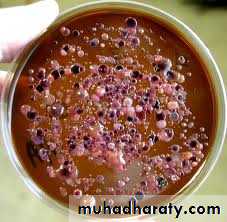
Macroscopic characteristics of the microorganism in any culture
1-Size : very small (pinhead ≤ 1mm )Medium size =1-2 mm
Large size > 2 mm
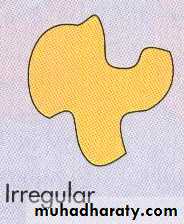
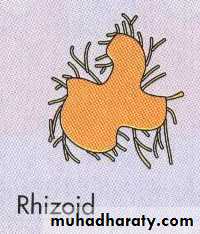
2-Shape :circular ,irregular ,radiated ,rhizoid , filamentous .
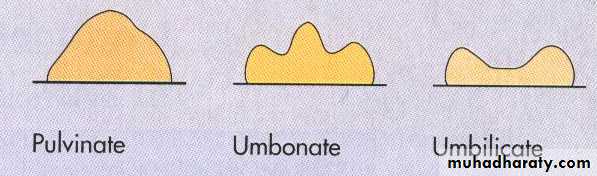
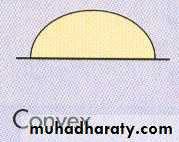
3-Elevation : flat , raised ,low convex ,convex dam , papillate .
4-Surface structure : smooth , rough ,granular ,ringed papillate .
5-Edge :entire , lobate ,cranate ,dentate,curled ,filament .
6-Color and opacity : transparent,translucent,opaque,fluorescence,metallic sheen .
7-Consistency :butyrous ,viscid ,friable ,membranous .
8-Emulsifinibility :easy or difficult ,homogenous granules, membranous .
9-phenomenon : swarming (Proteus ) Medusa head (Bacillus)
Swarming of Proteus mirabilis
Medusa head of bacillus anthracis• 10-pigmenta. exopigment :this pigment produce outside bacterial cell (in the media) e.g Pseudomonas aeruginosa produce pyocyanine (green pigment) and Pseudomonas fluorescens produce flourscine (blue pigment) Pseudomonas fluorescens
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
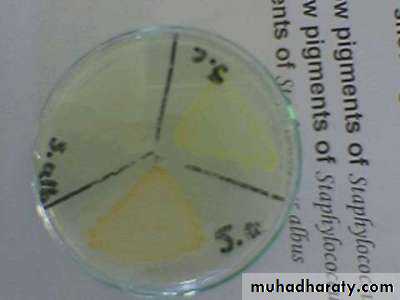
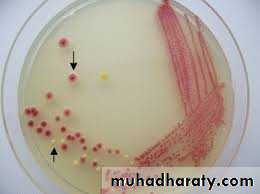
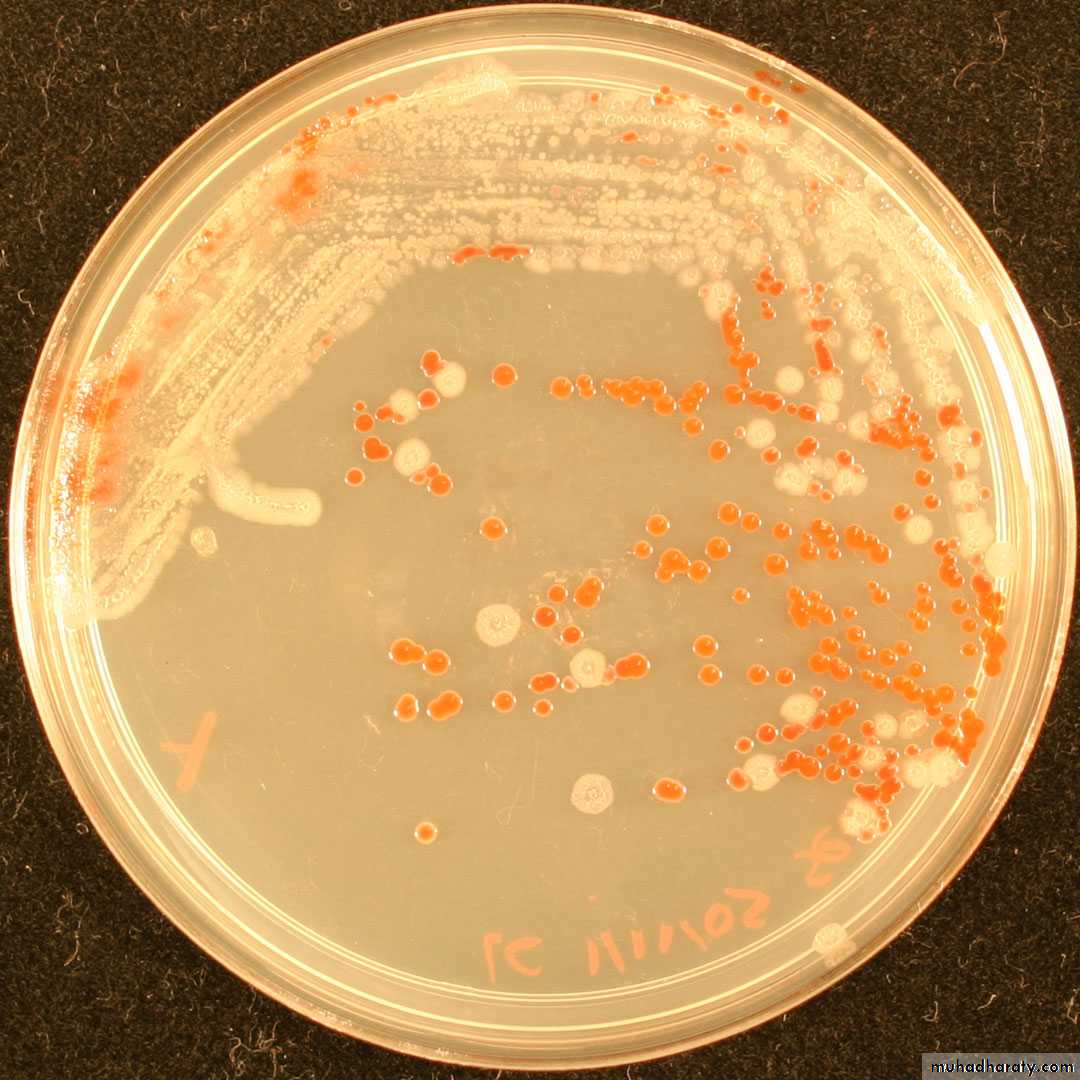
Pseudomonas fluorescensb. endopigment : this pigment produce inside bacterial cell e.g Staphylococcus aureus (golden colonies ), Staphylococcus citrus (yellow colonies) , Staphylococcus albus (white colonies ).
11-odor: sweet odor (apple) such as Pseudomonas. bad odor (fish) such as Proteus . 12-growth in semisolid media Gelatin test 13-haemolysis in blood
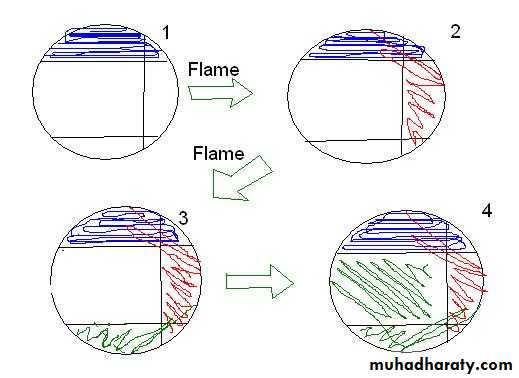
Methods of inoculation and isolation of pure cultureMixed bacterial population; sputum, urine, pus, infected wound, abscess, …. ect Pure culture: a single kind of m.o. growing alone in a protected environment.Bacterial colony: a mass composed of identical bacterial cells.Methods :1- the streak plate method (e.g. Quadrant steak) 2- the pour plate method3- the serial dilution method4- the micromanipulater technique