Dr. Shayma`a Jamal Ahmed
Prof. Genetic Engineering
& Biotechnology

At the end of this lecture the student will be able
to:
Define the cell
.
Recognize to the Cell Theory.
Describe the Characteristics of Cells.
Describe the Characteristics of life.
Compare between Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic.
Recognize to the Prokaryotic cell structure
.
Recognize to Eukaryotic cell structure.

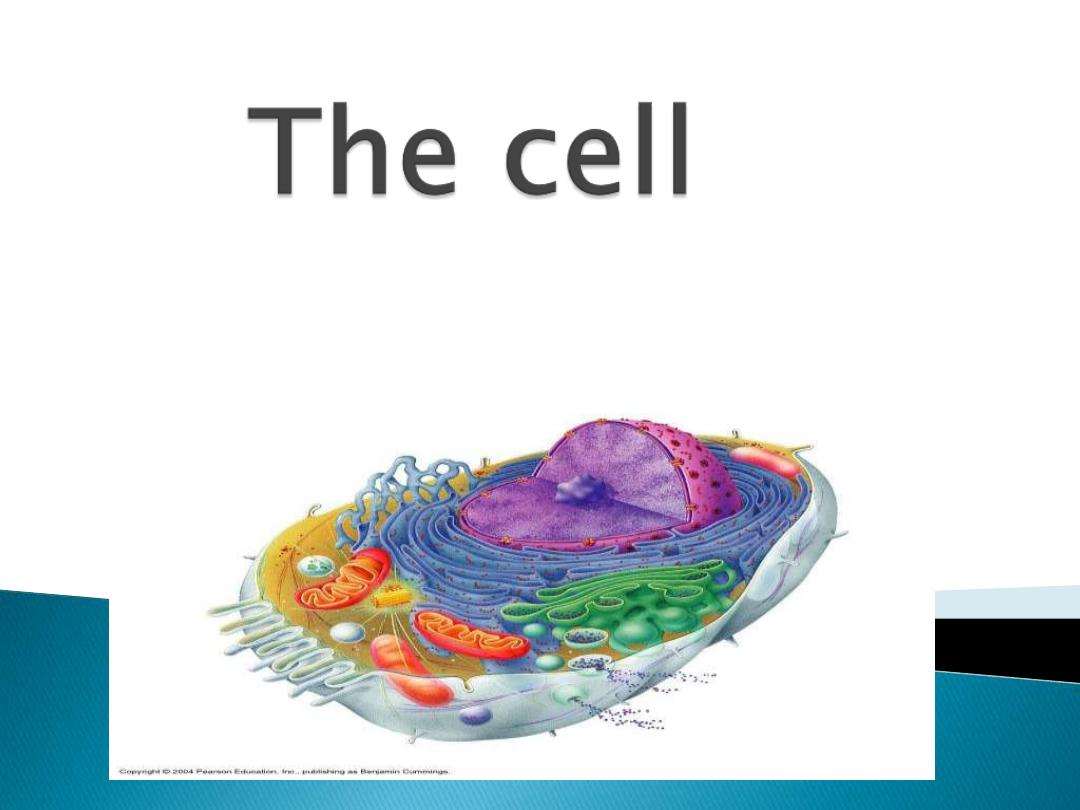
What is the cell?
it is the structural and functional
units of all living organisms .A cell is
the smallest unit that is capable of
performing life functions.
The organisms such as bacteria vs.
Human are unicellular and multicellular

Cells are the fundamental unit of life - nothing
less than a cell is alive.
All organisms are constructed of and by cells.
All cells arise from cells.
Cells contain the information necessary for their
own reproduction.
No new cells are originating spontaneously on
earth today.

Cells are the functional units of life. All
biochemical processes are carried out by cells.
Groups of cells can be organized and function as
multicellular organisms.
Cells of multicellular organisms can become
specialized in form and function to carry out sub-
processes of the multicellular organism.

•
All living things (single and multicellular) are
made of cells that share some common
characteristics:
◦
basic shape : spherical, cubical, cylindrical
◦
internal content : cytoplasm, surrounded by a
membrane
◦
DNA chromosome(s), ribosomes, metabolic capabilities
•
Two basic cell types:
Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic
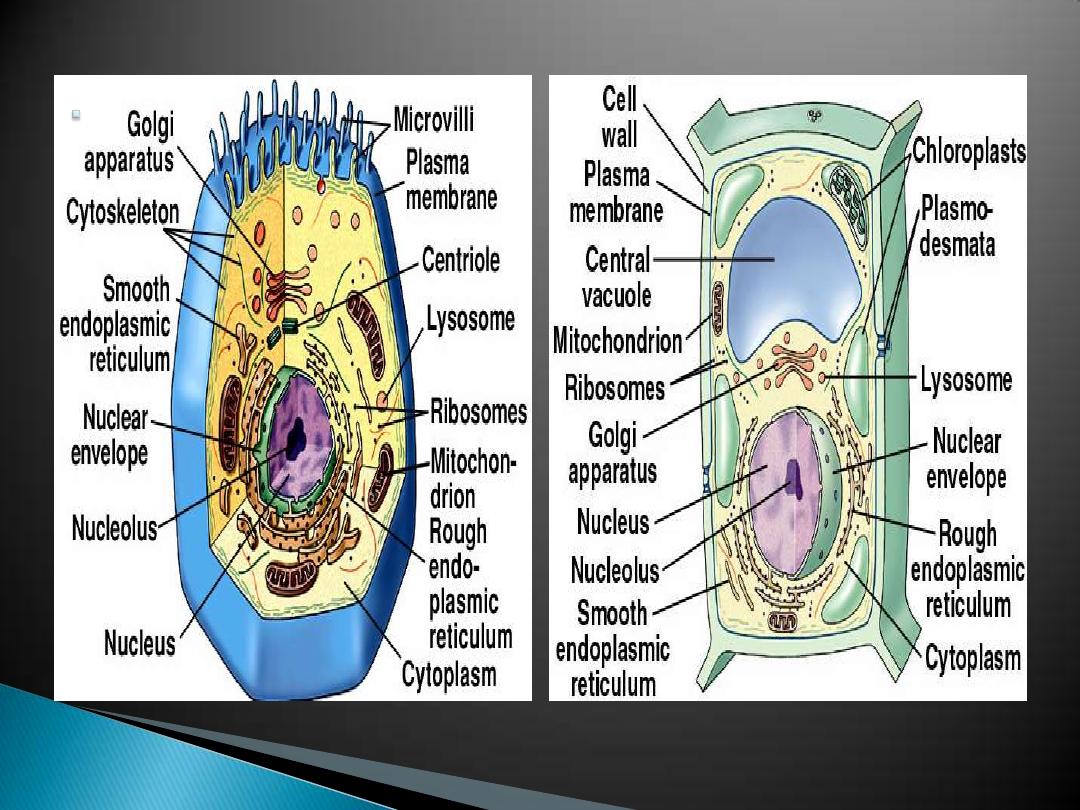
Animal cell
and
Plant cell
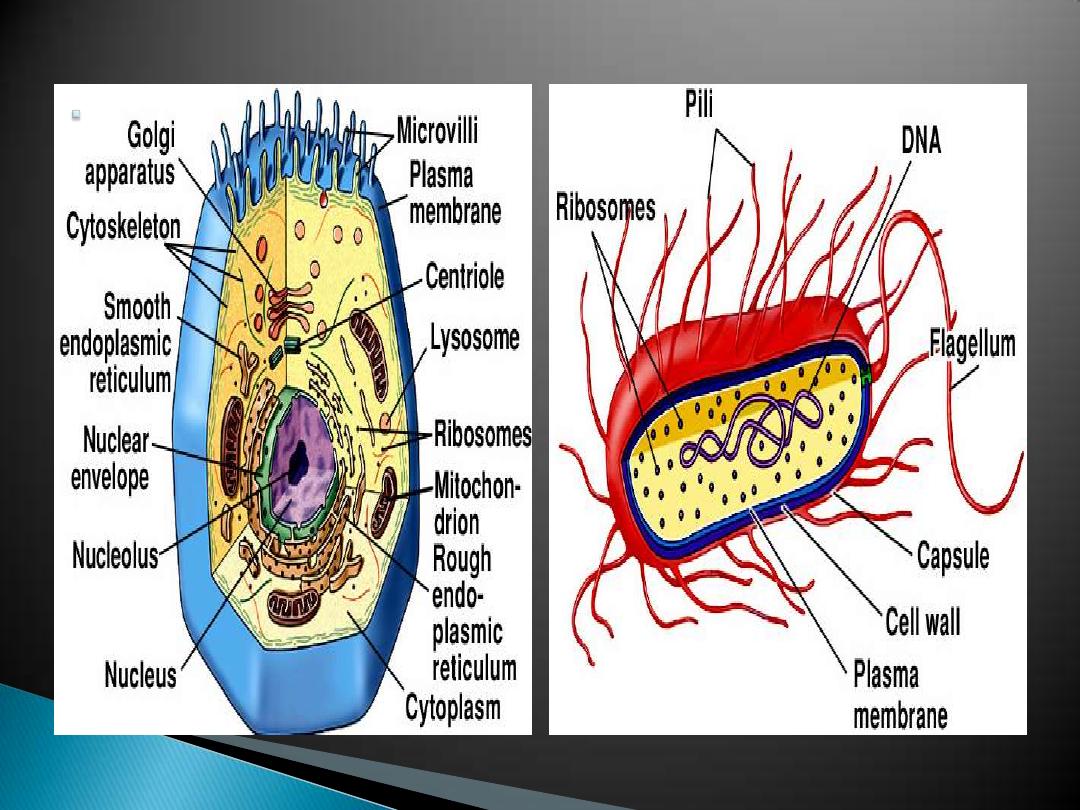

Growth
Reproduction
Metabolism
Movement
protection
storage , Transport of nutrients and
waste.

Prokaryotic:
◦
Smaller, 1
—5 µm
◦
No organelles
◦
No nucleus
◦
DNA in circular loop
◦
- Binary fission
Eukaryotic:
◦
Larger, 8
—100 µm
◦
Membranous organelles
◦
Nucleus
◦
DNA in linear chromosomes
◦
Cell growth by cell division
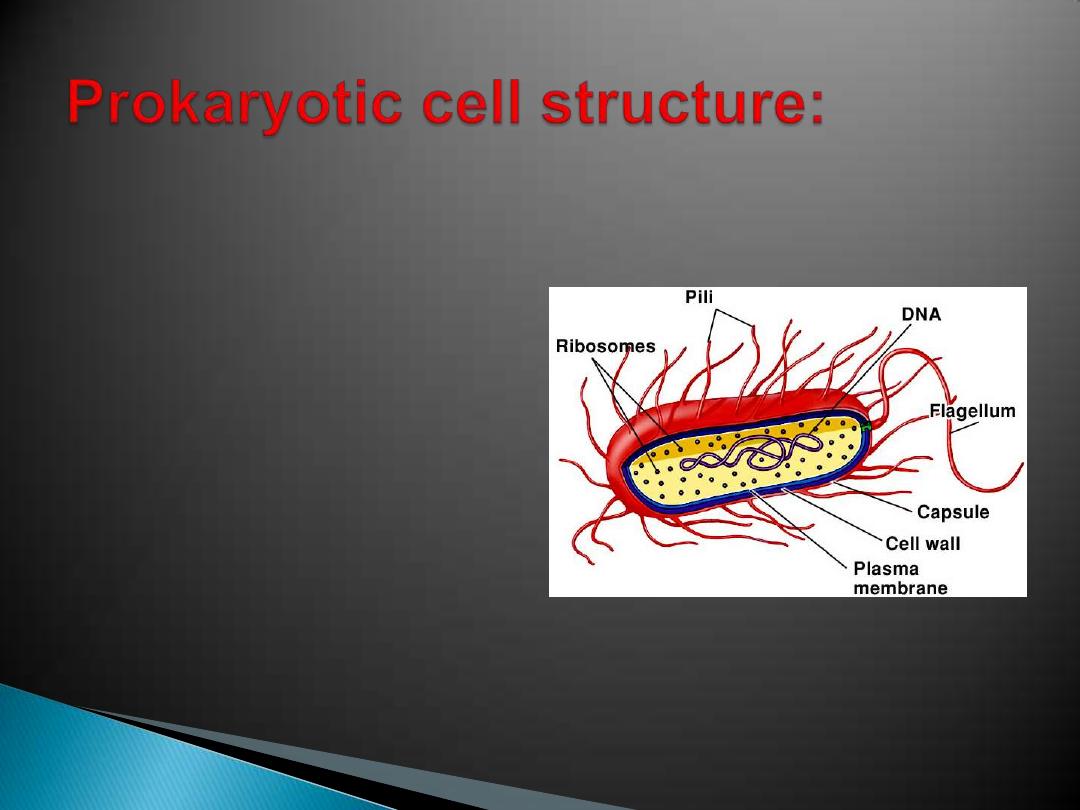
small, with a plasma
membrane surrounded by
a rigid cell wall ,in many
the cell wall is made of:
-carbohydrate
-cross-linked with
polypeptides
cell wall may be covered
with a capsule made of
polysaccharides

cell wall may be covered with a
capsule
made of polysaccharides few or no
membrane enclosed spaces within the
cytoplasm.
no nucleus
- DNA is in a region called the
nucleoid
- DNA is circular and naked (has no
protein associated with it).
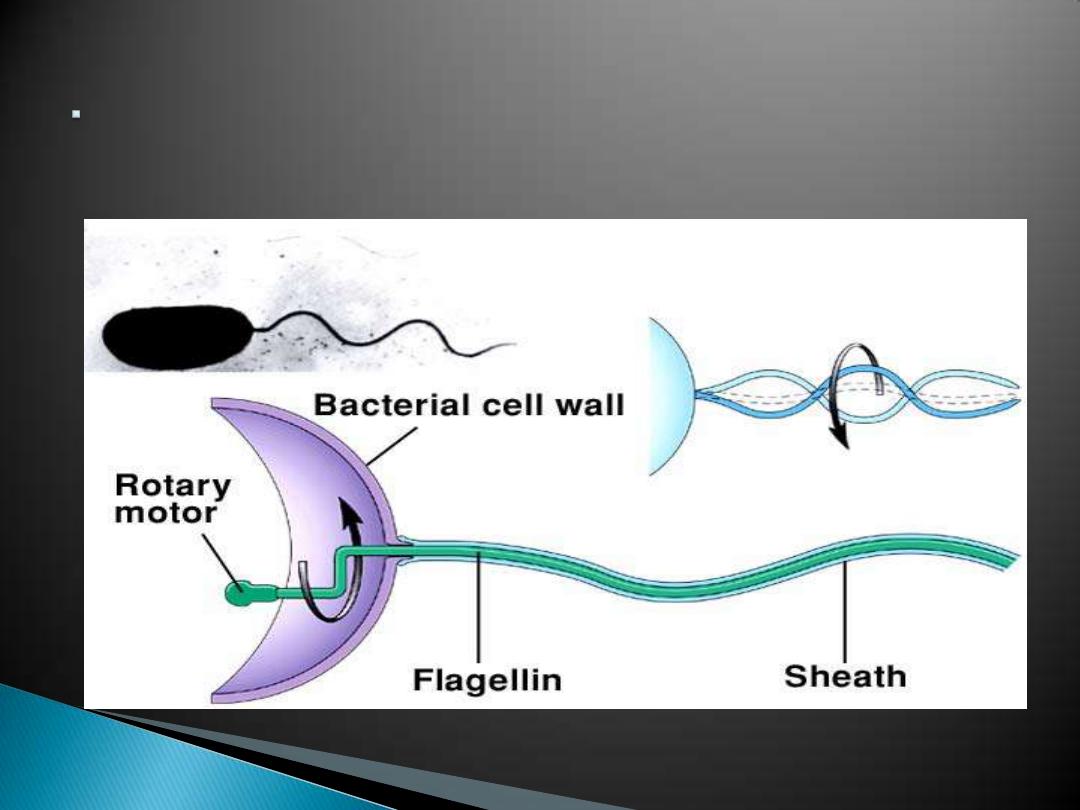
Bacteria often have flagella with a
single protein core (flagellin)
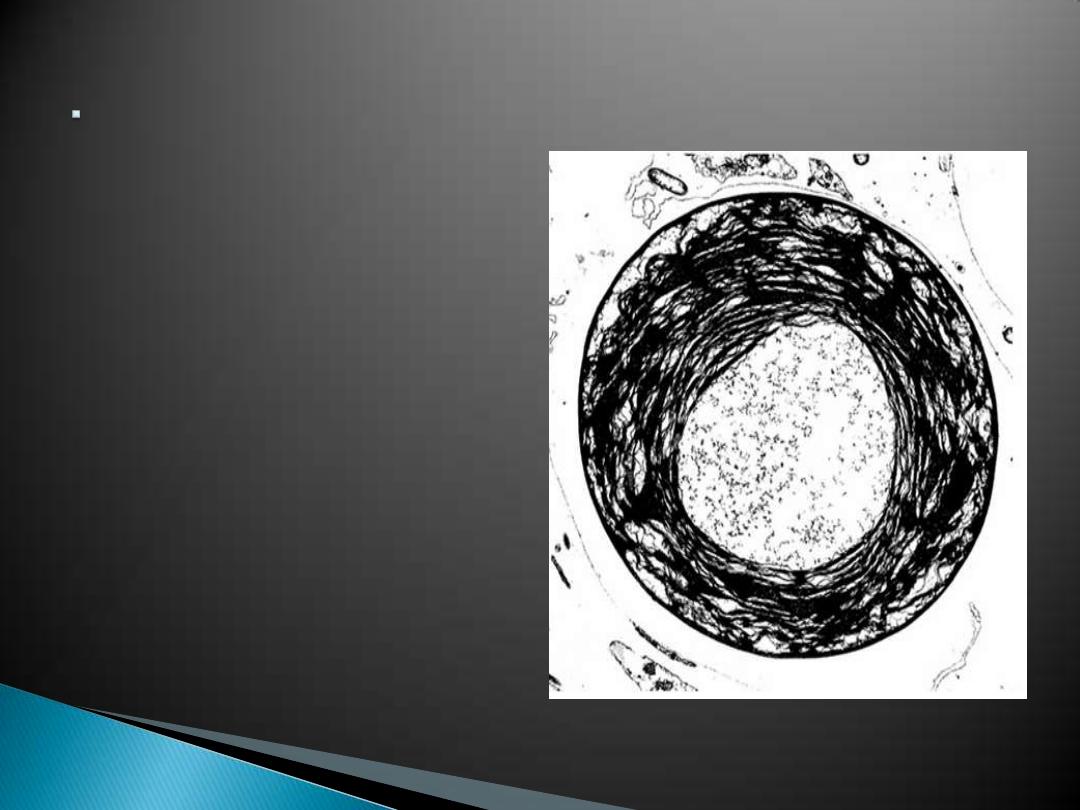
Membrane enclosed
spaces allow cell
functions to occar.
Prokaryotes lack
membrane enclosed
spaces in their
cytoplasm.
Some prokaryotes are
photosynthetic.

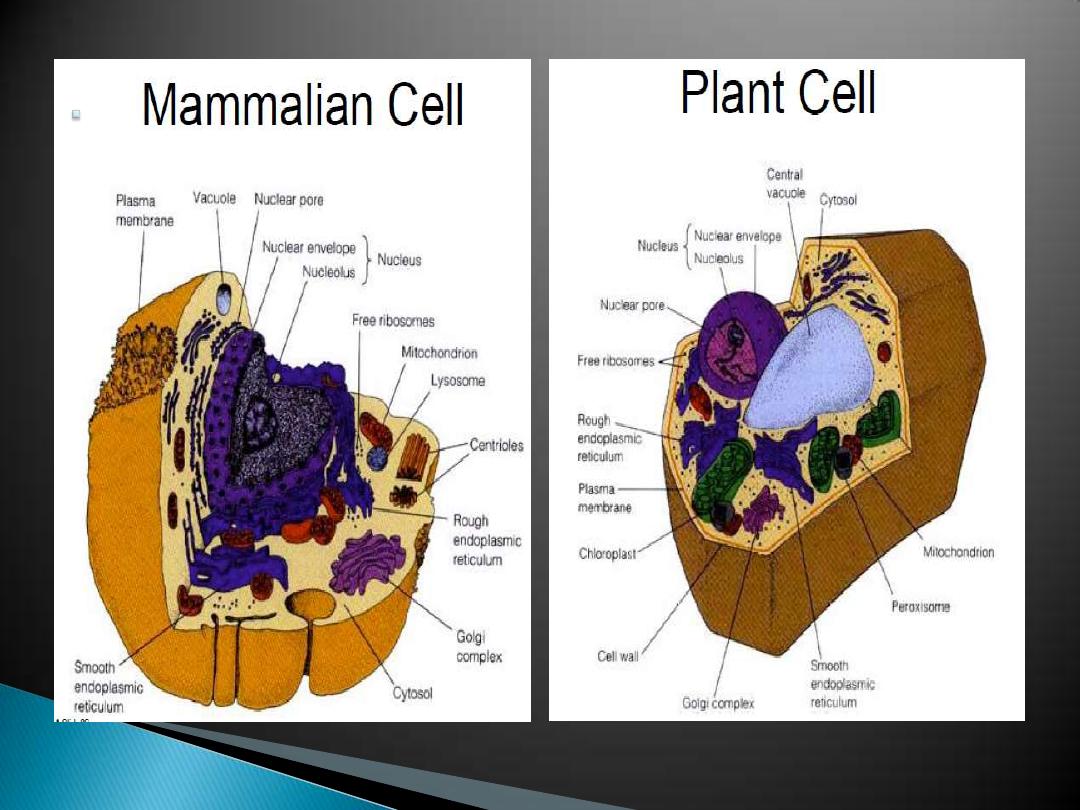
larger, with a typical plasma membrane - some
with a cell wall, many and other interior spaces
enclosed by membranes:
Nucleus, Endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus,
Mitochondria, Chloroplasts, Lysosomes, Vacuoles,
Vesicles
cell wall found in plants (cellulose), fungi(chitin).
Cytoplasm with a cytoskeleton - protein tubules
and fibers.

Micro
means "small" and
scope
means "to look" or "see“.
It is a:
device(instrument) used for
producing a much larger view(magnified
images ) of very small objects so that
they can be seen clearly by using a lens
or a combination of lenses to be seen by
the eye .

Which are:
1-
Compound microscopes
: are
A- light illuminated.
B- The image seen with this type of
microscope is two dimensional. This
microscope is the most commonly used.
You can view individual cells, even living
ones.
C- It has high magnification. However, it has
a low resolution.


There are many types of
compound(light) microscopes:
bright-field microscope
dark-field microscope
phase-contrast microscope
fluorescence microscopes

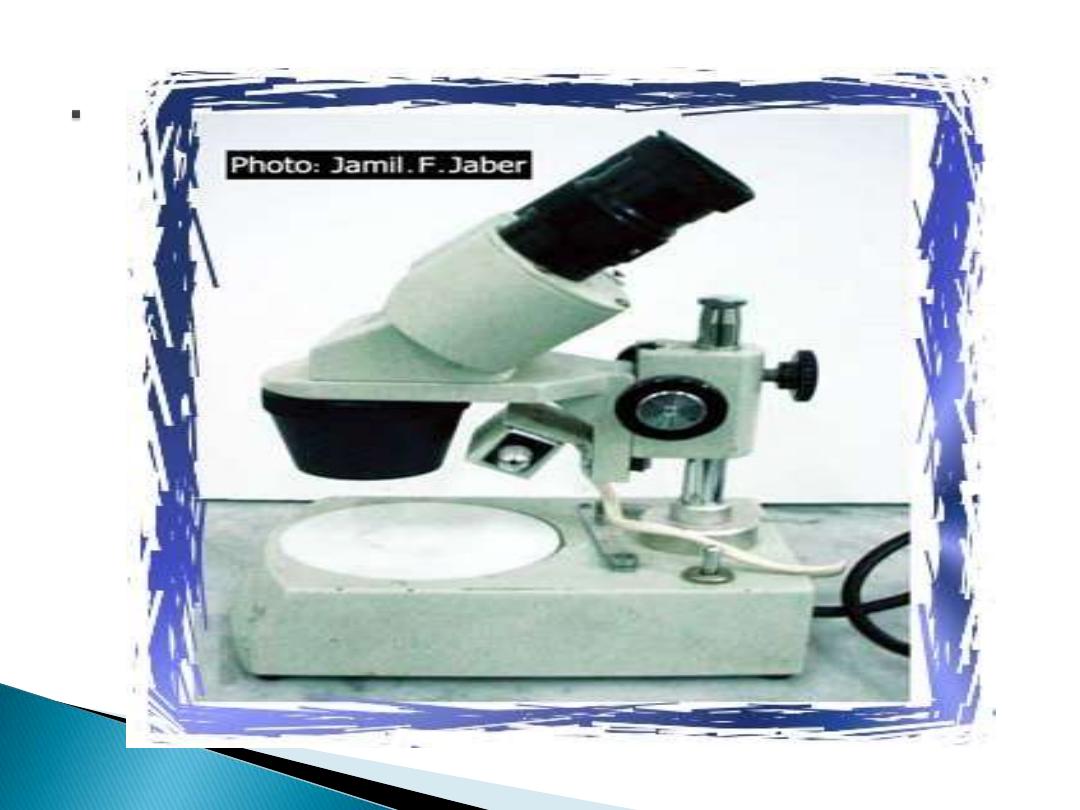
2- Dissection (stereoscope)
microscope:
A dissection microscope is
1- light illuminated.
2- The image that appears is three
dimensional.
3- It is used for dissection to get a
better look at the larger specimen.
You cannot see individual cells
because it has a low magnification.
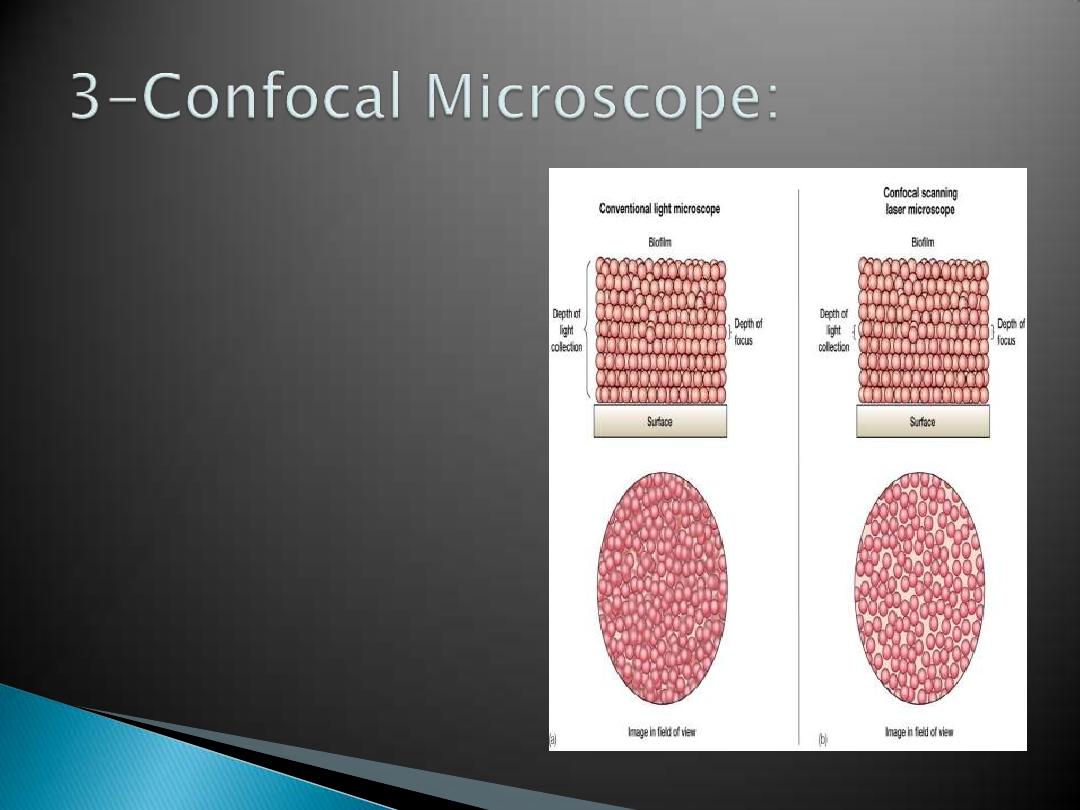
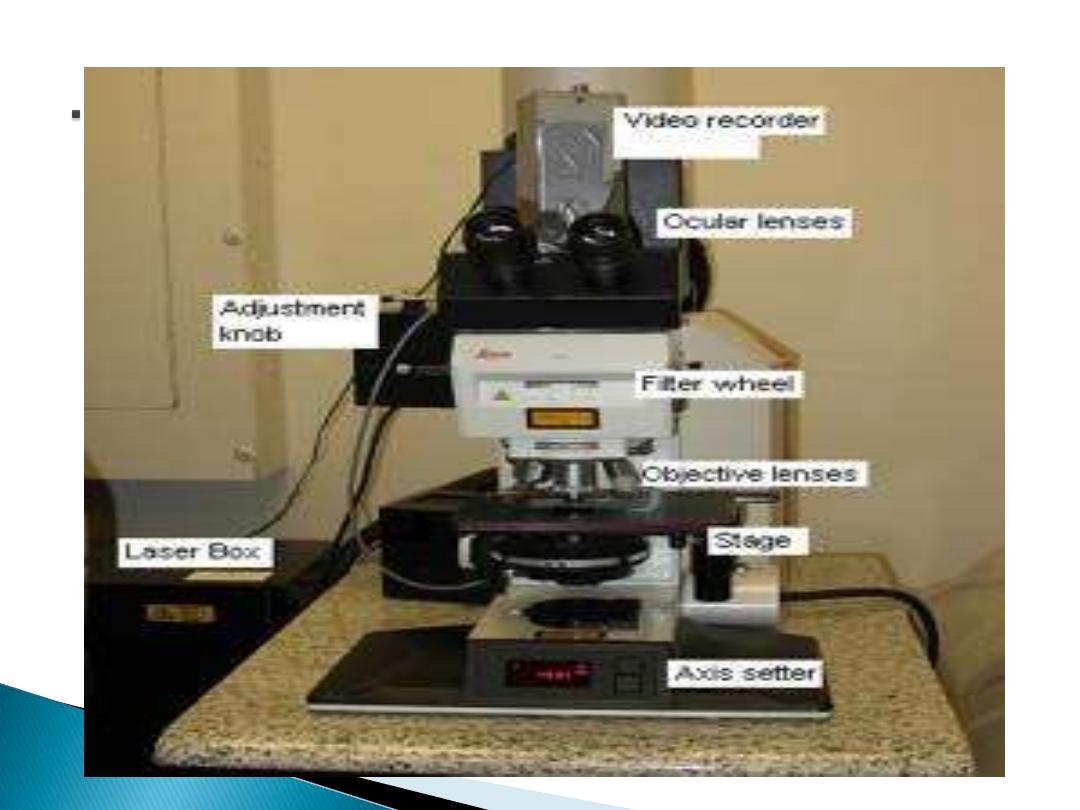
confocal scanning
laser microscope
laser beam used to
illuminate spots on
specimen
computer compiles
images created
from each point to
generate a 3-
dimensional image

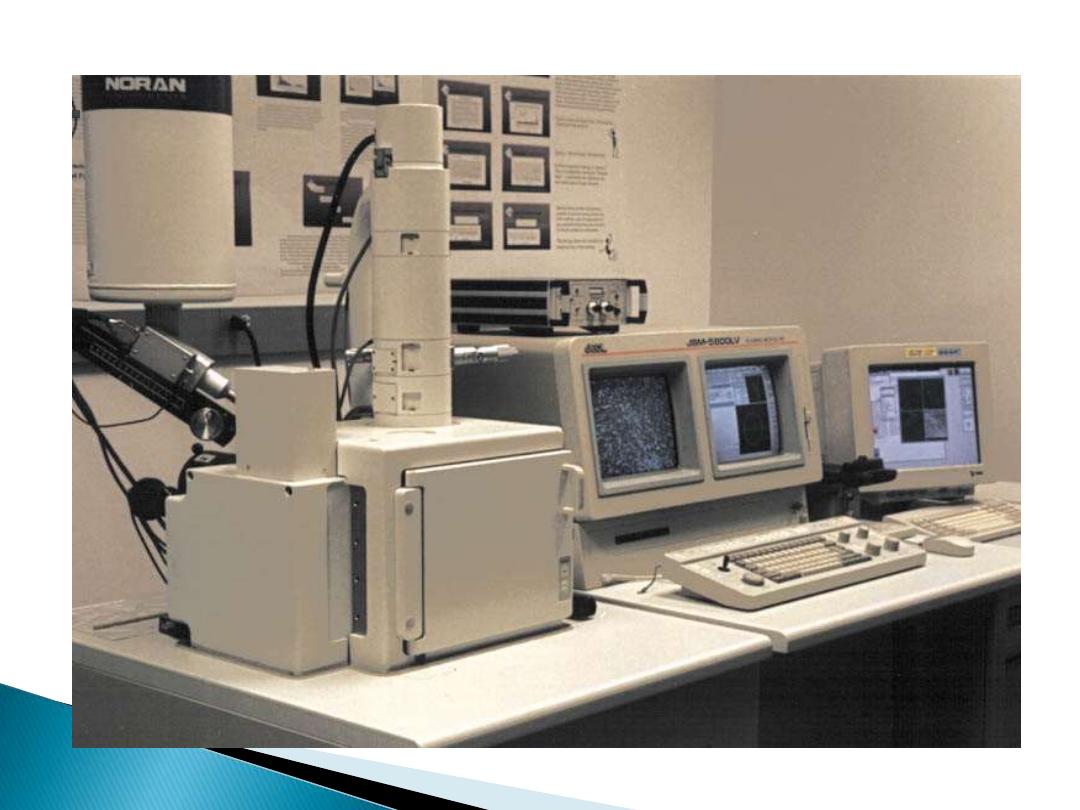
4- Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM):
SEM use
1- electron illumination.
2-The image is seen in three dimensional.
3- It has high magnification and high
resolution.
4-The specimen is coated in gold and the
electrons bounce off to give you and
exterior view of the specimen.
5-The pictures are in black and white.


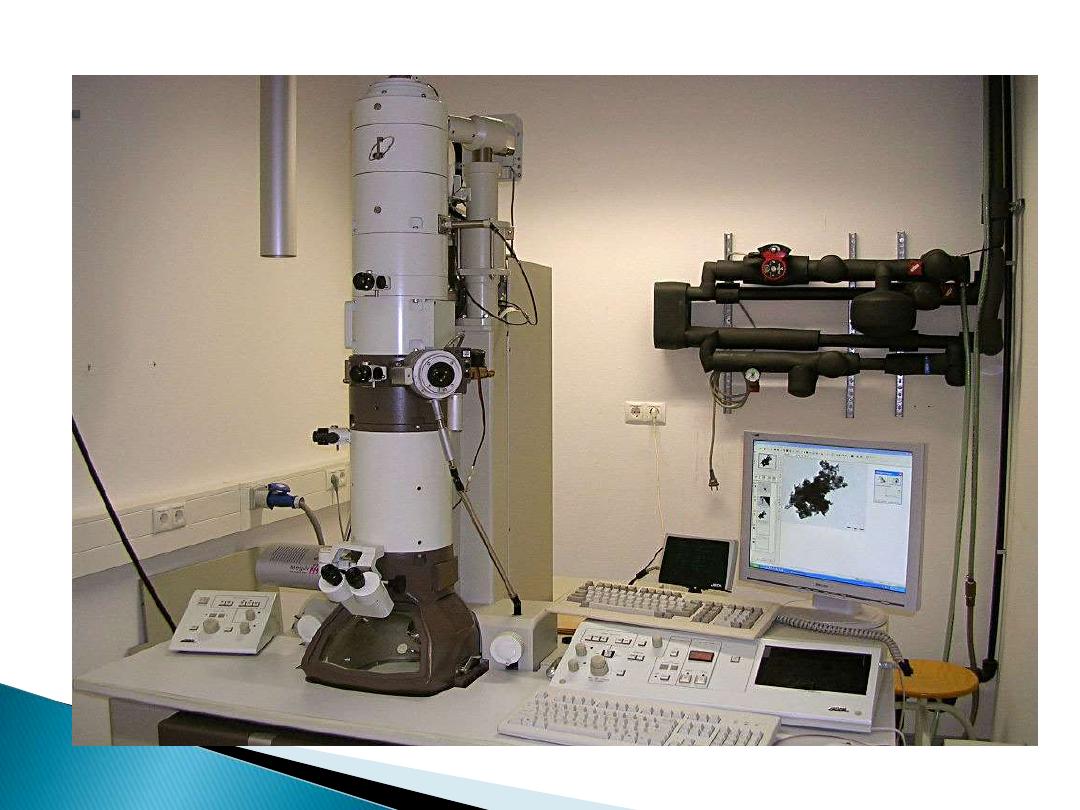
5- Transmission Electron Microscope
(TEM):
TEM is
1- electron illuminated.
2-This gives a two dimensional view.
3- Thin slices of specimen are
obtained.
4-The electron beams pass through
this.
5-It has high magnification and high
resolution.


cell
is the structural and functional units of
all living organisms .A cell is the smallest
unit that is capable of performing life
functions.
All living things (single and multicellular) are
made of cells that share some common
characteristics.
◦
basic shape : spherical, cubical, cylindrical
◦
internal content : cytoplasm, surrounded by a
membrane
◦
DNA chromosome(s), ribosomes, metabolic capabilities

Two basic cell types:
Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic
Animal cell
and
Plant cell
Microscope
is a:
device(instrument) used for
producing a much larger view(magnified
images ) of very small objects so that they
can be seen clearly by using a lens or a
combination of lenses to be seen by the eye .

-Microscopes are:
1-
Compound microscope.
2- Dissection (stereoscope) microscope.
3-Confocal Microscope.
4- Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM).
5- Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM).


