Dr. Shayma`a Jamal Ahmed
Prof. Genetic Engineering
& Biotechnology

At the end of this lecture the student will be able to:
Define the
Genetic tests.
Recognize to Diagnosis of genetic diseases.
Describe the Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) .
List the
Molecular detection methods.
Recognize to the Future Treatments.
Recognize to the:
- Karyotyping analysis.
- Types of PCR.
- Applications of PCR.

are tests on blood and other tissue to
find
genetic disorders
.
Over 2000 tests are available. Doctors use
genetic tests for several reasons.
These include:
Finding genetic diseases in unborn babies.
Finding out if people carry a gene for a
disease and might pass it on to their
children.

Screening embryos for disease.
Testing for genetic diseases in adults
before they cause symptoms.
Making a diagnosis in a person who
has disease symptoms.
Figuring out the type or dose of a
medicine that is best for a certain
person.

People have many different reasons for
being tested or not being tested. For
some, it is important to know whether a
disease can be prevented or treated if a
test is positive.
In some cases, there is no treatment.
But test results might help a person make
life decisions, such as family planning or
insurance coverage.
A
genetic counselor
can provide
information about the pros and cons of
testing.

Examination of entire chromosomes
Cytogenetic analysis is conventionally done by:
karyotyping
.
Done on metaphase cells; requires cell division in
vitro. Changes must be large enough to see a
difference in length or shape.
Fluorescence in situ hybridization
Can be done on interphase cells.
Rapid; requires only small sample.
Can detect subtle changes; Can map newly identified
genes to chromosome.
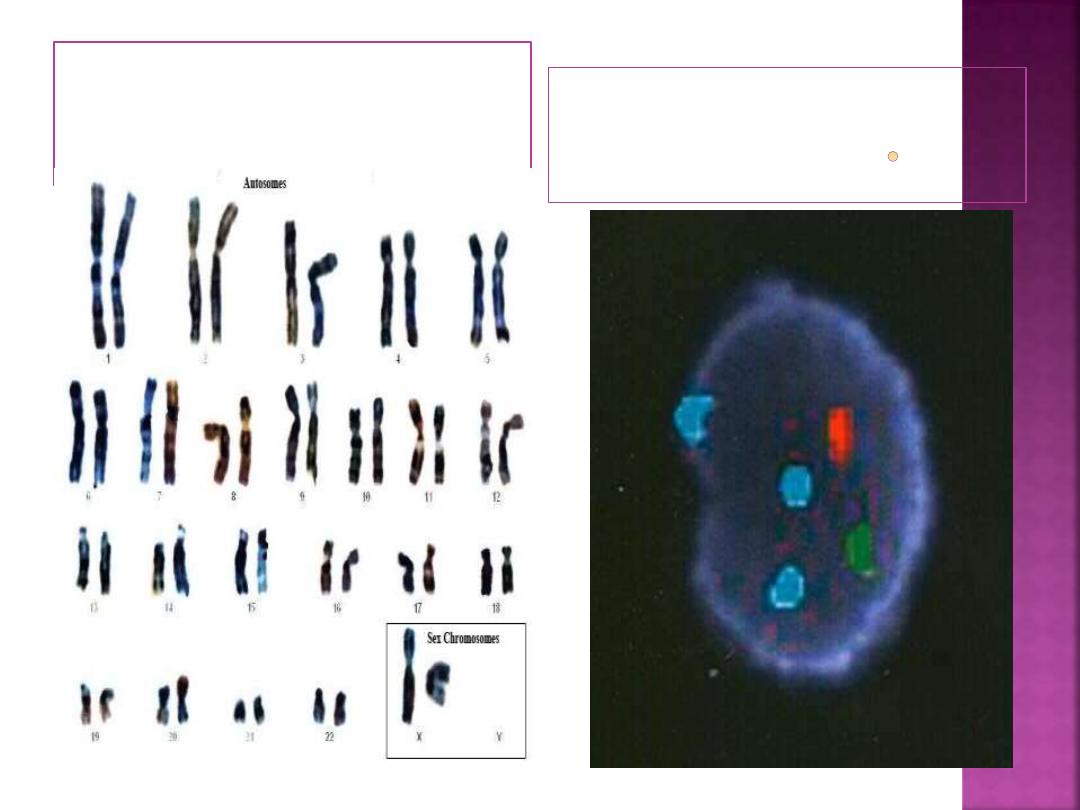
karyotyping
FISH in interphase cell. Male cell
with trisomy 18 BP 7-43A

It’s a valuable tool that can amplify the
amount of DNA in a sample from a few
copies to billions of copies in a few hours.
The PCR technique operates by repetitive
cycling of three basic steps:
Thermal denaturation
Primer annealing
Primer extension
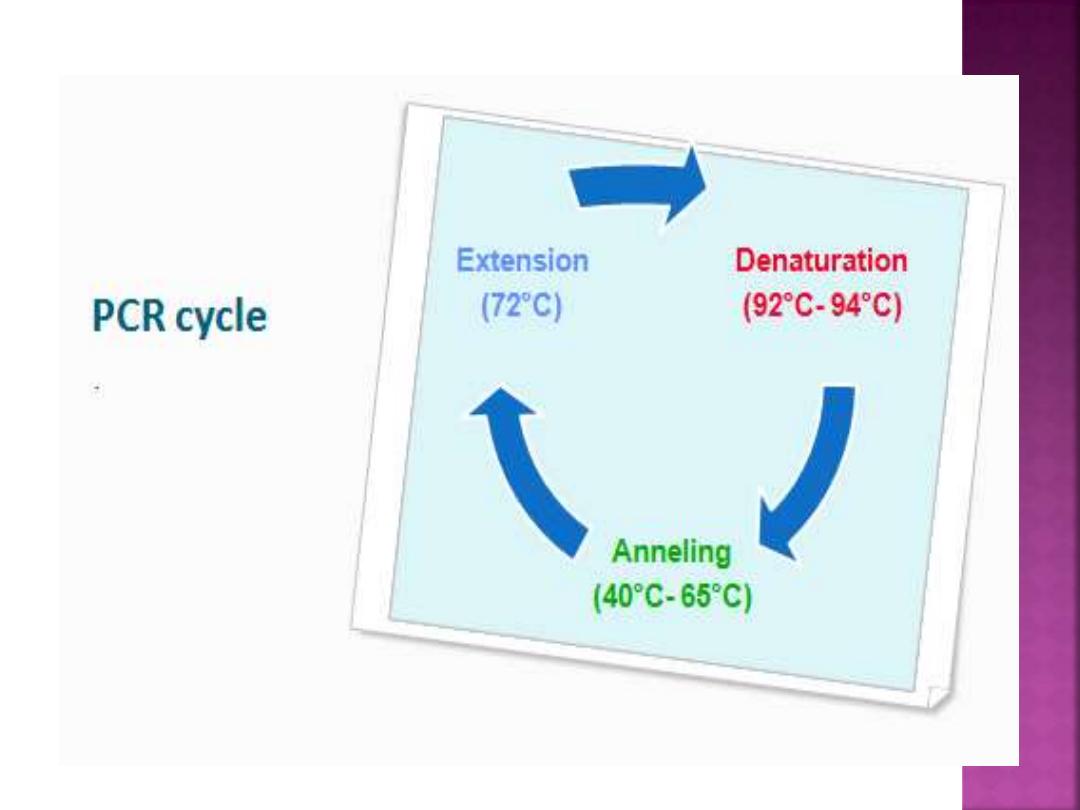
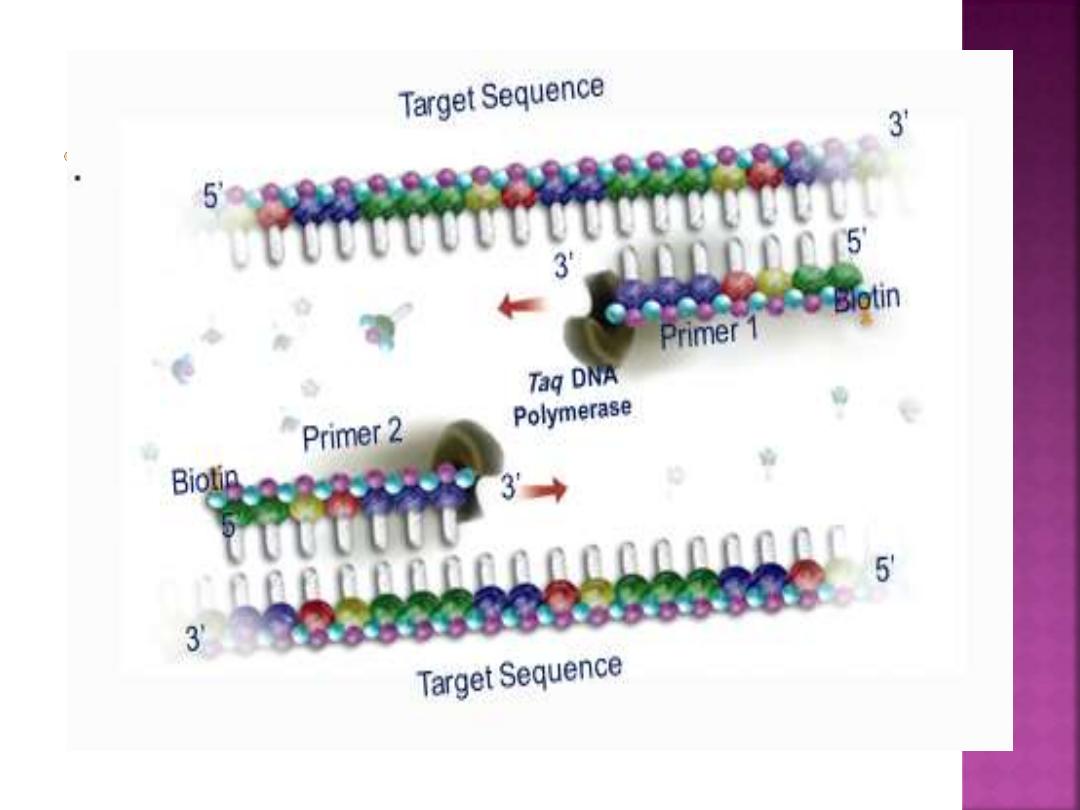


.
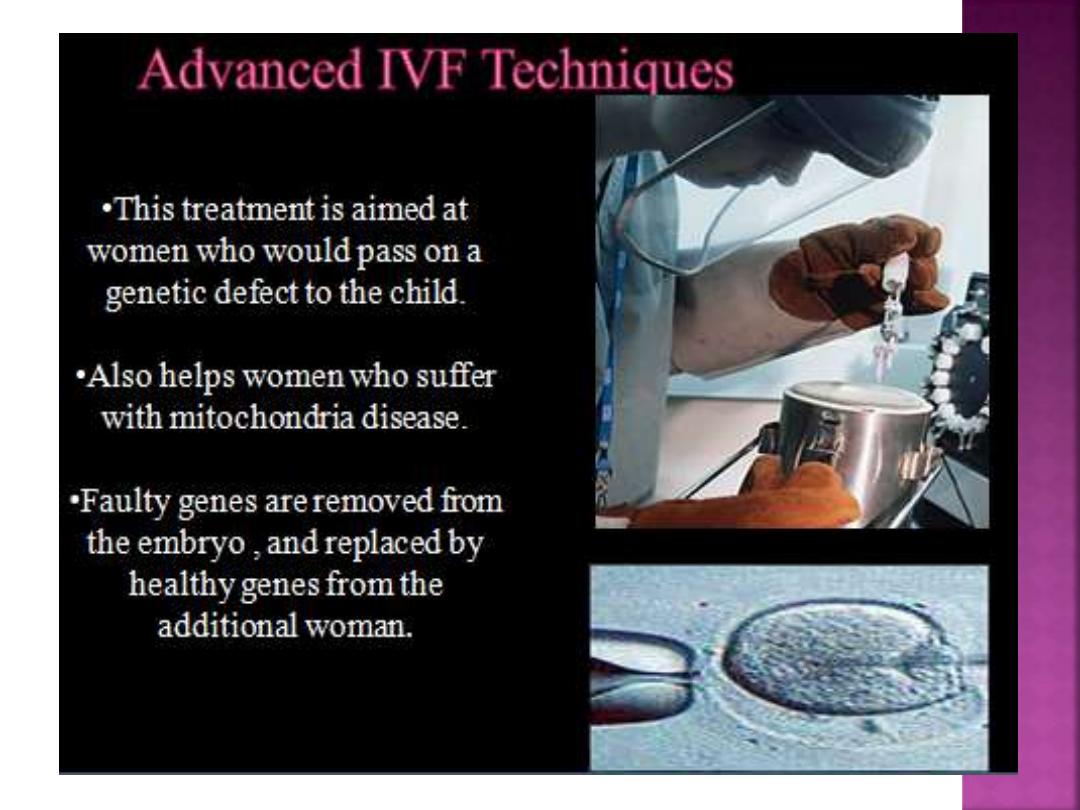

It’s a technique for replacing a faulty gene
with a normal one in people with fatal or
extremely debilitating genetic diseases.
The inherent benefit of this therapy is
permanently cure the physiologic dysfunction
by repairing the genetic defect.

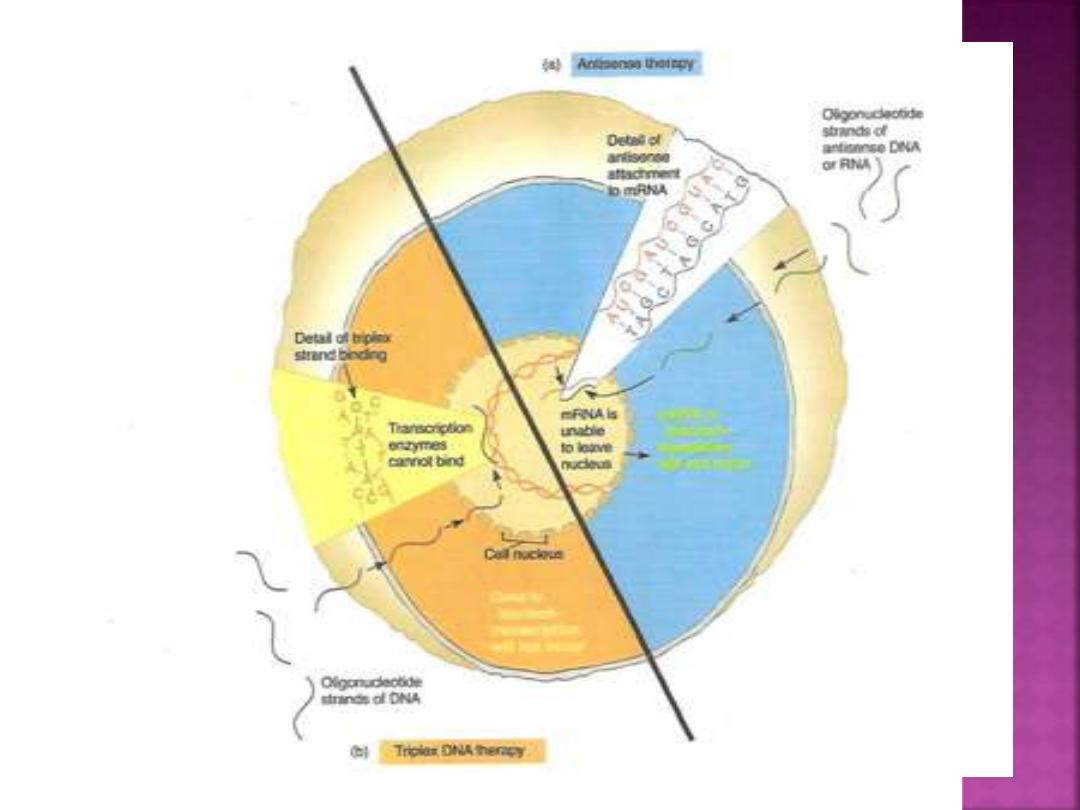
Antisense (Targeting Messenger RNA):
oligonucleotide drugs delivered into cells to block
undesirable expression of genes. Antisense refers to a
nucleic acid strand that is complementary to the sense
or translatable strand.
Antisense drugs are chemically active modified
agents that bind to a target mRNA, for example if
mRNA sequence reads AUGCGAGAC, then an antisense
RNA strand for it will read UACGCUCUG and interfere
with its reading on ribosomes .
Experimental antisense drugs show some success in
treating certain cancers, autoimmune disease,
infections and Alzheimer’s disease.

Triplex DNA (Three’s a crowd):
It’s a triple helix formed when a third strand
of DNA forms hydrogen bonds with the Purine
bases on one of the helixes.
This extra strand can make the DNA template
inaccessible to normal transcription.
Most drugs based on triplex DNA are made to
block gene sequences that regulate cancer
genes viruses, and immune reactions.

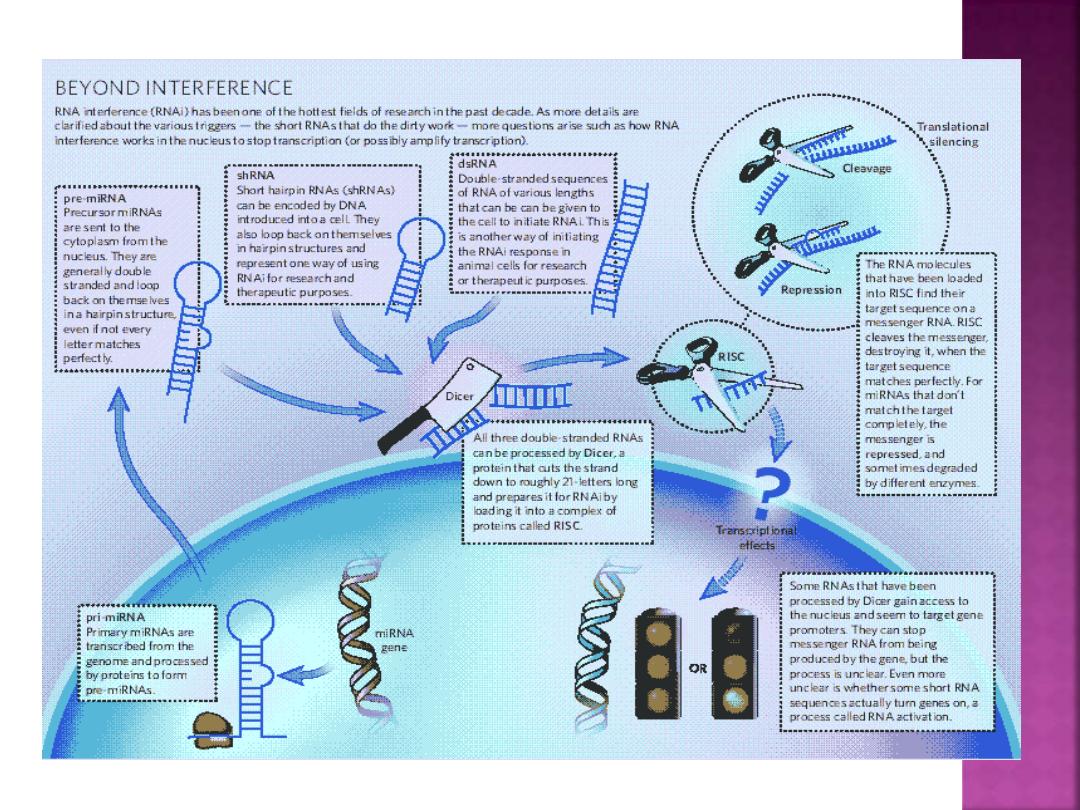
is a mechanism that inhibits or activates gene
expression at the stage of translation or by
hindering the transcription of specific genes
.
RNAi targets include RNA from viruses and
transposons (a form of innate immune response),
and also plays a role in regulating development
and genome maintenance.
Small interfering RNA strands (siRNA)
are key to
the RNAi process, and have complementary
nucleotide sequences to the targeted RNA strand.

Specific RNAi pathway proteins are guided by
the siRNA to the targeted
messenger RNA
(mRNA)
, where they "cleave" the target,
breaking it down into smaller portions that can
no longer be translated into protein.
A type of RNA transcribed from the genome
itself,
microRNA (miRNA
), works in the same
way.


Number of chromosomes
Sex chromosome content
Presence or absence of individual
chromosomes
Nature or extent of chromosomal
aberrations

Any cell with a nucleus
Lymphocytes
Skin cells
Tumor cells
Amniotic cells
Chorionic villi
Rare fetal cells from maternal blood

1. Advanced maternal age (>35 years).
2. A family with a previous child known to have
a chromosomal abnormality.
3. Clinical suspicion of a syndrome caused by a
chromosomal abnormality.
4. Part of males or females infertility screening.
5. To determine sex (gender) of an individual.
6. Unexplained mental retardation.
7. Unexplained growth retardation
8. Some cases of cancer.
9. Miscellaneous conditions.

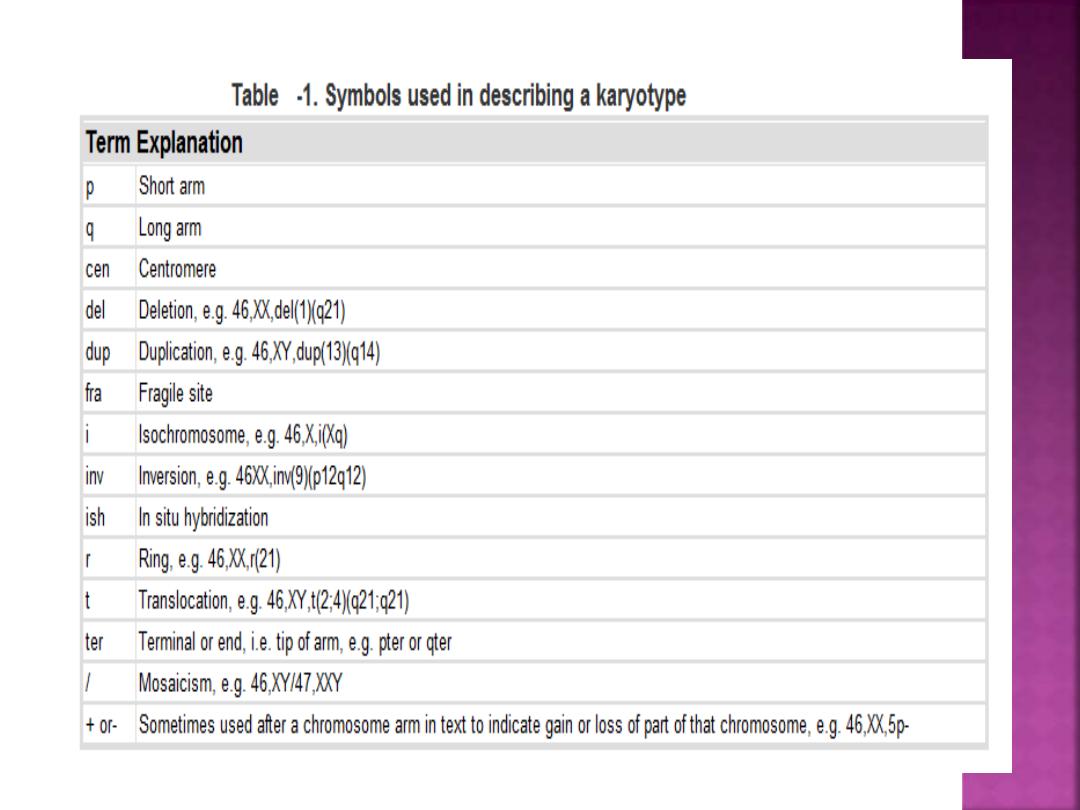
1- writ the chromosome number(46).
2- the sex of the patient (XX or XY).
3- followed by the sign of addition because
there is an extrachromosome.
4- then the number of additional
chromosome.
i.e. :
- 47XY, +21 (male Down's)
- 47 XX, +21 (female Down's)

1-Starting nucleic acid - DNA/RNA
Tissue, cells, blood, hair root,
saliva, semen
2-Heat-stable DNA polymerase
3-Two oligonucleotide primers.
4- Buffer
Tris-HCl (pH 7.6-8.0)
Mg2+
5- Deoxynucleotides
dNTPs (dATP, dCTP, dGTP, dTTP)

Restrication Frgament Length
polymorphism(RFLP).
Random Amplifed polymorphic(RAPD).
Amplify Fragment Length(AFLP).
Real Time PCR.
-Taq Man real-time PCR.
- SYBR Green real-time PCR.
- Molecular beacon real-time PCR.

Conventional PCR.
ELISA PCR.
Reverse Transcription ( RT-PCR).
Nested PCR.
Hot Start PCR.

Detection & diagnosis of diseases on molecular level.
Detection of pathogens especially when applied to
those which are:
- Difficult or costly to culture.
- Slow growing.
- Present in low concentration.
- Dangerous to propagate in the lab.
PCR facilitates the advancement of prenatal
diagnosis of genetic defects such as:
Cystic fibrosis
Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Haemoglobino diseases.

Making a cDNA library. By using Reverse
Trancriptase PCR ( RT-PCR), if one wants to
clone a cDNA from just one mRNA whose
sequence is known.
Paternity testing
Analysis of ancient DNA.
Induction of direct mutagensis for functional
analysis off regions of both genetic & non-
genetic DNA.
Construction of genetic maps.
Cloning .

In forensic cases.
Creation of synthetic DNA.
Analysis of gene expression.
Detection & characterization of mutations.

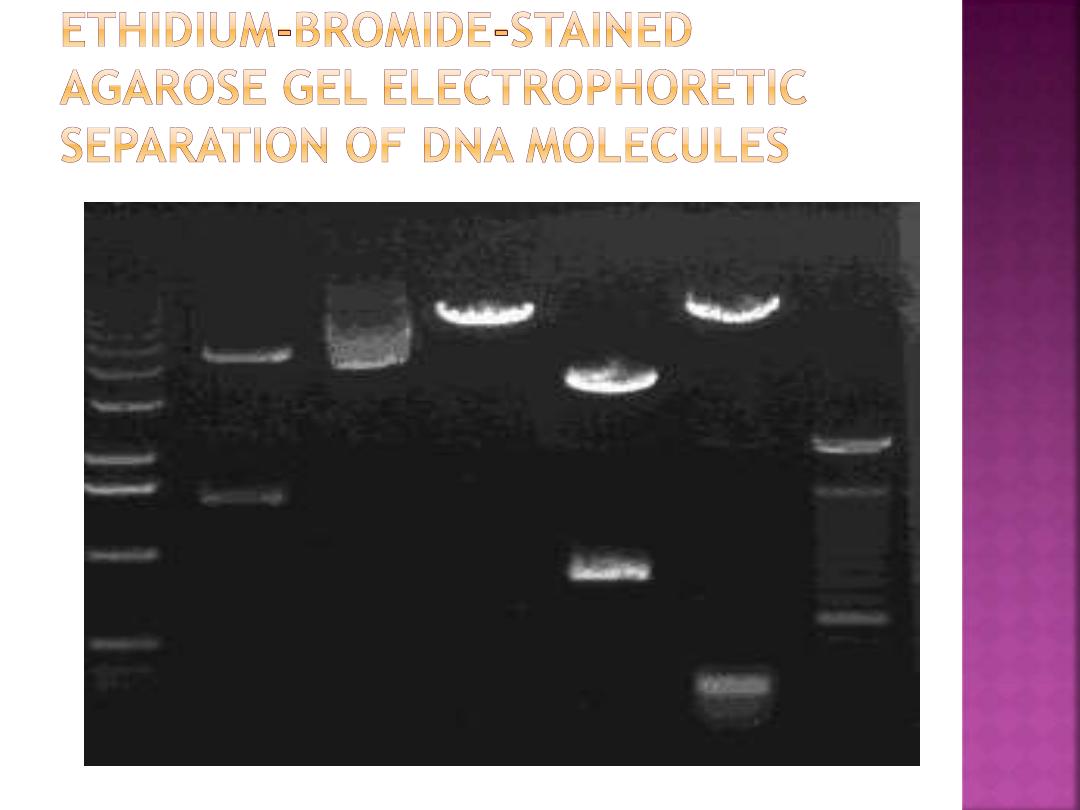
Can produce a readable pattern of DNA
fragments. When samples in gel are
subjected to an electric current,
the DNA
pieces migrate in the gel substrate toward
the positive pole
, forming a pattern based on
fragment size.
The pattern is analyzed by comparing it
against known standards to characterize
genetic similarities among individuals.