
3rd week of developement
Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar
HHDTD Module

Objevtives
1- define gastrulation, primitive node, notochord.
2- describe the developmental changes in 3
rd
week.
3- describe fate map.
4- describe the developmental changes in trophoblast.
Trilaminar Germ Disc
The most characteristic event is Gastrulation, the process that
establishes all three germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, and
endoderm) in the embryo.
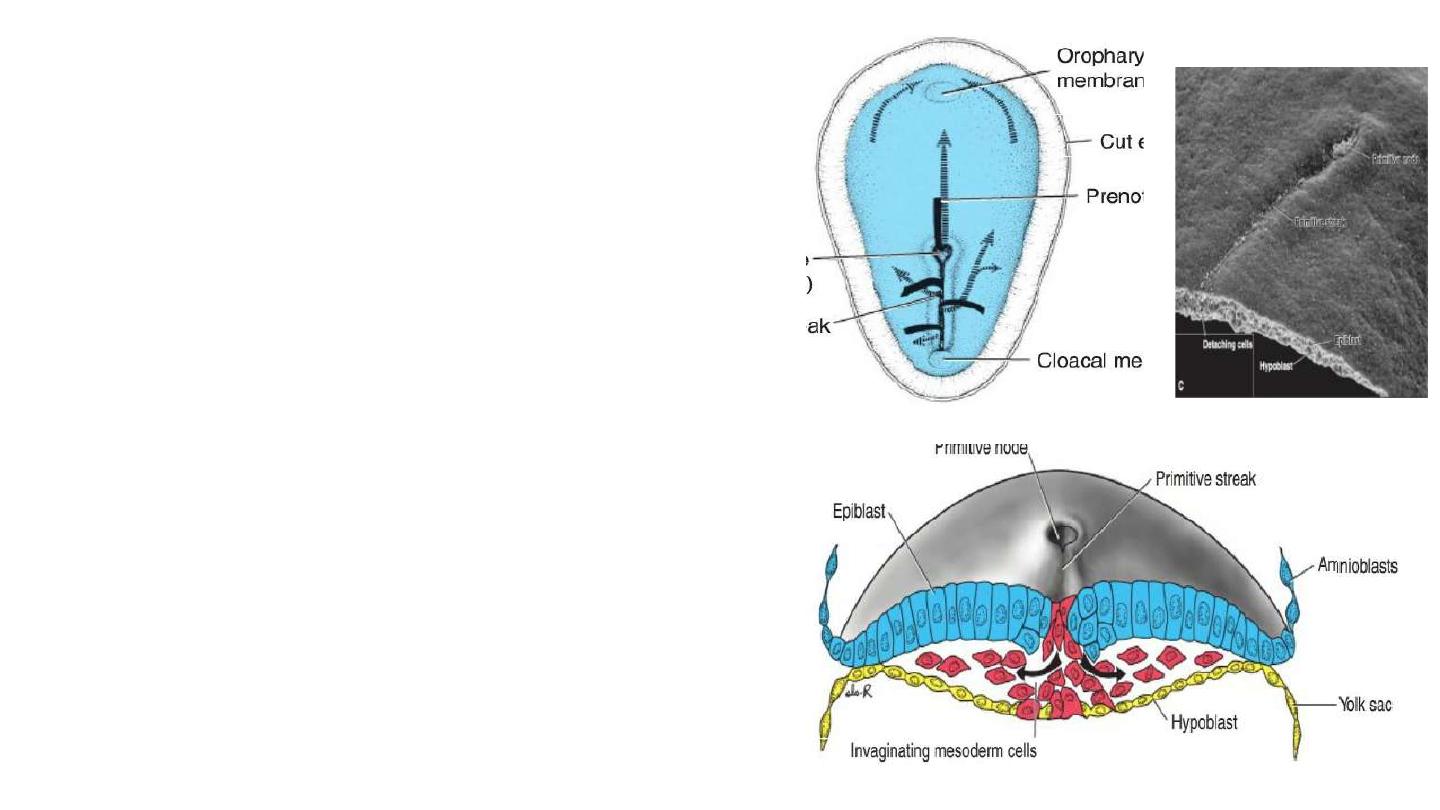
1- Gastrulation begins with formation of the Primitive streak on the
surface of the epiblast.
2- Primitive node: is the cephalic end of the streak, consists of a
slightly elevated area surrounding the small Primitive pit.
Trilaminar Germ Disc
3- Invagination: inward movement of cells of the epiblast
toward the primitive streak, then detach and slip beneath
epiblast.
4- Invaginated cells will end as follows:
a- some displace hypoblast, forming the endoderm.
b- some will lie between epiblast and endoderm, forming
mesoderm.
c- remaining cells of epiblast will form ectoderm.
Thus, the epiblast, through the process of
gastrulation, is the source of all of the germ
layers, and cells in these layers will give rise to all
of the tissues and organs in the embryo.
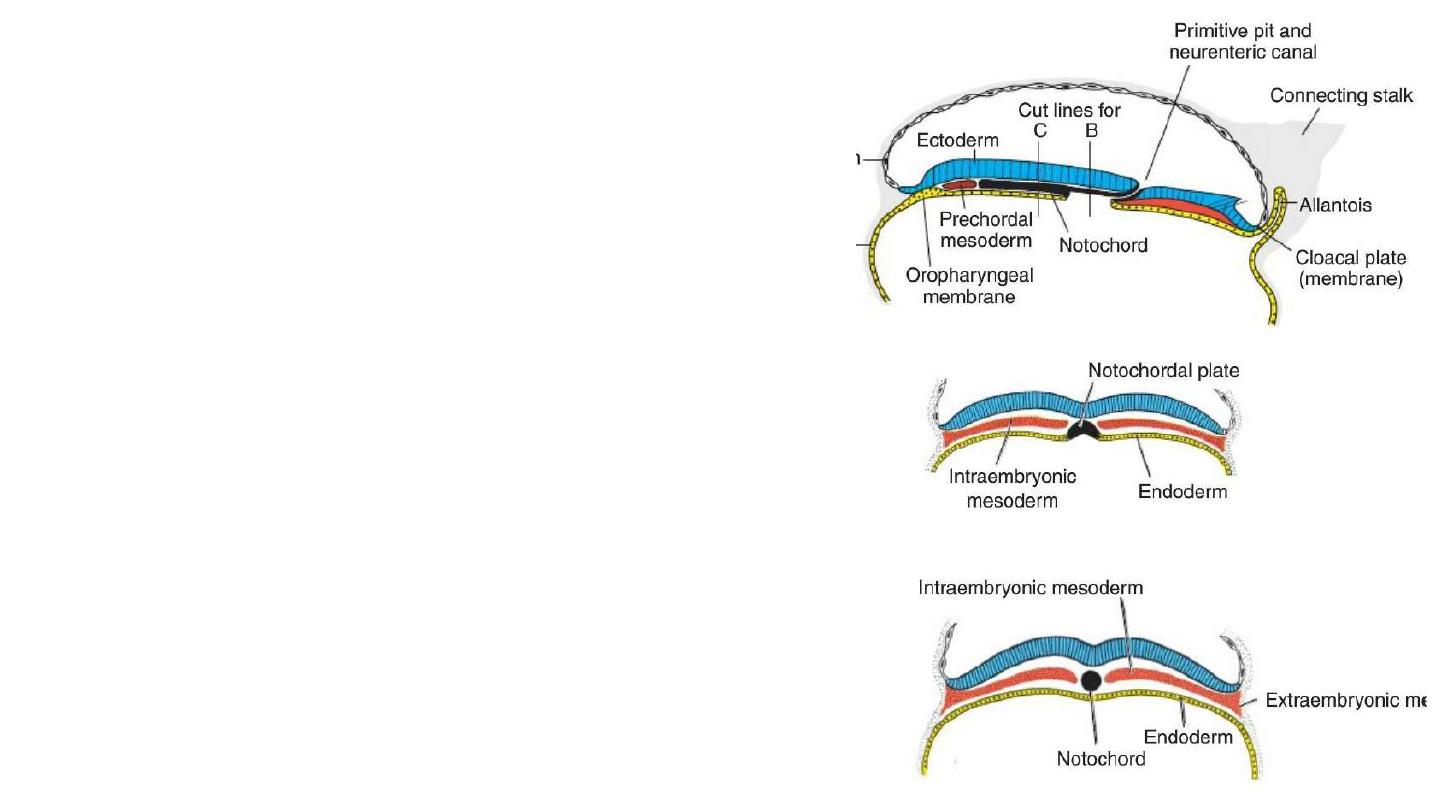
Formation of the Notochord
At day 16-17, Prenotochordal cells invaginating in the primitive pit move
forward and intercalated in the endoderm (hypoblast) to form
notochordal plate.
Then they detach from endoderm to form solid cord of cells; the
definitive notochord.
Notochord underlies the neural tube and serves as the basis for the axial
skeleton.
Prechordal plate: is a mesodermal cells that migrate ahead of
notochord. They assist in forebrain induction.
Neurenteric canal: is a temporary canal at the primitive pit, connects
amniotic and yolk sac cavities.
Buccopharyngial membrane: a thin membrane where ectoderm and
endoderm come in direct contact. It forms a septum between primitive
mouth and pharynx.
Cloacal membrane is formed at the caudal end of the embryonic disc. It
consists of tightly adherent ectoderm and endoderm cells with no
intervening mesoderm.
Allantoenteric diverticulum , or Allantois: a small diverticulum that
extends into the connecting stalk, from the posterior wall of the yolk sac.
It appears around the 16th day of development .
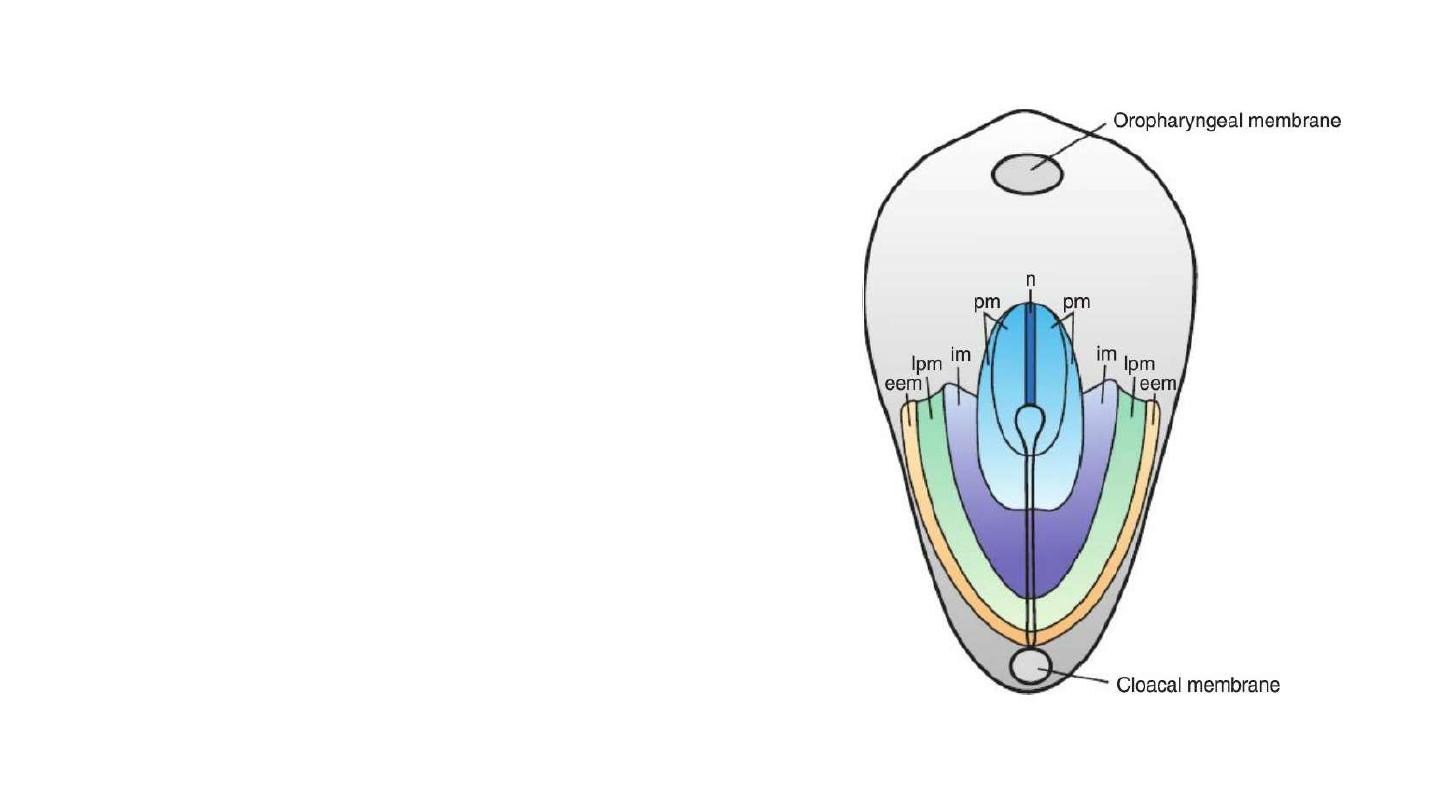
Fate Map Established During Gastrulation
Migrating epiblast cells are mapped, and their ultimate fates
have been determined.
1- Cells that ingress through the cranial region of the node
become notochord.
2- Those migrating at the lateral edges of the node and from
the cranial end of the streak become Paraxial mesoderm.
3- Cells migrating through the midstreak region become
Intermediate mesoderm.
4- Those migrating through the more caudal part of the
streak form Lateral plate mesoderm.
5- Cells migrating through the caudalmost part of the streak
contribute to extraembryonic mesoderm [the other source of
this tissue is the primitive yolk sac (hypoblast).

Growth of the Embryonic Disc
The embryonic disc gradually becomes elongated, with a broad cephalic and
a narrow caudal end.
Expansion of the embryonic disc is cephalo-caudal.
Invagination of surface cells in the primitive streak and migration continues
until the end of the fourth week.
Later, the primitive streak shows regressive changes, rapidly shrinks, and
soon disappears.
In the cephalic part, germ layers begin their specific differentiation by the
middle of the third week.
In the caudal part, differentiation begins by the end of the fourth week.
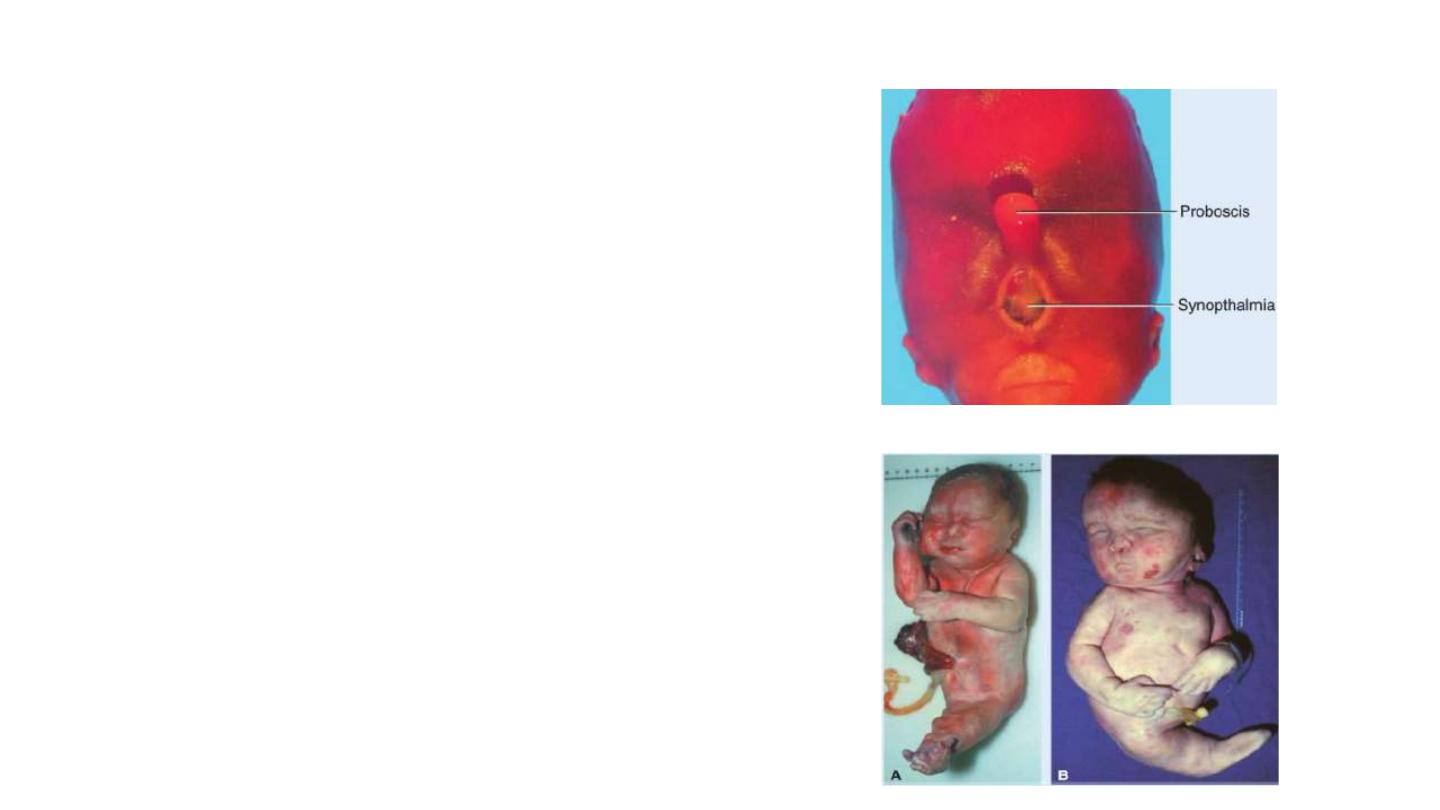
Clinical correlates
1- Teratogenesis Associated with Gastrulation:
a- high doses of alcohol at this stage kill cells in the anterior
midline of the germ disc, producing a deficiency of the midline
in craniofacial structures and resulting in holoprosencephaly.
b- Gastrulation itself may be disrupted by genetic
abnormalities and toxic insults. In caudal dysgenesis
(sirenomelia) , insufficient mesoderm is formed in the
caudalmost region of the embryo. Affected individuals have
hypoplasia and fusion of the lower limbs, vertebral
abnormalities, renal agenesis, imperforate anus, and
anomalies of the genital organs.
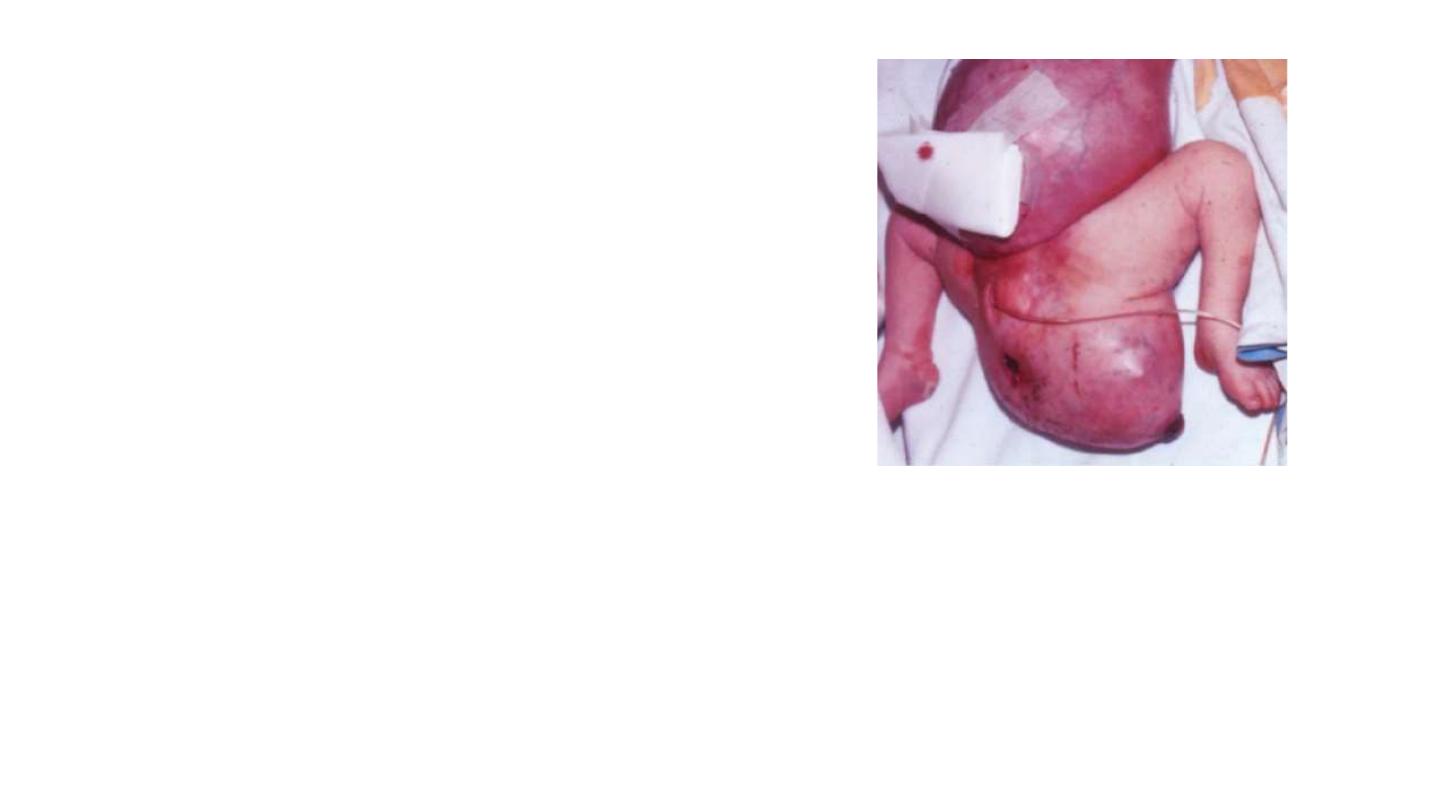
Clinical correlates
2-Tumors Associated with Gastrulation
Sometimes, remnants of primitive streak persist in the
sacrococcygeal region. These clusters of pluripotent cells
proliferate and form tumors, known as sacrococcygeal
teratomas , that commonly contain tissues derived from all
three germ layers .
3- Birth defects associated with laterality
Situs inversus: is a condition in which transposition of the
viscera in the thorax and abdomen occurs, due to failure to
properly establish the L-R axis.
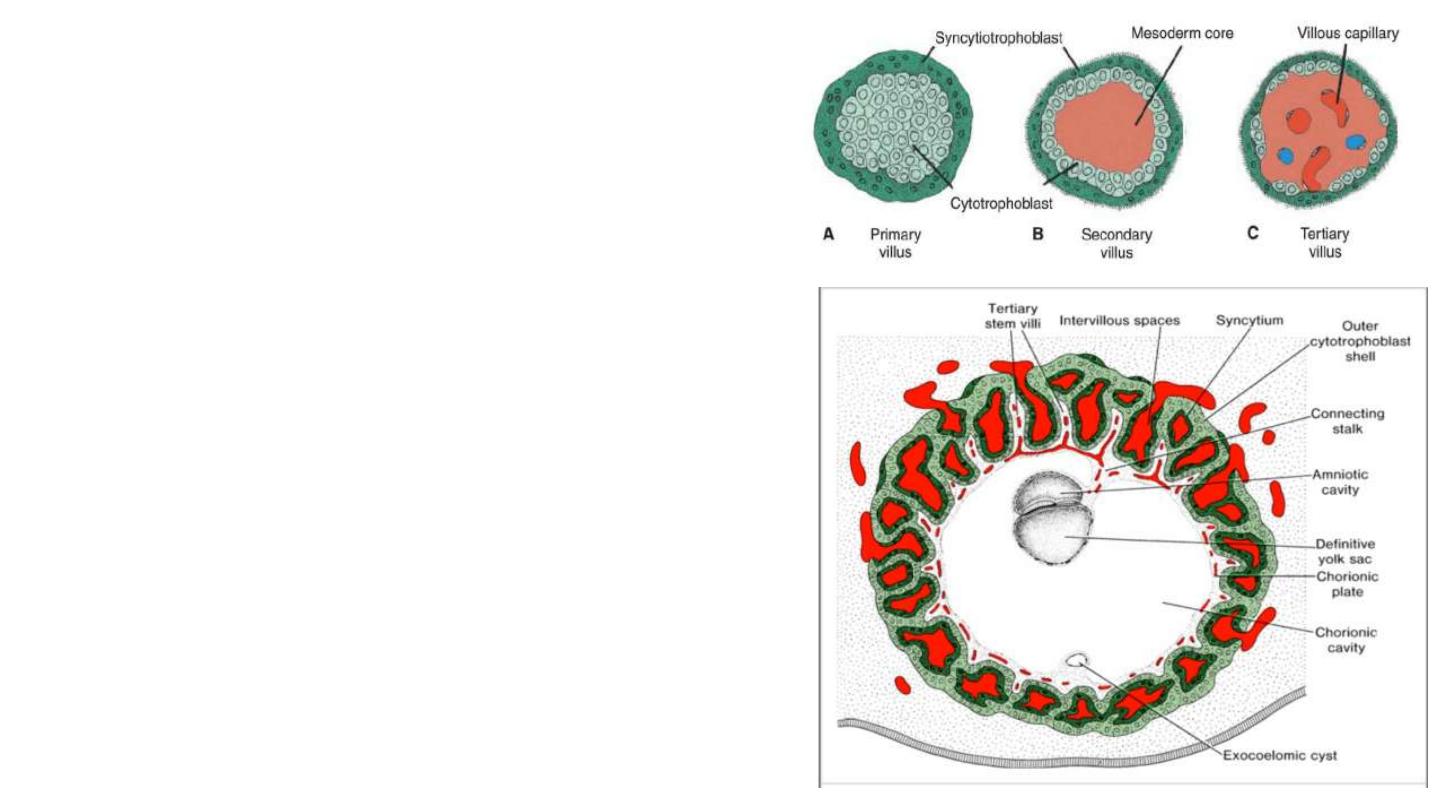
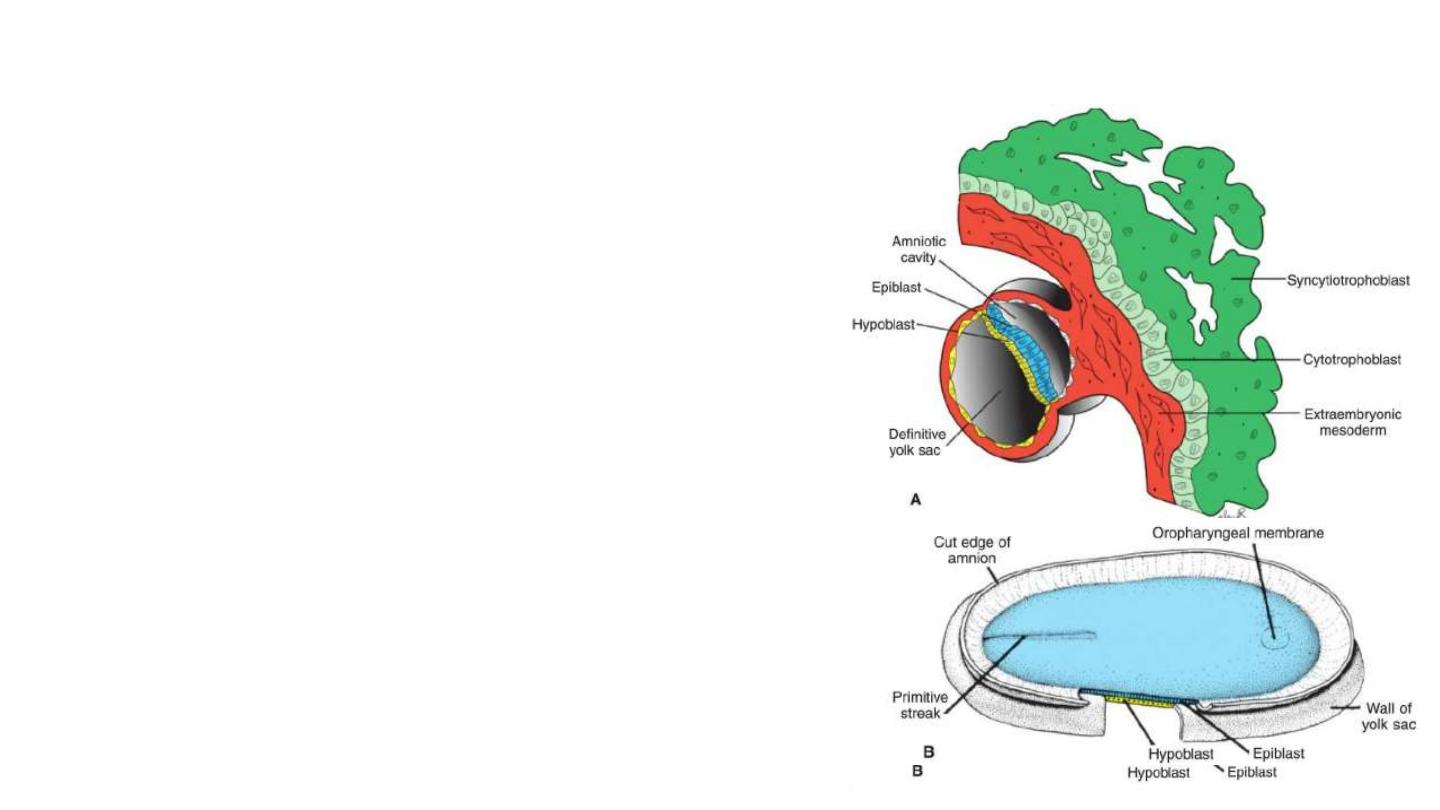
Further Development of the Trophoblast
1- Formation of secondary villus: where mesodermal cells penetrate
the core of primary villi and grow toward the decidua.
2- Formation of tertiary or definitive placental villus: By the end of the
third week, mesodermal cells differentiate into blood cells and small
blood vessels, forming the villous capillary system.
3- Capillaries in tertiary villi make contact with the intraembryonic
circulatory system, connecting the placenta and the embryo.
4- formation of outer cytotrophoblast shell: cytotrophoblastic cells in
the villi penetrate progressively into the overlying syncytium until they
reach the maternal endometrium and establish contact with similar
extensions of neighboring villous stems. This shell gradually surrounds
the trophoblast entirely and attaches the chorionic sac firmly to the
maternal endometrial tissue.
5- The chorionic cavity, meanwhile, becomes larger, and by the19th or
20th day, the embryo is attached to its trophoblastic shell by a narrow
connecting stalk . The connecting stalk later develops into the umbilic
cord.
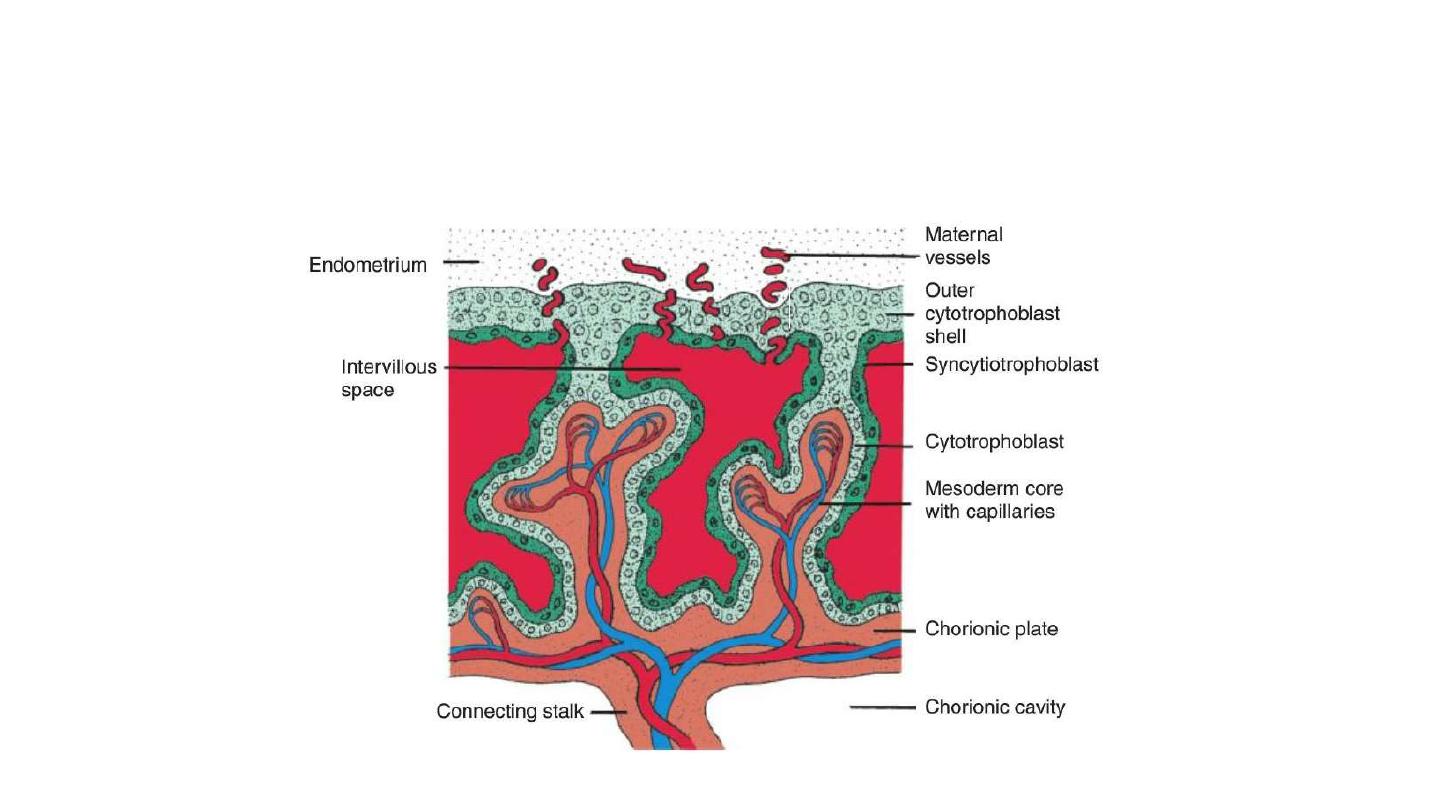
At the end of fourth week, maternal vessels penetrate cytotrophoblastic shell to
enter intervillous space.
