
Embryonic period
Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar
HHDTD Module

Objectives
1- Define embryonic period.
2- Identify the derivatives of ectoderm germ layer.
3- Define neurulation, neural crest and its derivatives.
4- Identify the derivatives of mesoderm germ layer.
5- Define paraxial, intermediate, and lateral plate
mesoderm.
6- Define vasculogenesis, and angiogenesis.
7- Identify the derivatives of endoderm germ layer.
8- Describe the appearance of an eight weeks embryo.
9- Recognize some clinical correlates during
organogenesis

Embryonic period
The embryonic period, or period of
Organogenesis, occurs from the third to the
eighth weeks of development and is the time
when each of the three germ layers,
ectoderm,
mesoderm
, and
endoderm
, gives
rise to a number of specific tissues and
organs.

Derivatives of the Ectodermal Germ
Layer/Neurulation
1- Appearance of the notochord and prechordal
mesoderm.
2- Formation of neural plate,which will form
neuroectoderm, which induces neurulation.
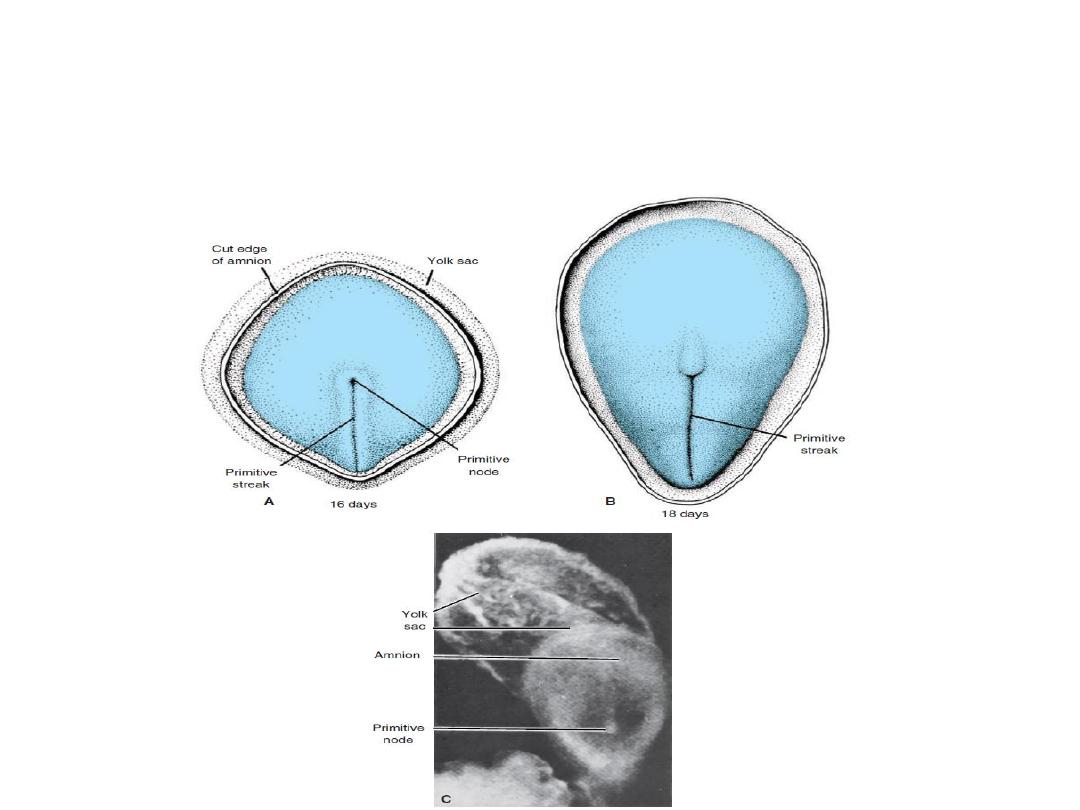
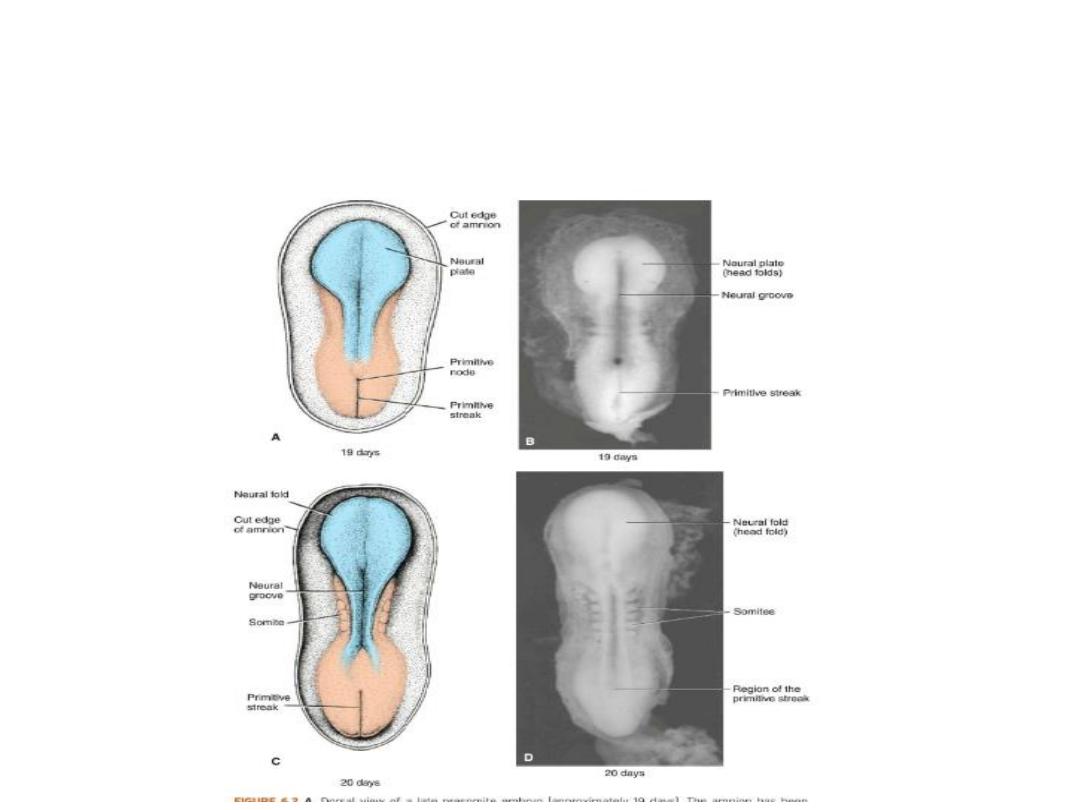
3- Neurulation is the process whereby the neural plate
forms the neural tube.
4- By closure of neural tube , central nervous system is
formed.
Derivatives of the Ectodermal Germ
Layer/Neurulation
Derivatives of the Ectodermal Germ
Layer/Neurulation
Derivatives of the Ectodermal Germ
Layer/Neurulation
Derivatives of the Ectodermal Germ
Layer/Neurulation
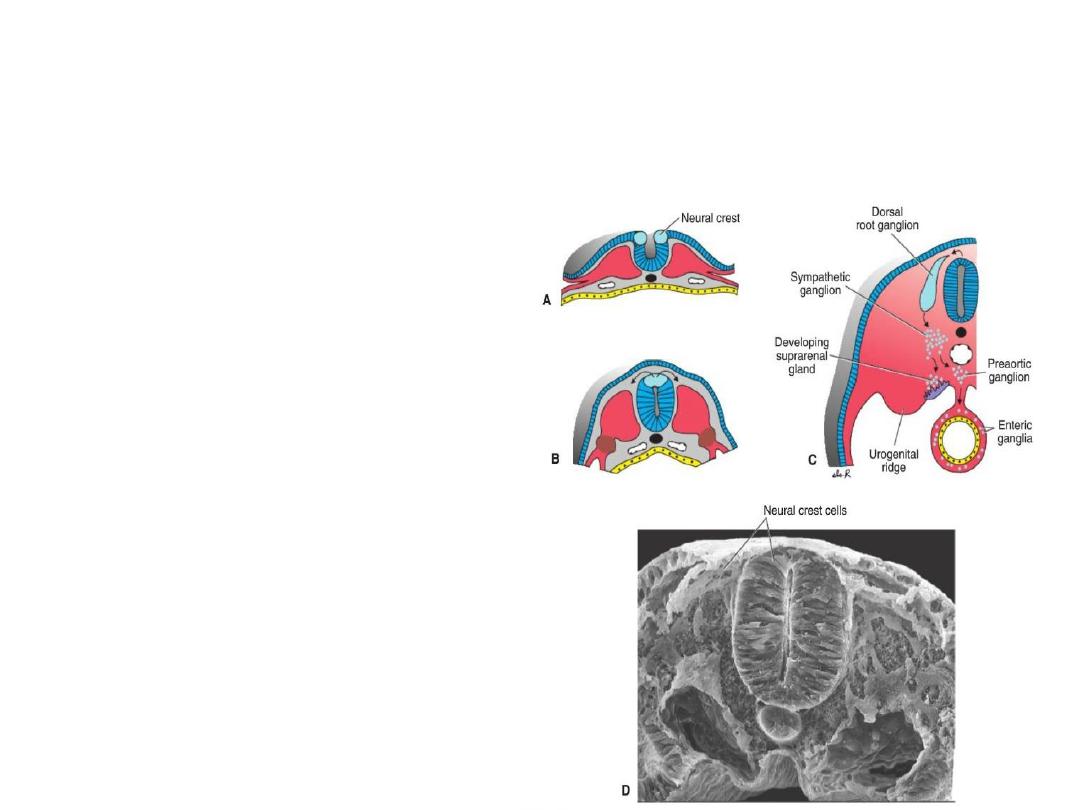
Derivatives of the Ectodermal Germ
Layer/Neural crest
Neural crset cells are
derived from lateral
borer of
neuroectoderm. They
migrate to the
mesoderm.

Derivatives of the Ectodermal Germ
Layer/Neural crest
Derivatives of neural crest cells:
Melanocytes in the skin and hair follicles,
sensory ganglia, sympathetic and enteric
neurons, Schwann cells, and cells of the
adrenal medidla, craniofacial skeleton as well
as neurons for cranial ganglia, glial cells, and
melanocytes.
Derivatives of the Ectodermal Germ
Layer/Neural crest

Derivatives of the Ectodermal Germ
Layer
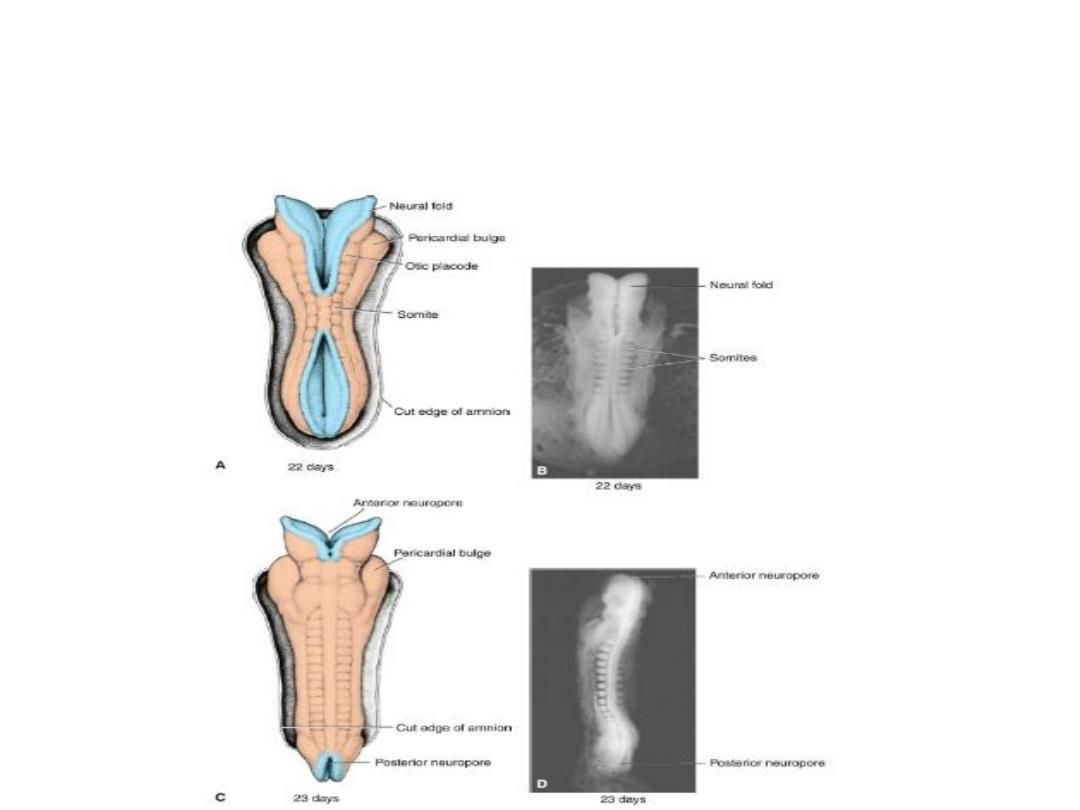
By the time the neural tube is closed, two
bilateral ectodermal thickenings, the otic
placodes and the lens placodes, become visible
in the cephalic region of the embryo(future
ear and eye).
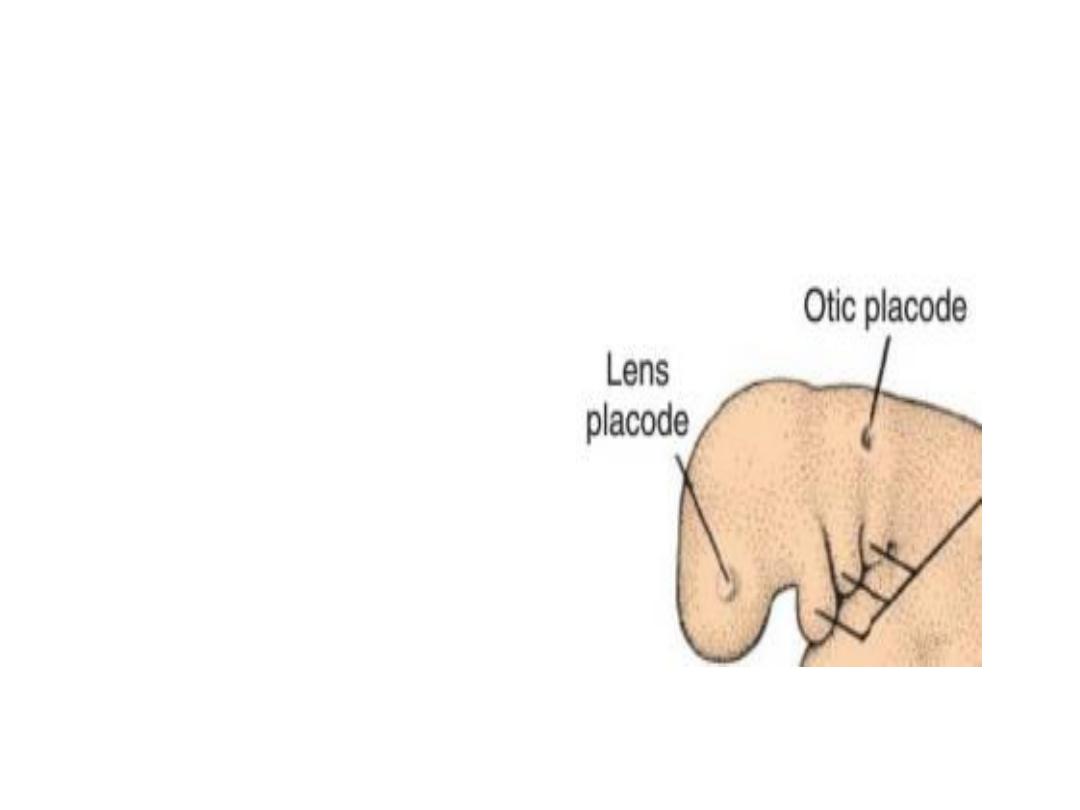
Derivatives of the Ectodermal Germ
Layer
By the time the neural
tube is closed, two
bilateral ectodermal
thickenings, the otic
placodes and the lens
placodes, become
visible in the cephalic
region of the
embryo(future ear and
eye).
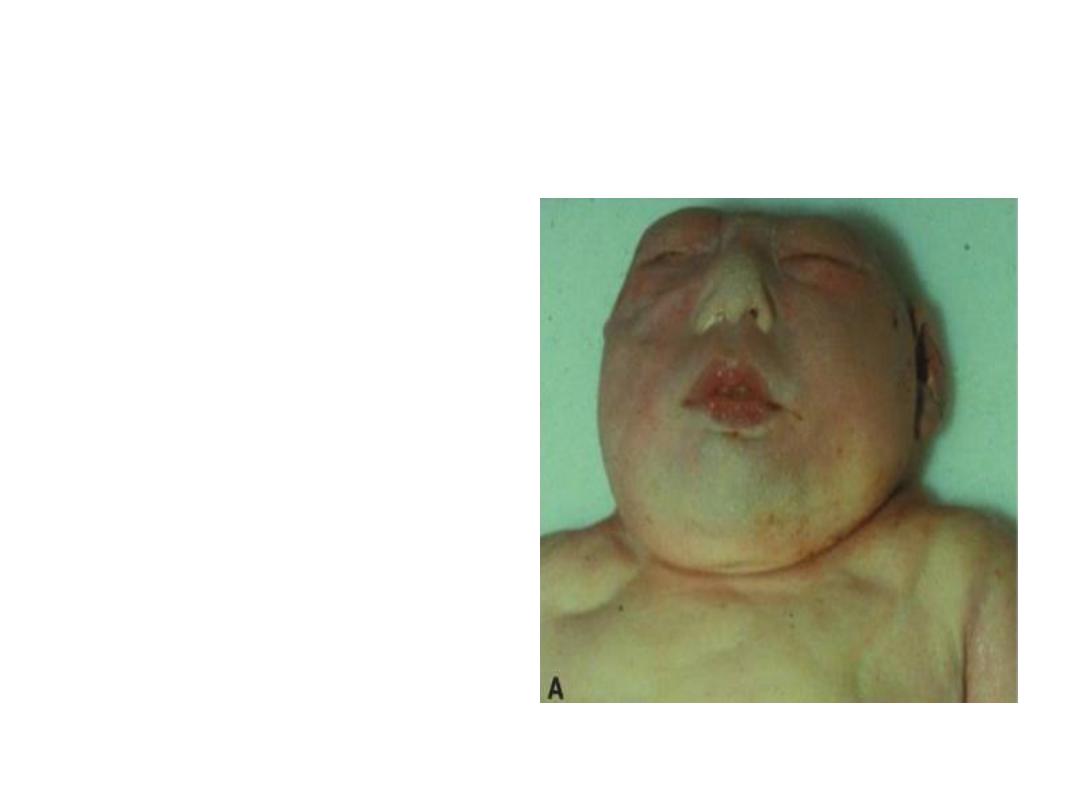
Clinical correlates
Neural tube defects:
Occur when neural tube
fails to close.
1- If failure is clise to
cranial region, the
defect is called
anencephaly.
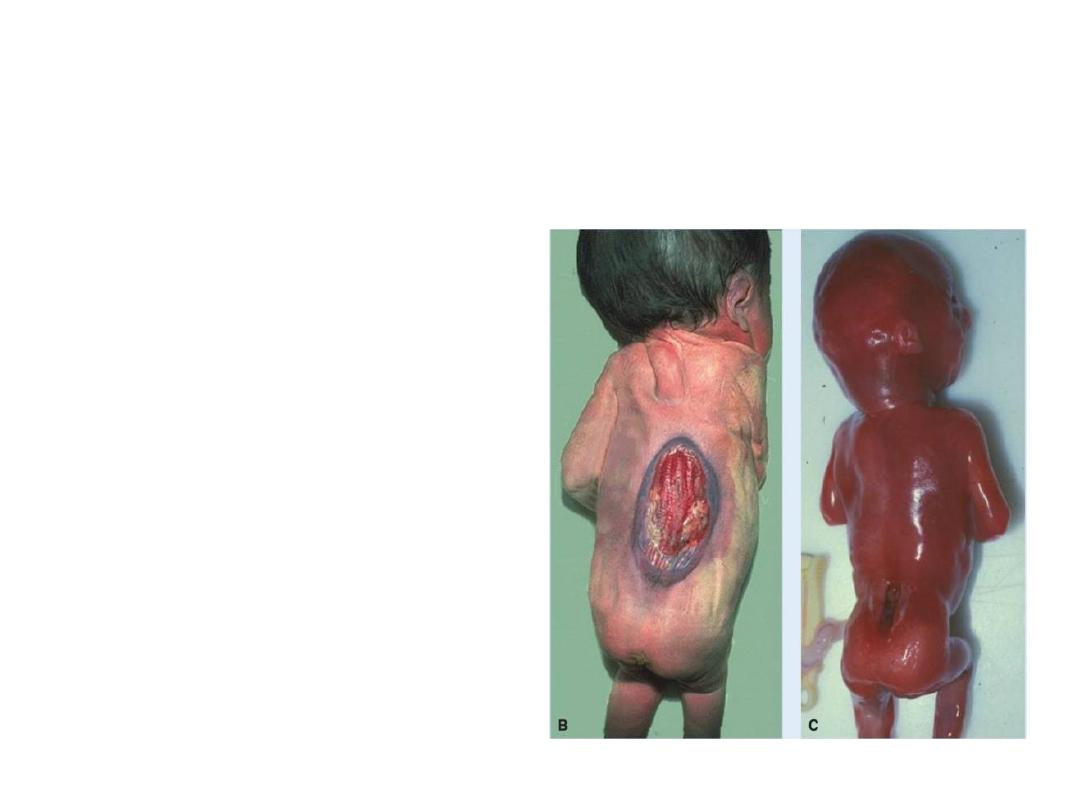
Clinical correlates
Neural tube defects:
Occur when neural tube
fails to close.
2- If failure is from cervical
region down, it is called
spina bifida

Folic acid
administration during
pregnency reduces the rate of NTD
up to 70%, if given in a dose of 400
µg/ day.
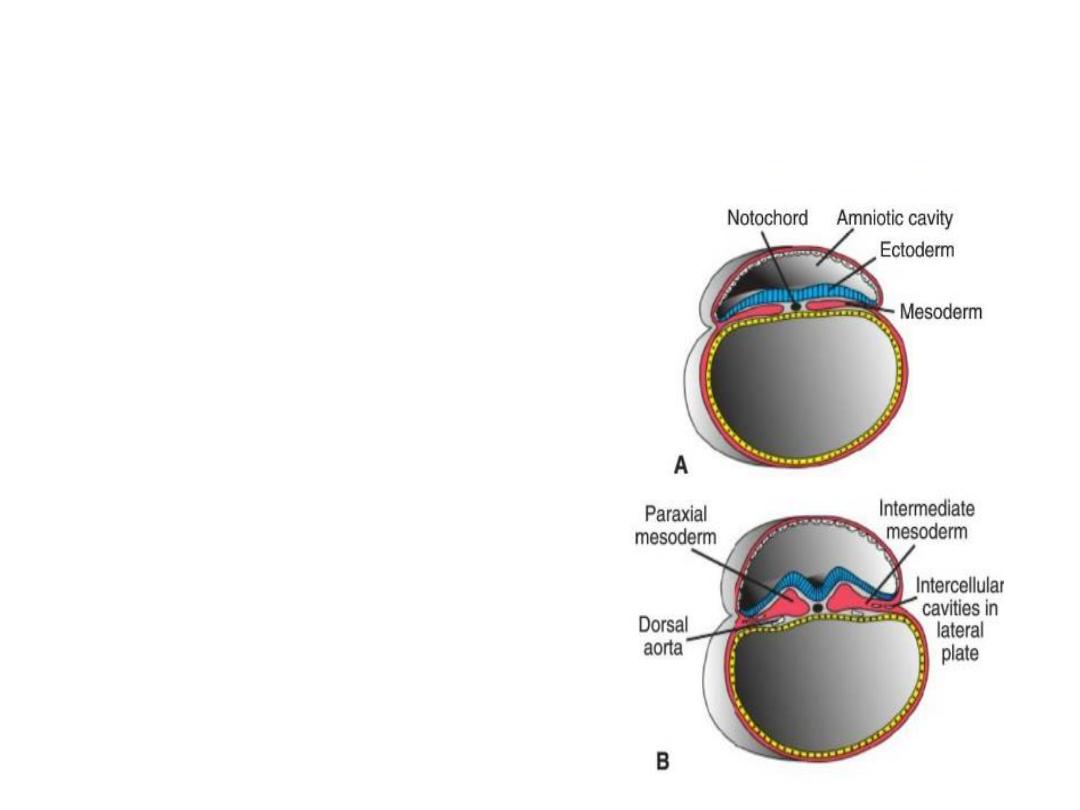
Derivatives of the Mesodermal Germ
Layer
At day 17, mesoderm will
form three groups of cells:
1- Paraxial mesoderm: a
thickened plate of tissue
close to the midline.
2- lateral plate : a thin layer
of mesoderm cell found on
lateral sides.
3- Intermediate mesoderm:
connects paraxial and
lateral plate mesoderm.
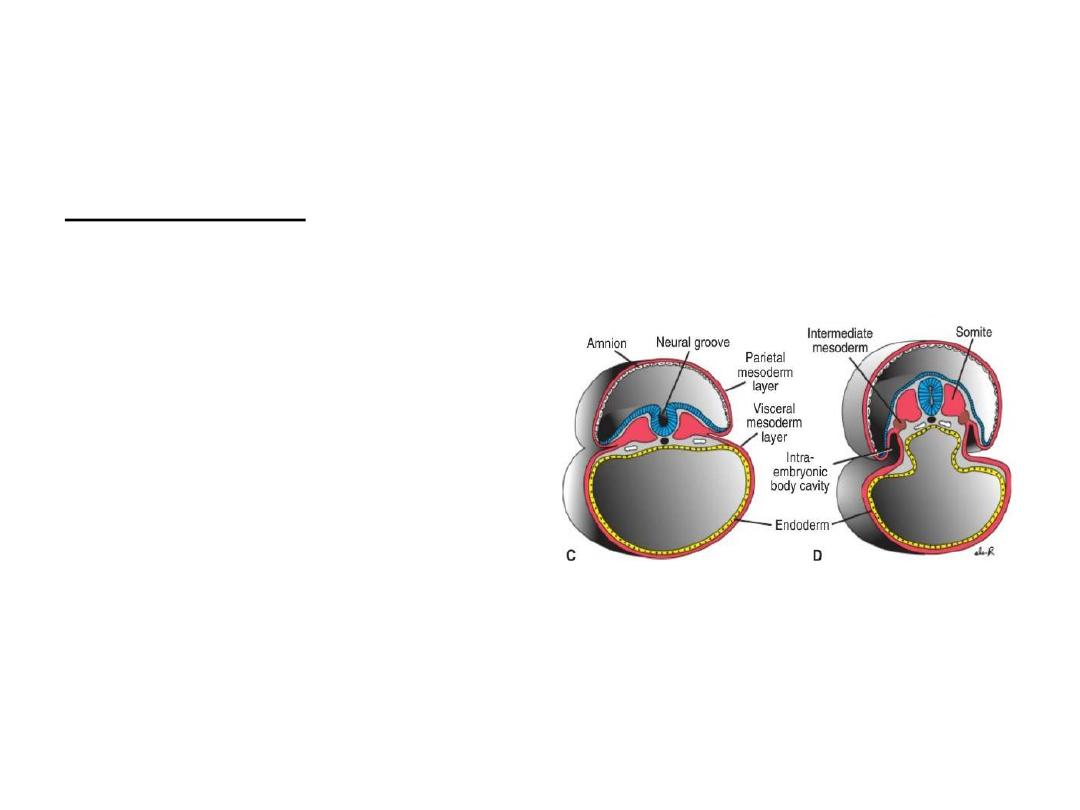
Derivatives of the Mesodermal Germ
Layer
Paraxial Mesoderm
At the beginning of third week
somitomeres appear.
In the head region,
somitomeres form in
association with
segmentation of the neural
plate into neuromeres and
contribute to mesenchyme
in the head
Bellow head region, caudally,
somitomeres further
organize into somites.
.
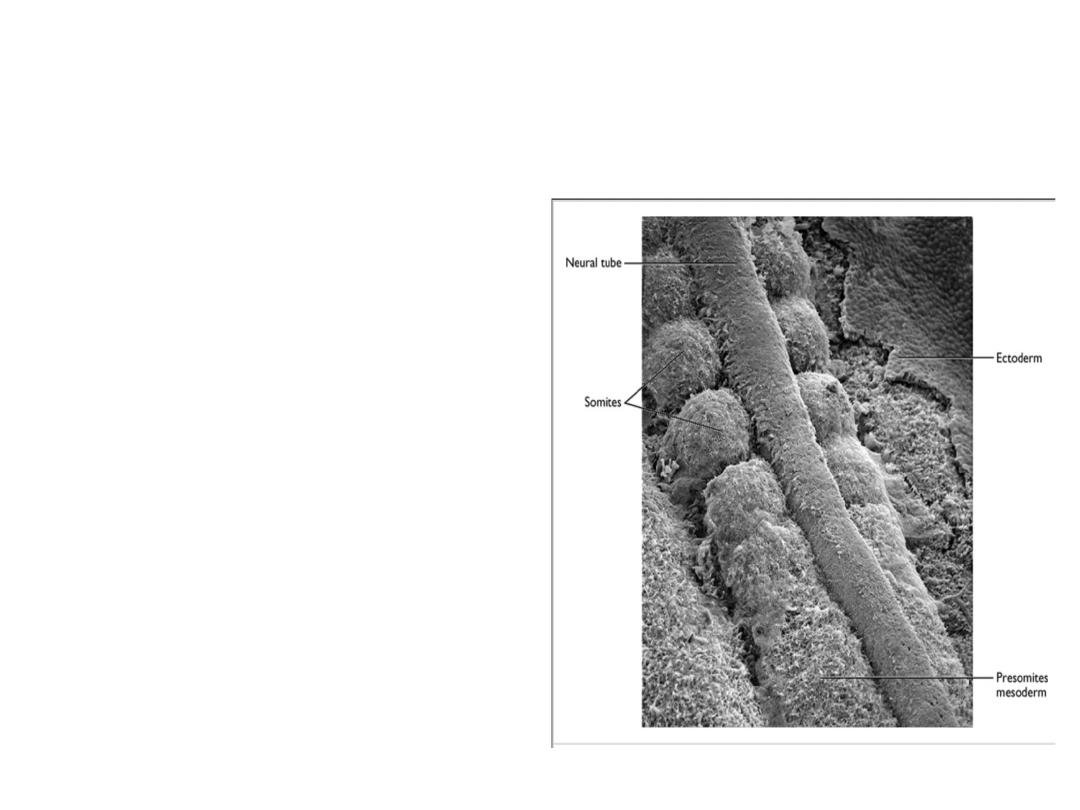
Derivatives of the Mesodermal Germ
Layer
at the end of the fifth week,
42 to 44 pairs are present
. There are 4 occipital, 8
cervical, 12 thoracic, 5
lumbar, 5 sacral, and 8 to
10 coccygeal pairs. The
first occipital and the last
five to seven coccygeal
somites later disappear,
while the remaining
somites form the axial
skeleton .
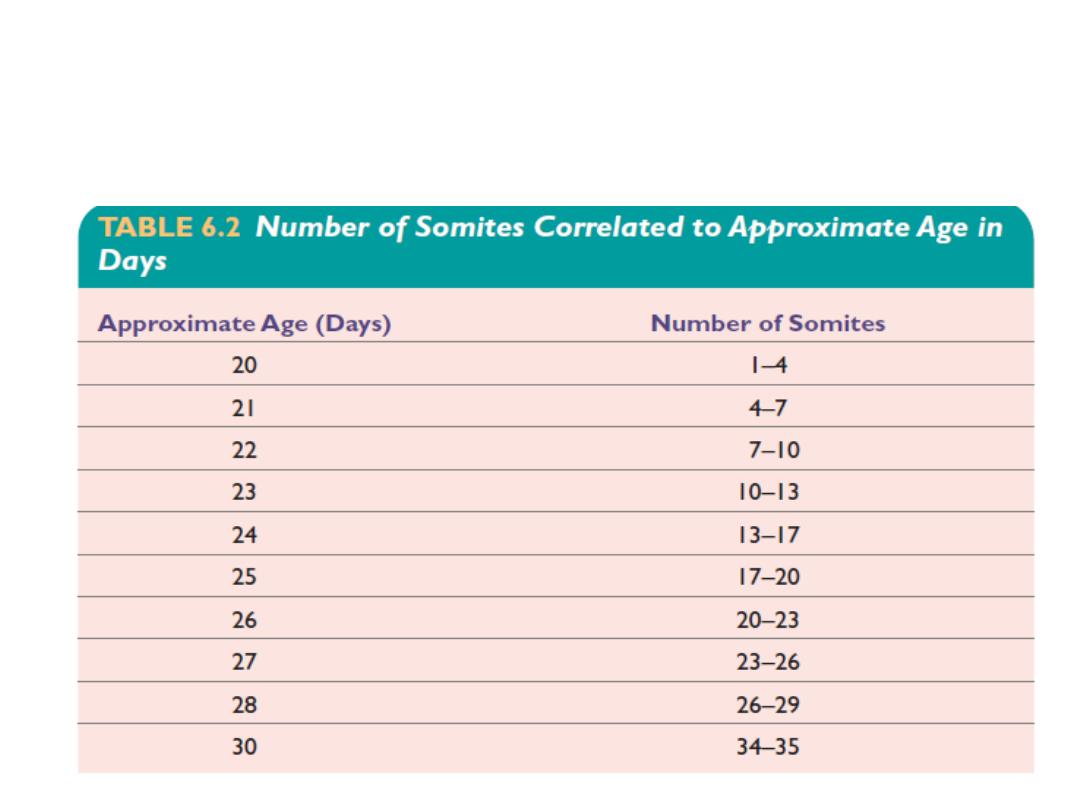
the age of an embryo can be accurately determined
during this early time period by counting somites
.
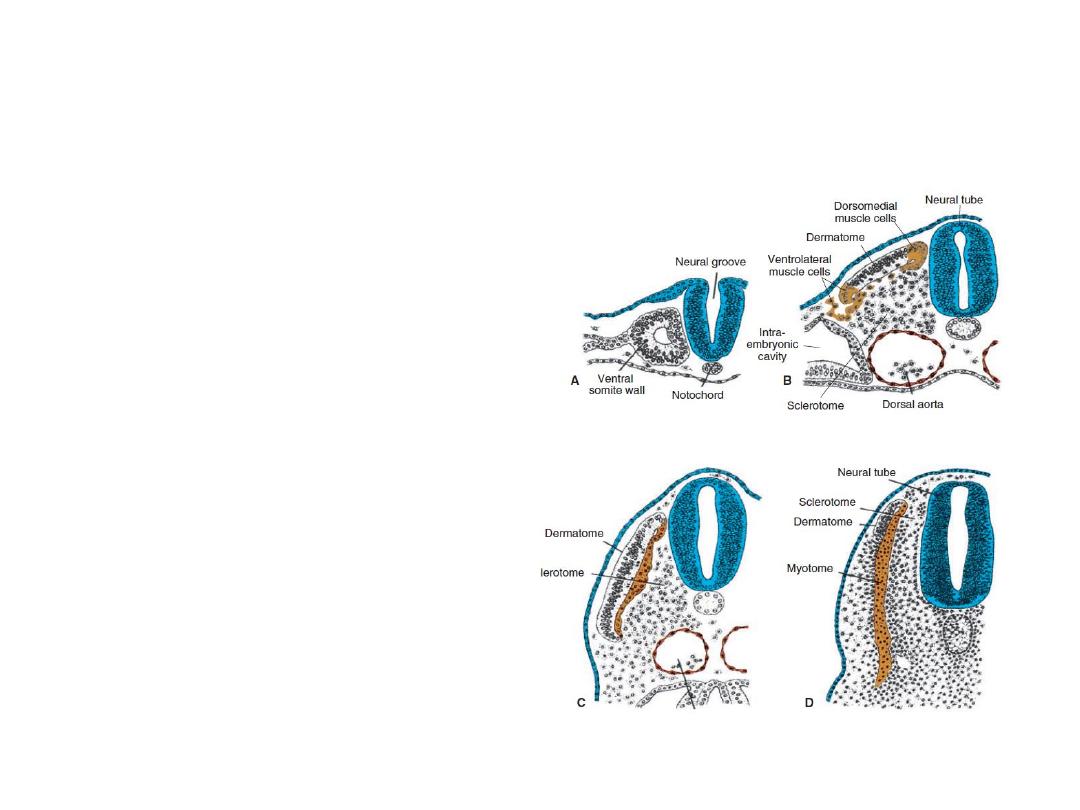
Derivatives of the Mesodermal Germ
Layer
Each somite forms its own
sclerotome (the tendon
cartilage and bone
component), its own
myotome (providing the
segmental muscle
component), and its
own dermatome ,
which forms the dermis
of the back.
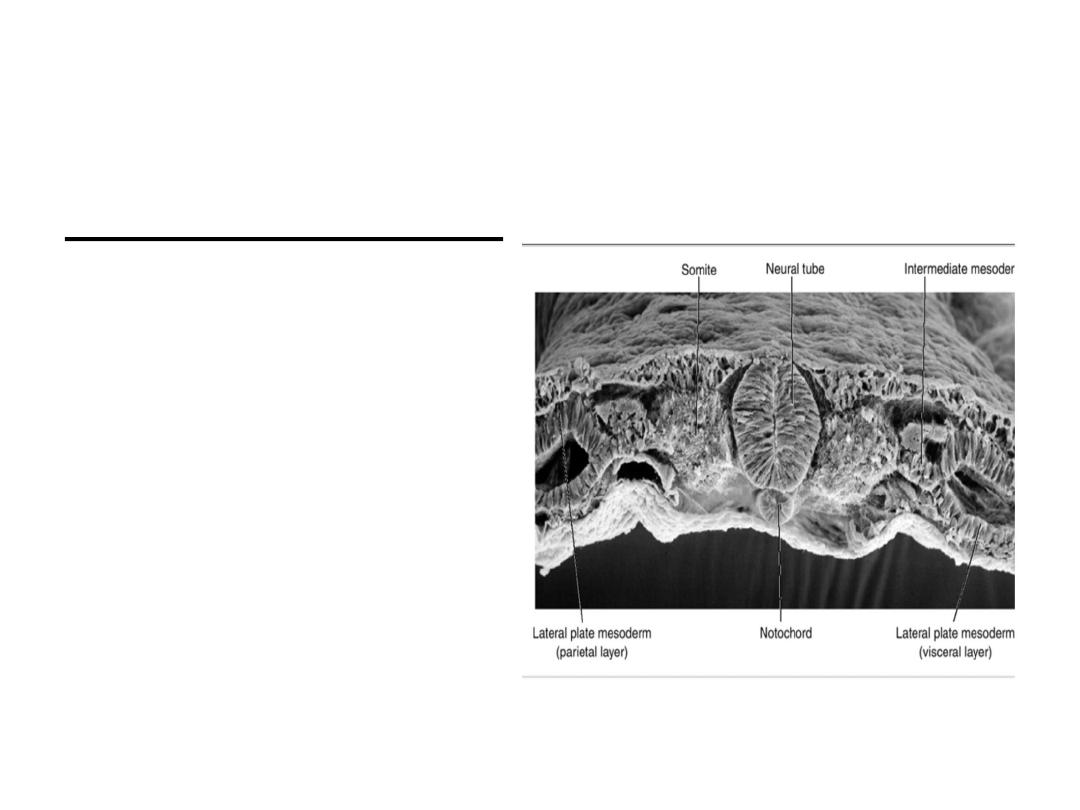
Derivatives of the Mesodermal Germ
Layer
Intermediate Mesoderm:
differentiates into
urogenital structures;
kidneys, gonads, and their
ducts (but not the
bladder).
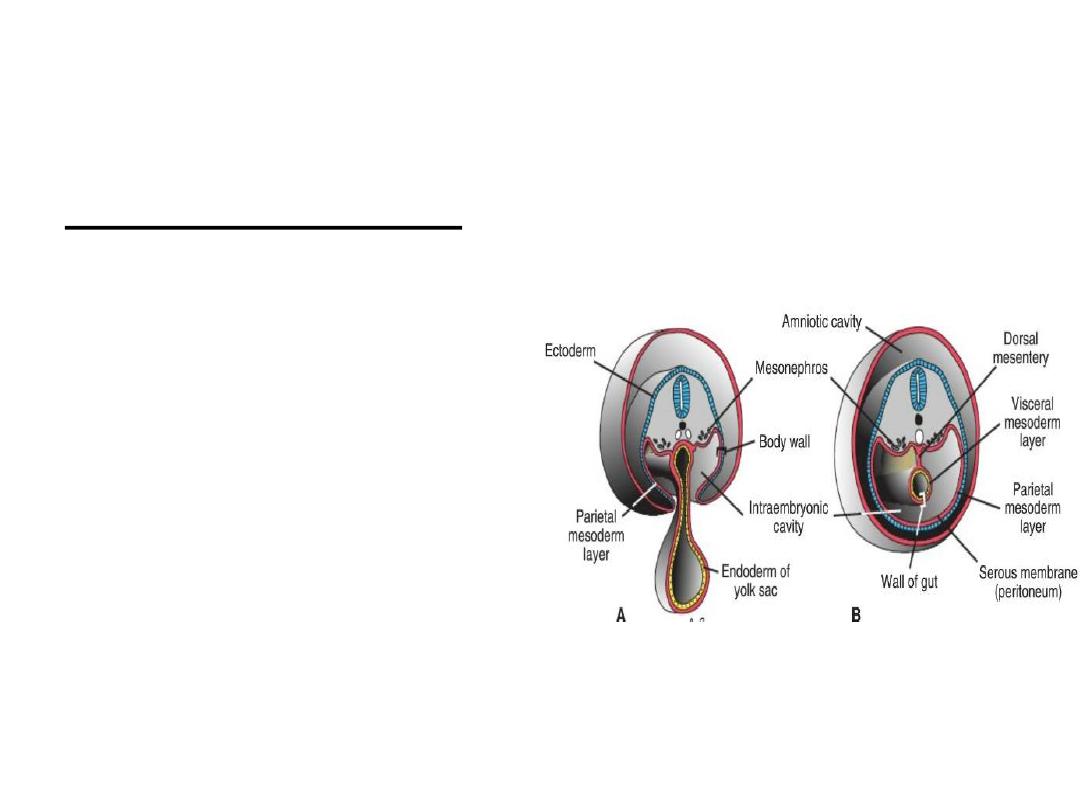
Derivatives of the Mesodermal Germ
Layer
Lateral Plate Mesoderm:
splits into parietal and
visceral layers.
Parietal layer: forms lateral
and ventral body wall.It
also forms mesothelial
membrans line
peritoneal, pleural, and
pericardial cavities
Visceral layer: forma wall of
the gut. It also forms a
thin serous membrane
around each organ.
Derivatives of the Mesodermal Germ
Layer
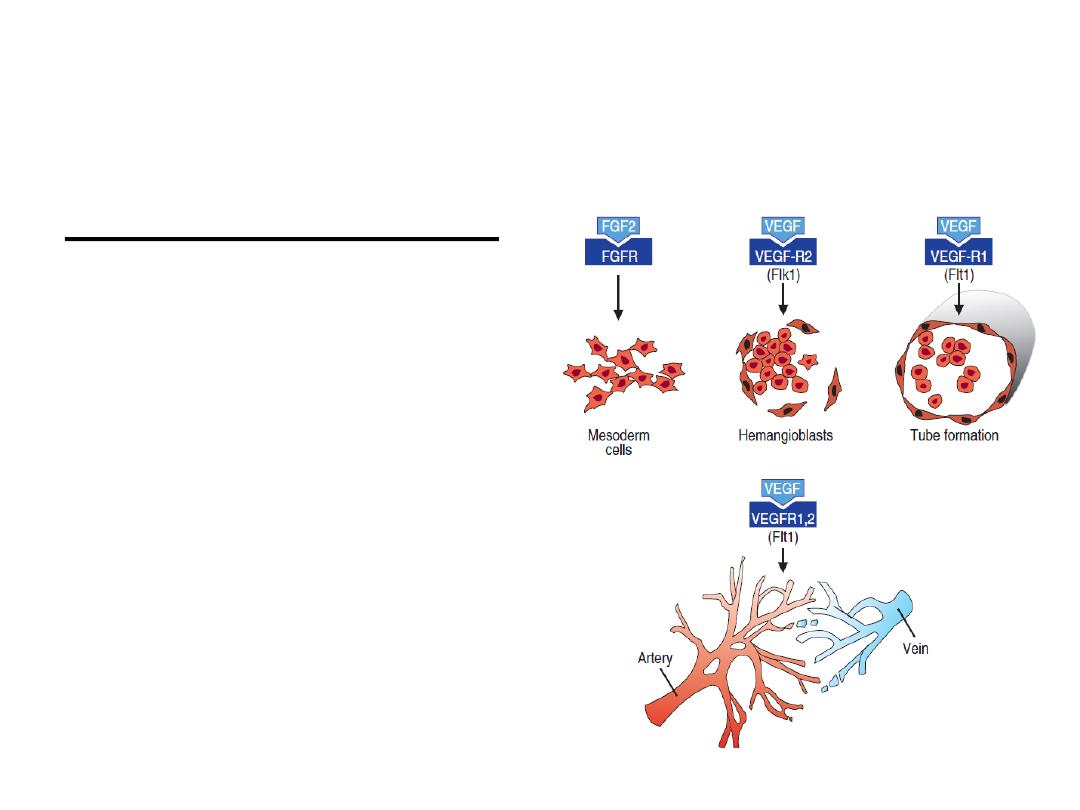
Blood and Blood Vessels:
form in two ways:
vasculogenesis, and
angiogenesis.
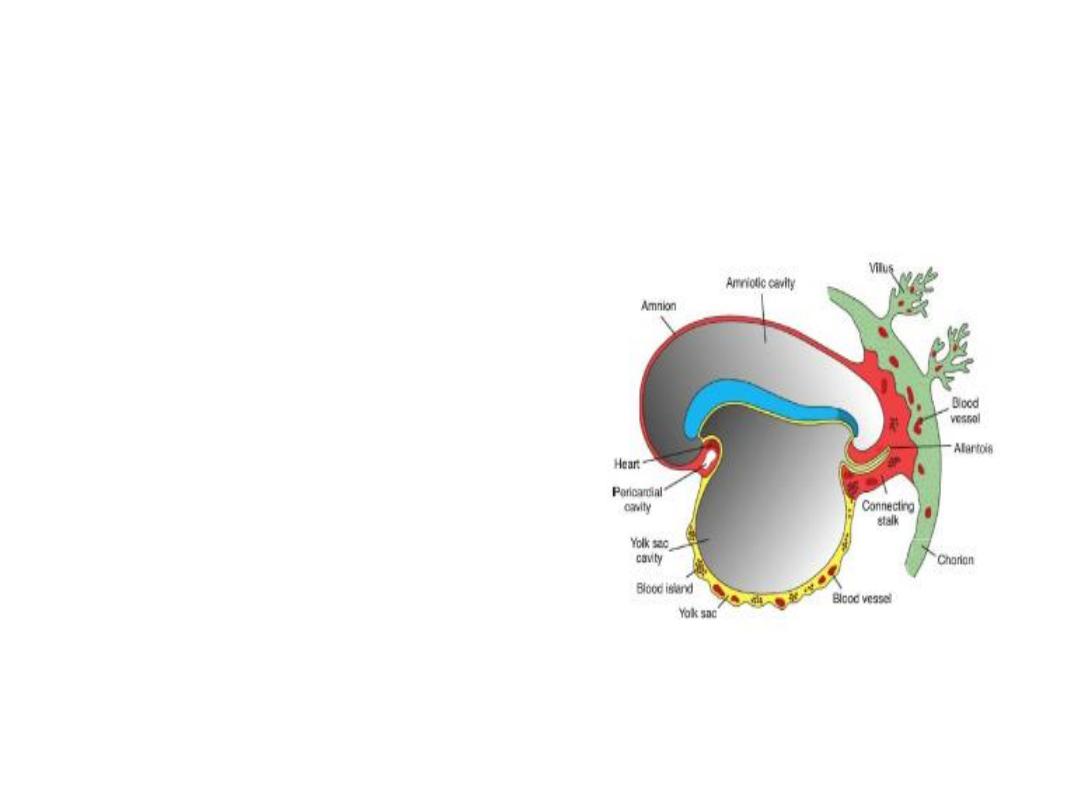
Derivatives of the Mesodermal Germ
Layer
The first blood islands
appear in mesoderm
surrounding the wall of
the yolk sac at 3 weeks
of development and
slightly later in lateral
plate mesoderm and
other regions.
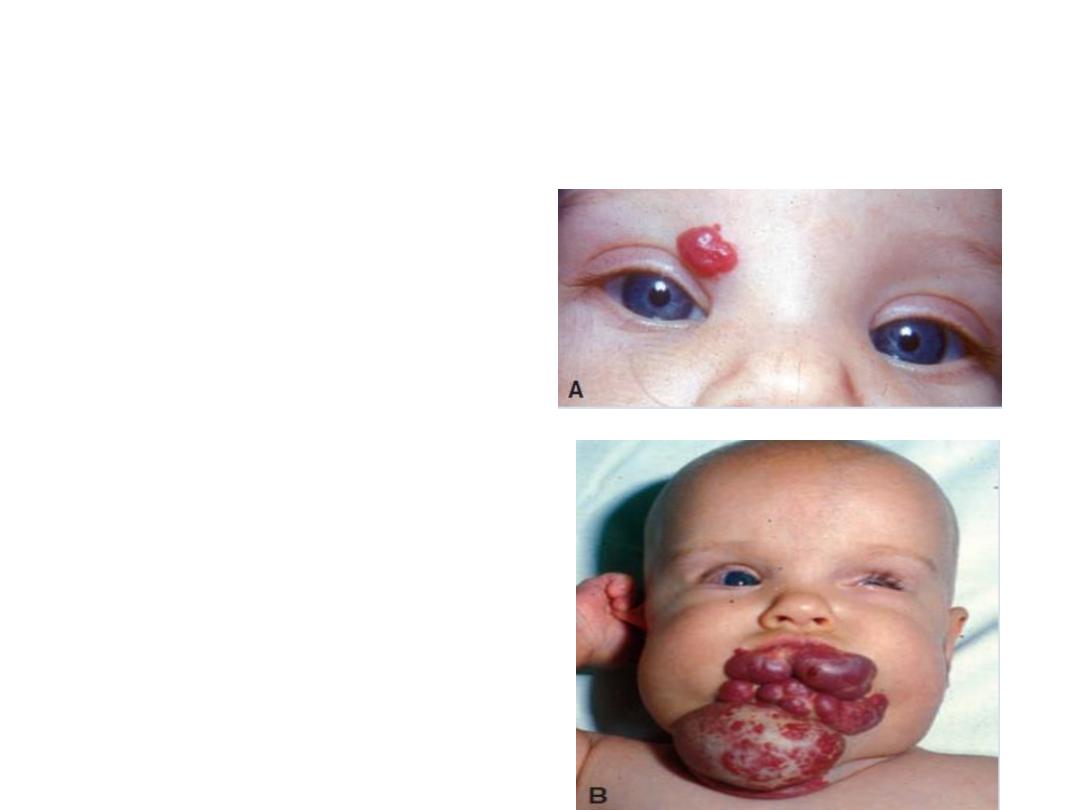
Clinical Correlates
Capillary hemangiomas:
dense collections of
capillary blood vessels
that form the most
common tumors of
infancy, occurring in
approximately 10% of
all births.
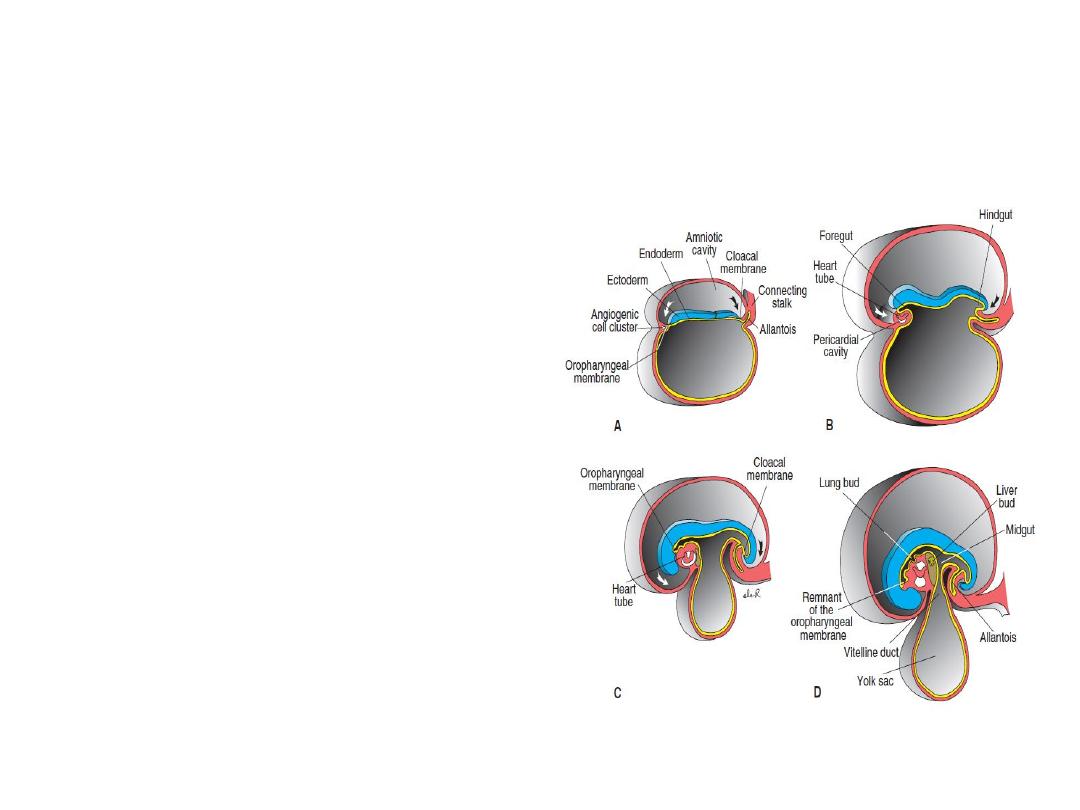
Derivatives of the Endodermal Germ
Layer
The gastrointestinal tract:
. In the anterior part, the
endoderm forms the
foregut ; in the tail
region, it forms the
hindgut . The part
between foregut and
hindgut is the midgut
The midgut temporarily
communicates with the
yolk sac by way of a broad
stalk, the vitelline duct .
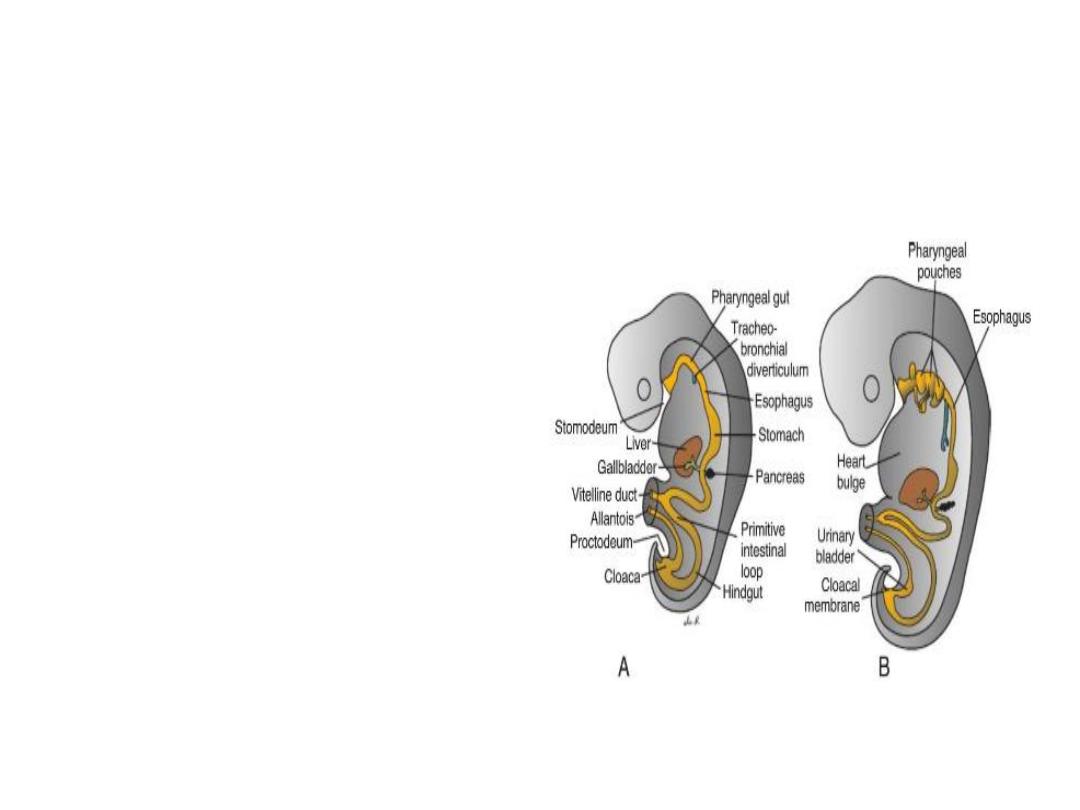
Derivatives of the Endodermal Germ
Layer
At its cephalic end, the foregut
is temporarily bounded by
an ectodermal- endodermal
membrane called the
buccopharyngeal
membrane .
The hindgut also terminates
temporarily at an
ectodermal - endodermal
membrane, the cloacal
membrane , which breaks
down in the seventh week
to create the opening for
the anus.

Derivatives of the Endodermal Germ
Layer
Other derivatives :
the epithelial lining of the respiratory tract; the
Parenchyma of the thyroid, parathyroids, liver,
and pancreas ; the reticular stroma of the
tonsils and thymus; the epithelial lining of the
urinary bladder and urethra; and the epithelial
lining of the tympanic cavity and auditory
tube .

External Appearance During the
Second Month
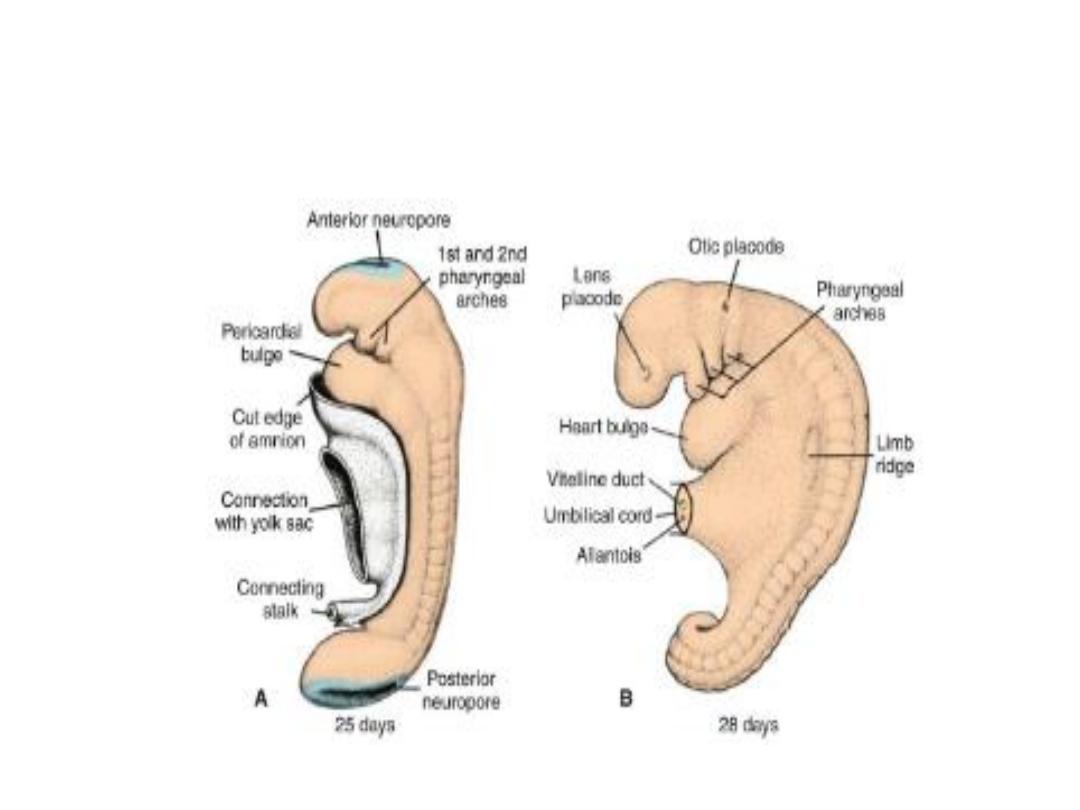
At the end of the fourth week, when the embryo
has approximately 28 somites, the main external
features are the somites and pharyngeal arches .
the age of the embryo is indicated as the crown -
rump length (CRL) and expressed in millimeters .
CRL is the measurement from the vertex of the
skull to the midpoint between the apices of the
buttocks.
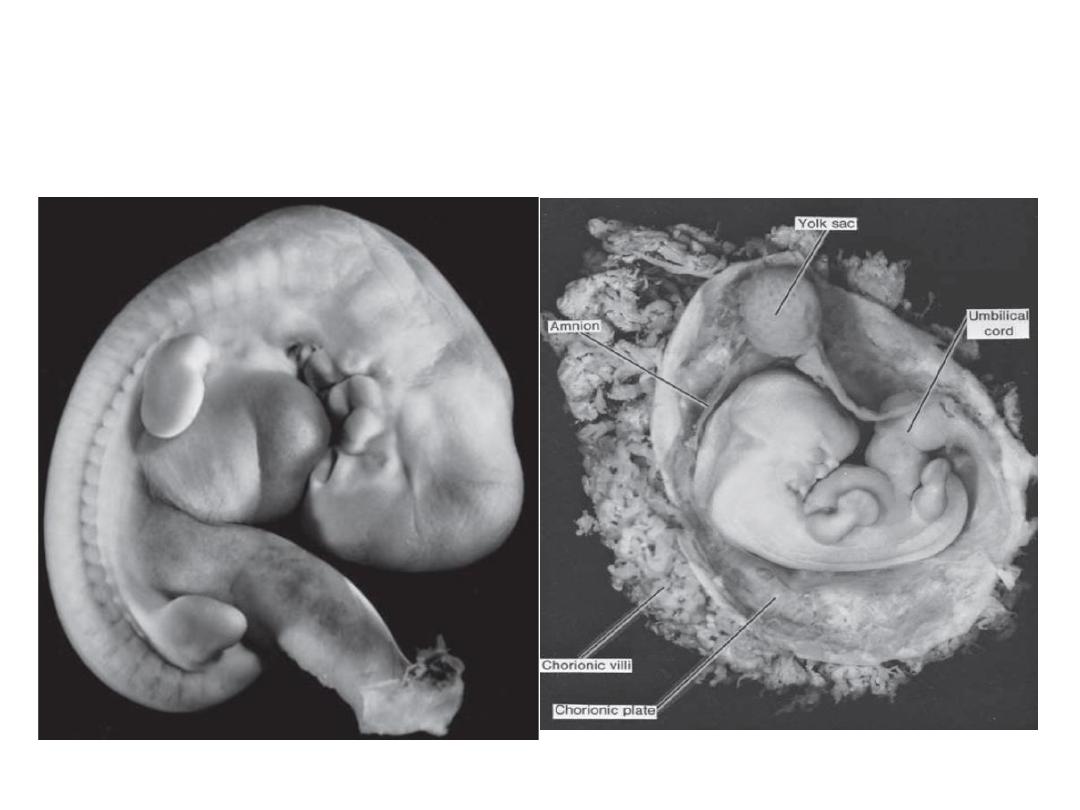
5 & 6 weeks embryo

Clinical correlates
Birth Defects:
Embryonic period is important because most of
the organs are formed during this period.
Thus, this period is when most gross structural
birth defects are induced.
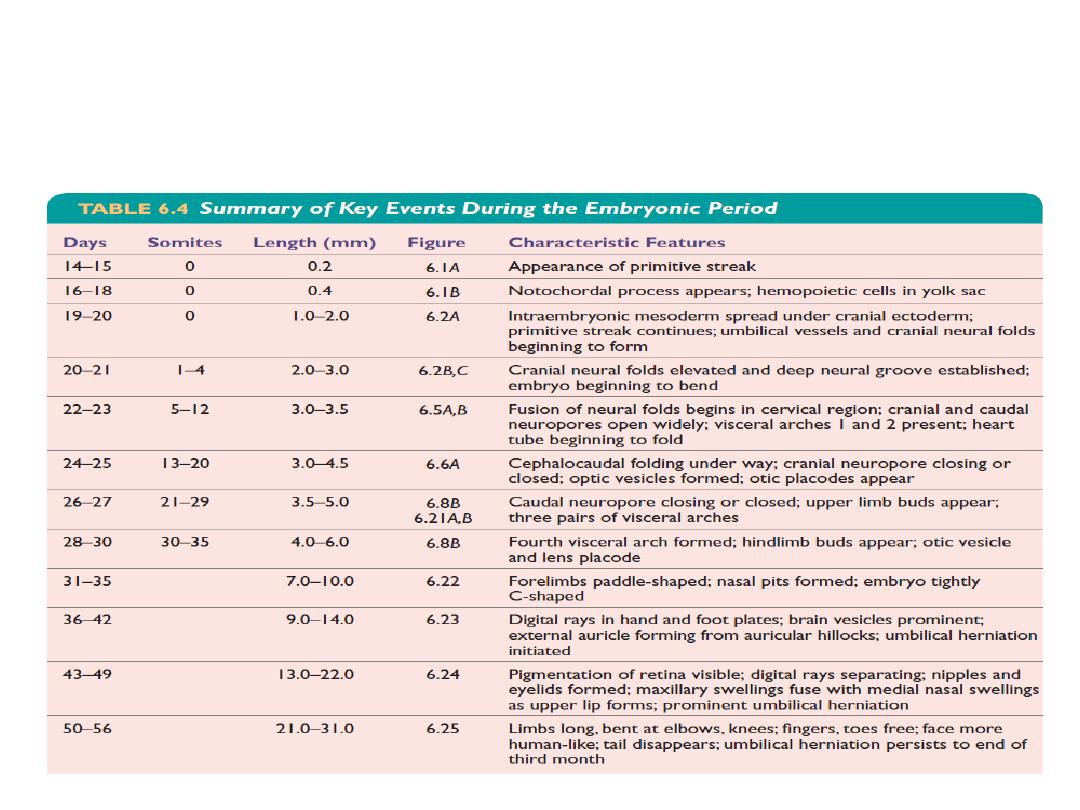
Summary of events during embryonic
period
