Structure of local anesthesia
Ester:Amide:
Example:Exception:
Benzocaine, which lacks a substituted amino groupR —COO—R —N
R —NHCO—R —N
12
R
R
3
4
2
1
R
R
3
4
H N—
—COO—(CH ) —N
2
2
2
C H
2
5
C H
2
5
R — Lipophilic aromatic residue.
R — Aliphatic intermediate connector.
R , R — Alkyl groups, occasionally
H. Constitute with N the hydrophilic
terminus.
1
2
3
4
PH and local anesthesia
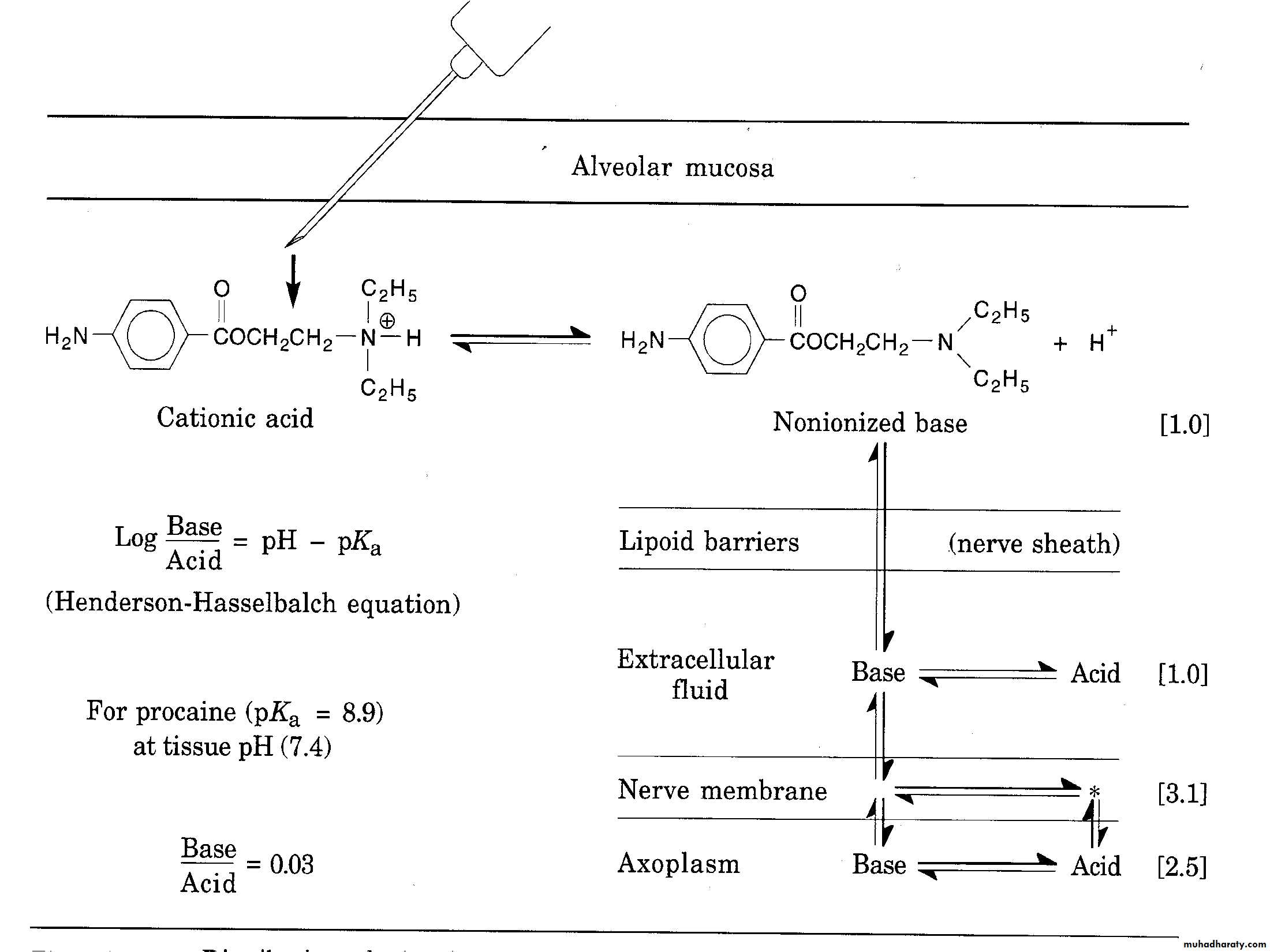
Dissociation constant PKa:pH at which 50% of drug present in free base form and 50% in cationic form (water soluble)
Most local anesthetic Pka(7-9)
How can local anesthesia cross nerve membrane?
Local anesthetic solution prepared as weak acid form at 4-5 pH to prevent precipitation of free base in neutral solution, thus it present as cataionic form that must converted to base form to be lipid soluble and cross cell membrane
Buffering capacity
Local anesthetic agent after injection and with function of plasma buffering will dissociate into free base form and cataionic formFree base form cross the cell membrane
After crossing the membrane an other dissociation occur and cataionc form resulted will bind the receptor
Onset (induction time)
• Time from injection of local anesthesia to the sign of adequate surgical anesthesia achieved
• Factors affect onset (induction time)
• Concentration
• pH
• PKa
• Anatomical barrier
• Lipid solubility
Recovery
Time from early sign appeared to the complete loss of all effects of drug occurThis results from reduced concentration of drug with no binding with the receptors
Recovery time
Concentration gradient depleted by:Dilution by interstitial fluid
Action of capillary and lymph
Absorption by other tissue
Hydrolysis of ester
Extraanuronal
Diffusion from intranuronal tissue (mantle fiber)
Duration
Time from induction to complete recovery from local anesthesiaIt depend on:
• Protein binding
• Vasoactivity
• concentration
• Vascularity of the site
Recovery slower than induction ?
Protein binding capacity
Principle of reinjection
Profound anesthesia:Increase concentration gradient to mantle fiber then to the core fiber
• Failure ??
• Edema• Localized hemorrhage
• Clot formation
• Reduced pH (poor buffer capacity)
• hypernatremia
After reinjection in prolonged procedure 2 situation may occur
Progression of local anestheticfunction
Dull pain
Temprature
Sharp pain
Touch
Deep pressure
Proprioception
Motor function