PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTSPFT))
Prof. Dr.ABDUL HAMEED AL QASEER
Lung volumes & capacities
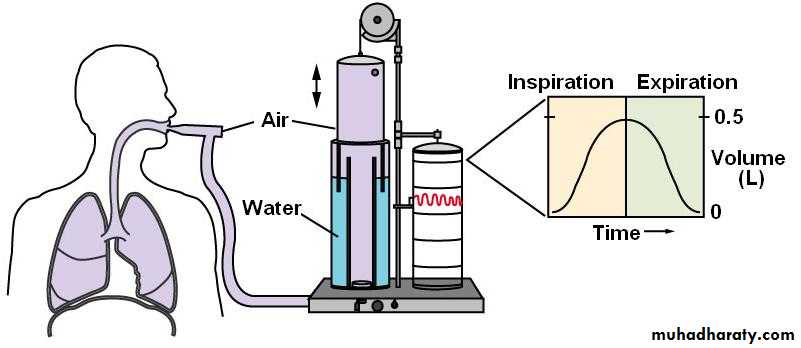
“Spirometer”SPIROMETER: An instrument which measure the volume of air moved into or out of the lungs.
SPIR0GRAM
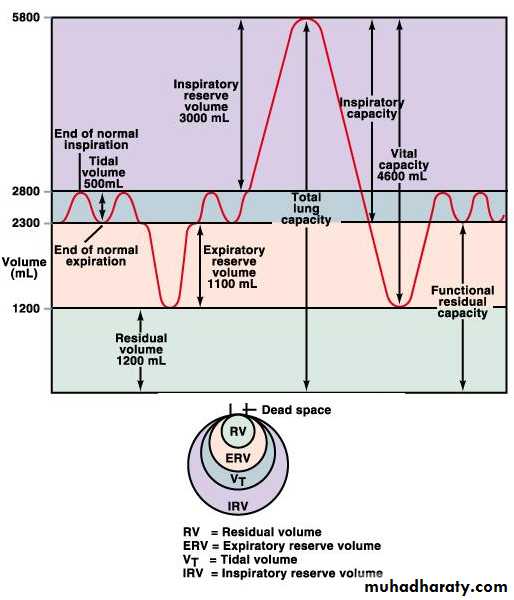
LUNG VOLUMESTIDAL VOLUME (TV): Volume inspired or expired with each normalハbreath. = 500 ml
INSPIRATORY RESERVE VOLUME (IRV): Maximum volume that can be inspired over the inspiration of a tidal volume/normal breath. Used during exercise/exertion.=3100 ml
EXPIRATRY RESERVE VOLUME (ERV): Maximal volume that can be expired after the expiration of a tidal volume/normal breath. = 1200 ml
RESIDUAL VOLUME (RV): Volume that remains in the lungs after a maximal expiration.ハ CANNOT be measured by spirometry.= 1200 ml
LUNG CAPACITIES
INSPIRATORY CAPACITY ( IC): Volume of maximal inspiration:IRV + TV = 3600 ml
FUNCTIONAL RESIDUAL CAPACITY (FRC): Volume of gas remaining in lung after normal expiration, cannot be measured by spirometry because it includes residual volume:ERV + RV = 2400 ml
VITAL CAPACITY (VC): Volume of maximal inspiration and expiration:IRV + TV + ERV = IC + ERV = 4800 ml
TOTAL LUNG CAPACITY (TLC): The volume of the lung after maximal inspiration.ハ The sum of all four lung volumes, cannot be measured by spirometry because it includes residual volume:IRV+ TV + ERV + RV = IC + FRC = 6000 ml
Peak flow(PEFR) measurement
The fastest flow rate of air during a forced expirationPEFR = 600L/min in healthy adult male &
450L /min in healthy female & children
AM-PM variation in healthy person < 20%
PEFM, easy to use, repeatable, inexpensive
Importance of long term peak flow measurements
To establish diagnosis and treatmentTo assess severity of an exacerbation
To assess response to treatment
To evaluate how well asthma is controlled
To alert patient to need for possible change in treatment
Serial recording of PEF IN ASTHMA
Diurnal variability in PEFR in asthma & showing the effect of steroidSpirometry
The spirometer measures the FEV1 & FVC .The technique involves a maximum inspiration followed by a forced expiration ( for as long as possible) into the spirometer .
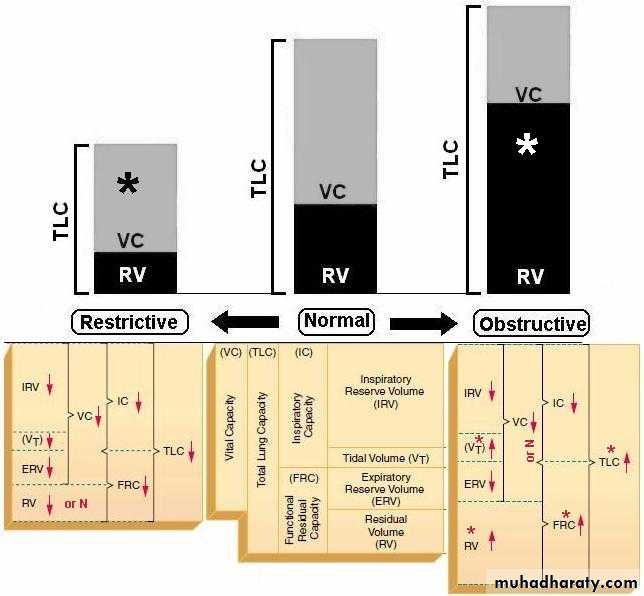
The FEV1 expressed as a percentage of the FVC is an excellent measure of airway limitation .
In normal subject it is around 75% .
With airway limitation the FEV1 falls proportionally more than the FVC , so the FEV1\ FVC ratio is reduced ( < 70%) . This is called obstructive pattern .
In restrictive lung diseases the FEV1 & the FVC are reduced in the same proportion & the FEV1\FVC ratio remain normal or even increase.
Reversibility test in asthma
Exercise – induced asthmaprovocative test in asthma
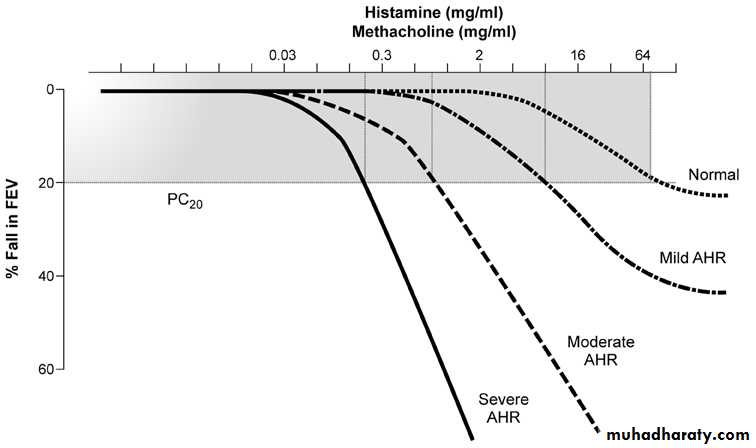
Measuring Airway Responsiveness
Flow – Volume LoopsThe ability to measure flow rate against volume .
To distinguish large airway narrowing from small airway narrowing e.g. COPD & asthma .
Flow\Volume loops are recorded using spirometry during maximum expiration & maximum inspiration .
Lung Volumes
Tidal volume(TV) & vital capacity ( VC )can be measured using a simple spirometry .Total lung capacity (TLC )& residual volume (RV) measured by helium dilution test . RV can be calculated by subtraction the VC from TLC .
Lung volume may be also measured by body plethysmograph , which determined the pressure /volume relationship of the thorax .
SPIR0GRAM
In chronic airflow limitation ( particularly in COPD & asthma ) TLC is usually increased .This trapping of air within the lung ( giving an increased RV) is a characteristic feature of these disease .
Transfer factor
To measure the capacity of the lung to exchange gas , patient inhale a test mixture of 0.3% carbon monoxide ( CO),which is avidly bound to hemoglobin in pulmonary capillaries .After a short breath –hold , the rate of disappearance of CO into the circulation is calculated from a sample of expirate , & expressed as the TLco or carbon monoxide transfer factor .
TLco also called DLco ( diffusing capacity of the lung for CO) .
Helium is also included in the test breath to allow calculation of volume of lung examined by the test breath . Transfer factor expressed per unit lung volume is termed Kco .
TLco is reduced in IPF & emphysema .
Arterial Blood Gases & Oxymetry
The measurement of PaO2 , PaCO2 & hydrogen concentration with bicarbonate concentration in arterial blood sample is essential in assessing the degree & type of respiratory failure .Pulse oximeters with finger or ear probe allow non-invasive assessment of oxygen saturation (SaO2). They measure the difference in absorbance of light by oxygenated & deoxygenated blood.