Triangles of neck
ByDr. Adel Sahib Al-Mayaly
FICMS, FACS
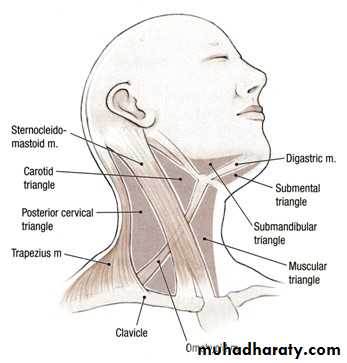
The side of the neck
It is quadrilateral outlineBoundaries:-
Above:- lower border of mandible and an imaginary line extending from the angle of the mandible to the mastoid process .
Below:- by the upper border of the clavicle.
In front:- the mid-line of the neck.
Behind:- the anterior margin of the Trapezius
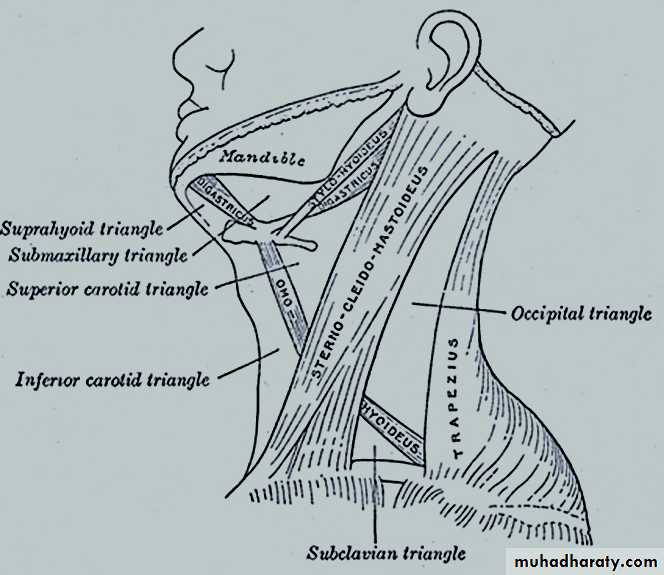
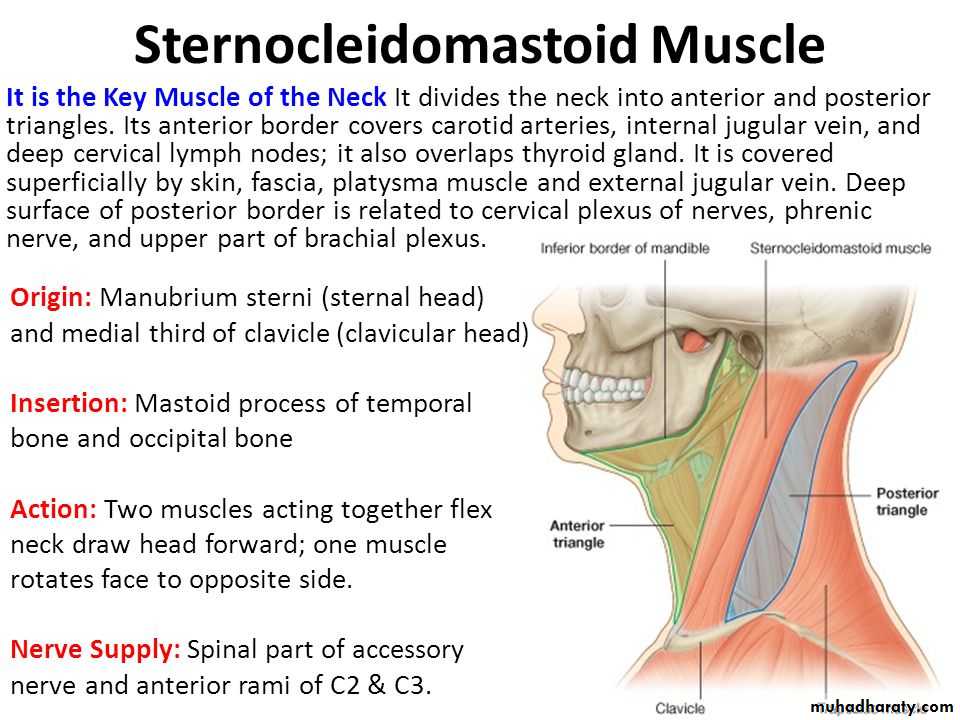
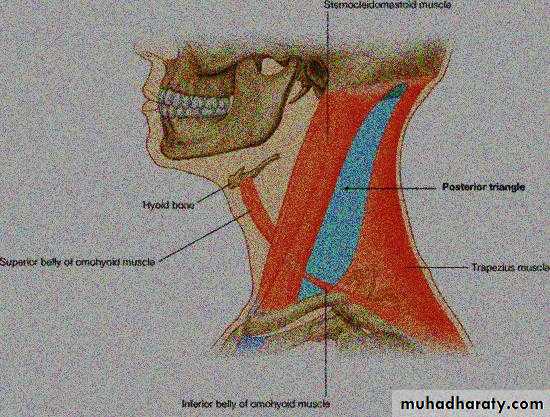
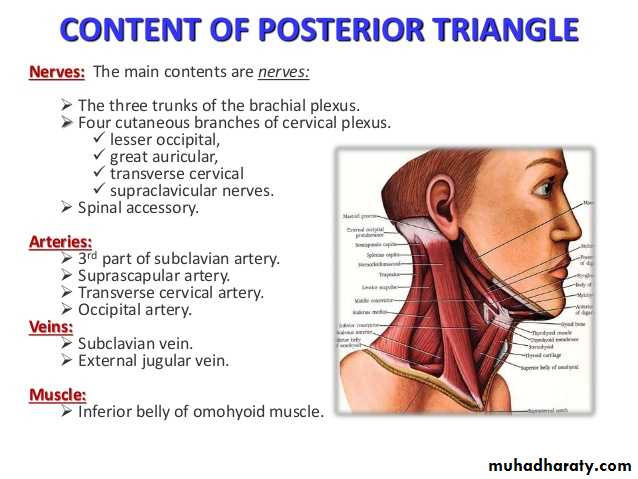
Posterior Triangle and Its Subdivisions
Boundaries:Anteriorly: posterior border of the SCM muscle. Posteriorly: anterior border of the trapezius muscle
Inferiorly: intermediate one-third of the clavicle
• Is subdivided into occipital and Subclavian triangles by inferior belly of omohyoid m.
Subdivisions
Subclavian (Omoclavicular) triangle.Ooccipital1-1-ccipital triangle.
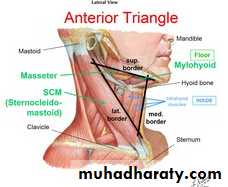
Anterior triangle
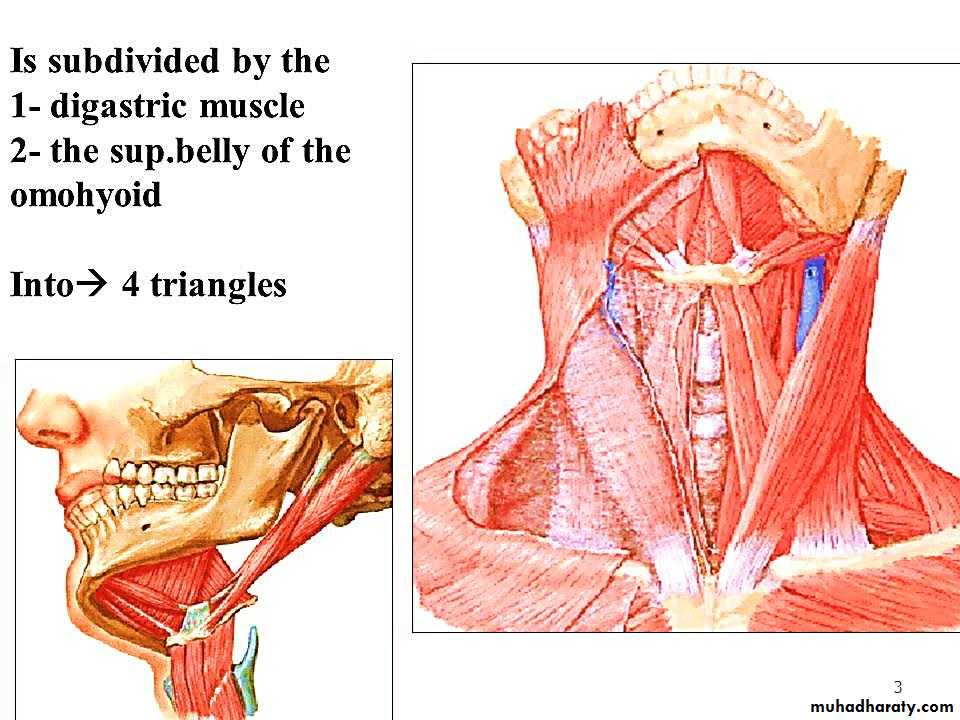
Subdivisions of anterior triangle
1-Submandibular triangle.2- Submental triangle.
3-Carotid triangle.
4-Muscular triangle.
Carotid triangle
Boundaries:Anteriorly: superior belly of the omohyoid muscle
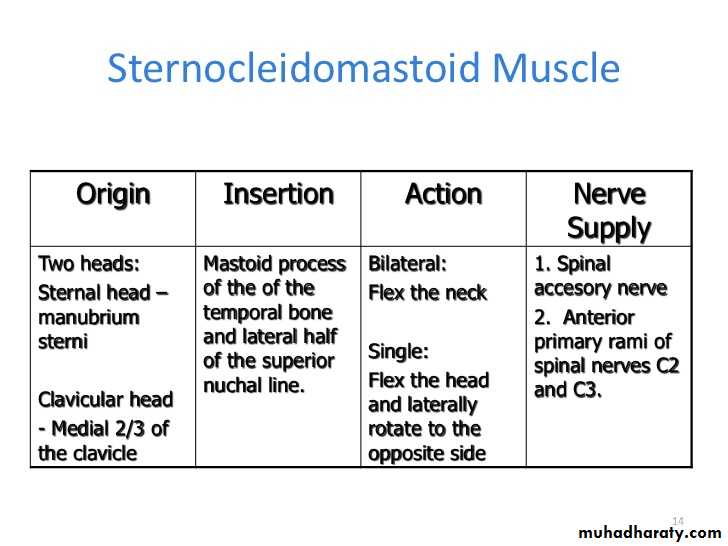
Posteriorly: sternocleidomastoid muscle
Superiorly: posterior belly of the digastric and the stylohyoid muscles
Floor: thyrohyoid, sternothyroid, and inferior constrictor muscles
Contents
the carotid arterial system, the internal jugular vein with tributaries, the hypoglossal nerve, vagus nerve, the superior laryngeal nerve, and the sympathetic trunk.
Muscular triangle
Superior belly of omohyoid above.Anterior border of SCM muscle behind.
Midline of neck infront.
Floor: strap muscles:-
1- sternohyoid m.
2- sternothyroid m.
3- thyrohyoid m.
4- superior belly of omohyoid m.
Submandibular triangle
Lower border of mandible above
Posterior belly digastric & stylohyoid behind .
Anterior belly of digastric infront
Floor:- the Mylohyoid, Hyoglossus, and superior constrictor of pharynx.
Contents :- submandibular g.& duct, submandibular L.Ns.
Submental (suprahyoid) triangle
Anterior belly of digastric on both sides.Body of hyoid bone below.
Floor:- mylohyoid muscle.
Contents;- Submental lymph nodes
Muscles of anterior triangle
1- superficial muscles:- platysma, SCM & trapezius.2- Infrahyoid muscles.
3- Suprahyoid muscles.
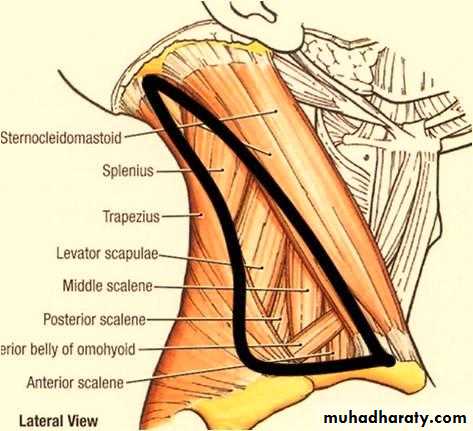
4- lateral vertebral muscles (scalenae muscles).
Blood vessels of anterior triangle.
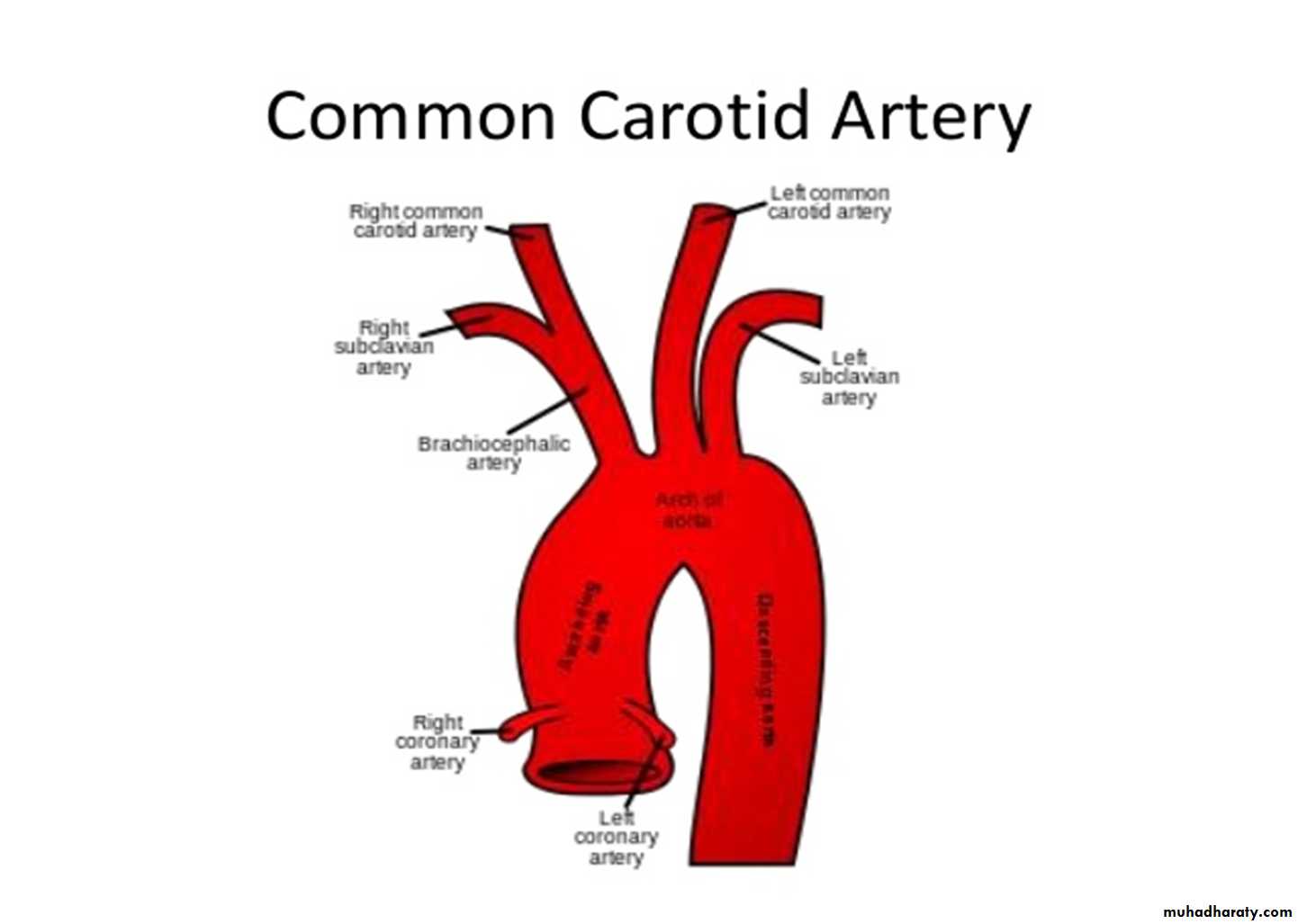
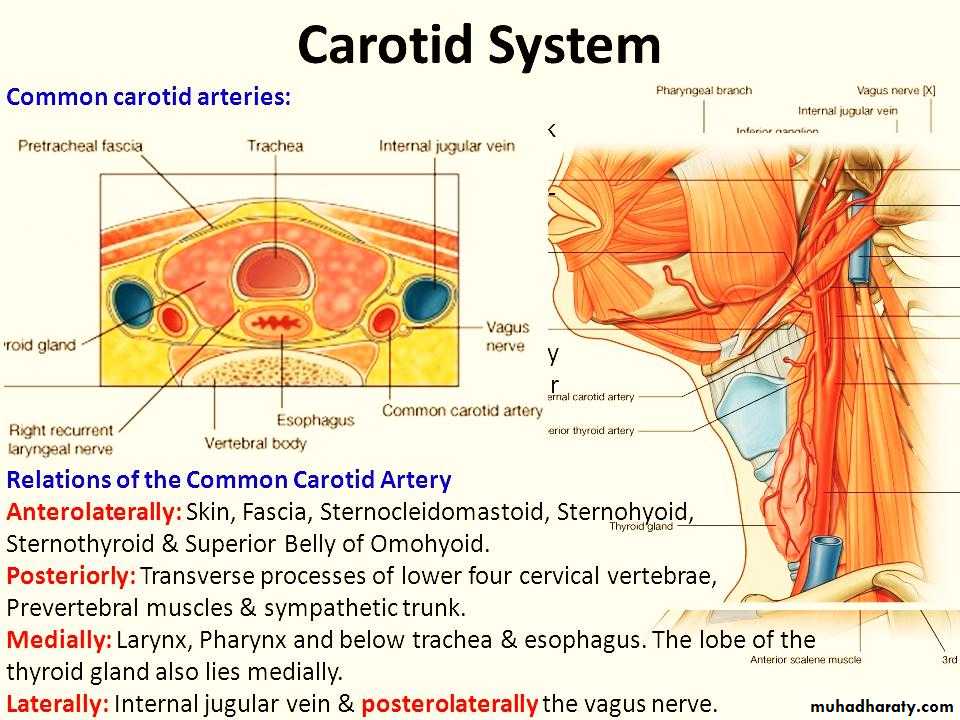
Carotid arterial systemCommon carotid artery:-
Origin :-
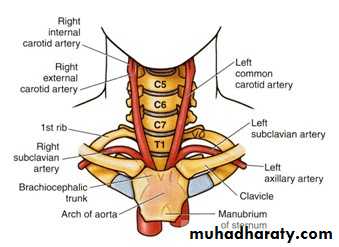
Right side:- brachiocephalic trunk behind sternoclavicular j.
Left side:- arch of aorta in the superior mediastinum
Carotid arterial system
Common carotid artery
On either side; it ascends upward within the carotid sheath.At the level of upper border of thyroid cartilage;
It bifurcates into
1- Internal carotid artery.
2- External carotid artery.
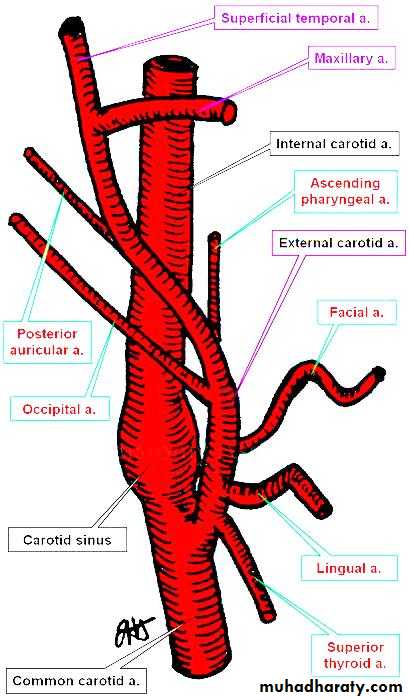
Internal carotid artery
It ascends upward within carotid sheath from its origin.First; it is SF to ECA but then it becomes behind & deep to ECA.
At base of skull; it enters carotid canal to gain access to cranial cavity.
It gives no branches in the neck.
External carotid artery
At first, it lies medial to the internal carotid artery,As it ascends in the neck; it passes backward and lateral to it.
It is crossed by the posterior belly of the digastric and the stylohyoid.
Branches of ECA
Superior thyroid arteryAscending pharyngeal artery
Lingual artery
Facial artery
Occipital artery
Posterior auricular artery
Superficial temporal artery
Maxillary artery
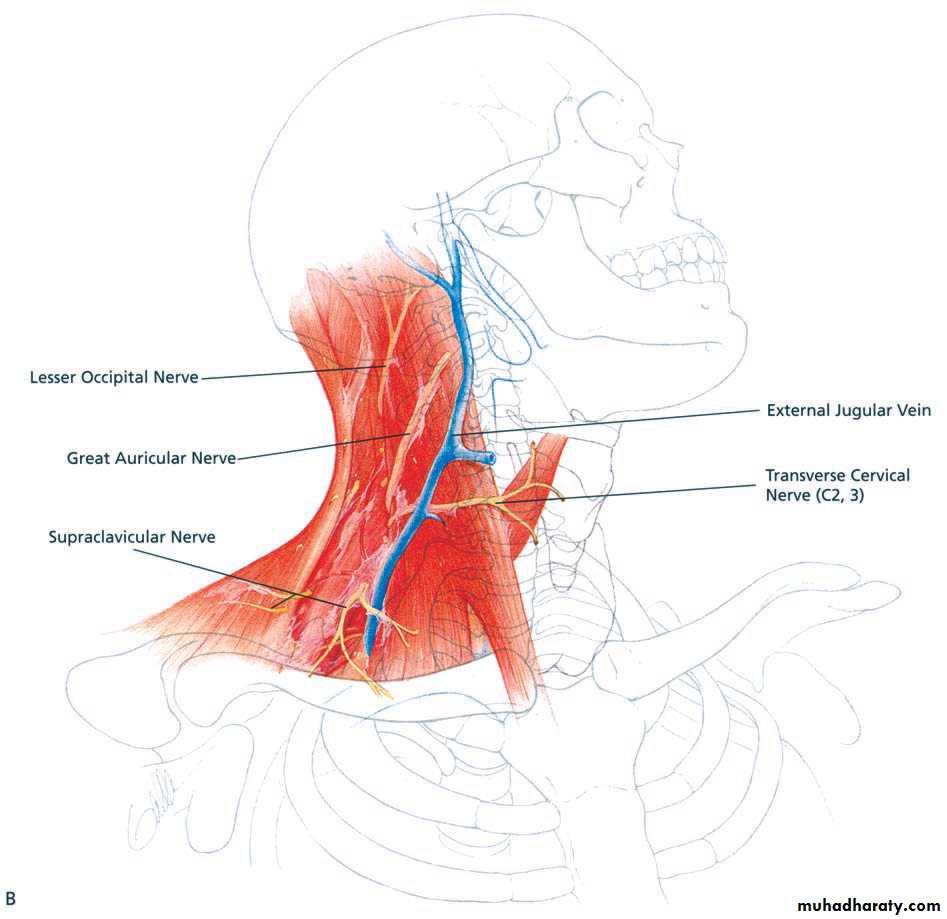
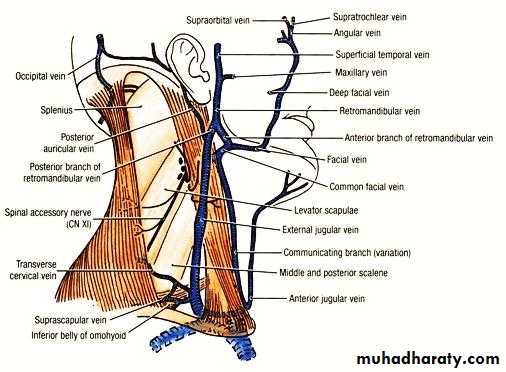
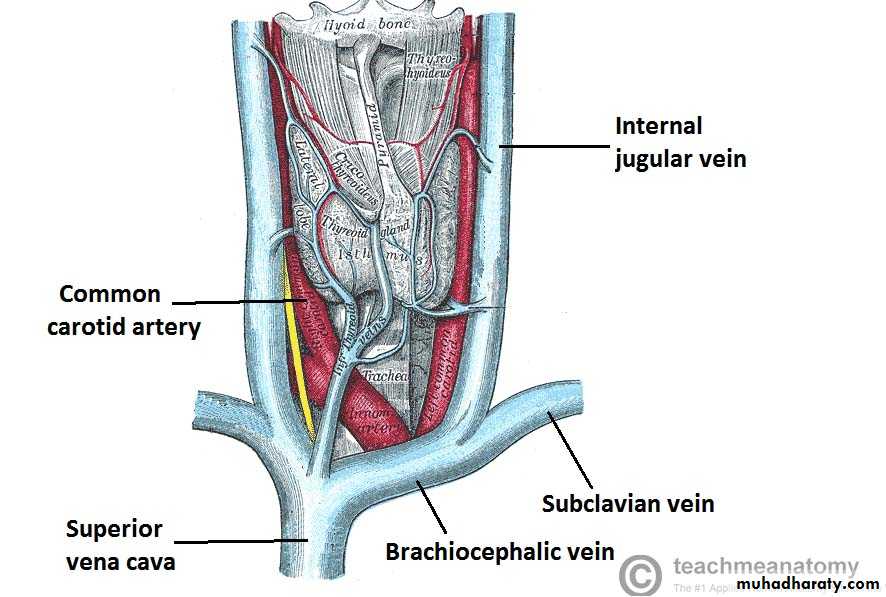
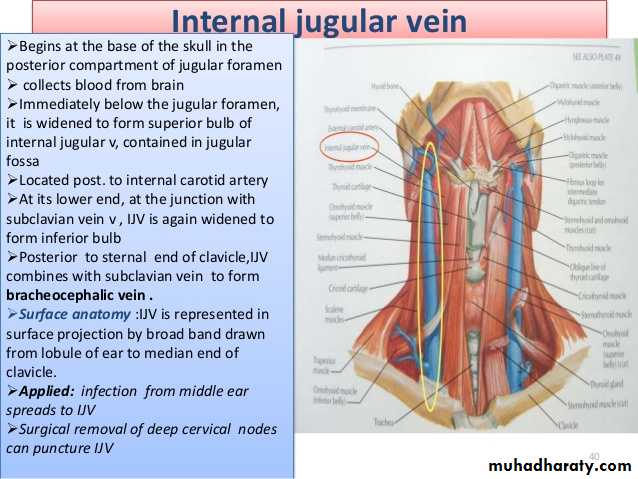
Internal jugular vein
It emerges from jugular foramen at the base of skull.
It lies behind ICA at first ( at the base of skull).
Here it receives the inferior petrosal sinus
It descends in the carotid sheath lateral to the ICA then CCA.
At root of neck; it joins the subclavian vein to form the brachiocephalic v.
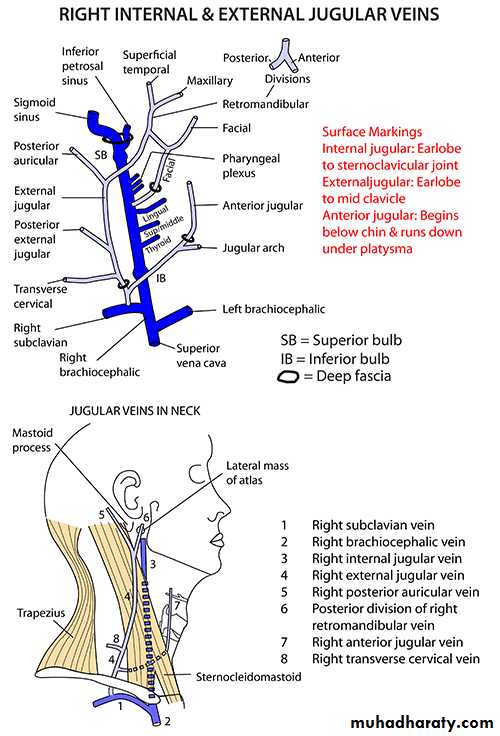
Surface anatomy of IJV
Tributaries of IJV
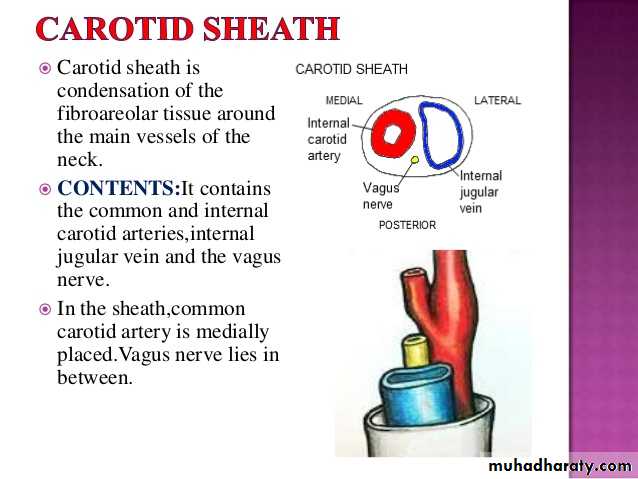
Carotid sheath
It extends from the base of skull (carotid canal) to the arch of aorta.It encloses the carotid art., IJV & vagus nerve in between.
The sympathetic trunk is lying behind the sheath.
The ansa cervicalis (C!,2,3) is embedded in its ant. Wall.