HISTOLOGY OF BLOOD(specialized connective tissue)
Plasma 55% (straw colored)
92% water8 % Salt, nutrients, proteins , waste, gases, hormones
BUFFY COAT (Gray- White) 1%
WBC
Platelets
RBCs 45%
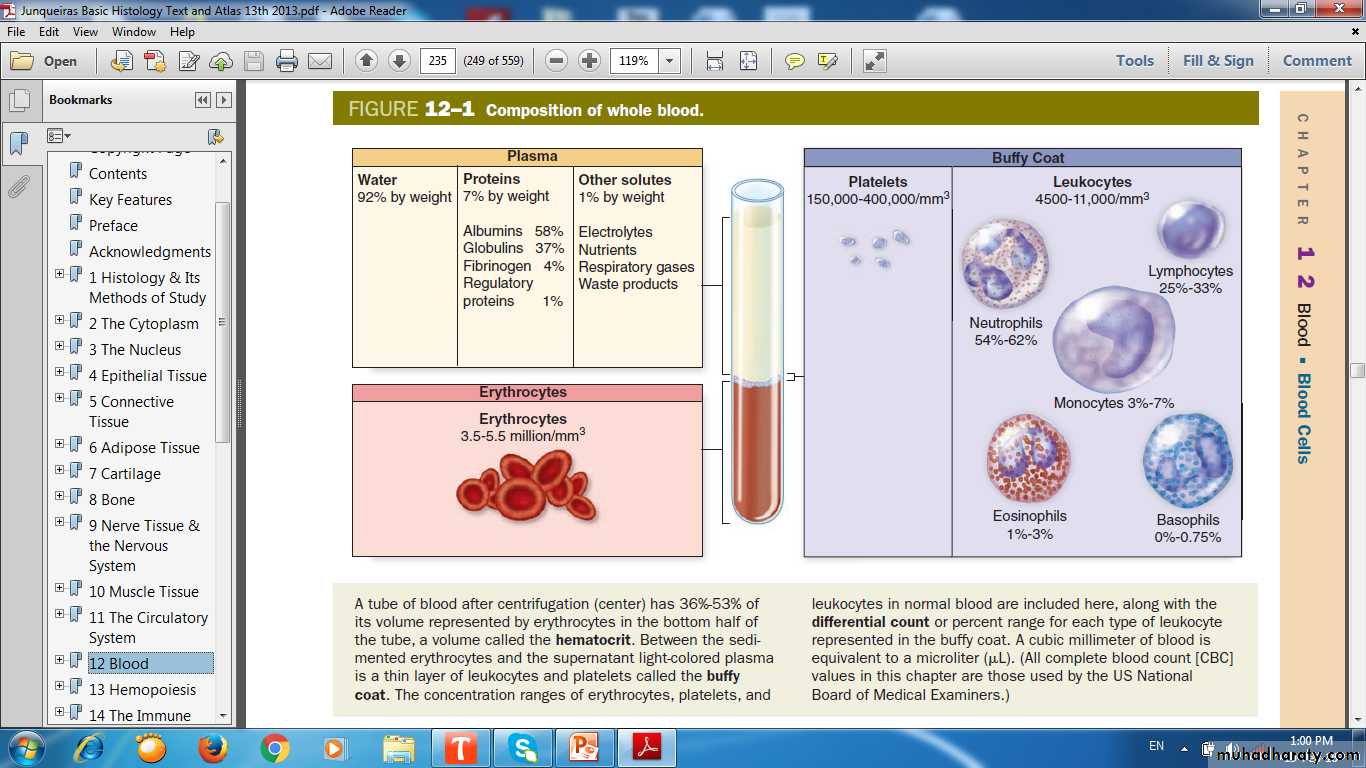
Blood is a viscous fluid formed of cellular elements suspended in plasma.
Composition of whole blood(5 L in adult)
Plasma Proteins:■ Albumin
■ α Globulins and β Globulins
■ γ Globulins
■ Fibrinogen
■ Complement proteins
HEMATOCRIT Ratio of RBCs to Plasma, 45%
Anticoagulant& Clot formation
Clotting prevented by (heparin or citrate)When Blood extravasated, Plasma proteins react with one another to produce a (clot) & serum
Serum is a pale yellow liquid
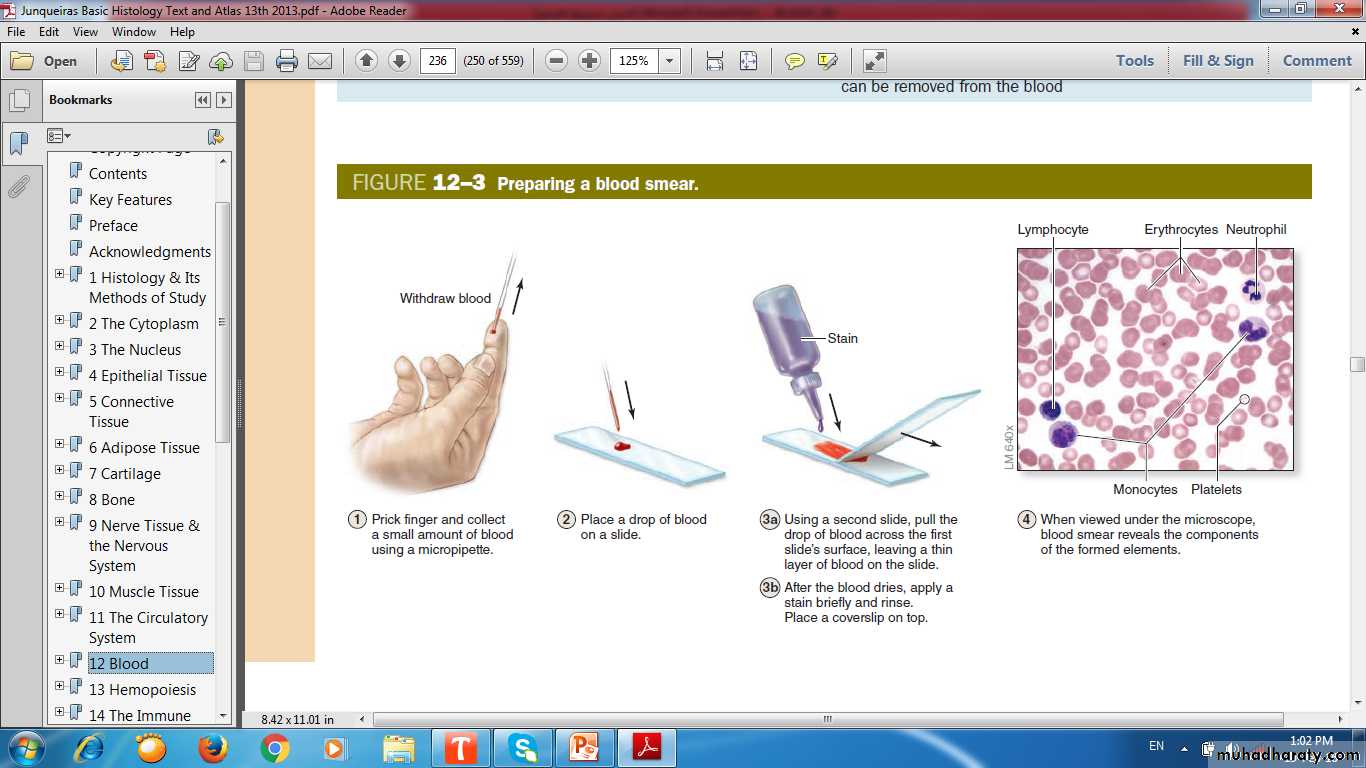
Blood smear
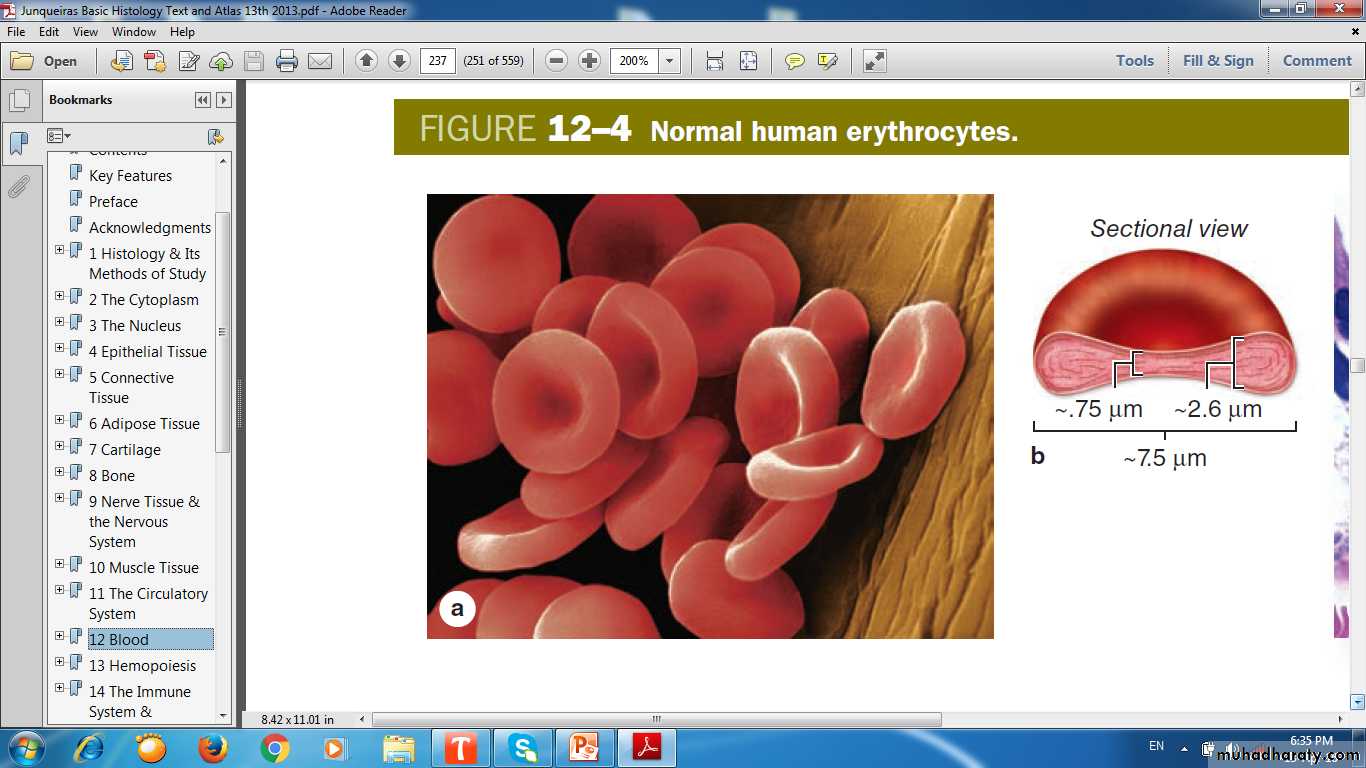
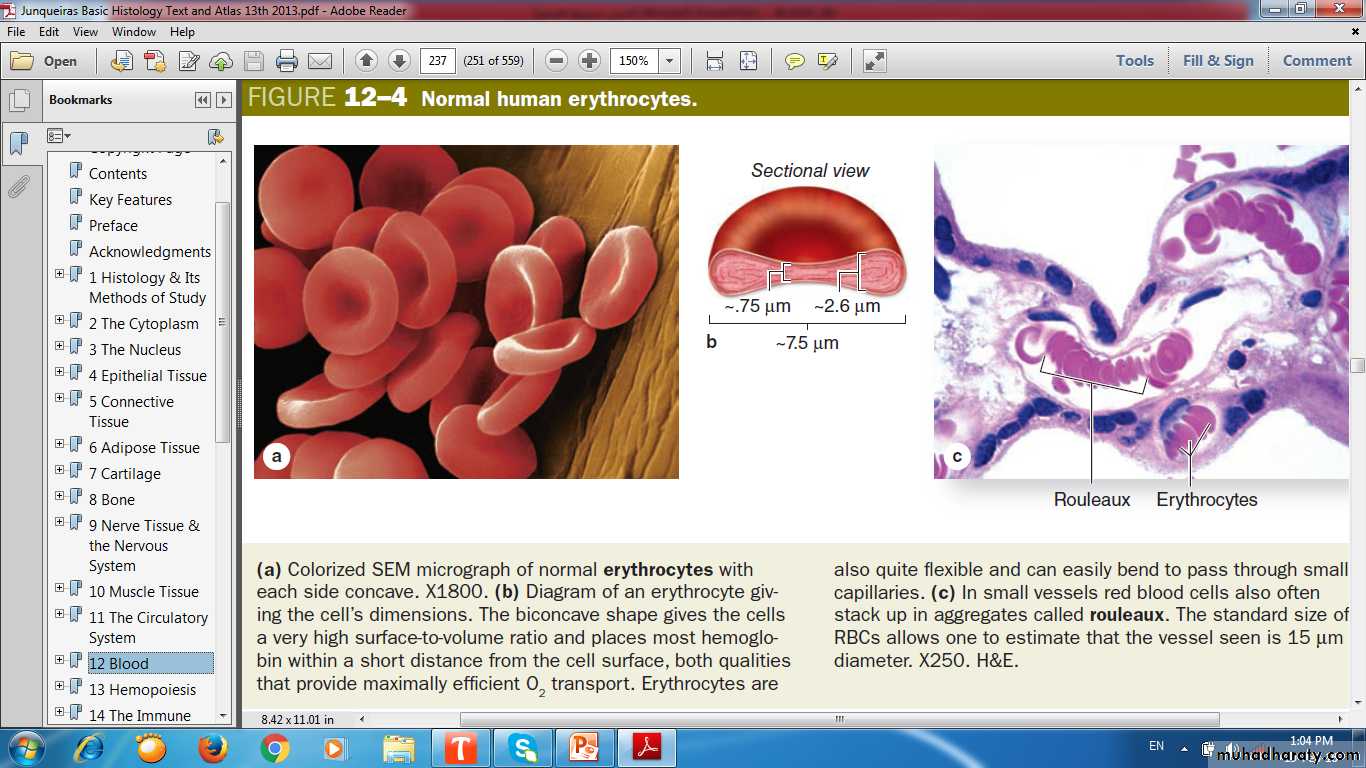
Erythrocyteslargest number of cells in the blood
3.9 to 5.5 million (μL, or mm3) in women
4.1-6.0 million/μL in men.
Biconcave discs
No nucleus
Contain Hemoglobin
Rouleaux RBCs adhere to one another loosely in stacks.
Plasma Membrane of RBC
40% Lipid10 % Carbohydrate
50 % Proteins------- (1) integral proteins
(2) peripheral proteins
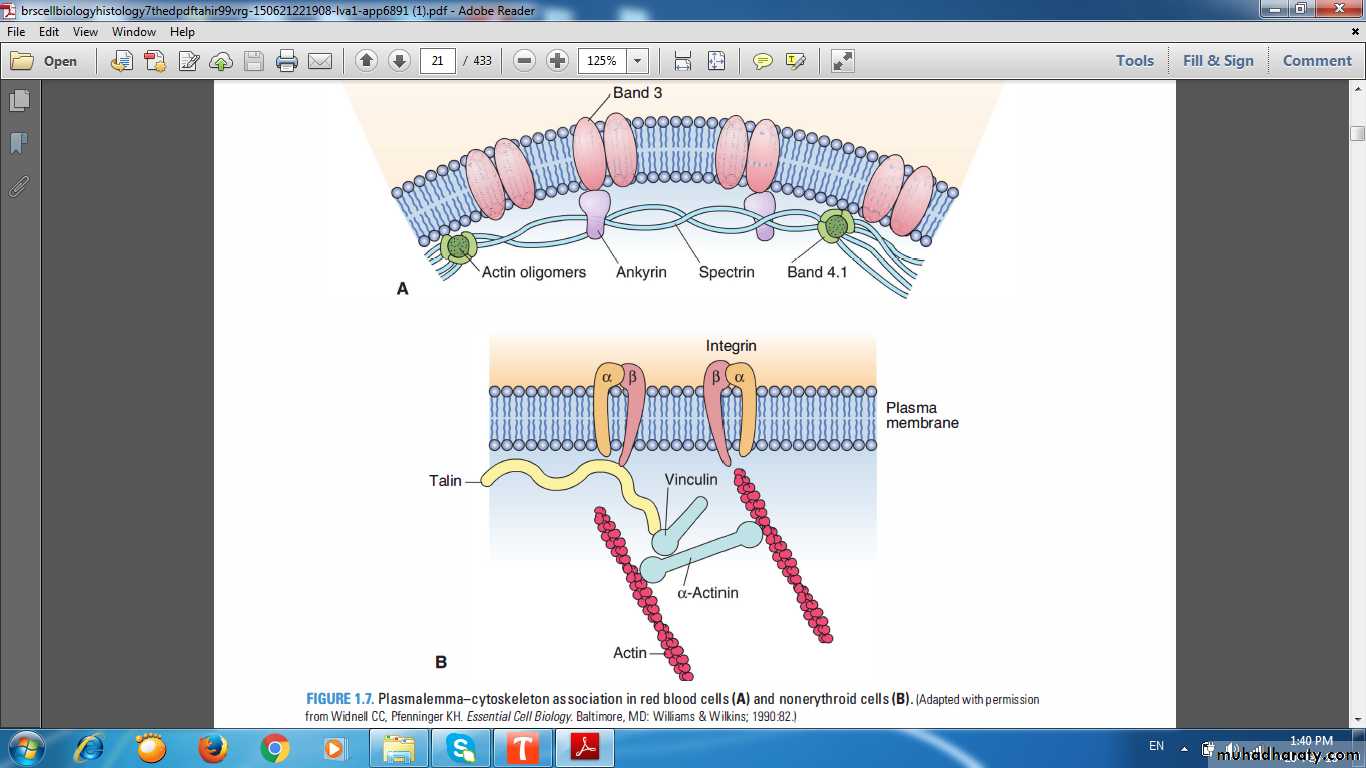
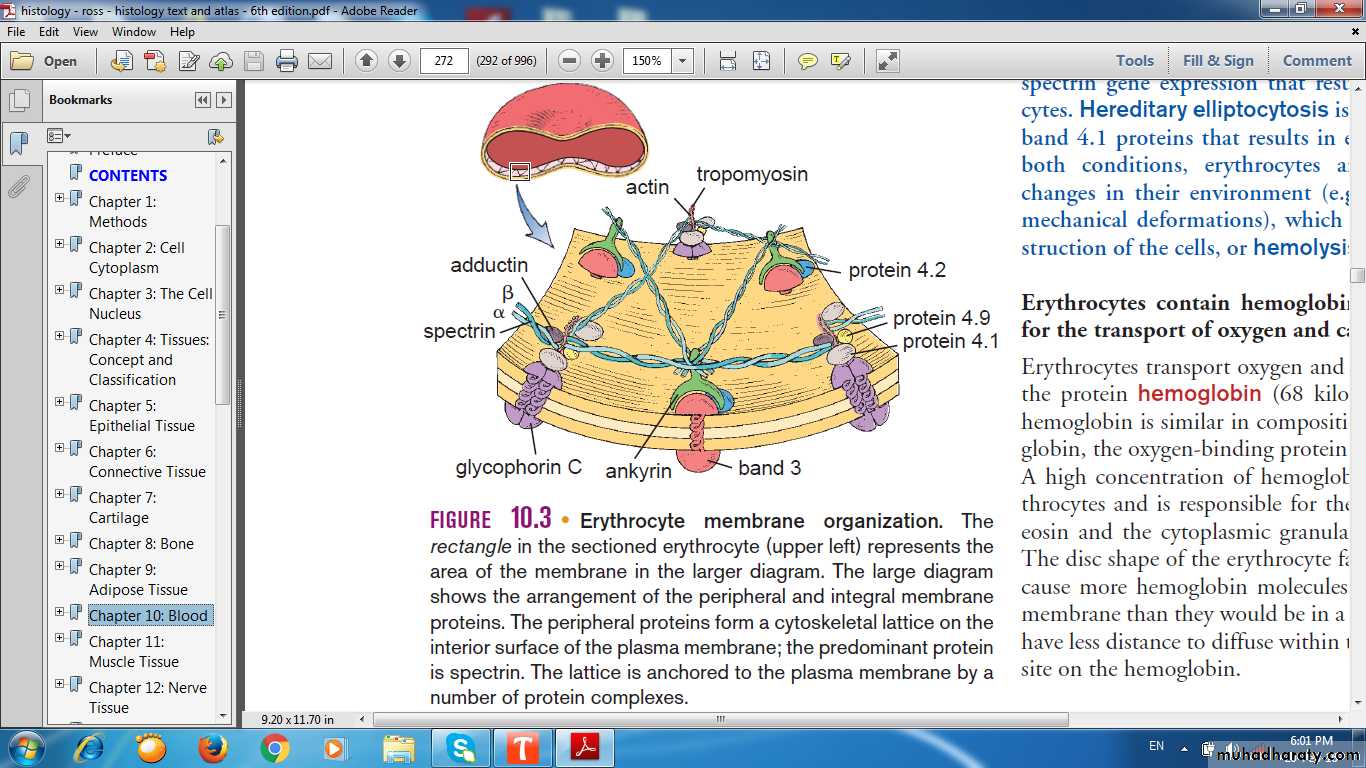
Integral Proteins Band3 proteinGlycophorinsperipheral proteinsspectrinAnkyrin
Integral & peripheral proteins
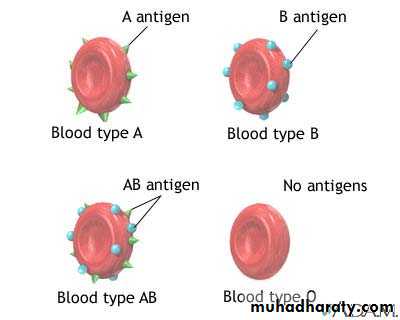
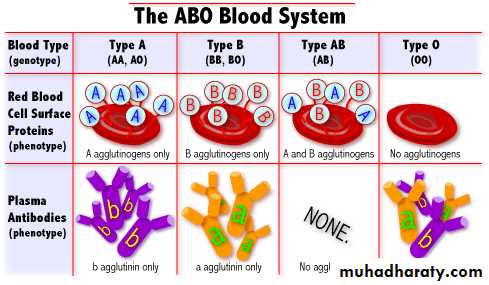
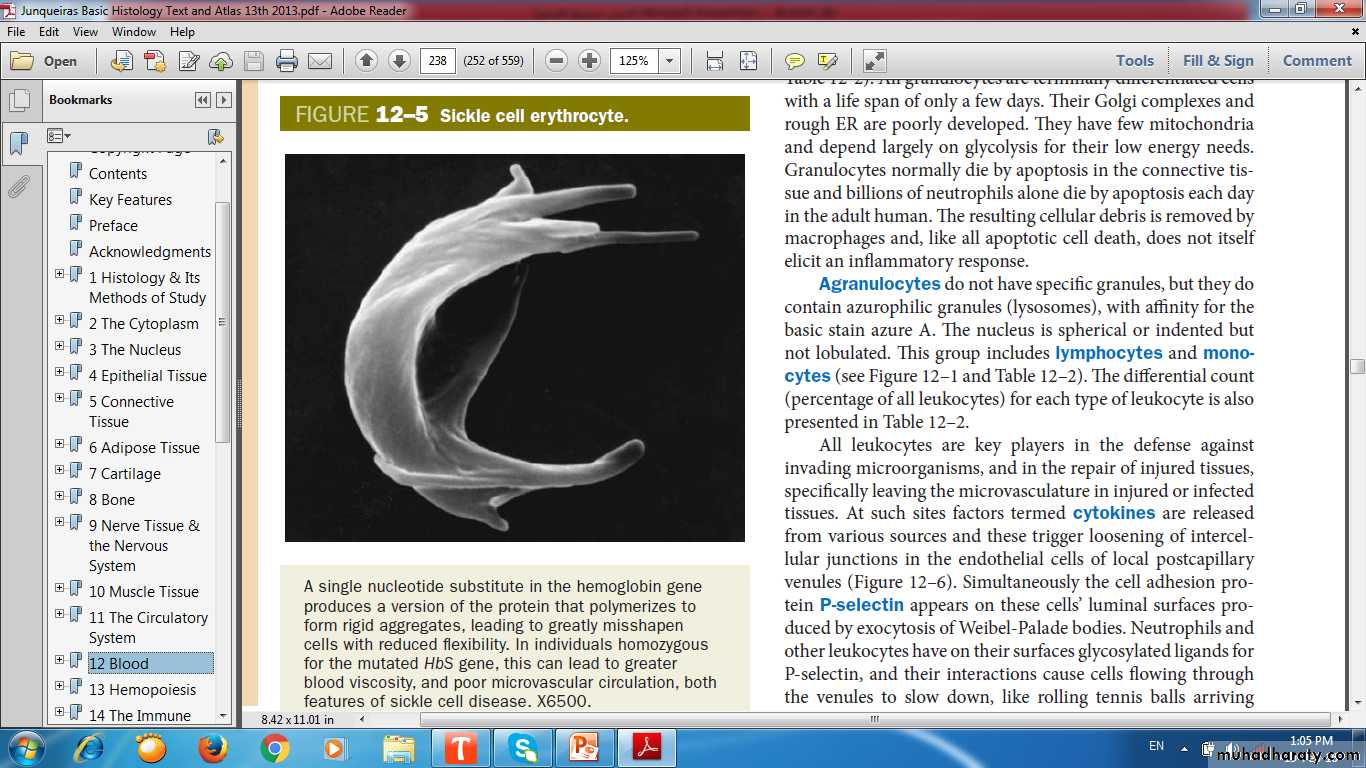
BLOOD TYPESAbnormal Hemoglobin HbS
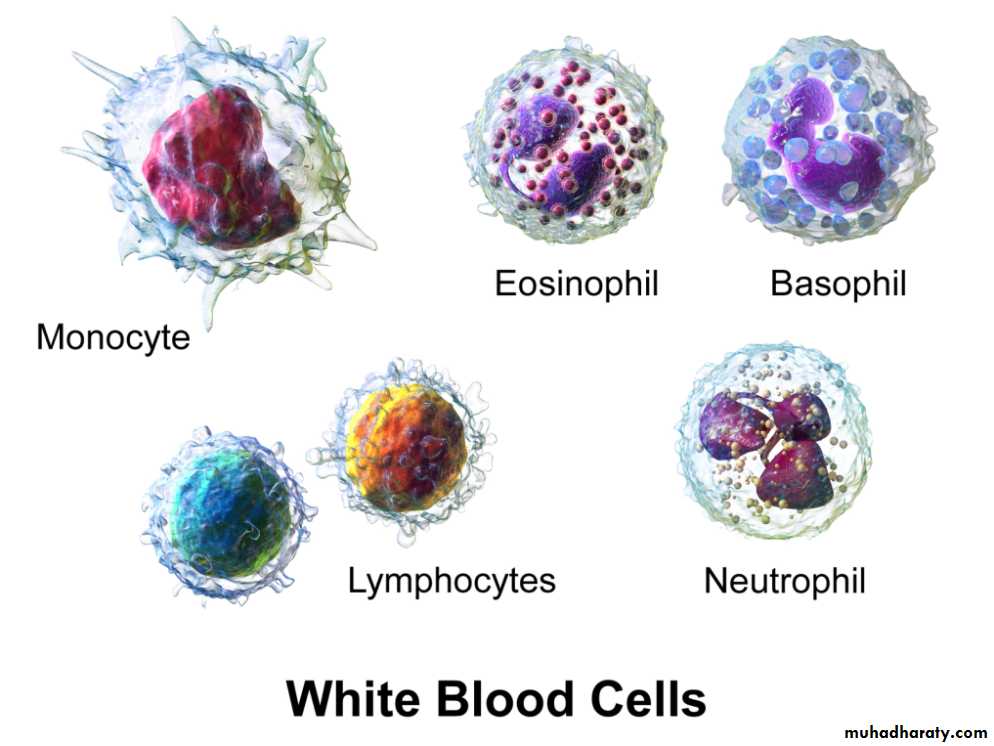
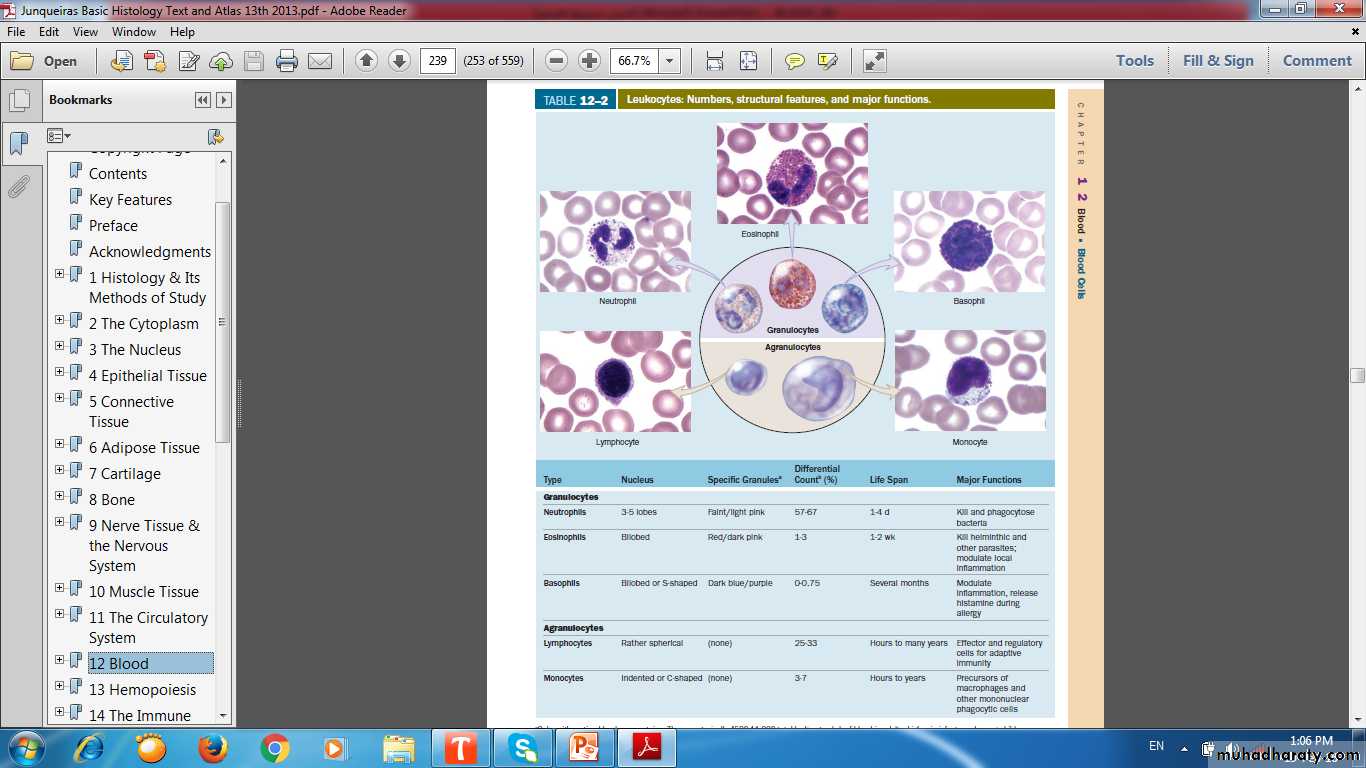
Leukocytes (4500 -11000/μl)GRANULOCYTES
AGRANULOCYTES
Granulocytes
NeutrophilsEosinophils
Basophils
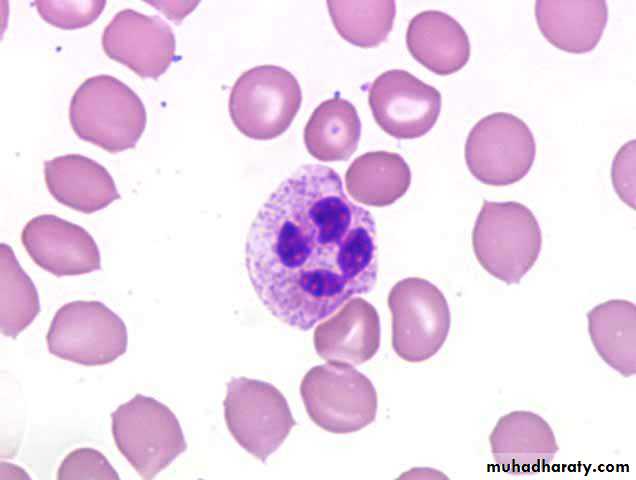
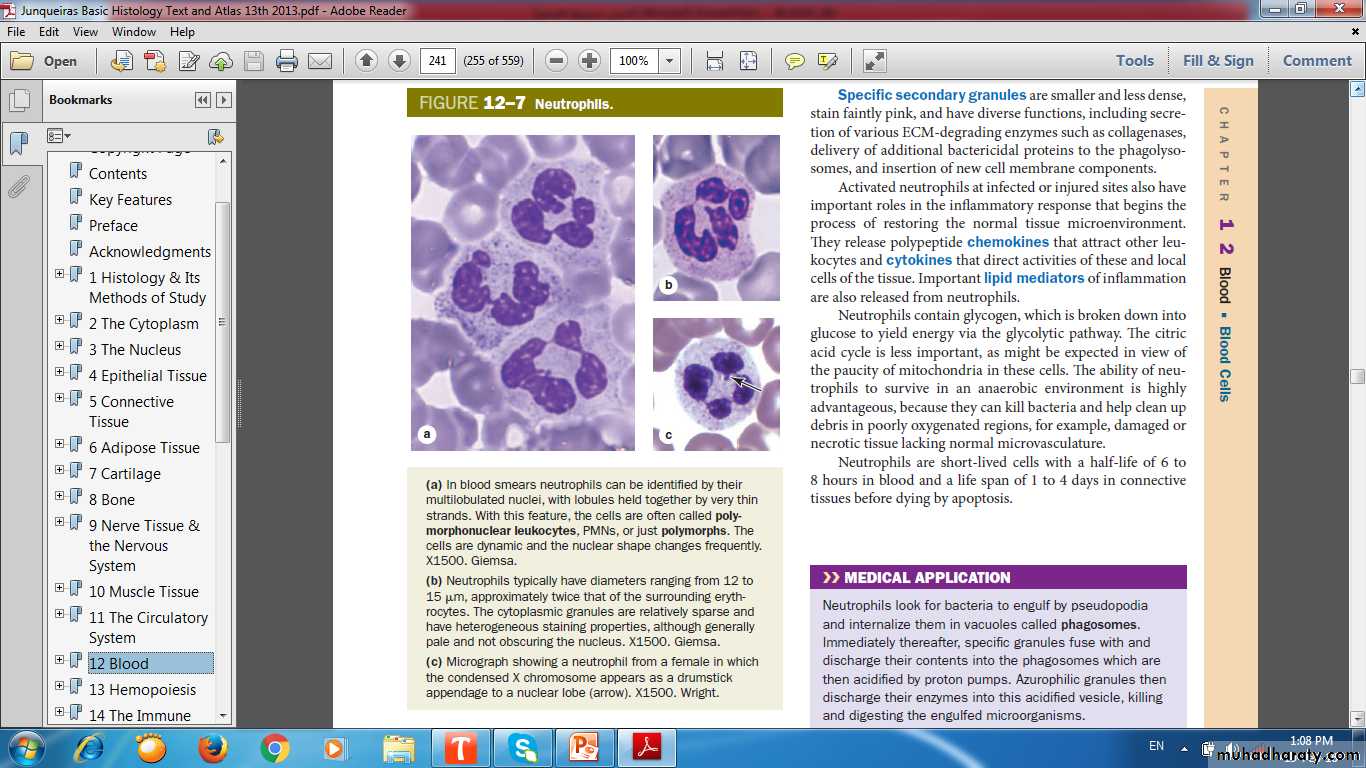
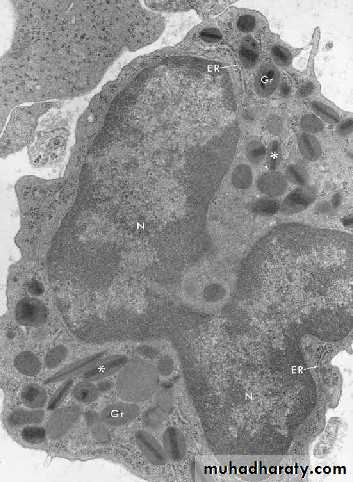
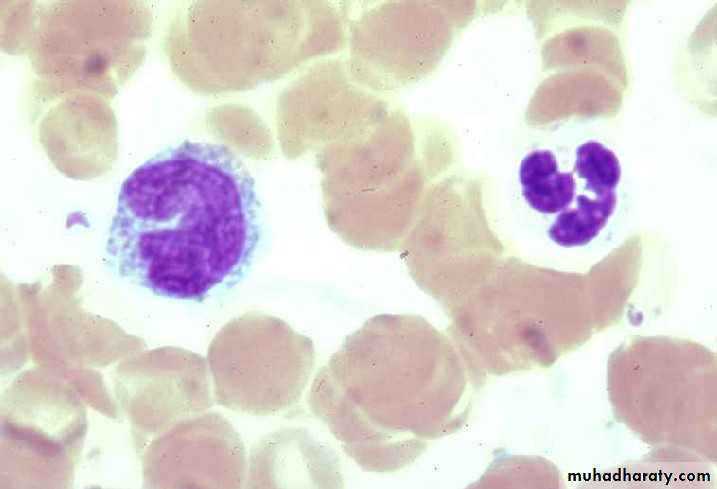
Neutrophils (PMNs)
Most numerous WBC in bloodMultilobed nucleus
Granules:
Azurophilic granules
Specific granules
Function
1st wave of cells in acute inflammation; can phagocytose bacteria
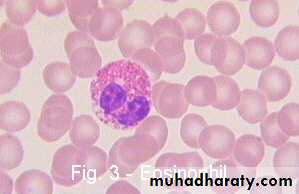
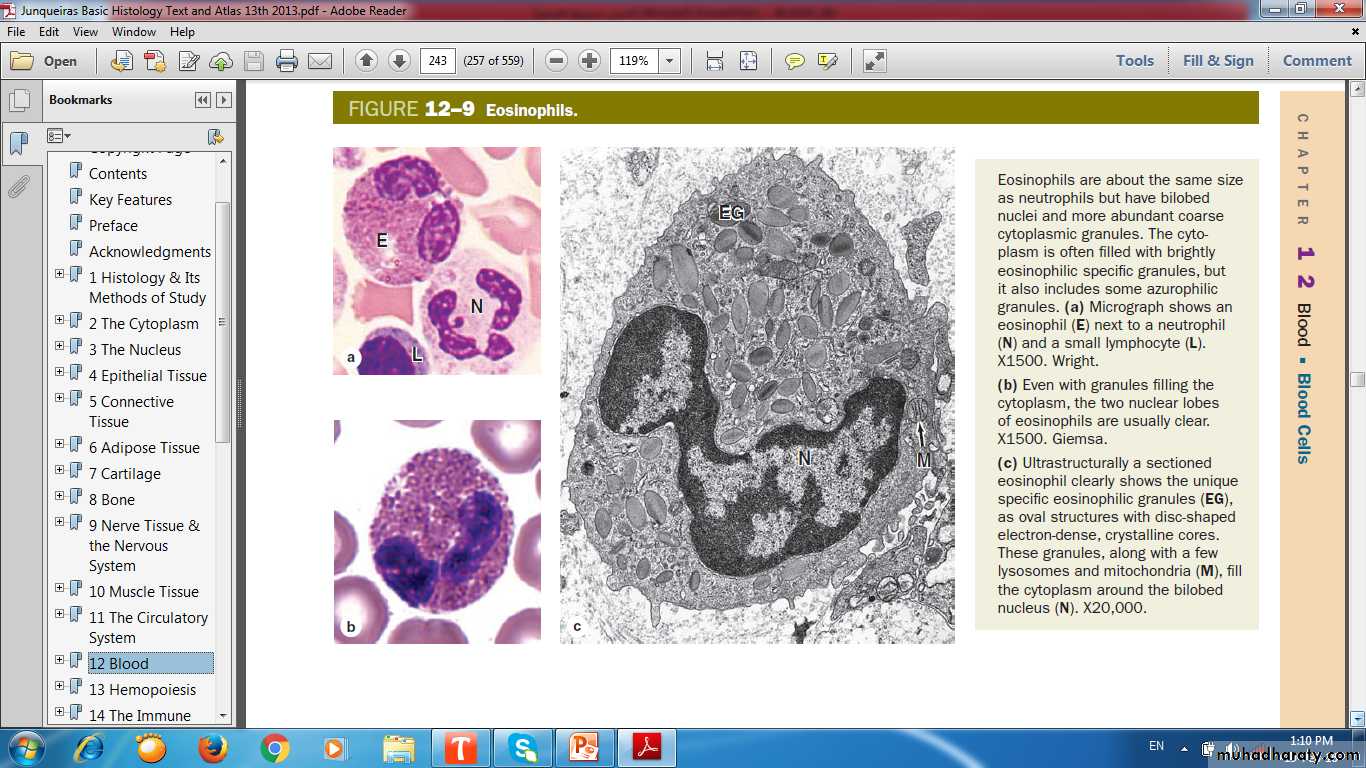
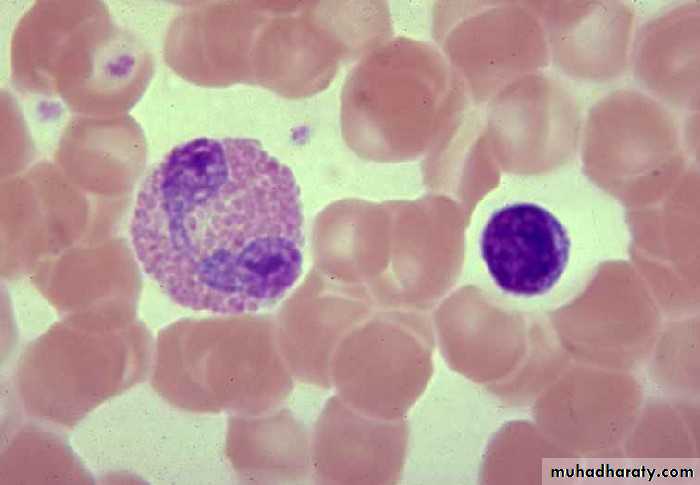
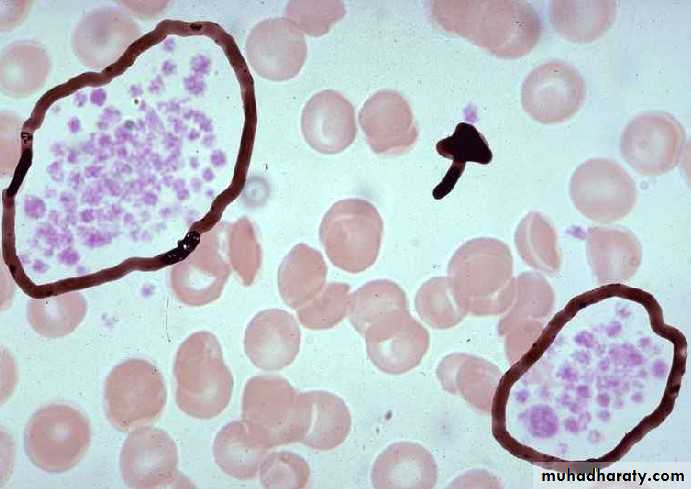
Eosinophils
Bilobed nucleusBright pink Granules
Function:
Important in allergic rxns, parasitic infections, and phagocytosis of Ab-Ag complexes
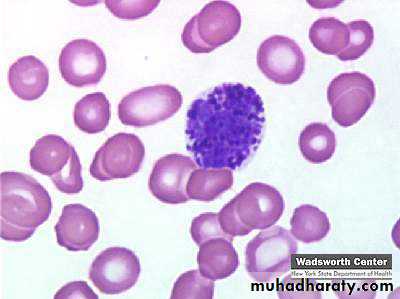
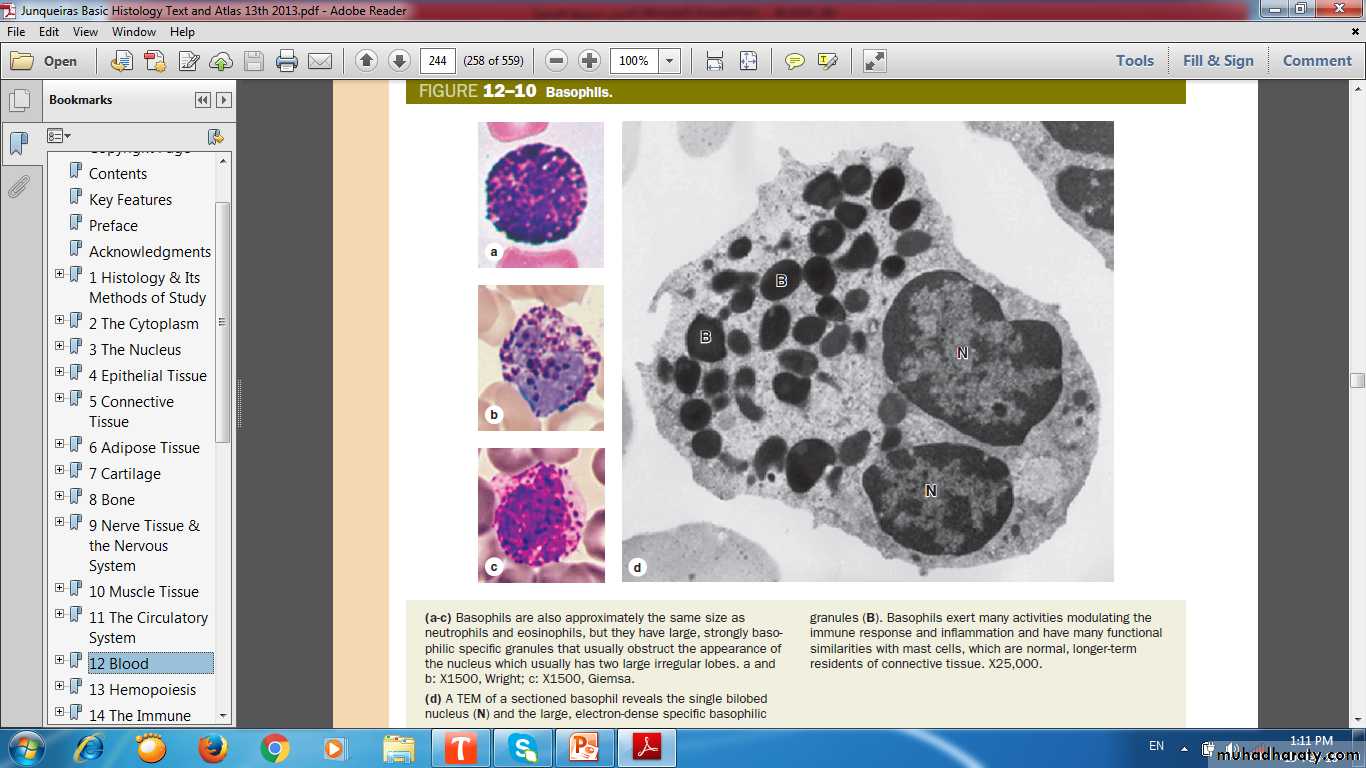
Basophils
Rare!Lobulated (S) shaped nucleus
Dark Blue Granules obscuring nucleus
Hydrolytic enzymes, heparin sulfate, histamine, SRS
Function
Role in hypersensitivity and anaphylaxis
Agranulocytes
Lymphocytes ( T & B cells)Monocytes (Macrophage)
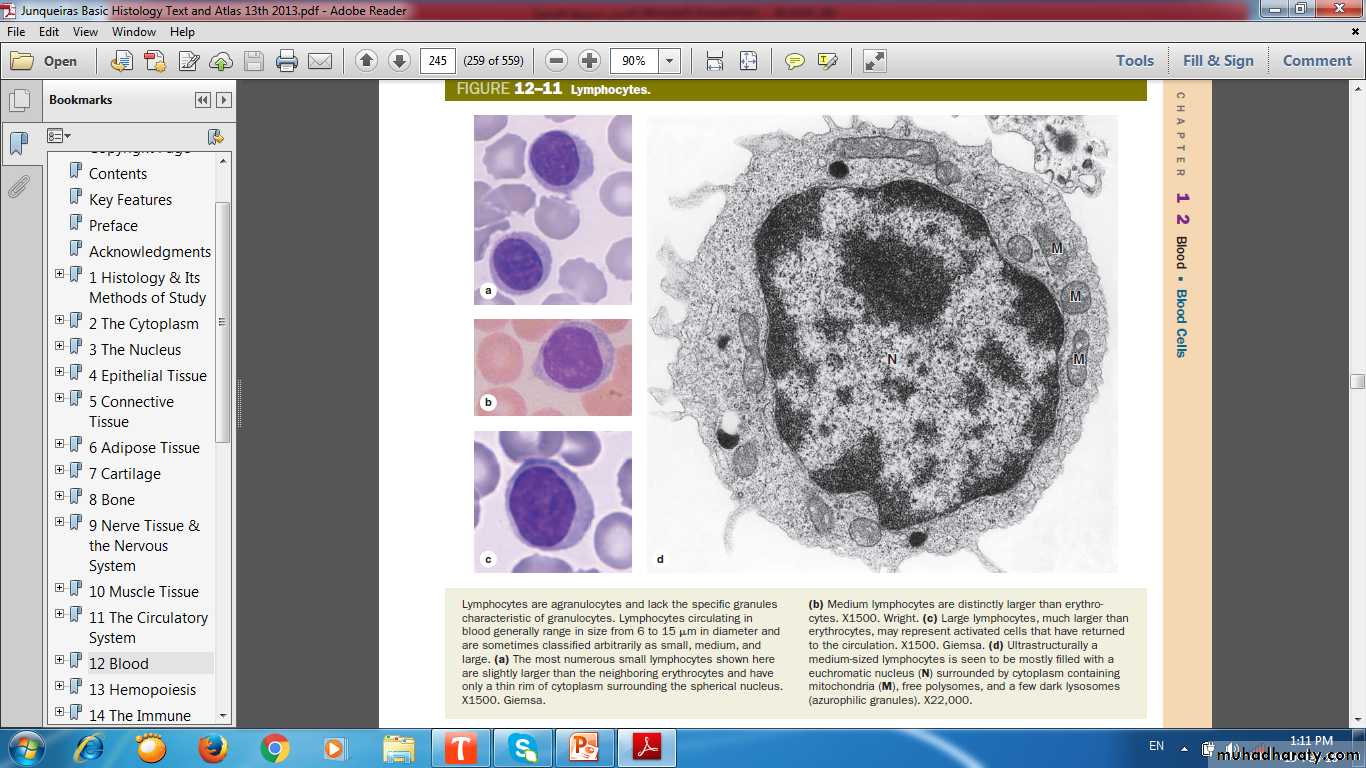
Lymphocytes
Smallest leukocytes, About size of RBCsMost numerous type of agranulocyte, 1/3 of all WBC
Spherical nuclei with rim of scant cytoplasm
TYPES
T cells(CD4, CD8)
B cells
Natural Killer (NK) cells.
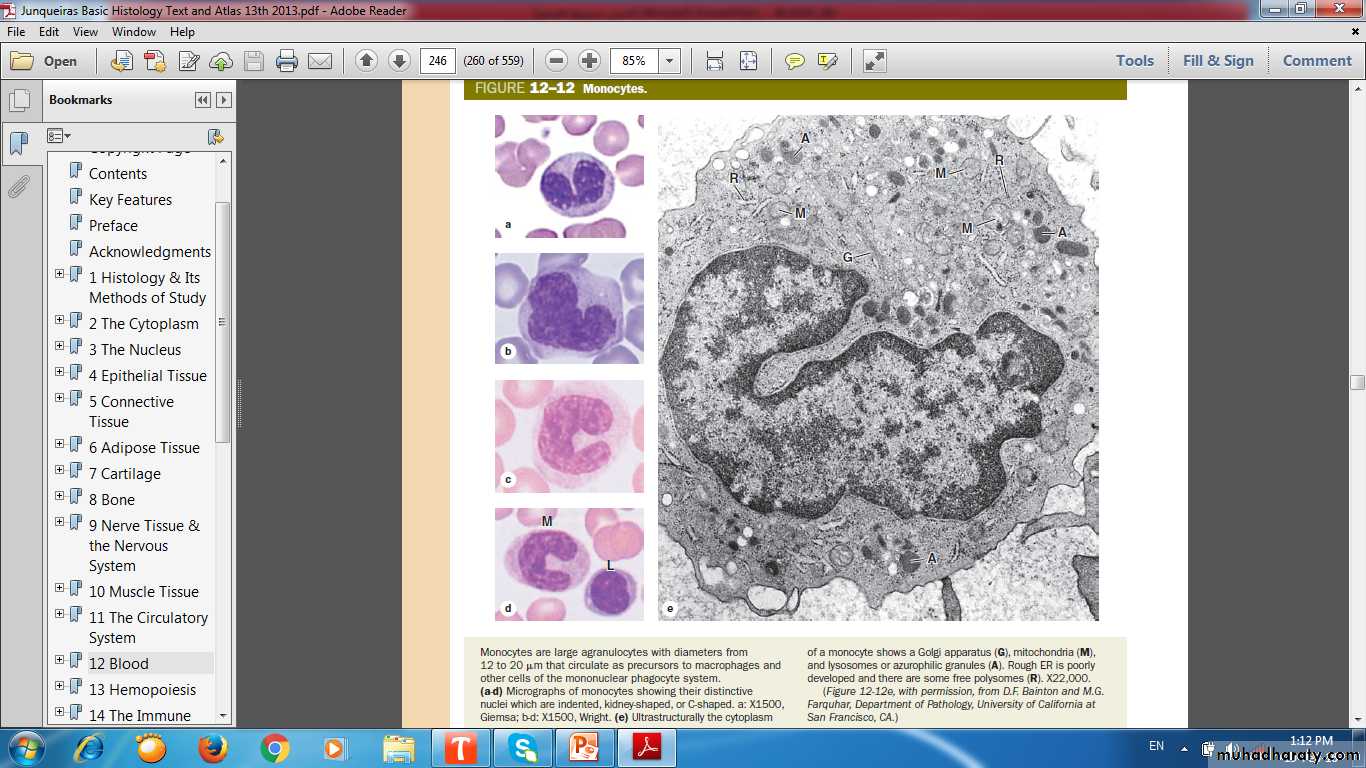
Monocytes
Largest WBCs in blood smearIndented (C ) shaped nucleus
Migrate through blood to the tissues; once in tissues they differentiate into phagocytes (macrophages)
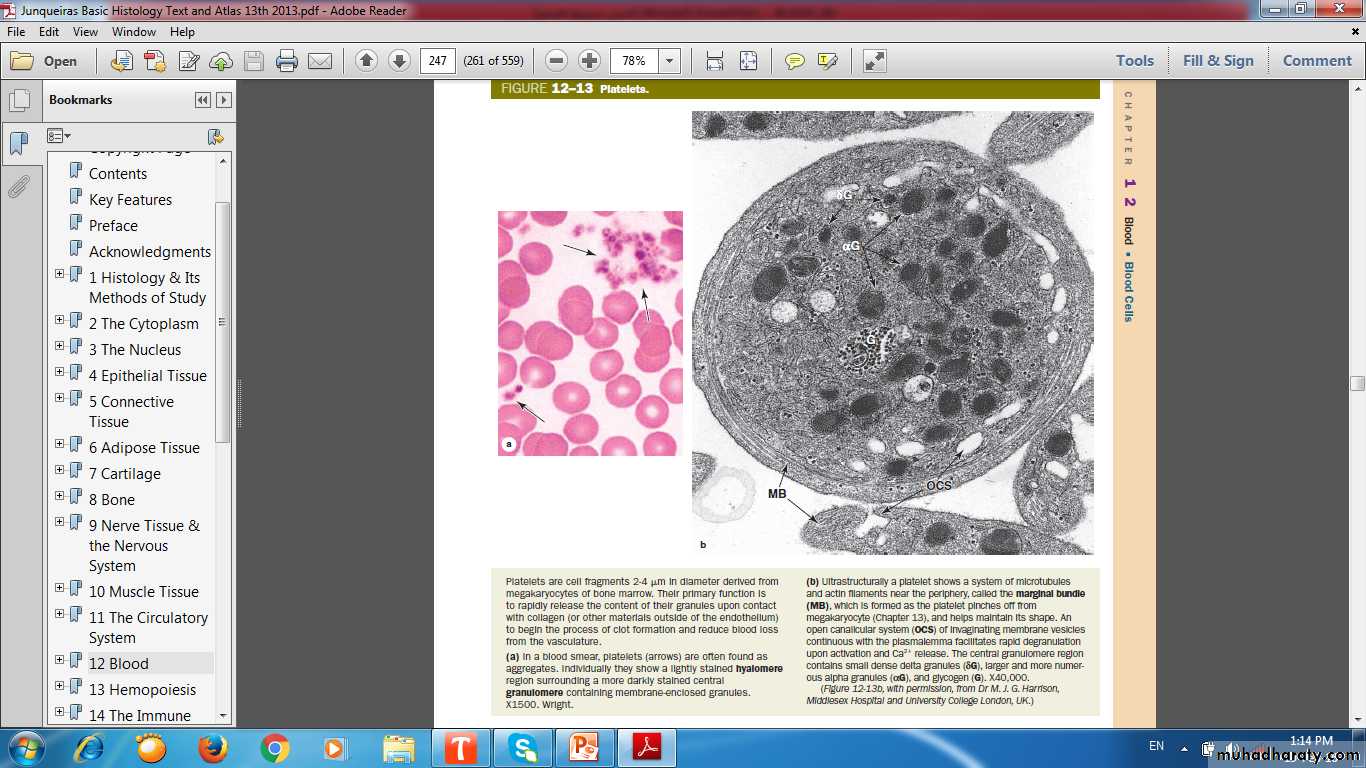
Platelets
Non-nucleatedMembrane- bound cell fragments
Derived from Megakaryocytes
2-4 μm in diameter
150,000 to 400,000/μL (mm3)
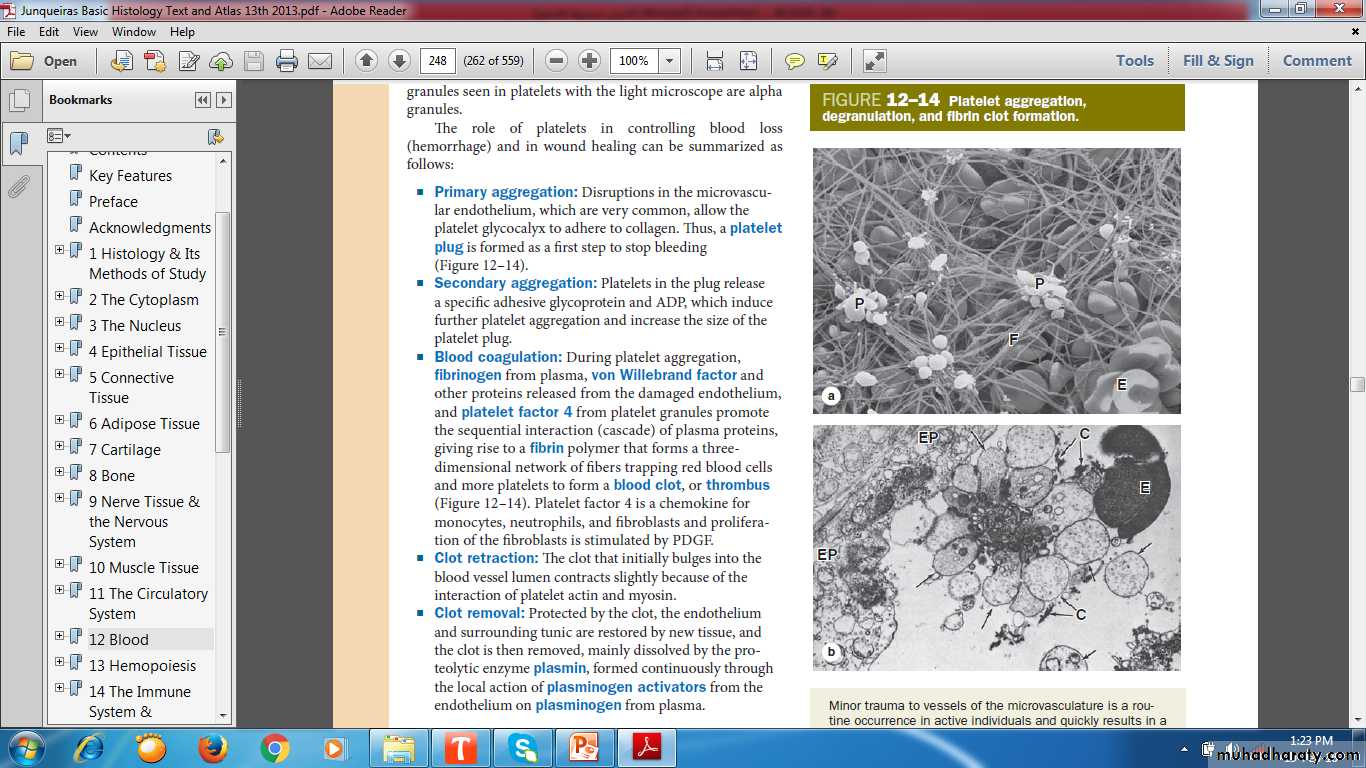
Function in blood clotting
Hyalomere ----------- Lightly stained peripheral zoneGranulomere ------ Darker-staining central zone containing granulesGlycocalyx --------- Involved in adhesion & activation during coagulation