Spinal Cord Lec: 4
• Assis.Professor Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas• MBChB, MSc, PhD
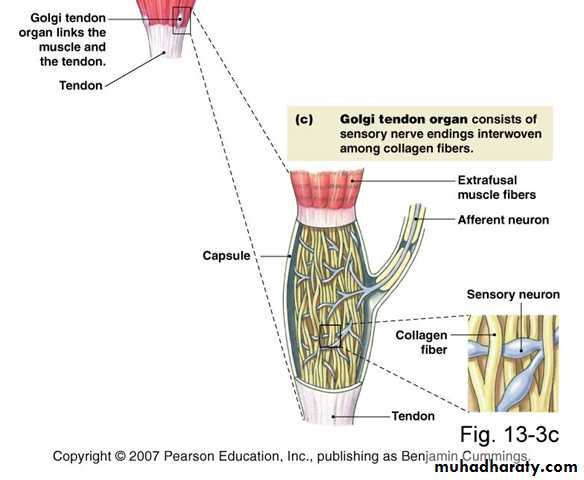
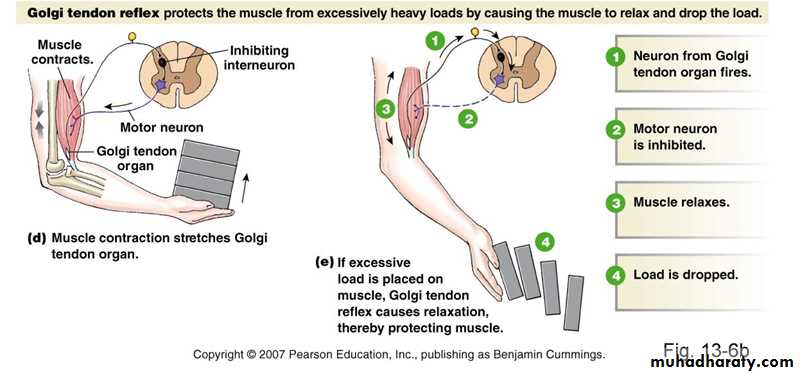
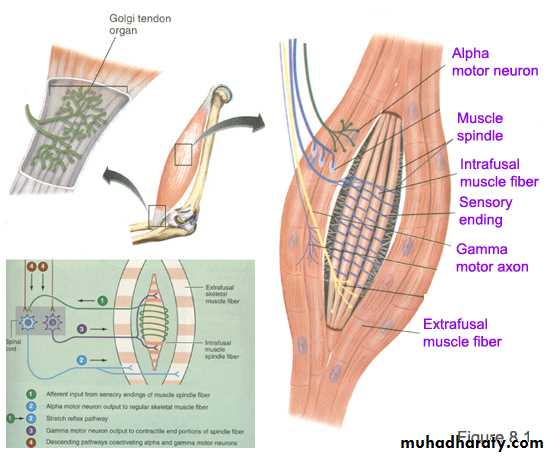
Golgi Tendon Organs
Encapsulated sensory receptors.Located in tendons near their junction with the muscle.
10-15 muscle fibers are connected in series with each Golgi tendon organ.
Endings of afferent nerve fibers wrapped around collagen bundles in tendon.
Golgi Tendon Organs
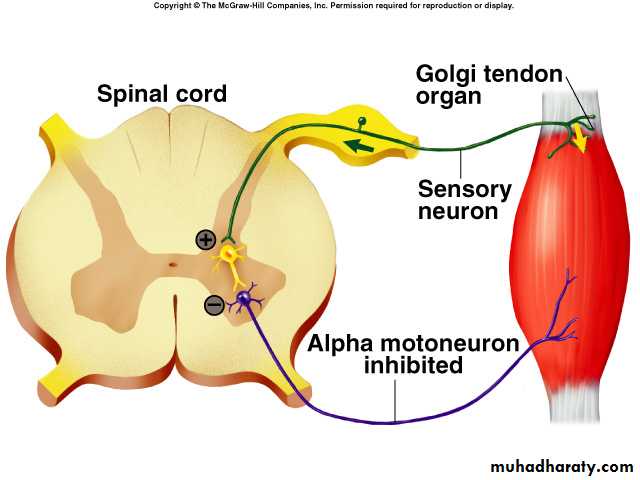
Contraction of attached extrafusal muscle fibers pull on the tendon straightens collagen bundles distorts receptor endings activating their afferent neuronsTransmission of APs to CNS via type Ib nerve fibers.
Inhibit via interneurons, of motor neurons to contracting muscle and its synergists.
Stimulate motor neurons of antagonistic muscles.
Inverse Stretch Reflex
• Golgi tendon organSense Organ
• Ib fiber
Afferent Neuron
CNS (spinal cord)
Synapse
Alpha Motor Neuron
Efferent Neuron
Muscle (extrafusal muscle)
• Effector
Importance
• Prevent muscle tearing or tendon avulsion from its attachments to the bone.• Equalize contractile forces of separate muscle fibers (fibers which exert excess tension become inhibited by the reflex spread muscle load over all fibers prevent damage in isolated areas of a muscle where small numbers of fibers might be overloaded
Polysynaptic Reflexes
• Withdrawal reflex
• Crossed-extensor reflex.
• Abdominal reflex
• Cremasteric reflex
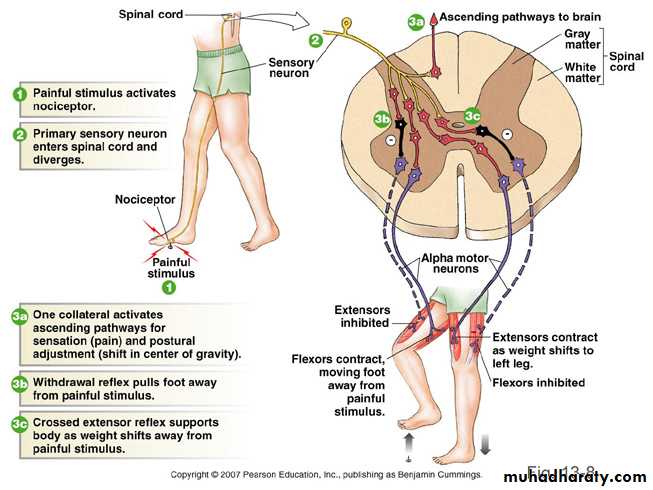
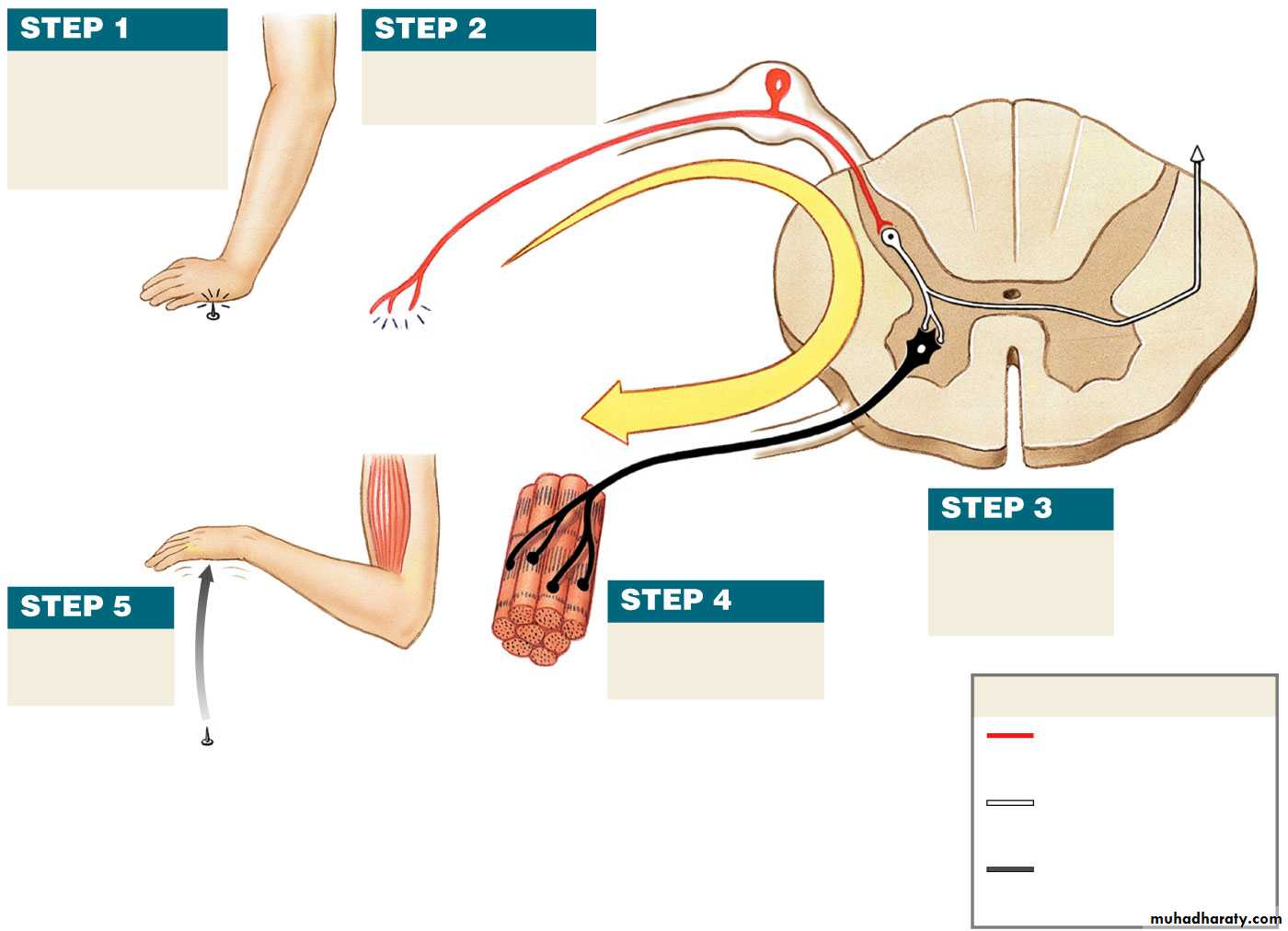
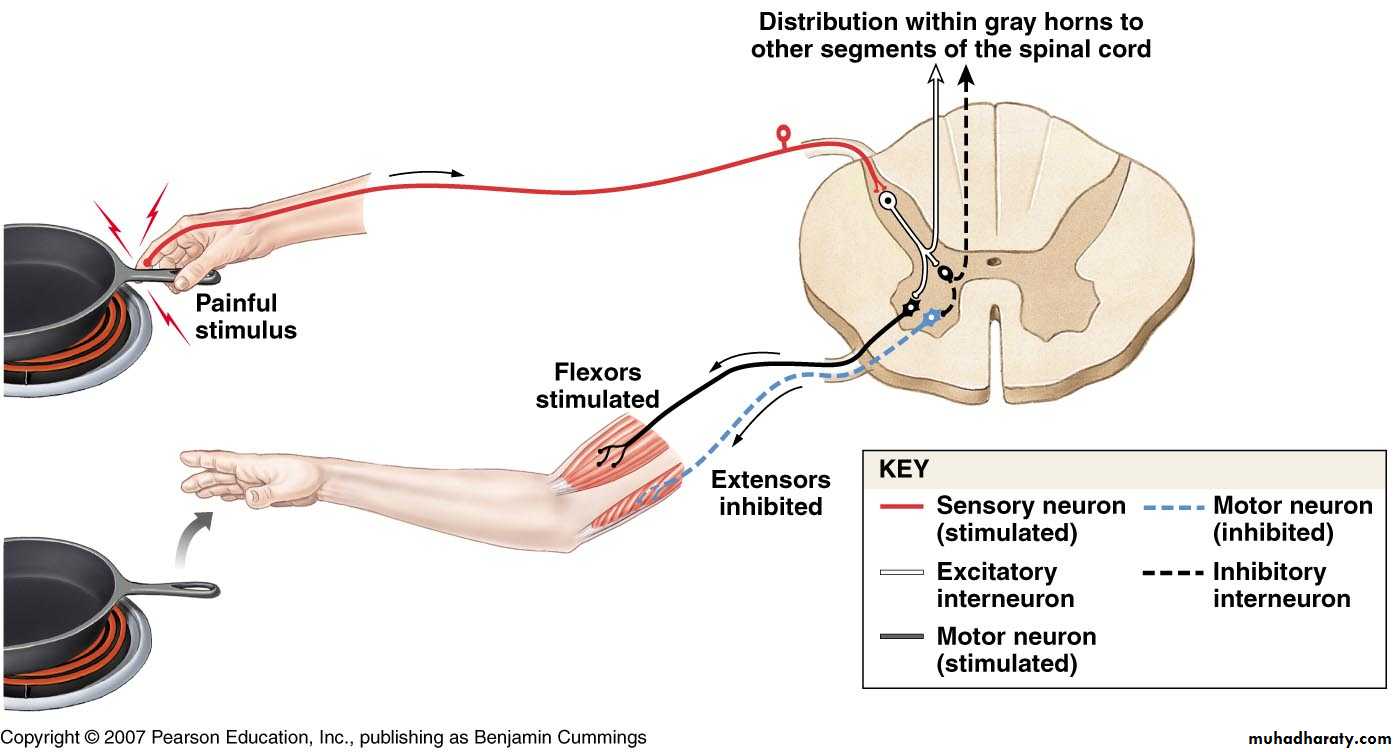
Withdrawal Reflex
Cutaneous sensory stimuli on a limb contraction of flexor muscles withdrawing limb “flexor reflex" or "nociceptive reflex" or "pain reflex".Polysynaptic reflex
• Contraction of flexor muscles
• Inhibition of extensor muscles.
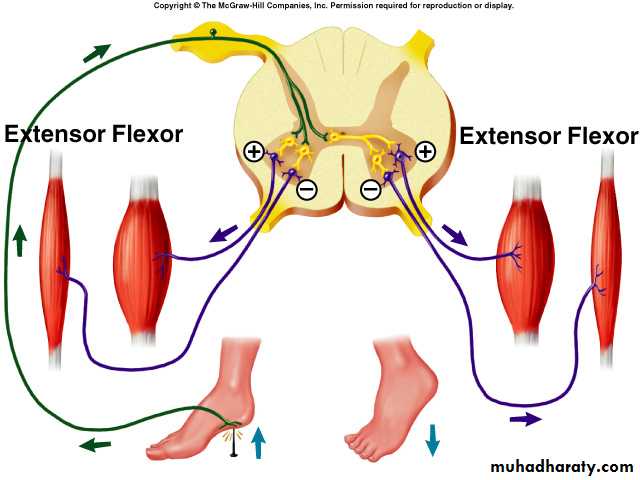
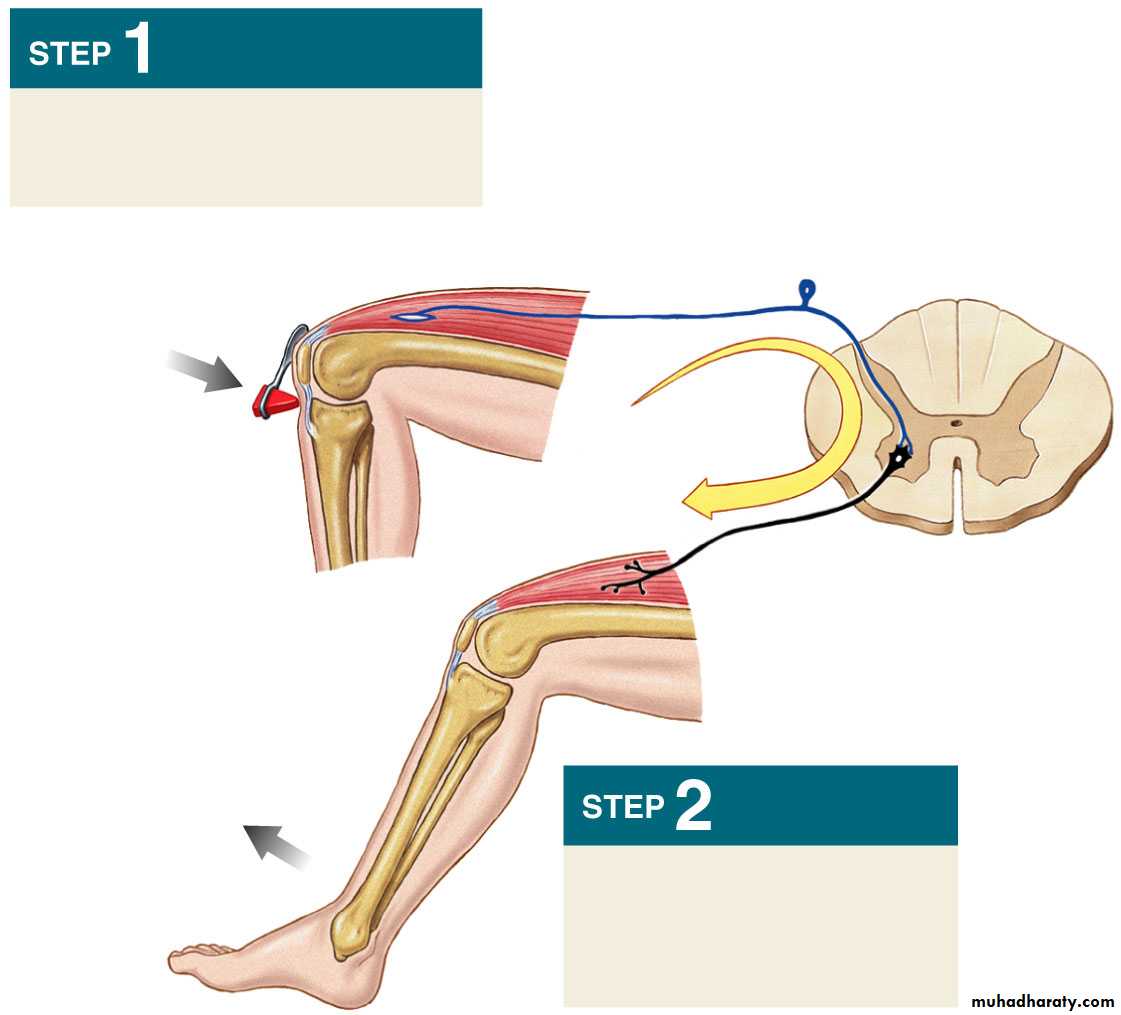
Crossed Extensor Reflex
Application of strong stimulus to a limb.Response includes:
• Flexion and withdrawal of that limb
• Extension of the opposite limb after 0.2-0.5 second.
Abdominal Reflex
Superficial reflexThoracic 7th -12th segments
Polysynaptic
Subject lie down in the supine position.
Gently stroke abdominal skin from lateral to medial aspect in all four quadrant → abdominal muscles contract → umbilicus deviate towards the area stimulated.
Absent Abdominal reflex
• Physiological (obesity, tolerance, children, multiparous lax abdominal wall).• Pathological:
Multiple Sclerosis
Motor Neuron Disease
Neurogenic Bladder
Brown-Séquard syndrome
Chiari Malformations
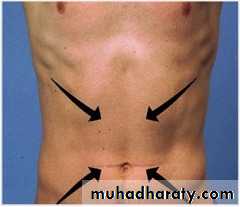
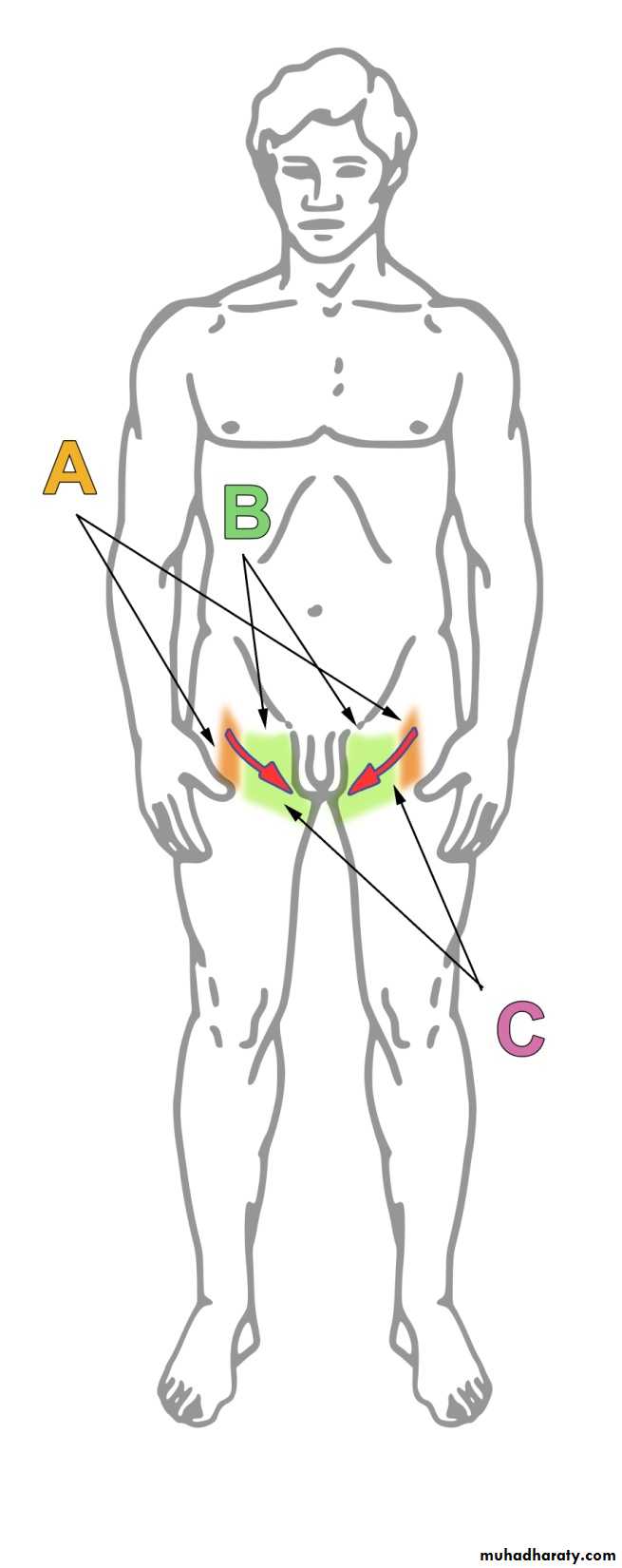
Cremaasteric Reflex
Area A (orange): area of sensory fibers controlled by the genitofemoral nerveArea B (green): area of sensory fibers controlled by the ilioinguinal nerve
Arrow C (red): direction and location where the skin must be stroked to elicit this reflex.
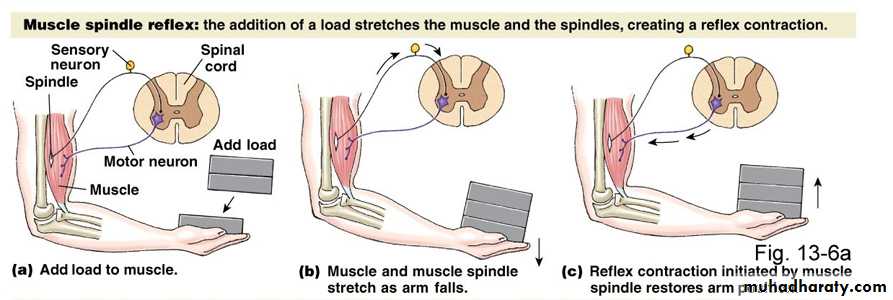
Functions of Stretch Reflex
• Skeletal Muscle Tone:Maintenance of erect posture against force of gravity, by producing a strong muscle tone in the antigravity muscle.
• Damping (smoothing) function:
Signals discharged to a muscle often have varying intensities irregular movements. However through muscle spindle and alpha-gamma linkage, signal are adjusted to produce smooth movements.
Functions of Stretch Reflex
• Servo-Assist Function: servo = force regulator:Stretch reflex assists the brain to produce and regulate force of muscle contraction as follow when the muscle contract:
• α and γ motor fibers are activated to same degree.
• Extrafusal & intrafusal muscle fibers equally contracted and shortened to same degree.
• Central part of intrafusal muscle fibers does not change, and intensity of stretch receptor remains unchanged.
Functions of Stretch Reflex
• If the muscle tries to left a heavy weight, extrafusal fiber contract isometrically and intrafusal fibers contract at the periphery and lengthen central part.
• Potentiates stretch reflex leading to strong muscle contraction to help lifting the weight.
• Antigravity Function:
To resist gravity effect which tends to flex muscle of lower limbs and trunk. Stretched muscles respond by reflex contraction to maintain upright position of body and prevent its fall down.
Arrival of
stimulus andactivation of
receptor
Stimulus
Receptor
Activation of a
sensory neuron
Effector
REFLEX
ARC
Dorsal
root
Ventral
root
Sensation
relayed to
the brain by
collateral
Activation of a
motor neuron
Information
processing
in CNS
KEY
Sensory neuron
(stimulated)
Excitatory
interneuron
Motor neuron
(stimulated)
Response
by effector
Reflex Action
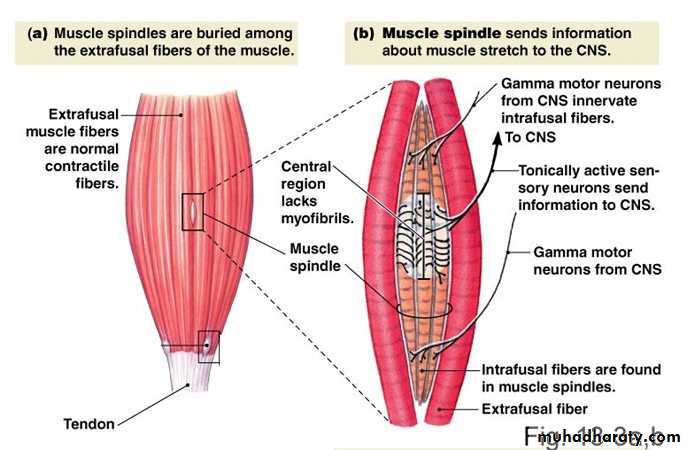
Stretching of muscle tendon
stimulates muscle spindlesStretch
Contraction
Muscle spindle
(stretch receptor)
REFLEX
ARC
Spinal
cord
Activation of motor
neuron produces reflex
muscle contraction