Carcinoma of Prostate
ByIssam S. Al-Azzawi, MD,FICMS,FEBU
Head of Urology Department
Al-Mustansiriya UniversityIncidence : Increase with age /over 65 Very common in west countries In Iraq : It is under estimated Aetiology : Genetic, Race, Diet ?
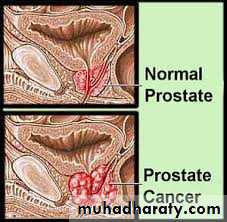
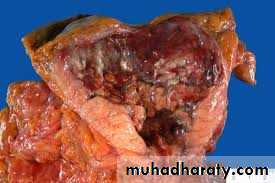
Pathology
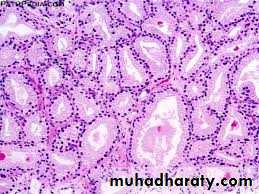
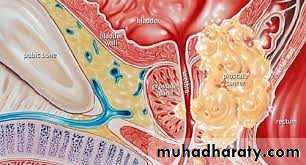
Adeno carcinomaPeriphral zone
Grading : Gleason systemPathology : TNM Staging system
Pathology : Types of Prostate Ca.1. Microscopic Latent cancer2.Early localized P cancer3. Advanced localized P cancer4. Metastatic P cancer
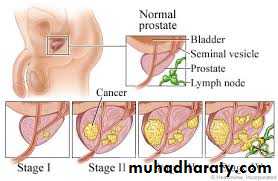
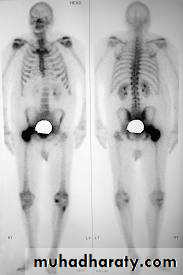
Metastasis of Prostate cancer
Local spread : seminal vesicles, B neck, trigone, distal sphincterLymph spread : Obturator, Int iliac, ext iliac / Mediastinal / Supraclavicular
Blood spread : Bones, liver , lungsClinical features
Asymptomatic
Features of BOO / LUTS
Hematuria
Pelvic pain
Bone pain / malaise / Anemia
Renal failure
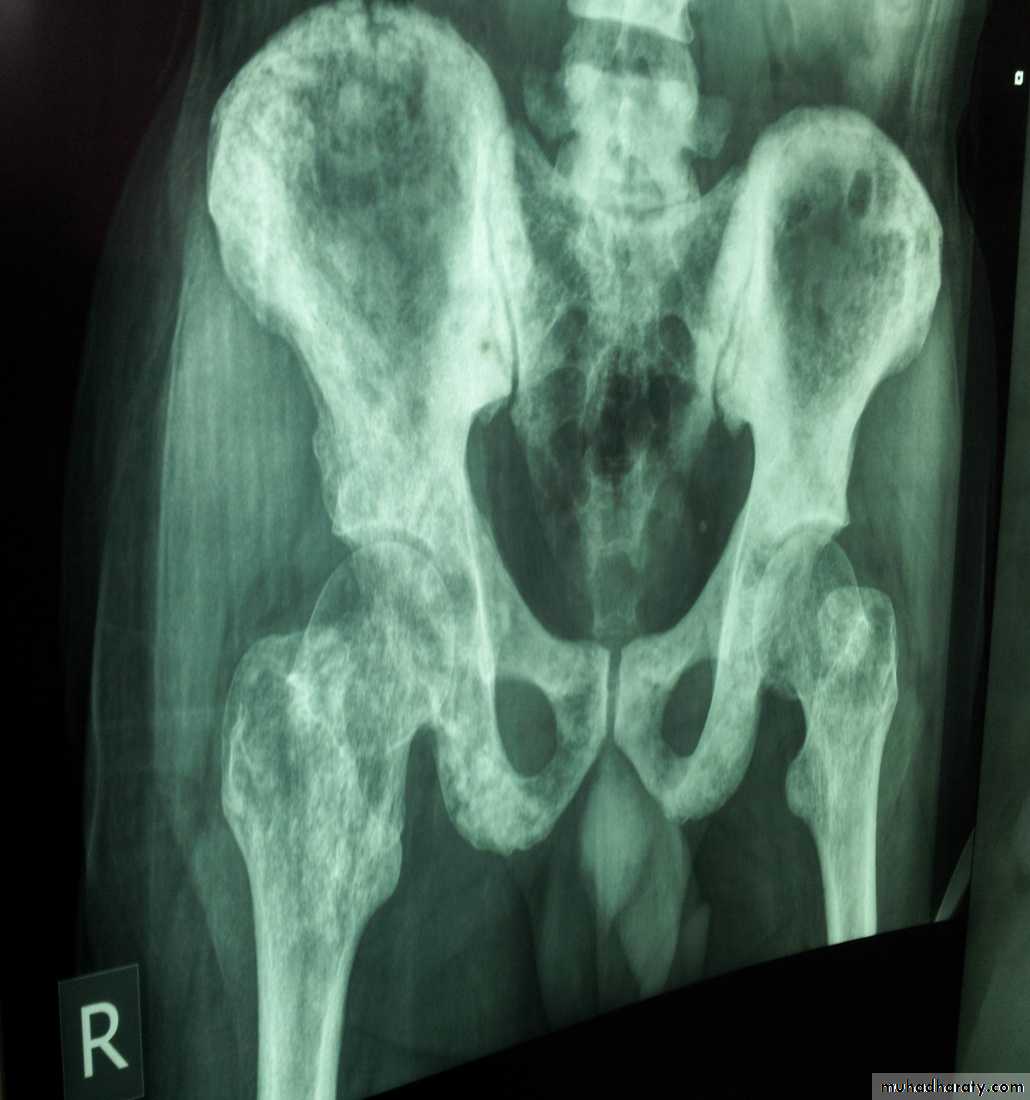
Pathologic fractures / paraplegia
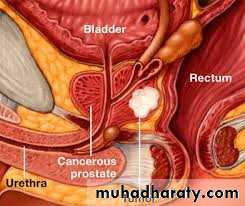
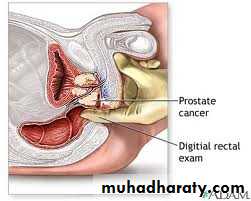
Digital Rectal Examination ( DRE )
Irregular indurationHard nodule
Fixed rectal mucosa
Investigations
Lab . TestsUrinalysis
CBC
Renal function tests
S. acid phosphatase
S. PSA : For screening / Follow up
less than 4 ng/ ml normal
4 – 10 ng / ml gray zone
more than 10 ng/ml suggestive of Ca.
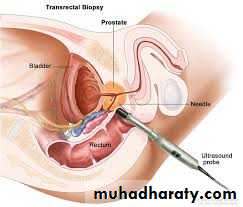
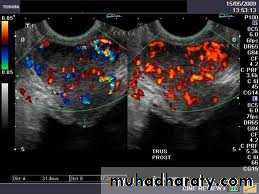
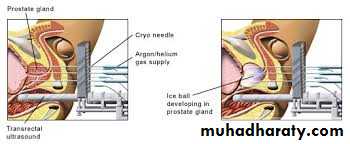
Transrectal Ultrasound ( TRUS ) + Biopsy
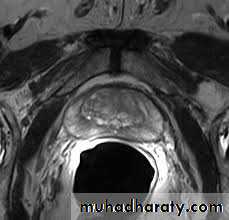
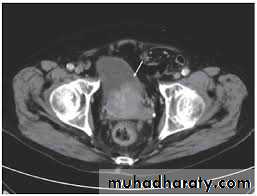
MRI and CT Scan
X-Ray of bones + Isotope Bone scan
Other Investigations for Prostate Ca.Abdominal U/SIVUCXRLaparoscopic pelvic lymphadenectomy
Treatment of prostate cancer
1. conservative ( watchful waiting )2. Radical prostatectomy ( open, Laparoscopic, Robotic )
3. Radical Radiotherapy
4. Brachytherapy / Cryotherapy / HIFU
5. TURP
6. Androgen ablation
7. Molecular targeted therapy
8. Supportive therapy : Bisphosphonates , analgesics, Tx of anemia, Tx of uraemia, Orthopedic intervention
Treatment of prostate cancer
Minimal invasive Tx :
1. Brachytherapy
2. Cryotherapy3. High intensity focused U/S ( HIFU )
Androgen ablation
1. Antiandrogens ( Flutamide, Bicalutamide)2. LHRH agonists ( Zoladex )
3. Estrogens
4. Bilateral Orchiectomy