

OVERVIEW
Major parts or levels of CNS contribute to the
motor system
1- motor cortex:- primary motor area, pre-motor
area & supplementary motor area,
2- hind brain :- red nucleus, basal ganglia &
cerebellum
3- spinal cord:- gray matter anterior motor
neurons & interneuron
white matter passage of motor tracts from the
brain
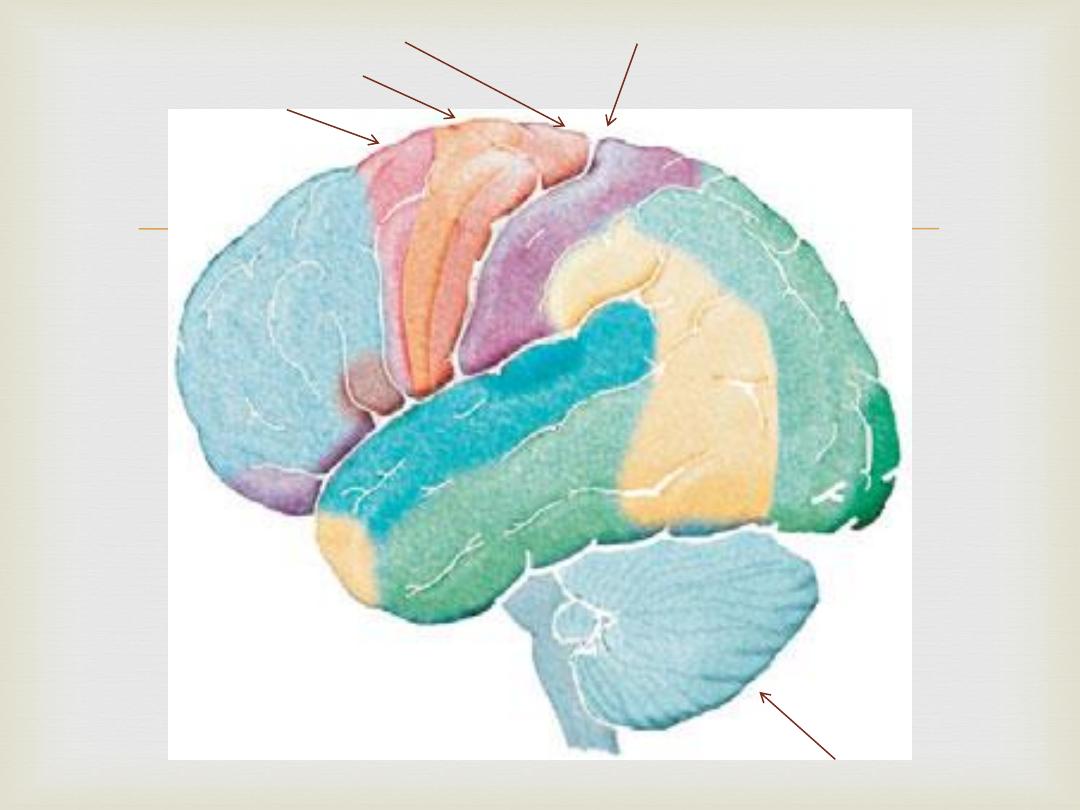
Central sulcus
Primary motor cortex
Supplementary motor cortex
Premotor cortex
Cerebellum
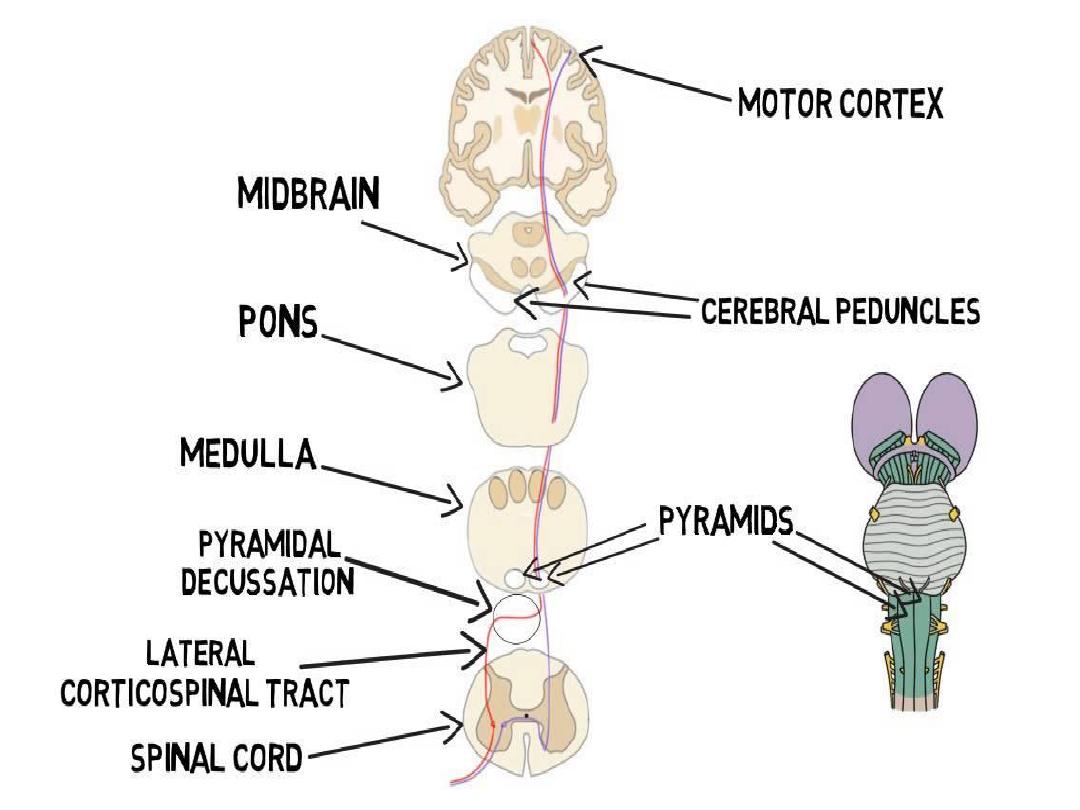

Other important motor pathways
1- extrapyramidal tract
2- rubrospinal tract
4- reticulospinal
5- vestibulospinal tract

Function of various parts of CNS to motor control
1- spinal cord
Reflexes (withdrawal), rhythmical motions (walking)
2- red nucleus serves as an accessory route for
transmission of relatively discrete signals (no fine
control of distal parts of body) from the motor cortex
to the spinal cord.
3- motor cortex- control of movements
4- cerebellum- balance & equilibrium, timing of motor
activities and in rapid, smooth progression from one
muscle movement to the next, control intensity of
muscle contraction, controlling instantaneous interplay
between agonist and antagonist muscle groups.

5- basal ganglia- plan and control complex patterns
of muscle movement, like writing, typing…
Control of subconscious learned movements
(skills)

Examination
Inspection
Palpation
percussion
Auscultation
Gate analysis

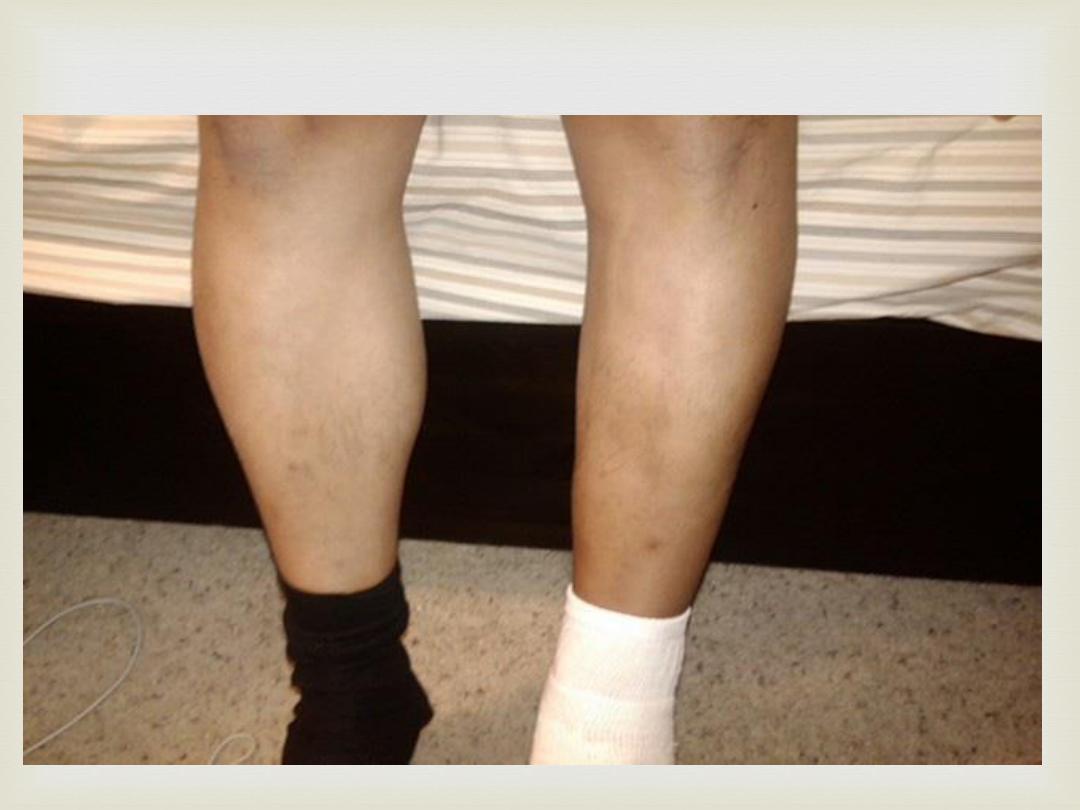
Inspection
Muscle wasting or atrophy
Muscle hypertrophy
Fasciculation
Tremor
Abnormal posture
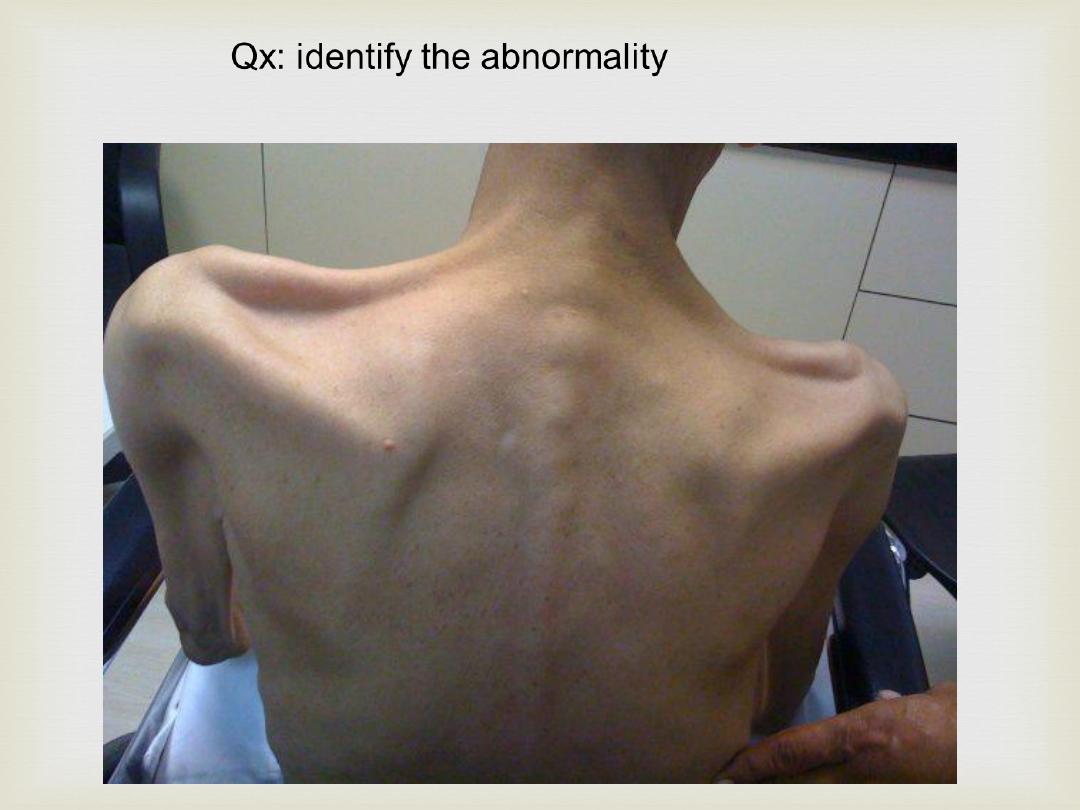
Qx: identify the abnormality
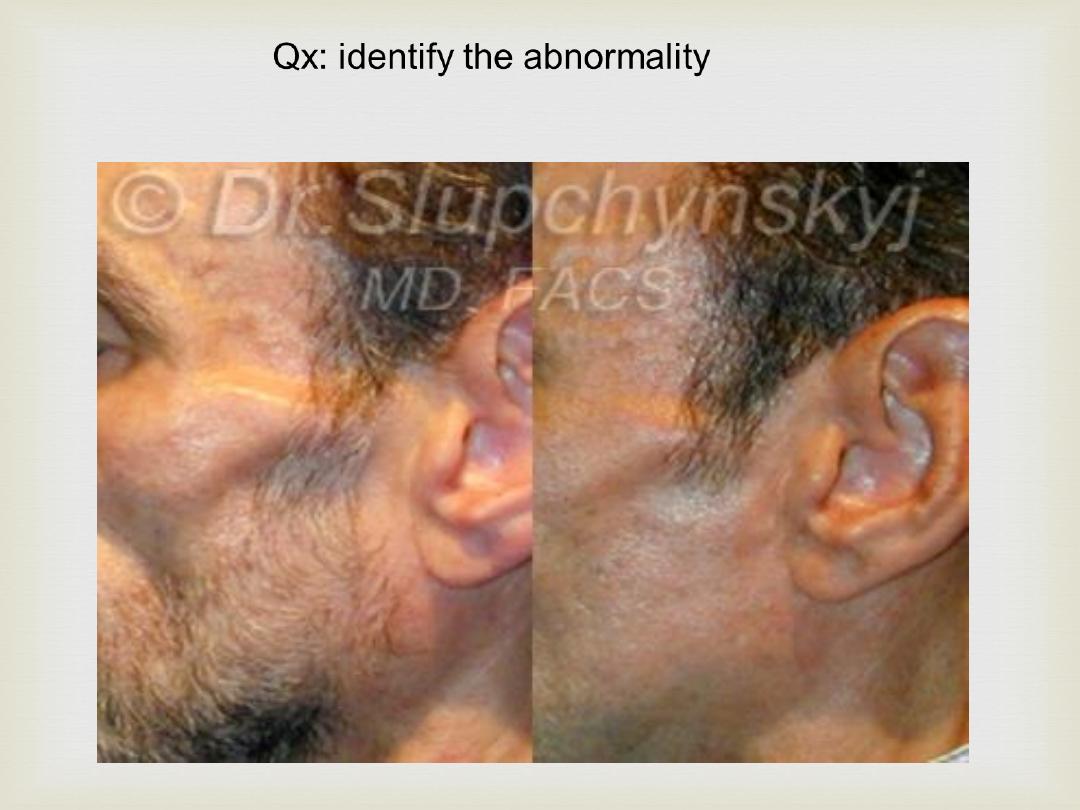
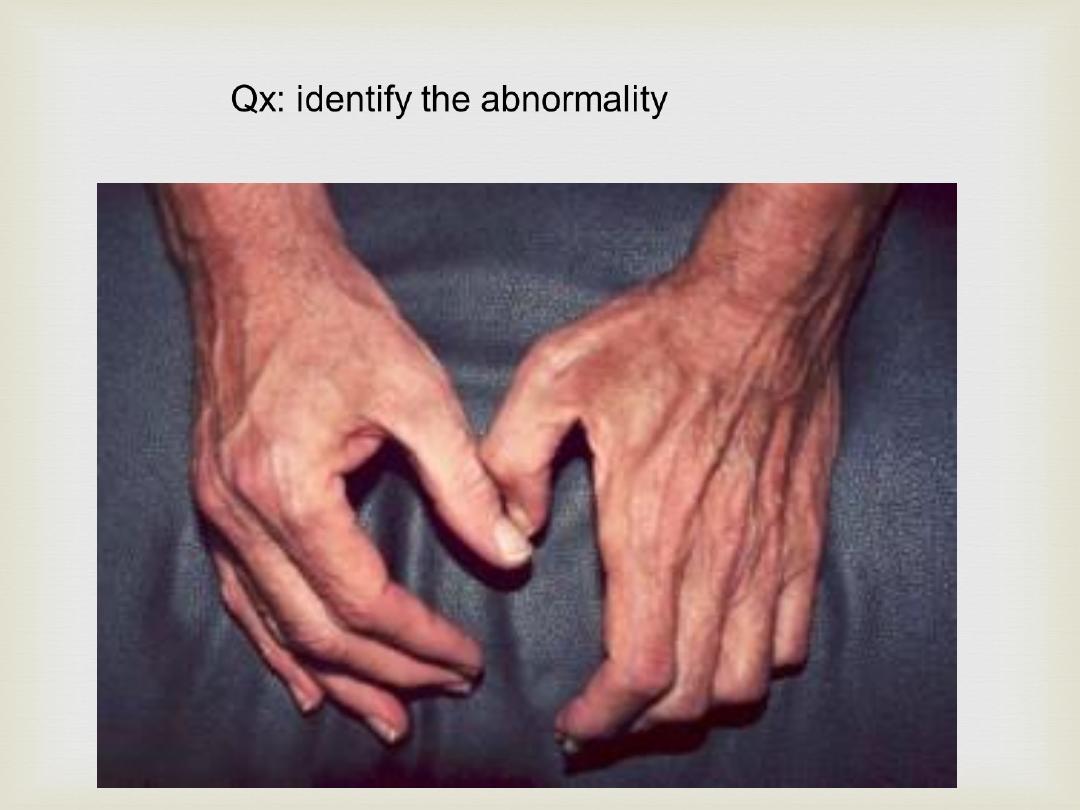
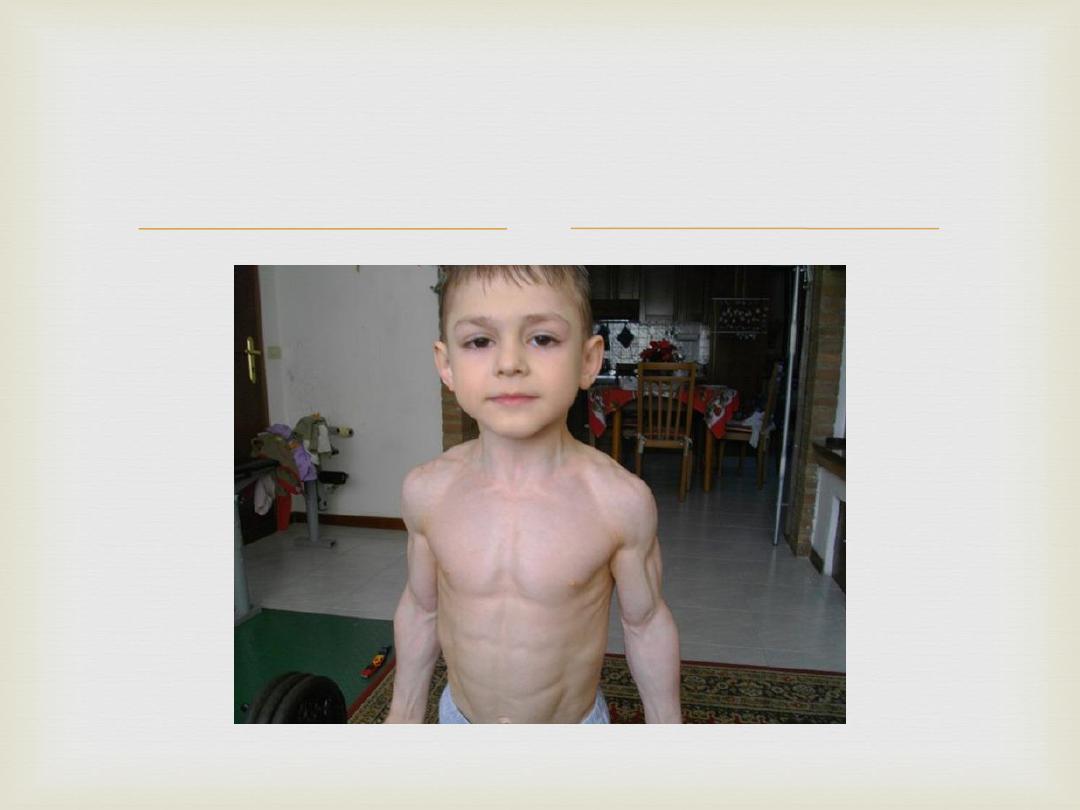
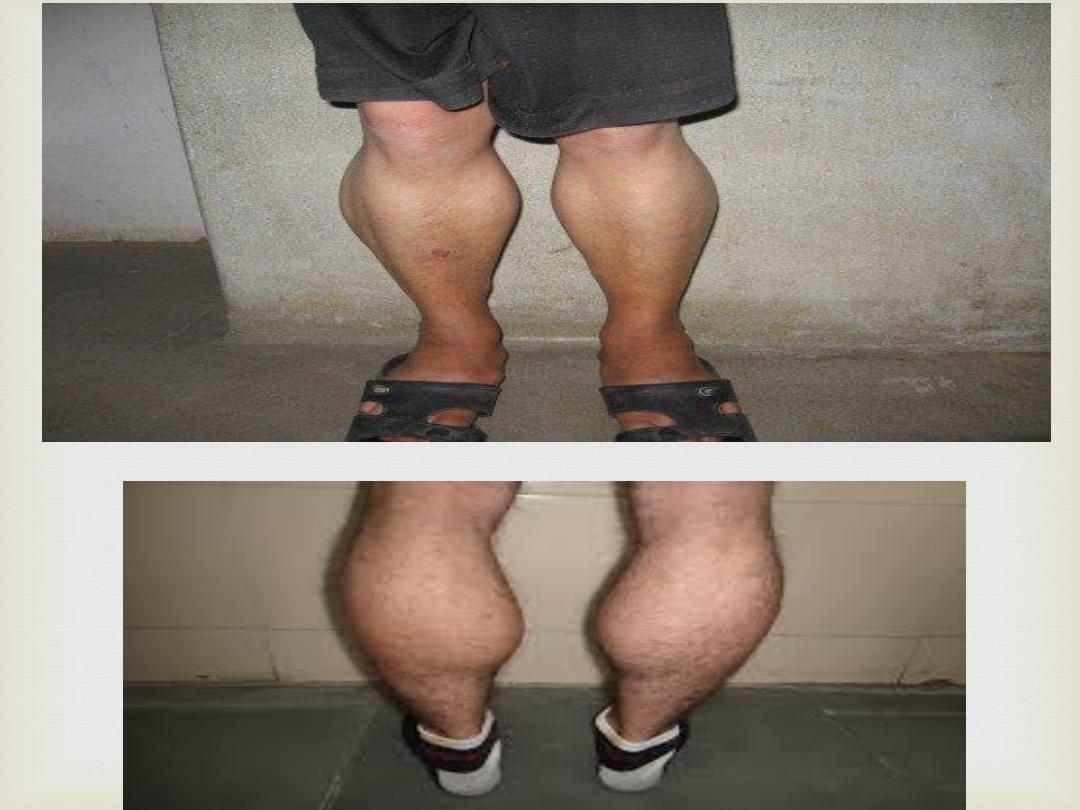

Palpation
Tone & clonus
Power
Reflexes (superficial, deep,
reinforcement)
Coordination
Gate analysis

Classification of muscle power:-
Grade 0: No muscle contraction visible.
Grade 1: Muscle contraction but no movement.
Grade 2: Joint movement with gravity.
Grade 3: Movement against the gravity.
Grade 4: Movement against gravity and the
resistance is weaker than normal. Grade 5:
Normal power.

Reflexes
Superficial reflexes
planter reflex
abdominal reflex (T7-L2)
cremasteric reflex (L1-L2)
Deep reflexes
biceps reflex (C5-C6)
Triceps reflex (C6-C7)
Supinator reflex (C6-C7-C8)
Knee reflex (L2-L3-L4)
Ankle reflex (S1-S2)
Upper motor neurons are
originate in the motor
or the
and carry motor information down to the final
common pathway, that is, any motor neurons
that are not directly responsible for stimulating
the target
.
Lower motor neurons (LMNs) are the
connecting the
, bringing the
from the
out to
the
. A lower motor neuron's axon
terminates on an effector (muscle).

A lower motor neuron lesion is a
which affects
nerve fibers traveling from the
of the
to the relevant
(s) –
the clinical features of
lesion
&
or
-.
or power is reduced
The extensor
Muscle wasting.

An upper motor neuron lesion is a
of the
neural pathway above the
Decreased control of active movement, particularly
slowness
, a velocity-dependent change in
muscle tone
Hypereflexia
Reduced power of muscles or limbs
(extended) rather than curled downwards (flexed)
upon appropriate stimulation of the sole of the foot.
The presence of the Babinski sign is an abnormal
response in adulthood.

Patterns of motor weakness
Paresis-------partial muscle weakness
Plegia----------complete muscle weakness
Monoplegia---------involvement of single limb
Hemiplegia---------involvement of one half or side
of the body
Paraplegia---------involvement of both legs
Tetraplegia---------involvement of all 4 limbs






