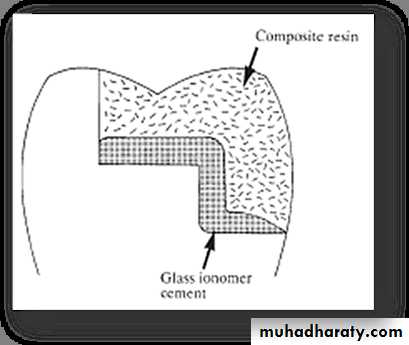
GLASS IONOMER
CEMENT1
معالجة نظري / ثالث اسنان كركوك
د.فاضل
2017/3/6
111
INTRODUCTION
Glass ionomer cement is a tooth coloured material, introduced by Wilson & Kent in 1972.Material was based on reaction between silicate glass powder & polyacrylic acid.They bond chemically to tooth structure & release fluoride for relatively long period.2
DEFINITION of cement
A cement is a substance that hardens to act as a base , liner , filling material or adhesive to bind devices or prosthesis to the tooth structure or to each other.Glass ionomer cement is a water based cement
3
CLASSIFICATION
• For luting• For restoration
• III. For liner & bases
• IV. Fissure & sealent
• V. As Orthodontic cement
• VI. For core build up
Type II.1 Restorative esthetic
Type II.2 Restorative reinforcedType
TypeType
Type
Type
Type
4
5
6
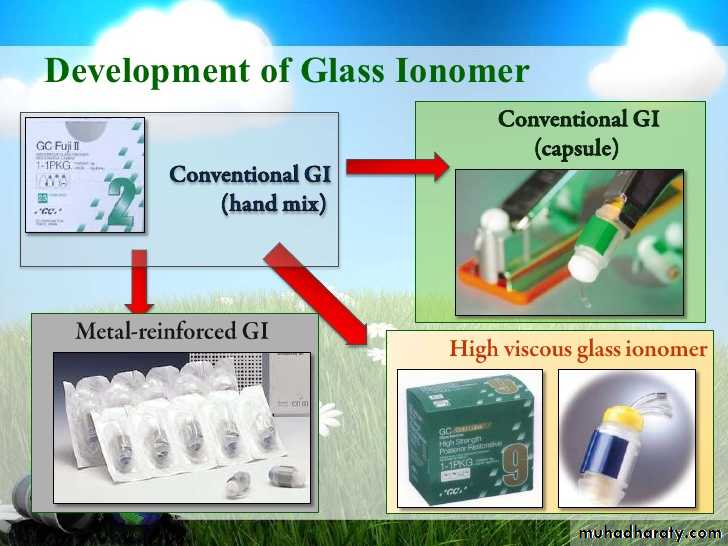
RMGI products
Liner / BaseFuji lining LC
Vitrebond
7
• Restorative buildup
RMGI productsFuji II LC
Vitremer Ketac Nano
8
COMPOSITION
Powder :-Acid soluble calcium fluroalumino silicate glass.
Silica - 41.9%
Alumina - 28.6%
Aluminum fluoride - 1.6%
Calcium fluoride - 15.7%
Sodium fluoride - 9.3%
Aluminum phosphate - 3.8%
Fluoride portion act as ceramic flux. Strontium,
Barium or zinc oxide provide radio opacity.
9
Liquid :-
1.Polyacrylic acid in the form co-polymer with itaconic acid & malice acid .2.Tartaric acid: improves handling characteristic
& increase working time.
3.Water : Medium of reaction & hydrates the
reaction products
10
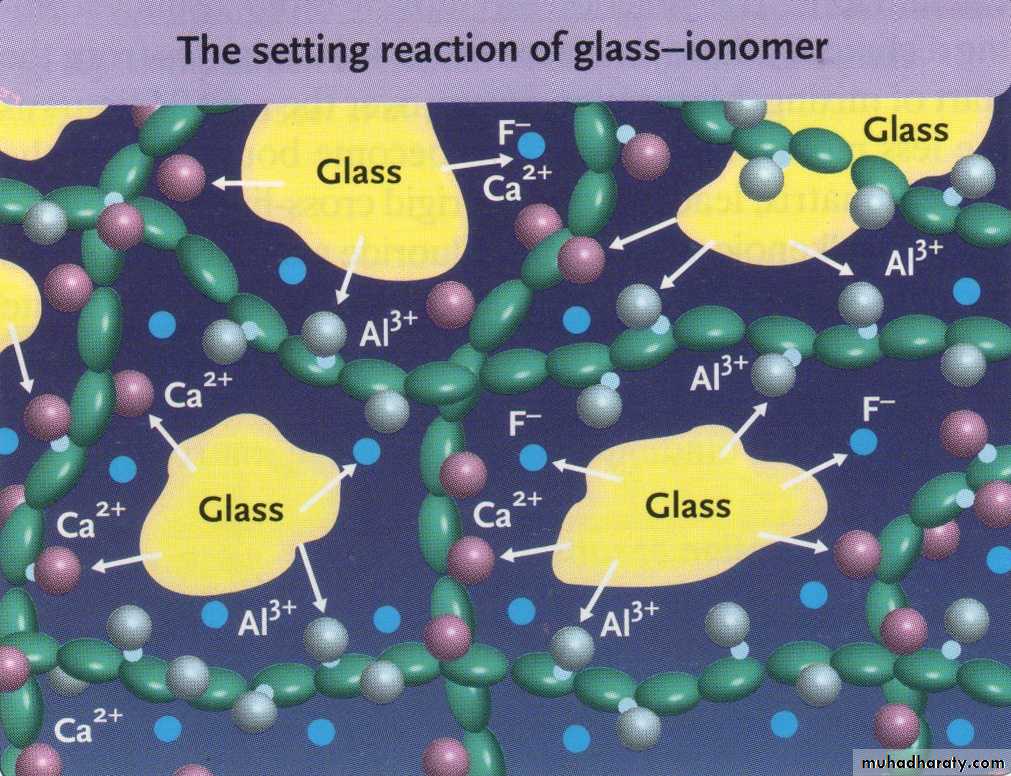
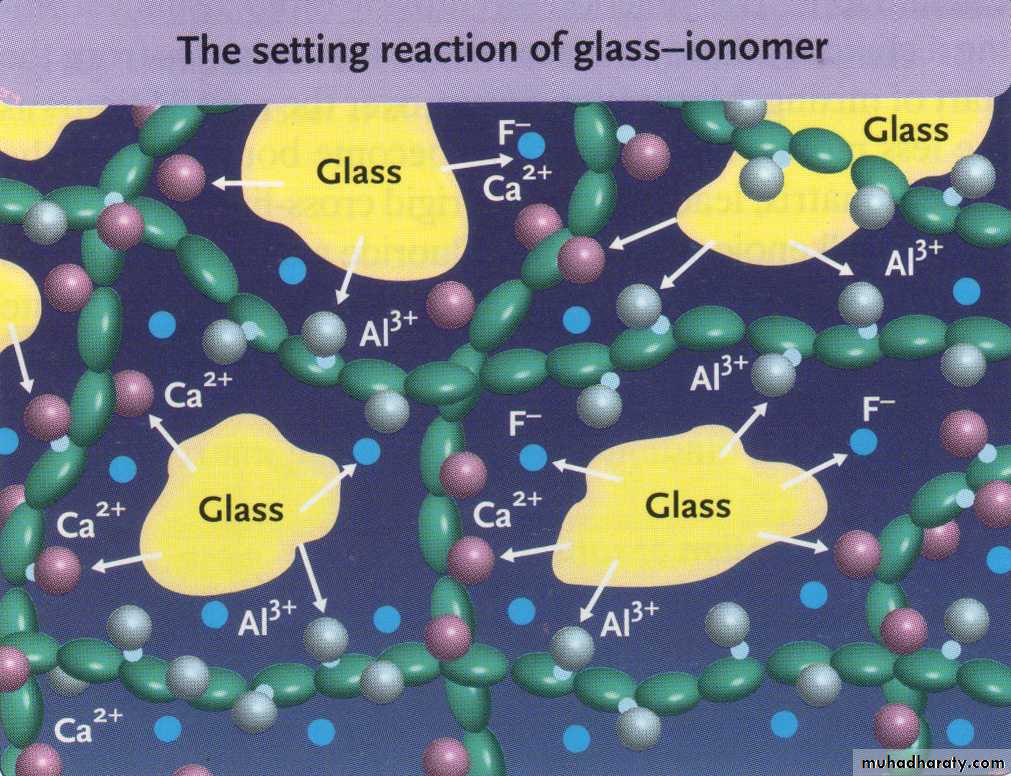
SETTING REACTION
When the powder & liquid are mixed, Surface of glass particles are attacked by acid. then Ca, Al, sodium, & fluoride ions are leached into aqueous medium.11
Calcium poly salts are formed first, then followed by aluminum poly salts which cross link with poly anion chain.
Set cement consist of unreacted powder particle surrounded by silica gel in amorphous matrix of hydrated calcium & aluminum poly salts.
Calcium poly salts are responsible for initial set.
Aluminum poly salts form the dominant phase.
12Water plays an important role in structure of cement.
After hardening, fresh cement is extremely prone to the cracking & crazing, due to drying of loosely bound water .Hence these cements must be protected by application of varnish.
13
SETTING TIME
Type I 4 - 5 minutesType II 7 minutes
14Setting reaction
1. acid-base reaction2. light activated polymerisation
ACID – BASE REACTION
GIC formed by the reaction of three materials
Fluoro alumino silicate glass powder
Poly acrylic acid
Water
An acid – base reaction occurs between the glass powder and the ionic polymer.
Water is essential because that is the medium through which ion transfer takes place
15
16
PROPERTIES
Compressive strength - 150 mpaTensile strength - 6.6 mpa.
Hardness - 49 KHN.17
Solubility & Disintegration:-
Initial solubility is high due to leaching of intermediate products.The complete setting reaction takes place in 24 hrs, cement should be protected from saliva during this period.
18
Adhesion :-
Glass ionomer cement bonds chemically to the tooth structure.Bonding is due to reaction occur between carboxyl group of poly acid & calcium of hydroxyl apatite.
Bonding with enamel is higher than that of dentin ,due to greater inorganic content.
Esthetics :-
GIC is tooth coloured material & available in different
shades.
Inferior to composites.
They lack translucency & rough surface texture.
Potential for discolouration & staining.
19
Biocompatibilty :-
Pulpal response to glass ionomer cement is favorable.
Pulpal response is mild due to
- High buffering capacity of hydroxy apatite.
- Large molecular weight of the polyacrylic
acid ,which prevents entry into dentinal tubules.
Anticariogenic properties :-
Fluoride is released from glass ionomer at the time of mixing & lies with in matrix. Fluoride can be released out without affecting the physical properties of cement.
20
MANIPULATION
1.Preparation of tooth surface :-The enamel & dentin are first cleaned with pumice slurry followed by swabbing with polyacrylic acid for 5 sec. After conditioning & rinsing ,tooth surface should isolate & dry.
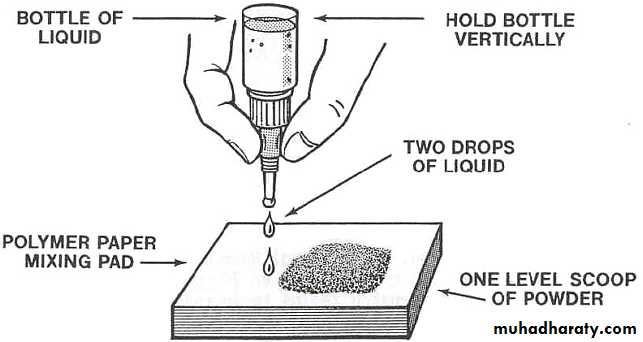
2.Proportioning & mixing :-
Powder & liquid ratio is 3:1 bywt. Powder & liquid is dispensed just prior to mixing.
First increment is incorporated rapidly to produce a homogenous milky consistency.
Mixing done in folding method to preserves gel structure.
Finished mix should have a glossy surface.
21
22
3. Protection of cement during setting :-
Glass ionomer cement is extremely sensitive to air & water during setting.Immediately after placement into cavity, preshaped matrix is applied to it.
4. Finishing :-
Excess material should be trimmed from margins.
Hand instruments are preferred to rotary tools to avoid ditching.
Further finishing is done after 24hrs.
23
Finishing technique
Best surface –cement allowed to set under matrixCarving the cement external to the cavity margins with sharp knives or scalers
Finest abrasive should be used to minimize tearing
Finishing with rotary instruments should be done at subsequent visit
24
5.Protection of cement after setting :-
Before dismissing the patient ,restoration is again coated with the protective agent to protect trimmed area.Failure to protect for first 24hrs results in weaken cement.
25
Advantages:-
Inherent adhesion to the tooth surface.Good marginal seal.
Anticariogenic property.
Biocompatibilty
Minimal cavity preparation required.
Disadvantages:-
Low fracture resistance.Low wear resistance.
Water sensitive during setting phase .
Less esthetic compared to composite.
26