Department of Surgery & Obstetrics
College of Veterinary MedicineUniversity of Mosul
Nosocomial infection
Infection that are acquired by the patient during the course of hospitalizationThese infection may occur in anatomical sites other than the surgical wound and may developed preoperatively, postoperatively or even after the patient has been discharged
Department of Surgery & Obstetrics
College of Veterinary MedicineUniversity of Mosul
Hemorrhage and Hemostasis
Department of Surgery & Obstetrics
College of Veterinary MedicineUniversity of Mosul
Hemorrhage and Homeostasis
Loss of blood from the vascular system may be result of diapedesis or rhexis. Control of bleeding is very important because, Aside from anesthetic problems, the only problem in surgery is bleeding. Bleeding is eventually accompanied by shock, and loss of red blood reduce the oxygen carrying capacity of bloodDepartment of Surgery & Obstetrics
College of Veterinary MedicineUniversity of Mosul
Causes:
1- penetrating wound2- Incisions
3-Contusions or laceration
4- Blood may fail to clot within normal time because, Liver disease, irradiation, chemical poisoning, Walfarin, phosphorus, arsenic
Department of Surgery & Obstetrics
College of Veterinary Medicine
University of Mosul
Types of Hemorrhage:
According to sourceArterial hemorrhage
Blood is bright red, and flow under pressureVenous hemorrhage
Blood is bluish-red and flow freelyCapillary hemorrhage
The blood oozes under very low pressureDepartment of Surgery & Obstetrics
College of Veterinary MedicineUniversity of Mosul
According to time of occurrence as
Primary hemorrhageOccurs at the time of injury
Intermediate hemorrhage
Occurs within 24 hours of injurySecondary hemorrhage
Occurs more than24 hours after initial injury, usually result of necrosis, ulceration, occur due to slip ligature
Department of Surgery & Obstetrics
College of Veterinary MedicineUniversity of Mosul
According to extent
Petechial hemorrhage
Small hemorrhagic areas within skin, serosa, mucosa
Brushing bleeding
Which refers to larger areas of subcutaneous or submucosal hemorrhageDeep hemorrhage
Which refers to extravasations into soft tissue.
Department of Surgery & Obstetrics
College of Veterinary MedicineUniversity of Mosul
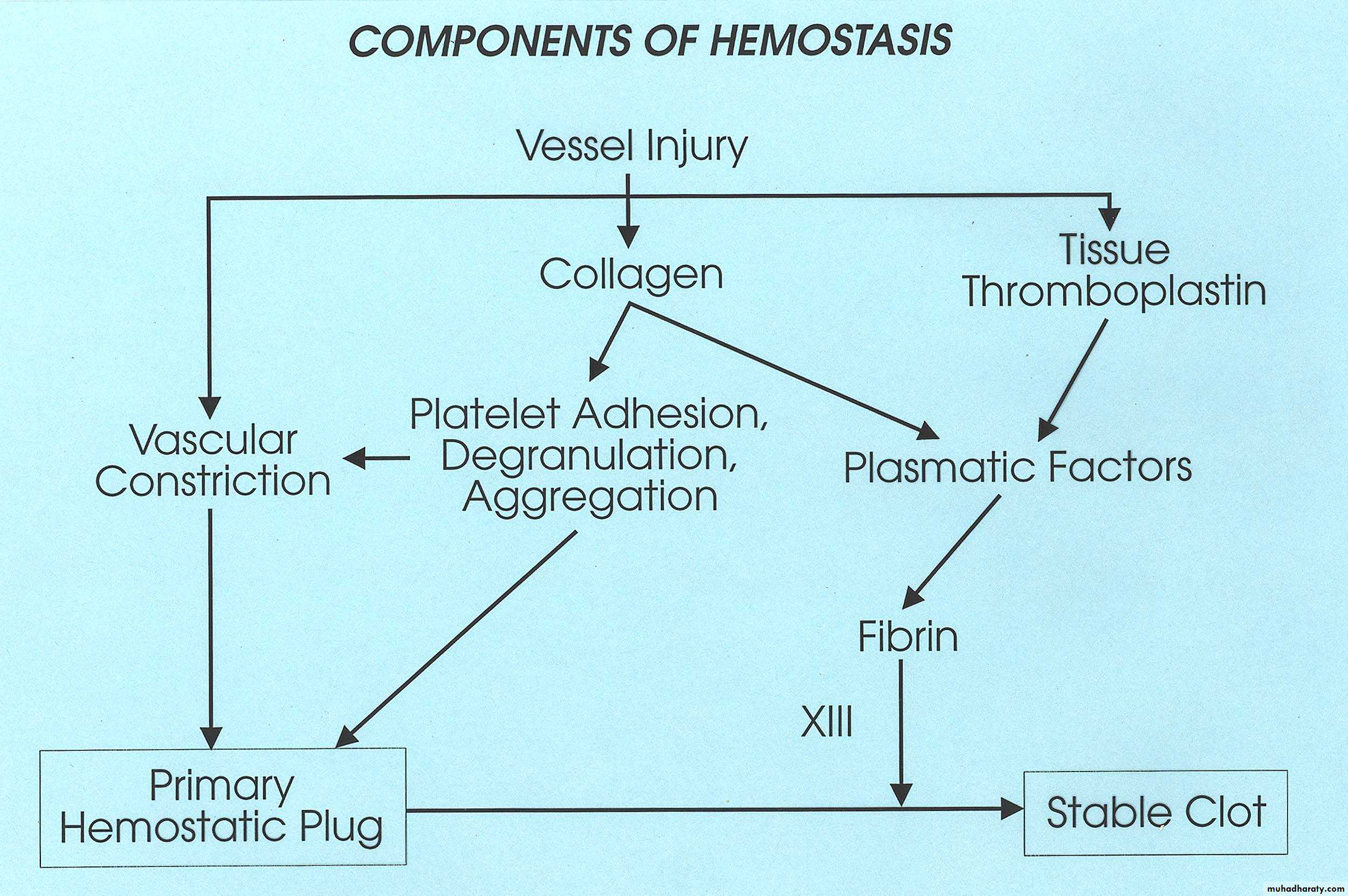
Haemostais
Process of Hemostasis
Vascular injury
Platelet adhesion and activation
Platelet aggregation (1o hemostatic plug)
Fibrin formation via cascade (2o hemostasis)
Clot retraction (thrombasthenin)
Fibrinolysis and healing
Role of Platelets
Surveillance for vascular integrityFormation of 1o hemostatic plug
Activation of 2o hemostasis
Healing
Department of Surgery & Obstetrics
College of Veterinary MedicineUniversity of Mosul
Hemostasis
There are at least 3 factors involved in the spontaneous arrest of bleedingExtravascular:
Location of vessels, elastic nature of surrounding tissue, vessels passing through bone or cartalige are protected, vasoconstriction tend to reduce hemorrhage
Vascular:
When B.V injured the intima rolls inward and vessels end retract, provided suitable surface for accumulation of platelet and clot formation
Intravascular:
A series of blood clotting factors become activated when blood platelets undergo morphological changes in the presence of damaged endothelial tissue.Department of Surgery & Obstetrics
College of Veterinary MedicineUniversity of Mosul
Mechanical arrest of haemorrhage
1-Crushing
2-Torsion: can be twisting vessels by artery forceps
3-Ligation: This involves tying the end of bleeding vessels to prevent further escape blood materials which used same which used in suture
4-Suturing: Although suturing is used primarily to appose wound edges
5- pressure: Bleeding from surgical incision can be stopped by pressing a gauze sponge against the bleeding point
6- Tourniquet: by constricting band , should used for short time, tourniquets should be released every 20 minute
7- Electrosurgery and Electrocoagulation, Thermocautery burns tissues, and the coagulated tissues act as hemostatic plug
Department of Surgery & Obstetrics
College of Veterinary MedicineUniversity of Mosul
Hemostasis with topically applied substances
Substance have an astringent effect on tissue and blood vessels, applied topically to small cut, example feeric sulfate, feeric chloride, glacial acetic acid, silver nitrate, alum, tannic acid
Specific coagulant:
Gelfoam is a spongelike substance which a large surface on which blood will clot, topical thrompin is specific coagulant factor
Systemic hemostatic agents:
Vit K is necessary for formation of prothrombin, and helpful in preventing excessive hemorrhage
Department of Surgery & Obstetrics
College of Veterinary MedicineUniversity of Mosul
Wound
Department of Surgery & Obstetrics
College of Veterinary MedicineUniversity of Mosul
Wound:
A traumatic separation of skin, mucous membrane or organ surface.
Loss continuity of skin, mucus membrane
Closed woundsContusions
Abrasion
Open wound:
IncisionLaceration
Puncture
Penetrating
Department of Surgery & Obstetrics
College of Veterinary MedicineUniversity of Mosul
Closed wound:
Abrasions:
These wounds result from scraping or friction applied to the skin. Surgical intervention is unnecessary
Contusions:
In these wound the skin is damaged but remains unbroken. Only connective tissue may be damaged, it is possible that muscles, tendons, nerve and even bone are involved.
Department of Surgery & Obstetrics
College of Veterinary MedicineUniversity of Mosul
Closed wound:
Abrasions:
These wounds result from scraping or friction applied to the skin. Surgical intervention is unnecessary
Contusions:
In these wound the skin is damaged but remains unbroken. Only connective tissue may be damaged, it is possible that muscles, tendons, nerve and even bone are involved.
Department of Surgery & Obstetrics
College of Veterinary MedicineUniversity of Mosul
Open Wounds
Incisions wound:
Whether planned or accidental, incision are made by sharp object. The tissues are cleanly, and bruising of the margins is minimal
Laceration wound:
A laceration are made by a blunt object that tears tissue, some laceration produced a skin flap, or subcutaneous pocket, some laceration produce skin flapPunctures wound:
These wound are caused by sharp-or blunt pointed objects, usually deep but have small opening. Foreign material may be detection
Department of Surgery & Obstetrics
College of Veterinary Medicine
University of Mosul
Penetrating wound:
These wound communicate with the body cavities, they may result in internal infection such as peritonitis or empyema
Open Wound Classification
• depended on the time.Clean Wounds
Most common is elective surgical incisionPrimary closure
1-5% rate of infection
Clean Contaminated
Wounds contaminated by local flora despite aseptic techniqueCholecystectomy, appendectomy and hysterectomy
3-11% infection rate
Contaminated
Open traumatic wounds in nonsterile environmentOpen fractures
Surgical procedures in which there is a gross deviation from sterile technique (emergent open cardiac massage)
10-17% infection rate
Dirty or Infected
Gross/heavy contamination or active infection
Perforated viscera, abscess and traumatic wounds
>27% infection rate