The Submandibular Region
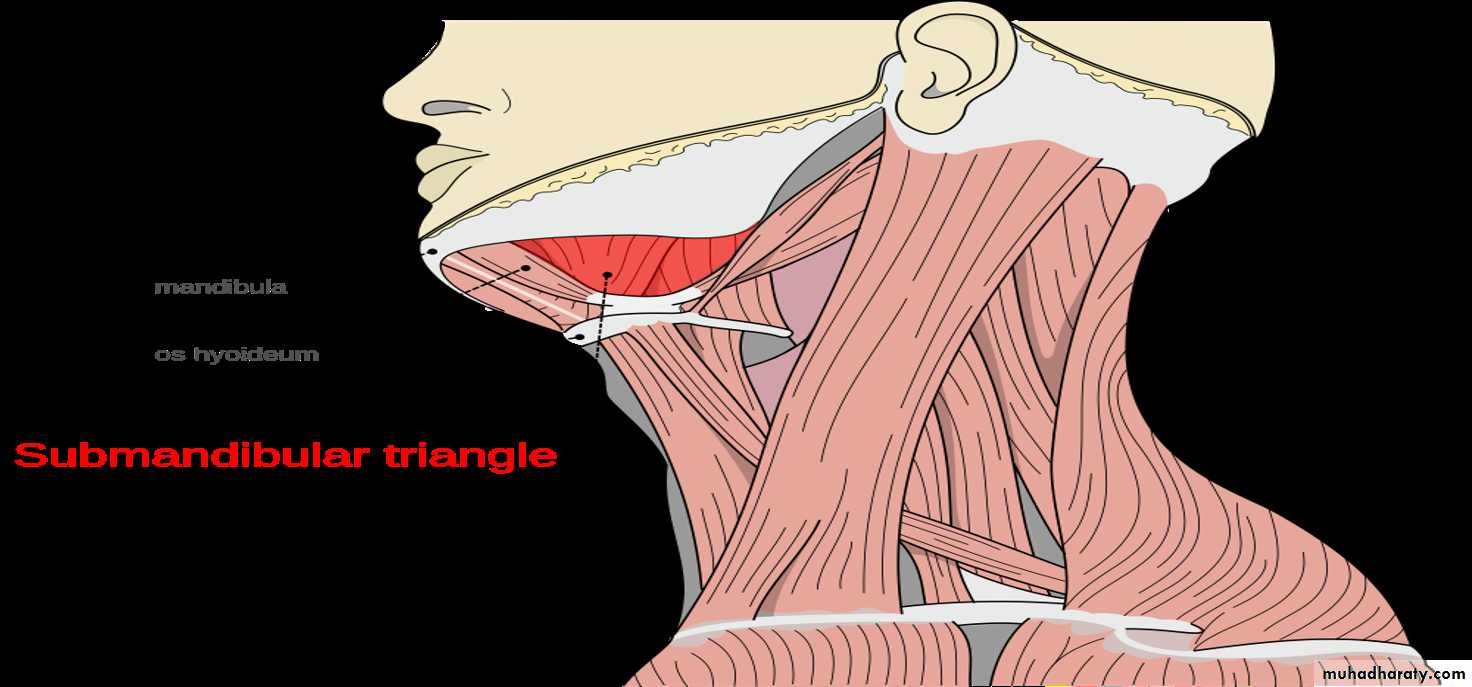
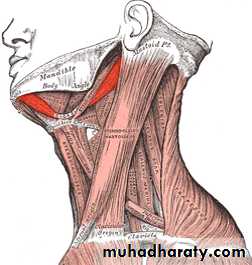
The Submandibular RegionThe submandibular region lies under cover of the body of the mandible, between the mandible and the hyoid bone. It contains the following structures:
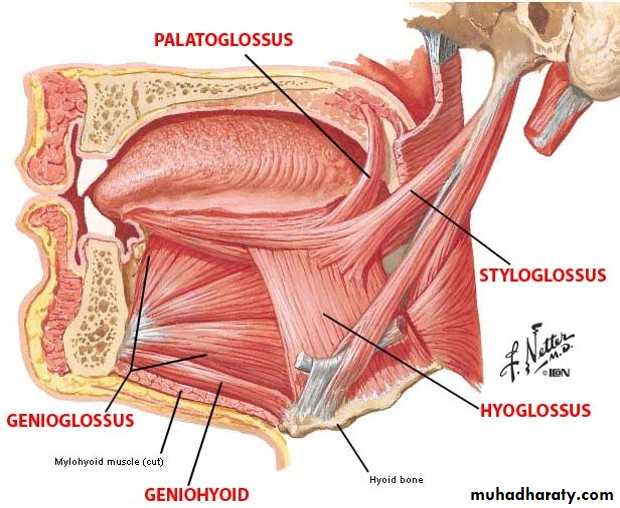
• Muscles: Digastric, mylohyoid. hyoglossus. geniohyoid, genioglossus, and styloglossus.
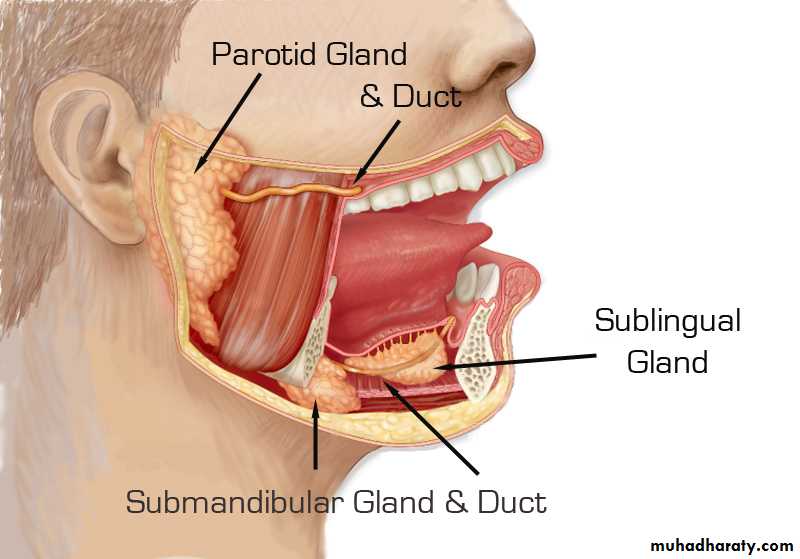
• Salivary glands: Submandibular and sublingual.
• Nerves: Lingual, glossopharyngeal and hypoglossal.
• Parasympathetic ganglion: Submandibular.
• Blood vessels: Facial artery and vein and lingual artery and vein.
• Lymph nodes: Submandibular group.
MUSCLES OF THE SUBMANDIBULAR REGION
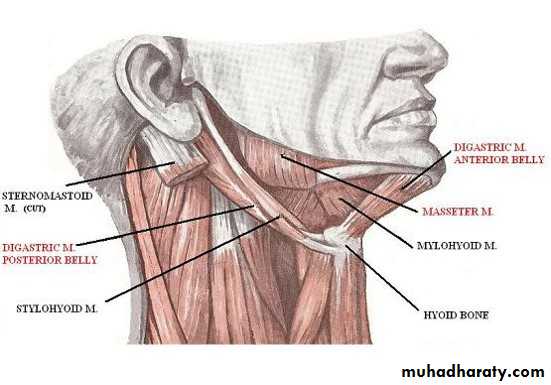
Digastric MuscleThe digastric muscle has a posterior belly, an intermediate tendon, and an anterior belly.
Origin and Insertion: The posterior belly arises from the medial surface of the mastoid process of the temporal bone, passes downward and forward across the carotid sheath, and ends in the intermediate tendon. The intermediate tendon pierces the stylohyoid insertion and is held in position by a loop of deep fascia, which binds the tendon down to the junction of the body and greater cornu of the hyoid bone. The anterior belly runs forward and medially and is attached to the lower border of the body of the mandible, near the median plane.
• Nerve supply: The posterior belly is supplied by the facial nerve and the anterior belly is supplied by the nerve to the mylohyoid, which is a branch of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve.
• Action: Depresses the mandible or elevates the hyoid bone.
Stylohyoid Muscle
The stylohyoid muscle is a small slip that passes along the upper border of the posterior belly of the digastric muscle.• Origin: From the styloid process of the temporal bone.
• Insertion: The muscle passes downward and forward and is inserted into the junction of the body with the greater cornu of the hyoid bone. It is pierced near its insertion by the intermediate tendon of the digastric muscle
• Nerve supply: Facial nerve.
• Action: Elevates the hyoid bone.
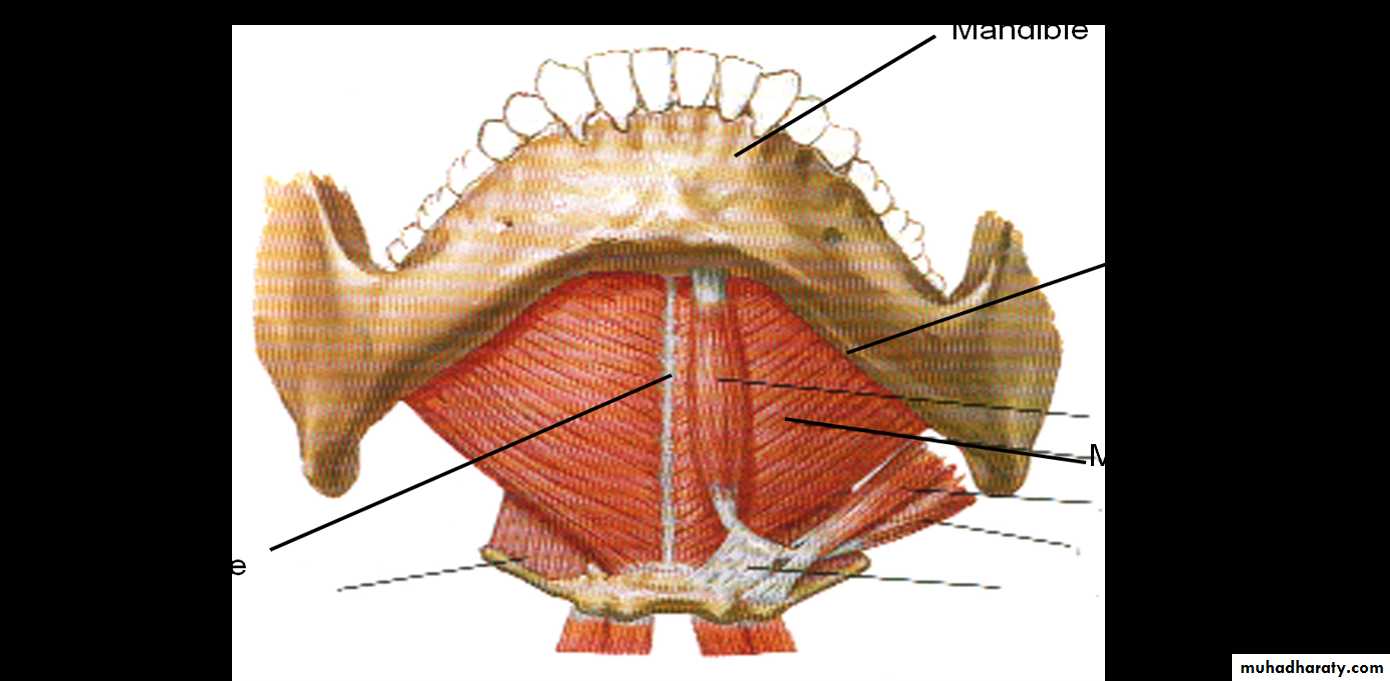
Mylohyoid
• Origin: This flat, triangular sheet of muscle arises from the whole length of the mylohyoid line of the mandible.• Insertion: The fibers run downward and forward. The posterior fibers are inserted into the body of the hyoid bone: the anterior fibers are inserted into a fibrous raphe, which extends from the symphysis menti to the body of the hyoid bone.
• Nerve supply: Mylohyoid branch of the inferior alveolar nerve.
• Action: The two mylohyoid muscles form a muscular sheet that supports the tongue and the floor of the mouth. When the mandible is fixed. they elevate the floor of the mouth and the hyoid hone during the first stage of swallowing. When the hyoid bone is fixed, it assists in the depression of the mandible and the opening of the mouth.
Hvoglossus
Origin: From the upper border of the body and greater cornu of the hyoid bone.Insertion: The muscle is quadrilateral and runs upward deep to the mylohyoid muscle to enter the side of the tongue. It ends when its fibers mix with those of other muscles of the tongue.
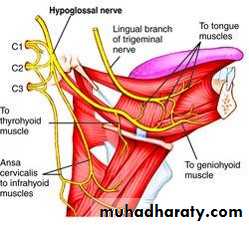
Nerve supply: Hypoglossal nerve.
Action: Depresses the tongue.
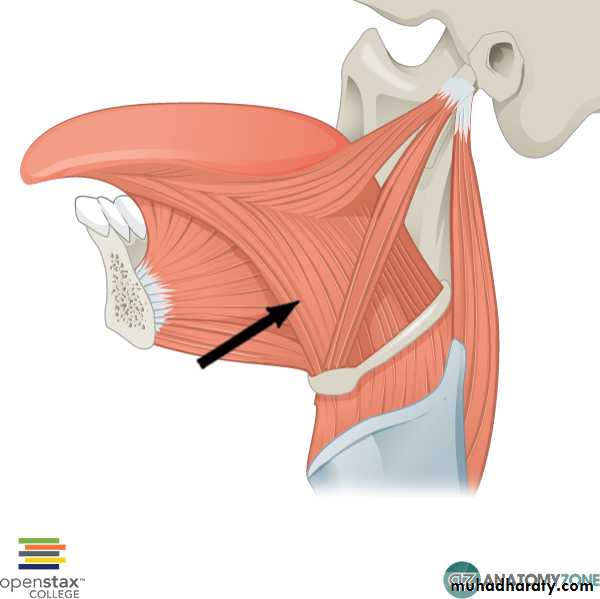
Geniohyoid
Origin : From the inferior mental spine, behind the symphysis menti of the mandibleinsertion : It is a narrow muscle that lies above the mylohyoid and is inserted onto of the body of the hyoid bone. Its medial surface lies in contact corresponding muscle of the opposite side.
• Nerve supply: First cervical nerve through the hypoglossal nerve.
• Action: Elevates the hyoid bone and draws it forward; or depresses the mandible.
Genioglossus
Origin: From the superior mental spine, behind the symphysis menti of the mandible.Insertion: This fan-shaped muscle widens as it extends backward into the tongue . The superior fibers pass to the tip of the tongue, and middle fibers pass to the dorsum of the tongue, and a few of the inferior fibers are attached to the body of the hyoid bone.
Nerve supply: Hypoglossal nerve.
Action: Draws the tongue forward and protrudes the tip so that it points to the opposite side, The two muscles acting in union protrude the tongue in the midline
Styloglossus
Origin: From the styloid process.Insertion: The fibers pass downward and forward on the lateral surface of superior constrictor muscle. On reaching the interval between the superior and middle constrictor muscles, the styloglossus passes forward to enter the side of the tongue.
Nerve supply: Hypoglossal nerve.
Action: Draws the tongue upward and backward.
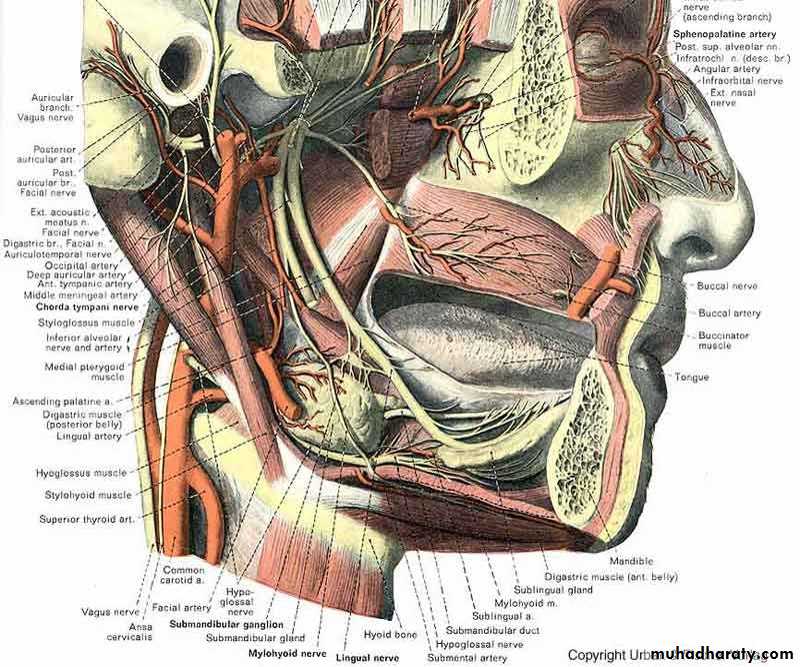
The submandibular gland
The submandibular gland is a large salivary gland and is composed of a mixture of serous and mucous acini, the former predominating. It lies partly under cover of the body of the mandible and is made up of a large superficial part and a small deep part. which are continuous with each other around the posterior border of the mylohyoid muscle.The superficial part of the gland lies in the digastric triangle, reaching upward under cover of the body of the mandible.
Relations of the Superficial Part of the Gland
Anteriorly: The anterior belly of the digastric musclePosteriorly: The stylohyoid, the posterior belly of the digastric, and the parotid gland.
Medially: The mylohyoid, the hyoglossus, and the lingual and hypoglossal nerves.
Laterally: The gland lies in contact with the submandibular fossa in the medial surface of the mandible.
Inferolaterally it is covered by the investing layer of deep cervical fascia , the Platysma muscle, and skin. It is crossed by the cervical1 branch of the facial nerve and facial vein. The submandibular lymph nodes also lie lateral to it.
The facial artery is related to the posterior and superior aspects of the superficial part of the gland.
The deep part of the gland extends forward in the interval between the mylohyoid below and laterally and the hyoglossus and styloglossus medially. Its posterior end is continuous with the superficial part of the gland around the posterior border of the mylohyoid muscle; its anterior end reaches as far as the sublingual gland.
Relations of the Deep Part of the Gland
• Anteriorly: The sublingual gland .• Posteriorly: The stylohyoid, the posterior belly of the digastric, and the parotid gland.
• Medially: The hyoglossus and styloglossus.
• Laterally: The mylohyoid muscle and the superficial part of the gland.
• superiorly :it is related superiorly to the lingual nerve and the submandibular ganglion Fit is covered by the mucous membrane of the floor of the mouth.
•Inferiorly: The hypoglossal nerve.
Capsules of the Gland
The submandibular gland is a tabulated mass surrounded by a connective-tissue capsule. In addition, the gland is partly enclosed in a dense fibrous capsule derived from the investing layer of deep cervical fascia.Submandibular Duct
The submandibular duct emerges from the anterior end of the deep part of the gland. It passes forward along the side of the tongue, beneath the mucous membrane of the floor of the mouth. It is crossed laterally by the lingual nerve and then lies between the sublingual gland and the genioglossus muscle. It opens into the mouth on the summit of a small papilla, which is situated at the side of the frenulum of the tongue.
Clinically, it is important to remember that the submandibular duct and the deep part of the gland can be readily palpated through the mucous membrane of the floor of the mouth alongside the tongue. Saliva can usually be seen emerging from the orifice of the duct .
Sublingual Gland
Type and LocationThe sublingual gland is the smallest of the three main salivary glands. It contains both serous and mucous acini, the latter predominating. It lies beneath the mucous membrane of the floor of the mouth, close to the midline.
Relations
• Anteriorly: The gland of the opposite side.• Posteriorly: the deep part of the submandibular gland.
• Medially: The genioglossus muscle, lingual nerve, and the submandibular duct.
• Laterally: The gland is related laterally to the sublingual fossa of the medial surface of the mandible.
• Superiorly: The mucous membrane of the floor of the mouth , which is elevated by the gland to form the sublingual fold.
• Inferiorly : The gland is supported by the mylohyoid muscle.
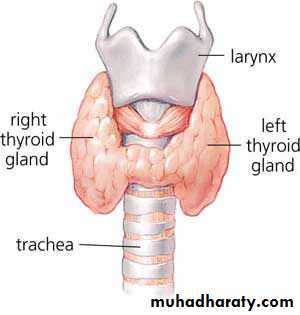
Thyroid Gland
Location and Description
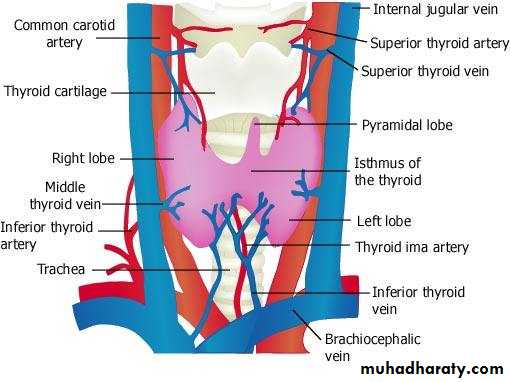
The thyroid gland consists of right and left lobes connected by a narrow isthmus It is a vascular organ surrounded by a sheath derived from the pretracheal layer of deep fascia. The sheath attaches the gland to the larynx and the trachea.
Each lobe is pear shaped, with its apex being directed upward as far as the oblique line on the lamina of the thyroid cartilage; its base lies below at the level of the fourth or fifth tracheal ring.
The isthmus extends across the midline in front of the second, third, and fourth tracheal rings. A pyramidal lobe is often present, and it projects upward from the isthmus, usually to the left of the midline: A fibrous or muscular band frequently connects the pyramidal lobe to the hyoid bone; if it is muscular, it is referred to as the levator glandulae thyroideae.
Relations of the Lobes
Anterolaterally :The sternothyroid , the superior belly of the omohyoid , the stemohyoid , and the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoidPosterolaterqlly : The carotid sheath with the common carotid artery, the internal jugular vein, and the vagus nerve
Medially : The larynx, the trachea, the pharynx, and the esophagus. Associated with these structures are the cricothyroid muscle and its nerve supply, the external laryngeal nerve. In the groove between the esophagus and the trachea is the recurrent laryngeal nerve.
The rounded posterior border of each lobe is related posteriorly to the superior and inferior parathyroid glands and the anastomosis between the superior and inferior thyroid arteries.
Relations of the Isthmus
Anteriorly: The stemothyroids, stemohyoids, anterior jugular veins, fascia, and skinPosteriorly: The second, third, and fourth rings of the trachea ,The terminal branches of the superior thyroid arteries anastomose along its upper border.
Blood Supply
The arteries to the thyroid gland are the superior thyroid artery, the inferior thyroid artery, and sometimes the thyroidea ima . The arteries anastomose profusely with one another over the surface of the gland.
1. The superior thyroid artery, a branch of the external carotid artery, descends to the upper pole of each lobe, accompanied by the external laryngeal nerve
2. The inferior thyroid artery, a branch of the thyrocervical trunk, ascends behind the gland to the level of the cricoid cartilage. It then turns medially and downward to reach the posterior border of the gland. The recurrent laryngeal nerve crosses either in front of or behind the artery, or it may pass between its branches.
3. The thyroidea ima, if present, may arise from the brachiocphalic artery or the arch of the aorta. It ascends in front of the trachea to the isthmus.
The veins from the thyroid gland are
1. The superior thyroid, which drains into the internal jugular vein .2. The middle thyroid, which drains into the internal jugular vein .
3.The inferior thyroid veins of the two sides anastomose with one another as they descend in front of the trachea. They drain into the left brachiocephalic vein in the thorax.
Lymph Drainage
The lymph from the thyroid gland drains mainly laterally into the deep cervical lymph nodes. A few lymph vessels descend to the paratracheal nodes.Nerve Supply
Superior, middle, and inferior cervical sympathetic ganglia
Functions of the Thyroid Gland
The thyroid hormones, thyroxine and triiodothyronine, increase the metabolic activity of most cells in the body. The parafolicular cells produce the hormone thyrocalcitonin, which lowers the level of blood calcium.
Parathyroid Glands
Location and Description
The parathyroid glands are ovoid bodies measuring about 6 mm long in their greatest diameter. They are four in number and are closely related to the posterior border of the thyroid gland, lying within its fascial capsule.
The two superior parathyroid glands are the more constant in position and lie at the level of the middle of the posterior border of the thyroid gland.
The two inferior parathyroid glands usually lie close to the inferior poles of the thyroid gland. They may lie within the fascial sheath, embedded in the thyroid substance, or outside the fascial sheath. Sometimes, they are found some distance caudal to the thyroid gland, in association with the inferior thyroid veins, or they may even reside in the superior mediastinum in the thorax.
Blood Supply
The arterial supply to the parathyroid glands is from the superior and inferior thyroid arteries.The venous drainage is into the superior, middle, and inferior thyroid veins.