Pelvic Fracture / 2
Severe vertical shear and compression injuries are the most dangerous and most
difficult to treat. The fracture or dislocation must be stabilized by external fixation or
posterior iliosacral screw, anterior plating with posterior iliosacral screw . Vertical
force fractures may be treated by open reduction and internal fixation or skeletal
traction and non weight bearing for 3 months
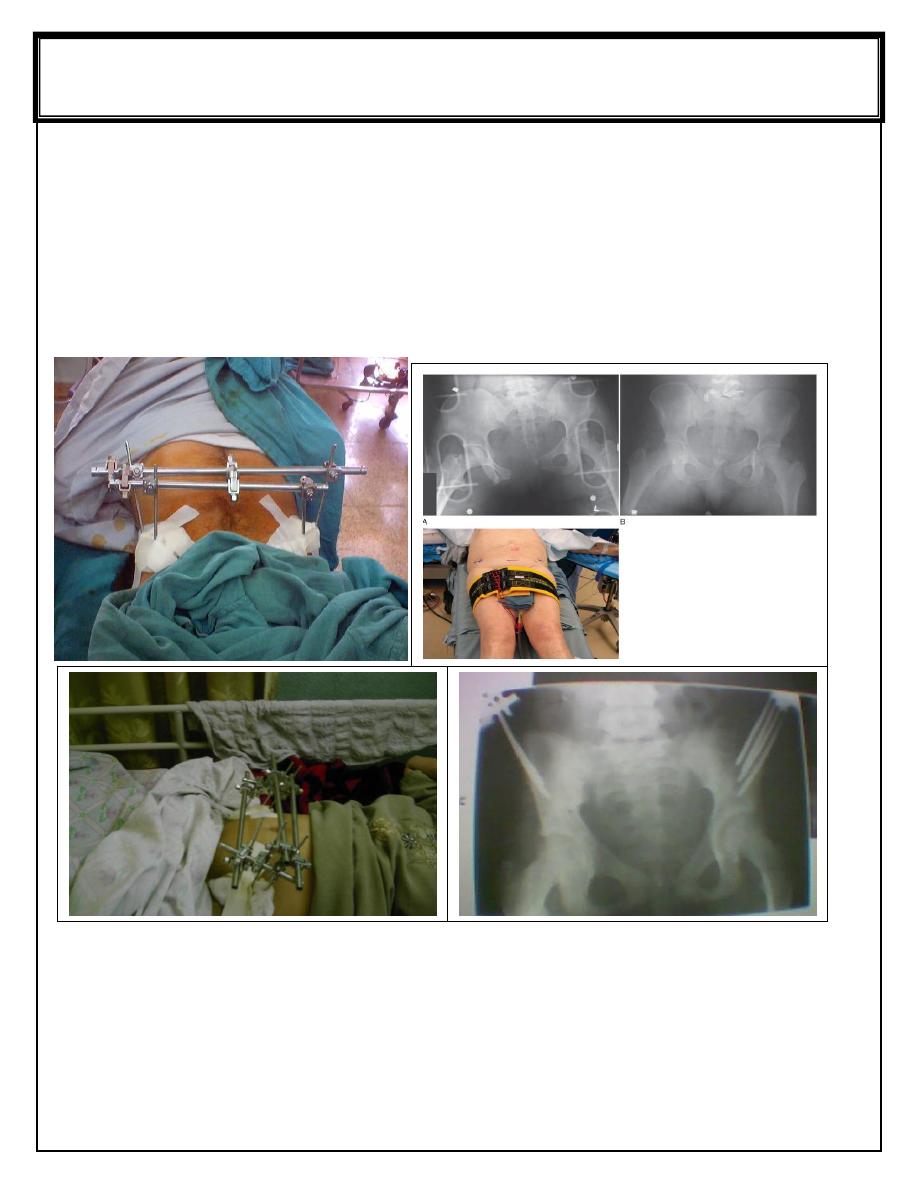
External fixation of fracture pelvis Pelvic binder
Fifth stage Lec-
DR.Yaqthan
Surgery
12/3/2017

Complications
:
1-Early complications
A. Shock : (hemorrhage) resuscitation stabilization of fractures or surgical
intervention.
B. Visceral injuries
C. Diaphragmatic injuries.
D. Nerve injuries
2-Late complications
A. Sacroiliac pain.
B. Distortion of pelvic canal.
C. Osteoarthritis.
Fracture acetabulum
Fractures of the acetabulum occur when the head of the femur is driven into the
pelvis.
This is caused either by a blow on the side (as in a fall from a height or road traffic accident ) or
by a blow on the front of the knee, usually in a dashboard injury when the femur also may be
fractured.
Clinical features
:
There is usually history of a severe injury; associated fractures are not uncommon
and may divert the attention from the more urgent pelvic injuries. Whenever a
fractured femur, a severe knee injury or a fractured calcaneum is diagnosed, the hips
also should be x-rayed. The patient may be severely shocked. There may be bruising
around the hip and the limb may lie in internal rotation (if the hip is dislocated).
Neurological examination is important, testing the function of the sciatic, femoral and
obturator . Several X-ray views of the hip are needed to visualize the fracture
accurately. CT scans are particularly helpful if surgical reconstruction is planned.
Fracture acetabulum

Treatment
:
The first priority is to counteracthe shock and reduce a dislocation. Skeletal traction
is then applied to the distal femur (10 Kg). During the next 3–4 days the patient’s
general condition is brought under control. Definitive treatment of the fracture is
delayed until the patient is fit and operation facilities are optimal.
Definitive treatment
:
undisplaced fractures and fractures that do not involve the roof ( weight bearing
portion), skeletal traction is applied for 6-8 weeks , followed by non weight bearing
for other 6 weeks. Operative treatment are indicated for all displaced fractures to get
perfect anatomical reduction.
Internal fixation of fracture acetabulum
Complication
:
shock, deep venous thrombosis, visceral injuries, sciatic nerve injury, heterotropic
bone formation, avascular necrosis of the head of the femur, hip stiffness and
secondary osteoarthritis.
