
1
Fifth stage
Surgery
Lec-part1
د.يقظان
19/3/2017
Knee Joint
Deformities of the knee joint:
In normal adult the knee are in 5-7 degree valgus ; any deviation from this may regarded
as deformity .
The three common deformities are :
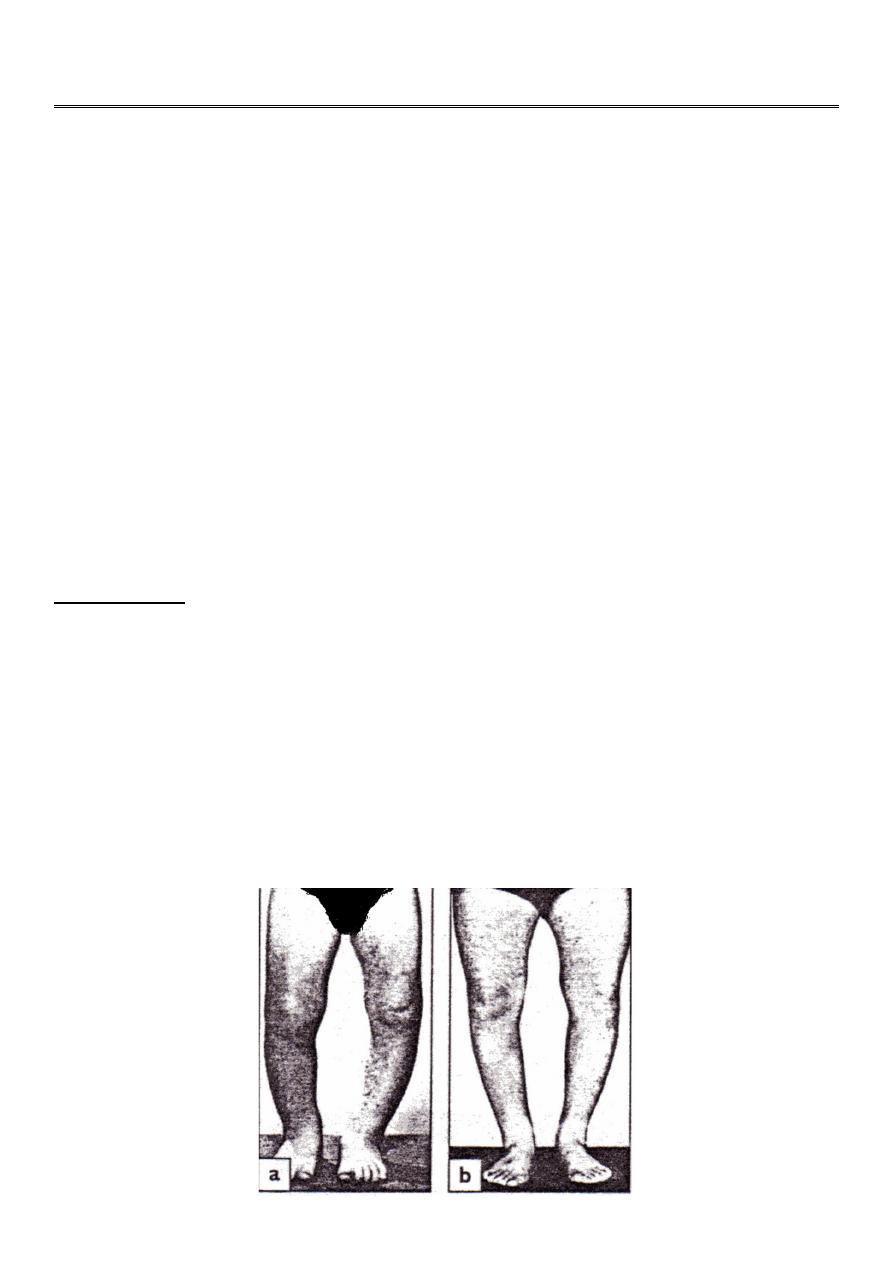
1- bow leg deformity (genu varum) .
2- knock knee (genu valgum) .
3- hyper extension(genu recurvatum).
Bow legs & knock knee in babies are so common that are consider to be normal stage of
development (physiological) ; in addition to this , rickets may play a role in developing
these deformities physiological or renal rickets .
Measurement :
Bilateral bow leg : distance between the femoral condyls with the legs held in full extension
, and the heel touching ; it should be less than 6 cm .
Knock knee : the distance between the medial malliolie when the knee are held touching; it
is usually less than 8 cm .
When the cause of the deformity is physiological , it will be corrected spontaneously . And
when caused by rickets it will be corrected by treating the rickets .
Surgical correction is indicated after this age by stapling or osteotomy usually after the age
of 10 .

2
BLOUNT’S DISEASE
It is progressive bow leg deformity due to abnormal growth of the posteromedial part of
the proximal tibial epiphysis , which is some time fragmented ; the metaphysis is some
what beak shape .
The deformity is usually bilateral and it is progressive .
The treatment is by corrective osteotomy .
PATELLO-FEMORAL PAIN SYNDROME (CHONDROMALACIA OF THE
PATELLA)
pain and tenderness in the anterior part of the knee. This syndrome is common among
active adolescents and young adults.
It is often (but not invariably) associated with softening and fibrillation of the articular
surface of the patella (chondromalacia patellae) .
Treatment :
conservative : by physiotherapy .
operative .
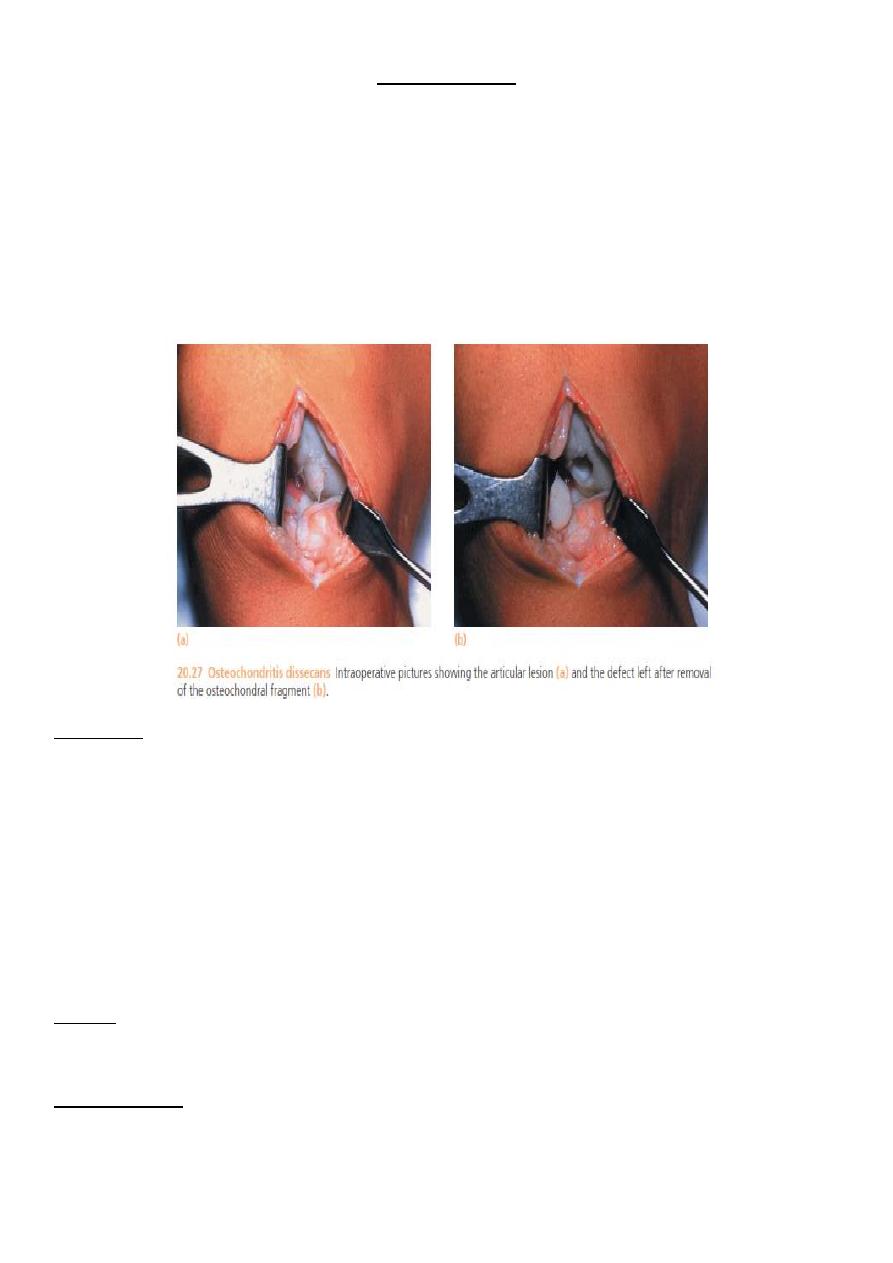
3
Loose bodies
The knee joint is a common site for loose bodies ; these may be produced by :
1- injuries (chip of bone or cartilage)
2- osteochondritis dissicans .
3- osteoarthritis(piece of bone or cartilage osteophyte) .
4- charcot’s disease .
5- synovial chondromatosis.
Clinically:
It can be symptom less .
The usual complaint is attack of sudden locking without injury , the joint get stuck in a
position which varies from one attack to another .
Some time the locking is momentary and usually the patient can wriggle the knee until it
suddenly unlocked .
Some time we can feel the L.B. and it usually tend to slip away during palpation so called
joint mouse .
X-RAY:
Most of the loose bodies are radio opaque so they can be seen by the ordinary x- ray.
TREATMENT :
Loose bodies should be removed unless the joint is severely affected by osteoarthritis.

4
Acute Knee Swelling
Causes :
1 – haemoarthrosis .
2 – traumatic synovitis .
3 – acute septic arthritis .
4 – aseptic non traumatic synovitis .
haemoarthrosis
Swelling immediately after the injury mean blood inside the joint .
The knee is very painful and it feel warm, tense and tender …. Later there may be doughy
feel .
X-ray : important to detect any fracture .
Treatment: aspiration under aseptic condition , crepe bandage and back slab , quadriceps
ex. Start from the beginning .
Traumatic synovitis
Injury stimulate reactive synovitis , typically the swelling appear only after some hours and
subside spontaneously over a period of days .
The knee may need to be splinted for several days , quadriceps ex. Some time if fluid
amount is large , it need aspiration .
Aseptic non traumatic synovitis
Acute swelling without history of trauma or sign of infection , suggest gout or pseudo gout .
Aspiration from the joint show turbid fluid resembling pus but it is sterile Microscopic ex. By
polarized microscope show crystals .
Treatment : by anti inflammatory drugs.
Chronic Swelling of Knee
Causes :
1 – T.B.
2 – rheumatoid arthritis .
3 – osteoarthritis .
