
1
EMBRYOLOGY
Lecture 1 & 2 Prof.Dr.Alhubaity
DEVELOPMENT OF THE URINARY SYSTEM
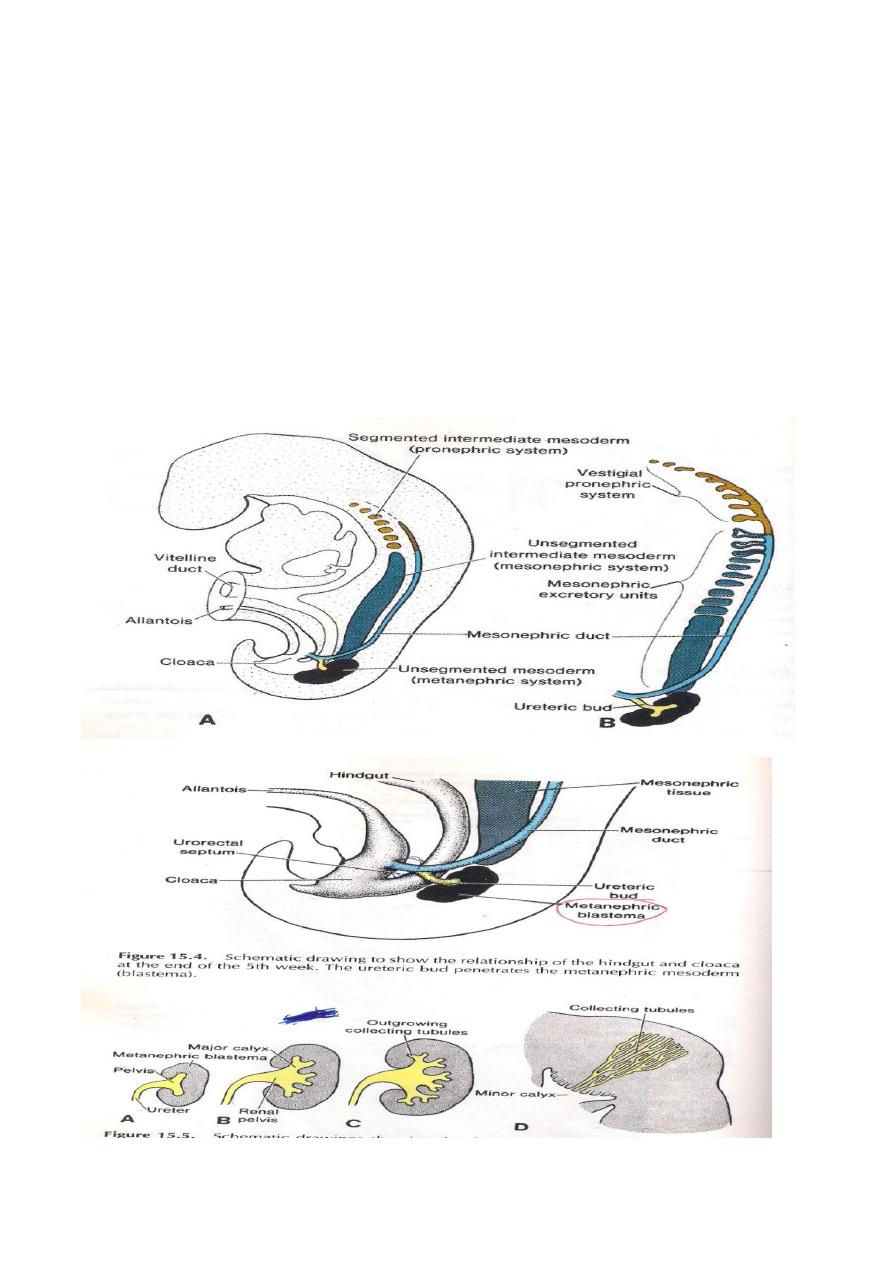
The kidney of fetus passes through three stages of development in succession
theses are
1-Pronephros
2-Mesonephros
3-Metanephros
They develop from the Nephrogenic cord.The three stages appear one after
another and one caudal to the other in succession The Pronephros develops in
the cervical region and from the cranial part of nephrogenic cord and it becomes
segmented,each segment will have elongated tubule called pronephric tubule
with medial and lateral end .The medial end opens in to the coelomic cavity,while
the lateral one leads in to the pronephric duct,later on the pronephric tubules will
degenerate completely and only the pronephric duct will remain to be used by the
second stage .
The Mesonephros: It arises from nephrogenic cord caudal to the
origin of the pronephros.It is also segmented and each segment has mesonephric
tubule which lies transversely one caudal to the other s.The mesonephric tubule
becomes S shaped with an expanded medial end & a narrow tubular lateral
end.The medial end becomes invaginated by internal glomerulus from the dorsal
Aorta,while the lateral end opens in to the pronephric duct which becomes known
as Mesonephric (Wolffian) duct.
The fate of mesonephric tubules are as follows:
A-in the males it gives
1-Afferent ductules of the testes.
2-Paradidymis.
3-Abberent ductules.
B-In females it gives tubules of opophoron & proophorone

2
The fate of the Mesonephric duct are as follows:
A-In the male it gives
Duct of epididymis.
Ductus deference.
Ejaculatory duct.
The seminal vesicle.
The appendix epididymis.
B- in the female it gives part of epiphorons while the rest will degenerate.
C- In both sexes ,the caudal part will give the Ureteric bud while the remaining
part of the caudal will be absorbed in to the posterior surface of the urinary
bladder.
The Metanephros ( Permanent kidney )
It is developed from 2 sources :
1-The ureteric bud ,which forms the collecting tubules of the kidney.
2-The Metanephric cap , which takes origin from the caudal part of Nephrogenic
cord.
The Ureteric bud arises as a diverticulum from the lower end of the mesonephric
duct close to the Cloaca.Its cranial part expand and comes in to contact with the
metanephric cap which lies in the pelvic region at this time.Elongation of the ureteric
bud will push the metanephric cap cranially to reach the level of the lumber
segments ( ascends of kidney).
The ureteric bud will give rise to the following parts:
A-The ureter.
B-The renal pelvis.
C- Major & Minor Calyces.
D-Collecting tubules.
At the mean time the collecting tubules becomes covered by a small mass of the
metanephric cap ,then this small mass will give the metanephric tubules which
becomes S shaped with 2 ends ,one end leads and will communicate with the

3
collecting tubule while the other end end expand to form the renal corpuscle
that invaded by capillary tuft (glomerulus) thus forming the nephrons of the
kidney.The kidney at first is lobulated later on the lobulations will disappear
completely.
CONGENITAL ANOMALIES
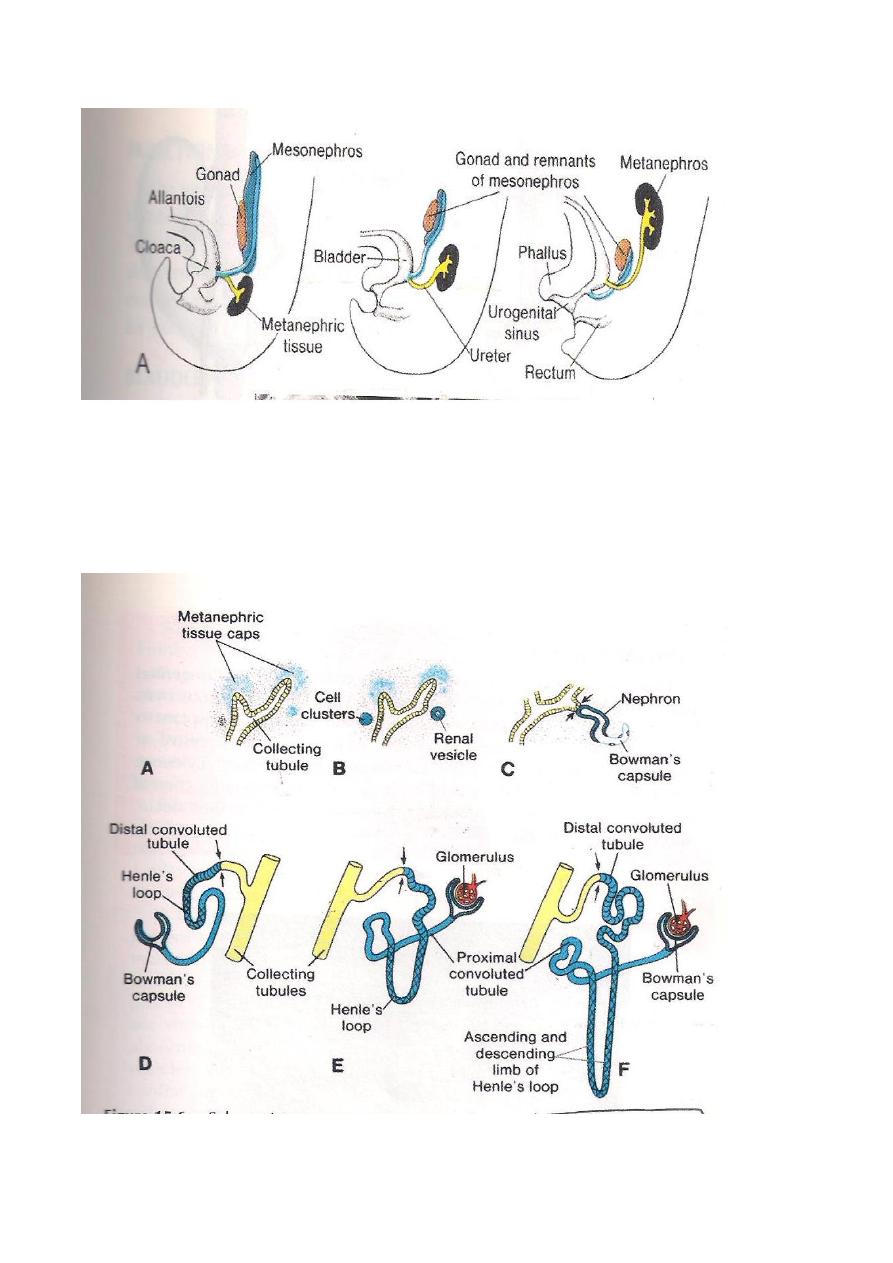
1-Renal a genesis i.e complete absence of one or 2 kidneys.
2-A horse – shoe kidney due to fusion of the 2 metanephric cap together.
3-Pelvic kidney due to failure of the kidney to a scend.
4-Congenital cystic kidney due to failure of communication between the collecting
tubules with the metanephric tubules.It could be solitary or multiple cysts.
THE URETER
It is formed from the ureteric bud which arises at the lower end of the
Mesonephric duct close to the cloaca.It then grows dorsally and cranially to
contact the metanephric cap and ascends upward together to reach the lumber
region at L2 vertebral level.The upper end of the bud divides repeatedly to give
rise to the following parts:
1-Pelvis of the ureter.
2-Major & Minor calyces.
3-Collecting tubules of the kidney.
It shows 2 dilatations along its length, an abdominal and pelvic fusiform
parts with 3 constrictions as follows;
1-At pelvi- ureteric junction.
2-At the point where it crosses the pelvic brim.
3-As it enters the bladder knows as intramural part.

4
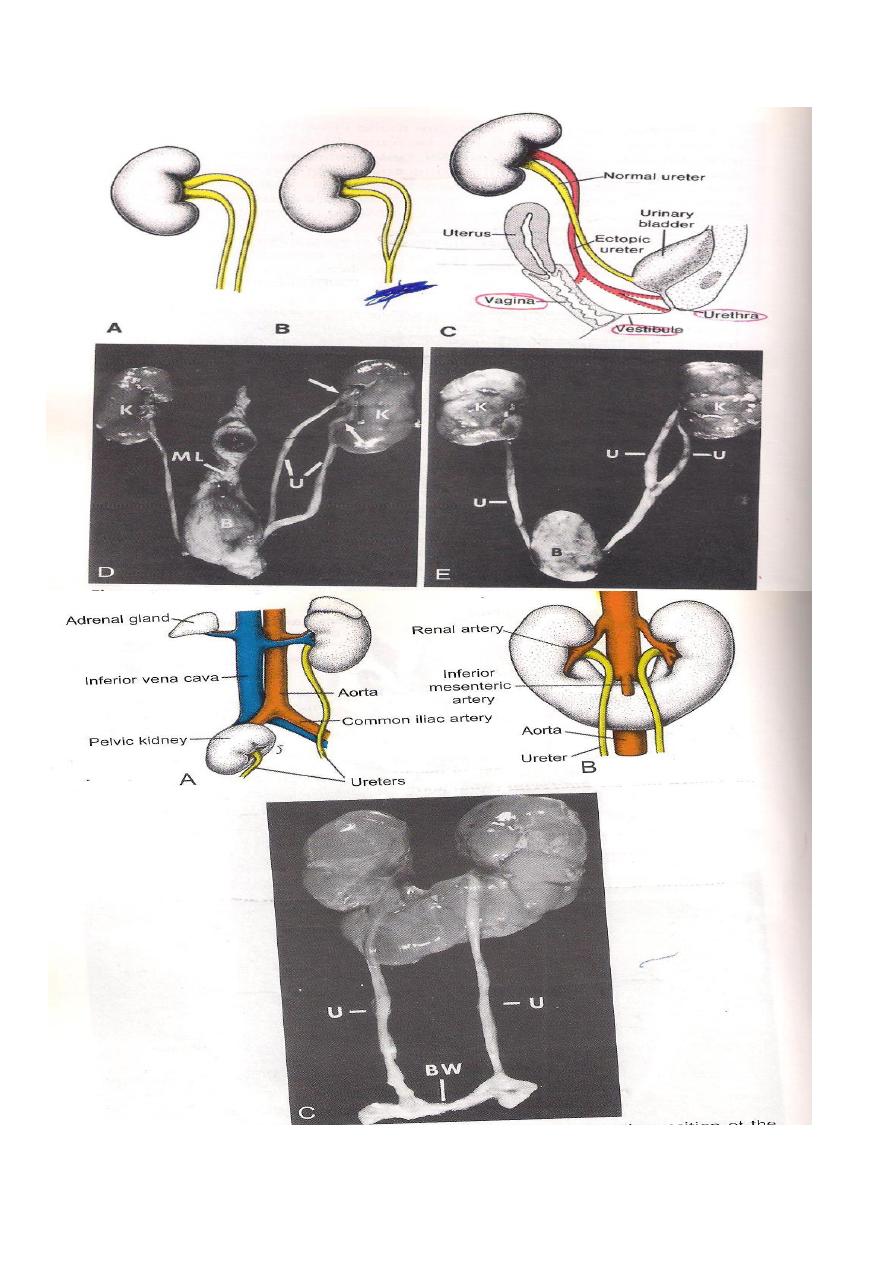
The absorption of the lower part of Mesonephric duct below the site of origin of the
ureteric bud in to the posterior part of the urinary bladder will free the ureter and
comes to open directly in to the urinary bladder.
Congenital anomalies of the ureter includes Double ureter and Bifid ureter or cleft
pelvis.
The Cloaca
Is the dilated lower part of the hind –gut just caudal to the point of allantois
attachment.The mesoderm will send urorectal septum which divides the cloaca in
to 2 parts;
1-Rectum & upper part of anal canal dorsally.
2-Urogenital sinus with the allantois attached to it ventrally.
At the mean time the Clocal membrane is divided in to the anal &perineal
membranes.
The Primitive urogenital sinus is divided in to :
1-Vesico- urethral canal (connected by the allantois) .It forms :
A-The urinary bladder except the trigon.
B-The upper part of the prostatic urethra in the male.
C-The whole urethra in the female.
2-The definitive urogenital sinus.Its upper part in known as pelvic part while its lower
part is known as phallic part.It forms the followings:
A-Most of male urethra includes the lower half of prostatic ,membranous and most
of the spongy (penile urethra).
B-The vestibule of the vagina in the female.

5
DEVELOPMENT OF THE URINARY BLADDER
It develops from 2 sources ,these are the followings:
1-The Vesico-urethral Canal.
2-The lower parts of the 2 mesonephric ducts.
These lower parts of the 2 mesonephric ducts are incorporated in to the back of
the urinary bladder to form the Trigon of the urinary bladder.As a result,the
ureteric opening come to open directly in to the bladder at the upper angles of
the Trigon.The allantois which is connected to the apex of the bladder becomes
the URACHUS which extends to the inner surface of the Umbilicusand is
converted in adult in to Median umbilical ligament.
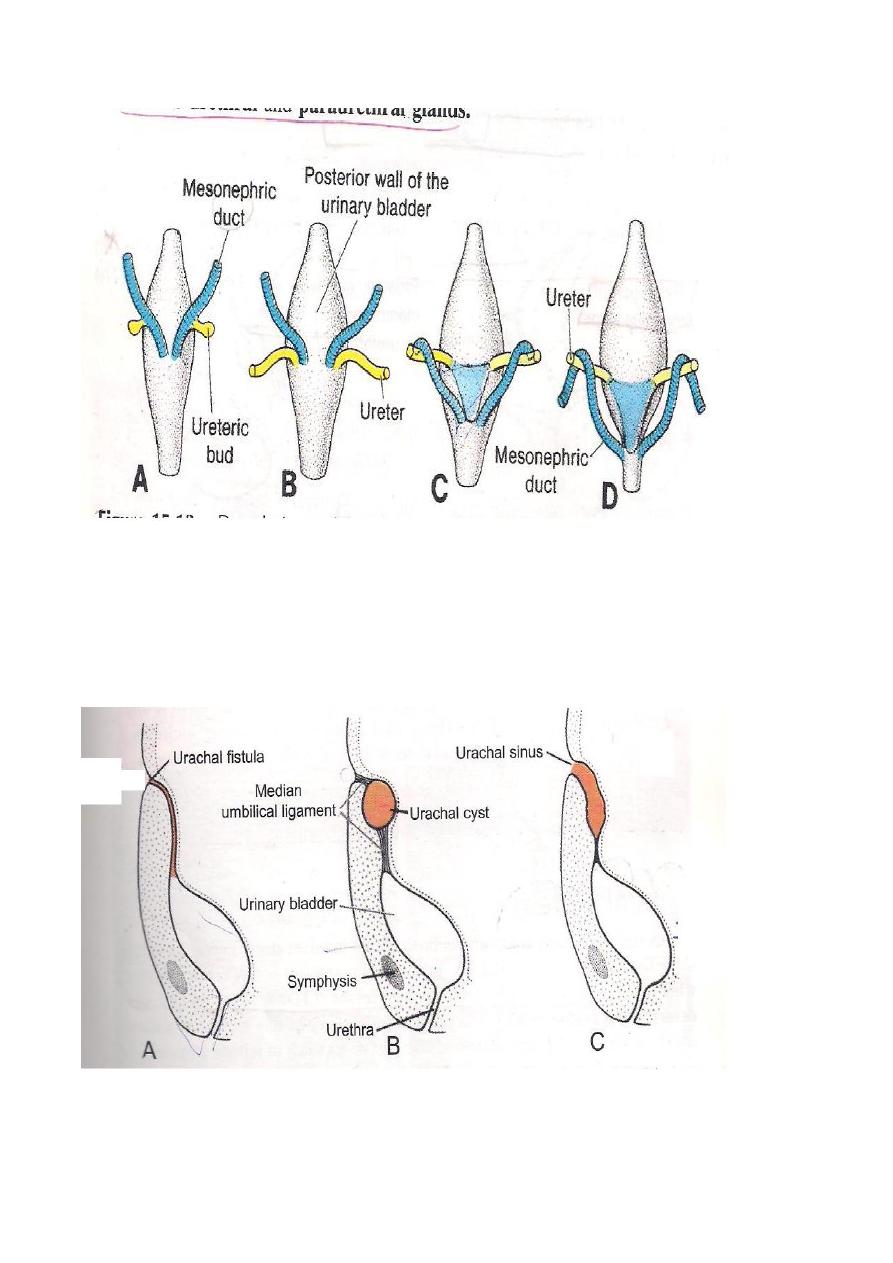
Congenital anomalies are the followings:
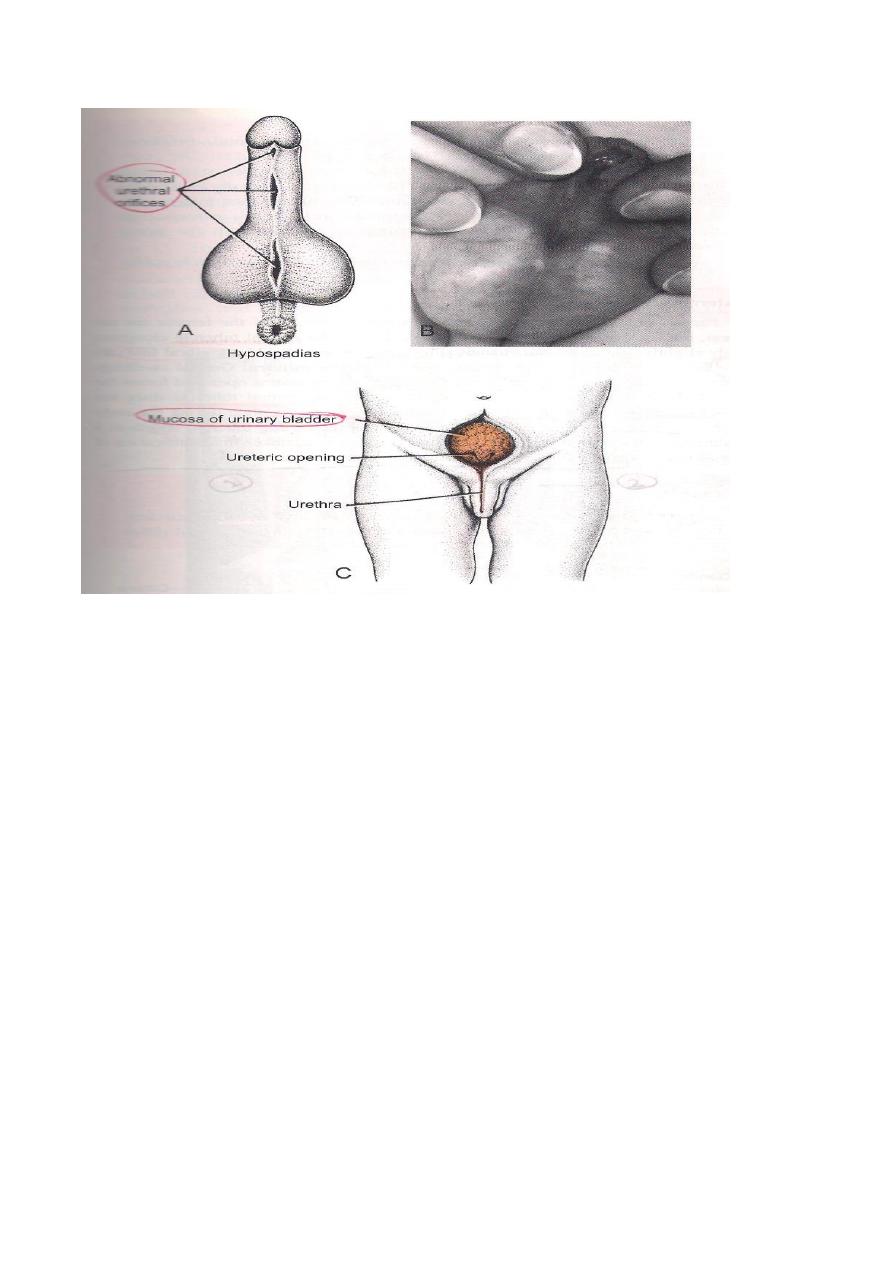
1-Ectopic Vesicae where the bladder opens into the surface just a bove the pubic
symphysis due to failure in the formation of the anterior wall of the Bladder.
2-Urachal Fistula connecting the Urinary Bladder to the Umbilicus due to patent
urachus.
3-Urachal Cyst due to patent segment of the urachus.
THE DEVELOPMENT OF
THE URETHRA
1-The upper half of the prostatic urethra forms from the Vesico-urethral canal(
from primitive urogenital sinus) and from the absorbed part of the mesonephric
duct ( the posterior wall of this part of the urethra).
2-The lower half of the prostatic urethra is derived from the pelvic part of the
primitive urogenital sinus.
3-The Membranous urethra is formed from the pelvic part of definitive urogenital
sinus.
6
4-The spongy urethra is developed from the phallic part of the definitive urogenital
sinus
CONGENITAL ANOMALIES
1-Hypospedias,where the urethra opens on the under surface of the penis.
2- Epispedias,where the urethra opens on the dorsum of the penis.
◦
3-Urethral stenosis ( stricture) due to incomplete canalization.
7
8
9
10
Edited by
: Aydin Othman
