LASER IN PROSTHODONTICS
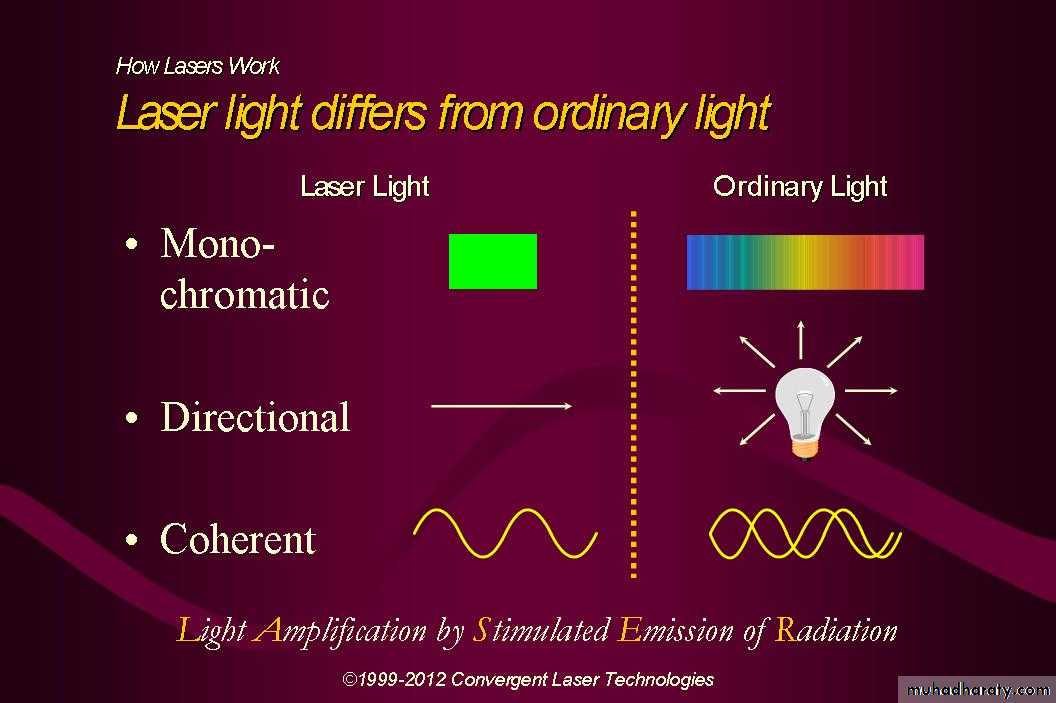
Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation
Term coined by GORDON GOULD ,1957
Father of laser: Albert EinsteinLaser light is a man-made single
photon wavelength.
LASER LIGHT
VISIBLE LIGHT
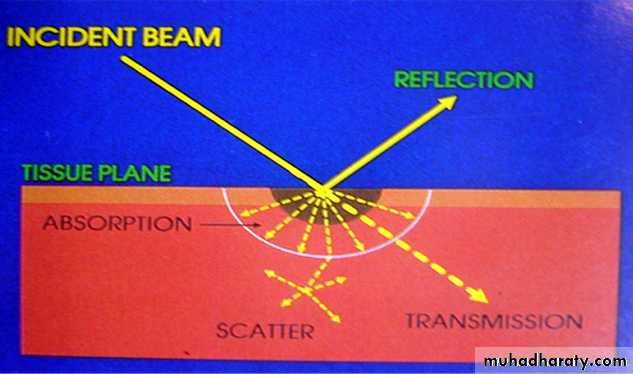
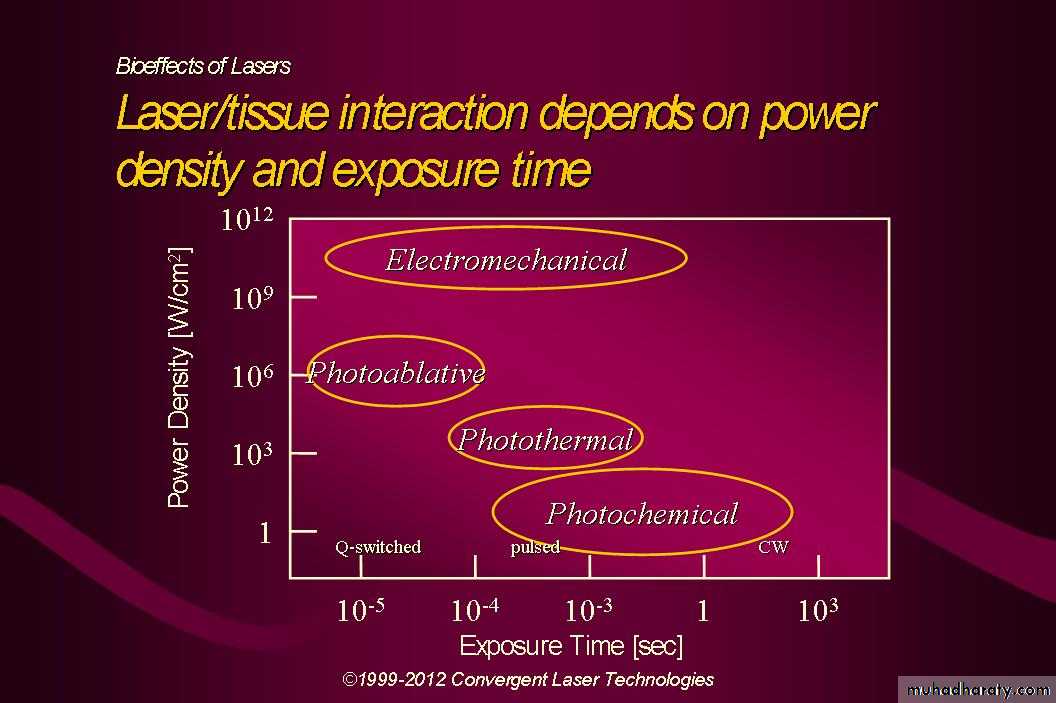
Laser interaction with oral biologic tissues
Four different interactionReflection
Scatter (diffusion)
Absorption
Transmission
Uses In Dentistry
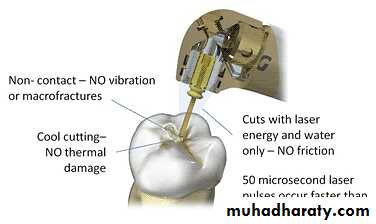
1. Excimer LasersHard tissue ablation/ Dental Caries removal. Argon Fluoride / Xenon fluoride lasers are used. They have a wave length from193nm to 308nm.
2. Gas Laser
Carbon dioxide lasers are used for intra oral and implant soft tissue surgery , aphthous ulcer , melanin pigmentation. Has a wavelength of 10600nm. Color- InfraredHelium Neon Lasers has a wavelength of 637nm and is used for dentin hypersensitivity , analgesia etc. Color-Red
Argon lasers having a wavelength of 488nm & are used for tooth whitening , curing of composites , curettage etc Color-Blue
3. Diode Lasers
Indium Gallium Arsenide Phosphorous are used for caries and calculus detection and has wavelength of 655nm. The color of the laser is Red.Gallium Aluminum Laser – Intra oral Surgery , Implant soft tissue surgery , sulcular debridement , Pulpotomy , root canal disinfection removal of enamel caries etc, Wavelength- 840nm Color-Infrared
4. Solid state Laser
Neodymium:YAG Laser – Intra oral soft tissue surgery , sulcular debridement , analgesia , Pulpotomy , root canal treatment, removal of gingival melanin pigmentation . Has a wave length of 1064nm and is infrared.5. Erbium Group
Erbium:YAG is used for modification of enamel and dentin surface , implant soft tissue surgery , sulcular debridement , osseous surgery , treatment of dentin hypersensitivity , apthous ulcer treatment etcWhy Lasers In Prosthodontics
Prosthodontics takes all concepts of dentistry and integrates effective comprehensive treatment planning.It include a wide variety of patients seeking a diverse range of care:
• Fearful patients
• Patients with complex medical histories• Patient allergic to anesthetics
Future Trends in Dentistry
Non-invasive DentistryHappy Dentistry
Advantages
Easy and safe to handlePainless, Bloodless & Clean surgical field.
Spot coagulation and vaporization gives excellent hemostasis.
Reduces Operating Time.
Anesthesia free soft and hard tissue cutting
No need for suturing
Instant sterilization of surgical site
No sensory disturbances
No postoperative discomfort, and swelling.
Superior and faster healing
Disadvantages
Lasers can't be used :fill cavities located between teeth
cavities around old fillings and large cavities (crown)
remove defective crowns or silver fillings
prepare teeth for bridges
Laser - more expensive
Classification of LASERS ON BASIS OF APPLICATION IN DENTISTRY
SOFT TISSUE LASERSHARD TISSUE LASERS
• SOFT TISSUE LASERS
• No suturing• Little or No bleeding
• Painless
• Quicker
• Atraumatic
• HARD TISSUE LASERS
• Quicker
• More accurate
• More comfortable
• Better results
Application in
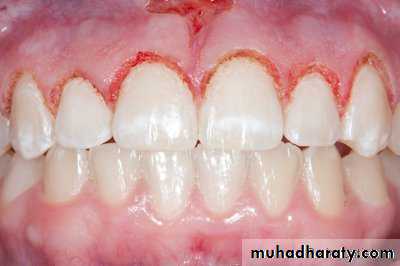
FIXED PROSTHETICS/ESTHETICS
Soft tissue management around abutments.Crown lengthening.
Osseous crown lengthening.
Troughing.
Formation of ovate pontic sites.
Soft tissue management around laminates
Bleaching
Removal of veneer
SOFT TISSUE MANAGEMENT AROUND ABUTMENTS
ARGON laser provide excellent Hemostasis and CoagulationGingival Retraction for making impression during a crown and bridge procedure becomes easy
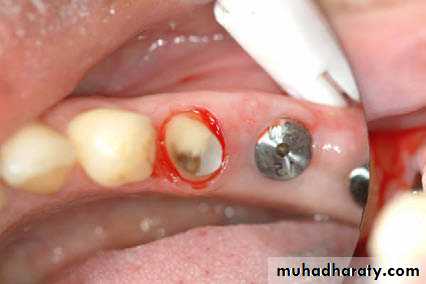
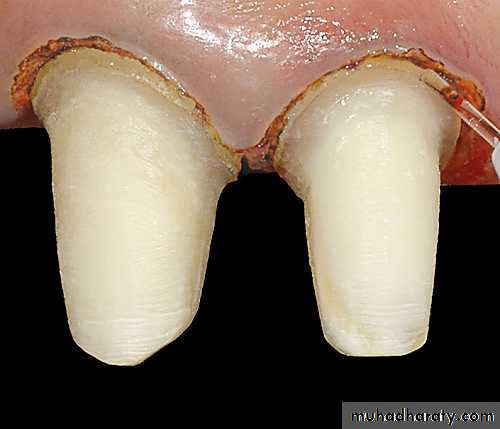
CROWN LENGHTNING
Insufficient clinical crown lengthCaries at gingival margin
Endodontic perforations near alveolar crest.
Unaesthetic gingival architecture.
Cosmetic enhancement.
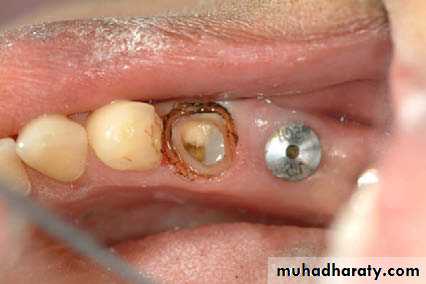
LASER TROUGHING
is created around a tooth before impression making using Nd:YAG laser.Minimizes impingement of epithelial attachment, less bleeding, reduced postopersative problems, lessen chairtime
This can entirely replace the need for retraction cord, electro cautery, and the use of haemostatic agents.
Gingival troughing with the diode laser exposes finish lines
FORMATION OF OVATE PONTIC SITES
Two most common causes of unsuitable pontic site:1. Insufficient compression of alveolar plates after an extraction
• 2.Unsuitable pontic site results in un esthetic and non self cleansing pontic design.
For favorable pontic design laser re-contouring of soft and bony tissue may be needed
MODIFICATION OF SOFT TISSUE AROUND LAMINATES
The removal and re-contouring of gingival tissues around laminates can be easily accomplished with the Argon laserBleaching: Esthetics and smile are important issues in our modern society. Bleaching of teeth can now be performed in the Dental OPD. Diode lasers are used to bleach teeth effectively without causing much tooth sensitivity and alteration of the complexion of the tooth.
Removal of veneer: Restoration can be dislodgedwithout cutting with the help of laser beams. The laser energy passes through porcelain glassunaffected and is absorbed by the water molecules present in the adhesive. Debonding takes place at the junction of the silane and the resin without causing any trauma to the underlying tooth.
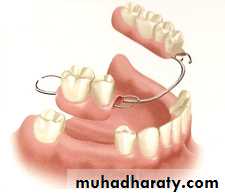
REMOVABLE PROSTHETICS
• Tuberosity reduction
• Torus reduction• Soft tissue lesions
• Residual ridge modification
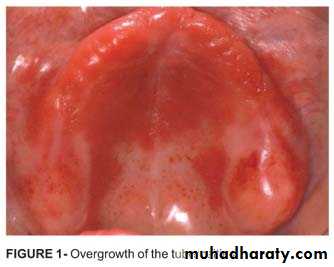
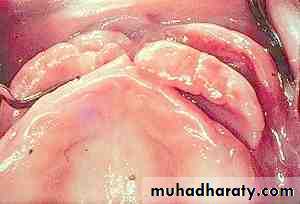
TUBEROSITY REDUCTION
Treatment of enlarged tuberosity: The mostcommon reason for enlarged tuberosities usually is soft tissue hyperplasia and alveolar hyperplasia accompanying the over-eruption of unopposedmaxillary molar teeth. The excision of the surplussoft tissue may be performed with any of the softtissue lasers. Cutting of the bony tissue may be done with Erbium laser.Surgical treatment of tori and exostoses
Tori and exostoses are formed mainly of compact bone.They may cause ulceration of oral mucosa.
They may also interfere with lingual bars or flanges of mandibular prostheses.
Soft tissue lasers may be use to expose the exostoses and Erbium lasers may be use for the osseous reduction.
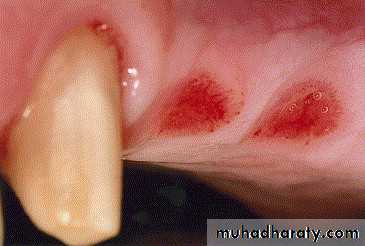
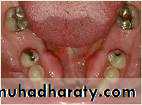
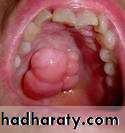
SOFT TISSUE LESIONS
Epulis fissurata and denture stomatitis caused by:Persistent trauma from a sharp denture flange
Over compression of the posterior dam area
The lesion can be excised with any of the soft tissue lasers and the tissue allowed to re epithelialize.
RESIDUAL RIDGE MODIFICATION
For proper retention, stability and support for the prosthesis, residual ridge modification is done with lasers, in pre prosthetic preparation phase forUnder cuts
Flabby tissue
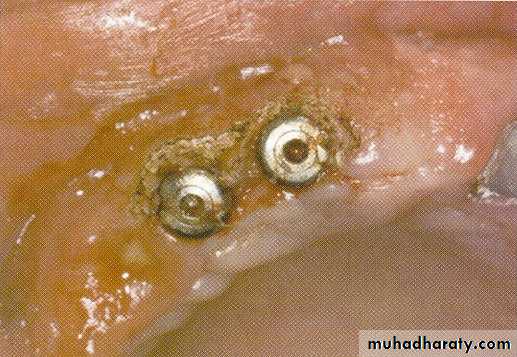
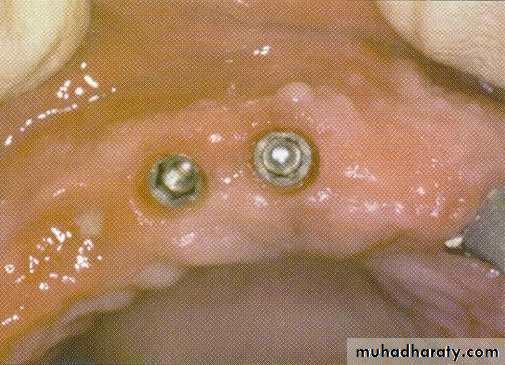
IMPLANTOLOGY
Second stage uncovering.Implant site preparation.
Peri-implantitis.
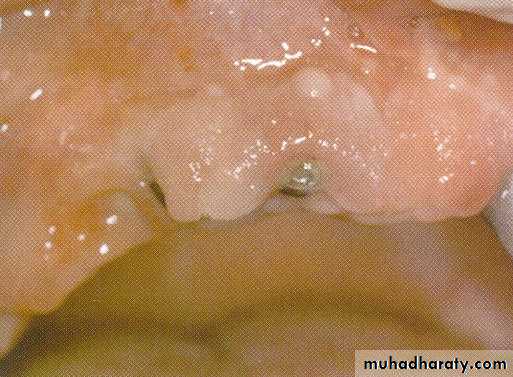
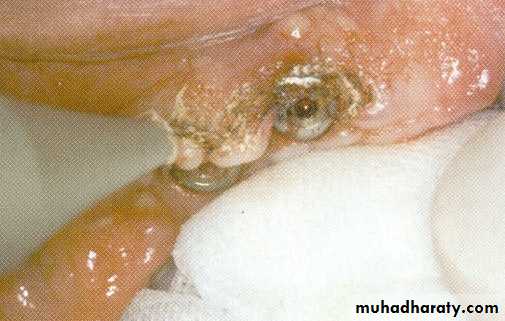
SECOND STAGE UNCOVERING
• removed using laser
Immediately healing caps are laser exposed and soft tissue is recontoured
Soft tissue healing within 2 weeksIMPLANT SITE PREPARTION
Lasers can be used for the placement of mini implants especially in patients with potential bleeding problems, to provide essentially bloodless surgery in the bonePERI-IMPLANTITIS
Lasers can be used to repair ailing implants by decontaminating their surfaces with laser energy.Lasers can also be used to remove inflamed granulation tissue around an already osseointegrated implant.
Diode, CO2 & Er:YAG lasers can be used for this purpose.
Sinus lift procedure: Lasers can also be used in thesinus lift procedure. The procedure can be done bymaking the lateral osteotomy with a decreasedincidence of sinus membrane perforation. Theyttrium-scandium-gallium-garnet (YSGG) laser isthe optimal choice for not cutting the sinusmembrane. The YSGG laser can also be used tomake the osteotomy for a ramal or symphysealblock graft. Bone grafts done with lasers have beendemonstrated to decrease the amount of bonenecrosis from the donor site and the osteotomy cutsare narrower, resulting in less postoperative painand edema.7
RECENT ADVANCES IN LASERS
MAXILLOFACIAL PROSTHESIS
Topologic data of the patient’s deformity is acquired using laser surface digitizing, the procedure is called Laser Holography ImagingLasers aid in creating a visually realistic prosthesis that can provide an illusion
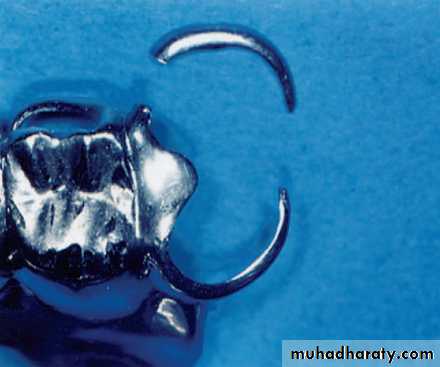
of normal appearance.Laser welding
No need for investment and soldering alloyWorking time is decreased
Easy to operate
Minimal heat damage to denture base resin
An attractive alternative method to join dental casting alloys such as broken claspUltraviolet (helium-cadmium) laser-initiated polymerization of liquid resin in a chamber, to create surgical templates for implant surgery and major reconstructive oral surgery.
Laser scanning of casts can be linked to computerized milling equipment for fabrication of restorations from porcelain and other materials.