Nucleic acid metabolism
Functions of nucleotides
1- Polymerization to make DNA and RNA.
2- Energy currency of the cell e.g. ATP, GTP.
3- Act as carriers of active intermediantes in vaeious metabolic pathways e.g. UDP- glucose in glycogen synthesis, SAM.
4- Component of coenzymes e.g. FAD,NADH, NADPH.
5- Act as 2nd messengers e.g. cAMP and cGMP.
6- Allosteric regulation of various metabolic pathways e.g. ATP inhibits PFK-1.
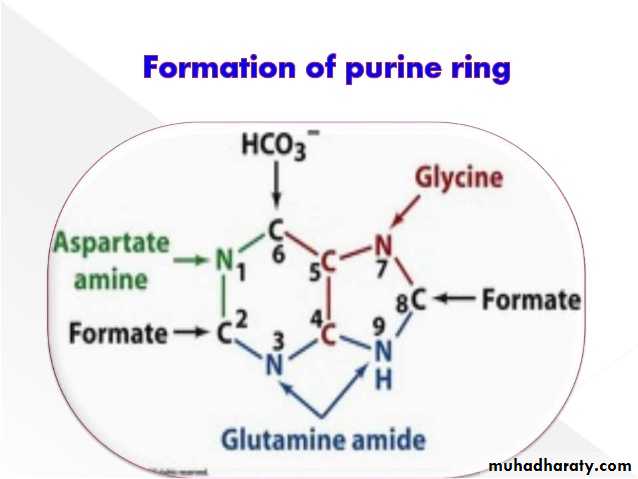
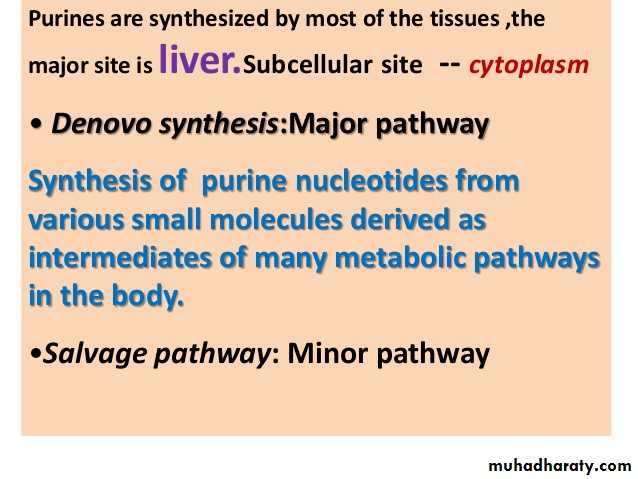
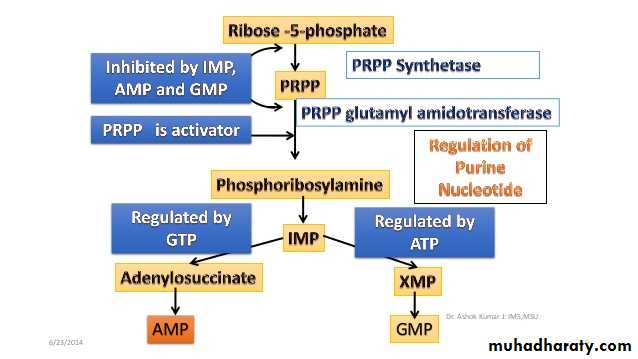
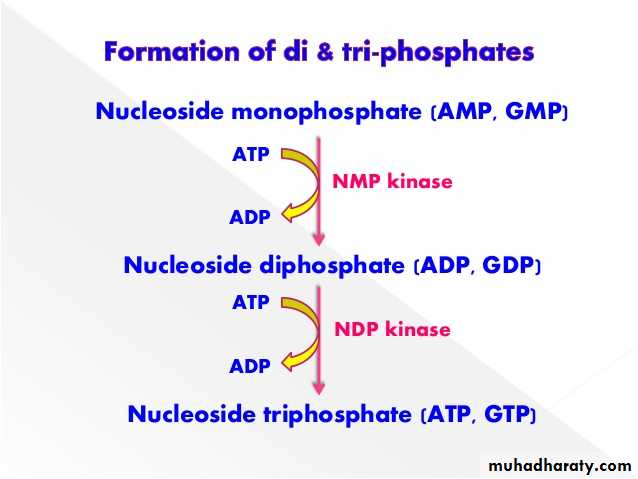
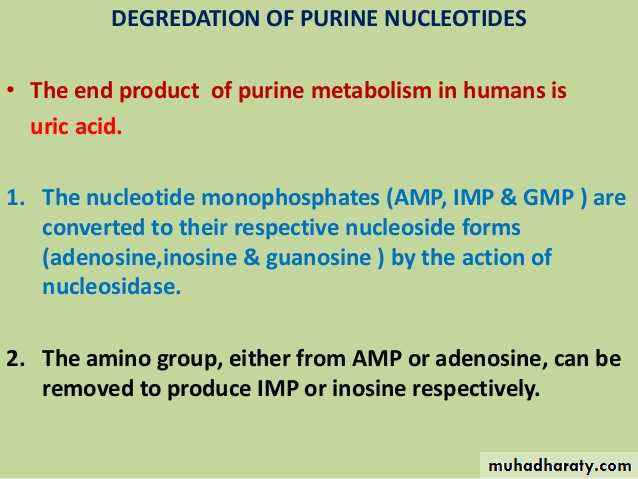
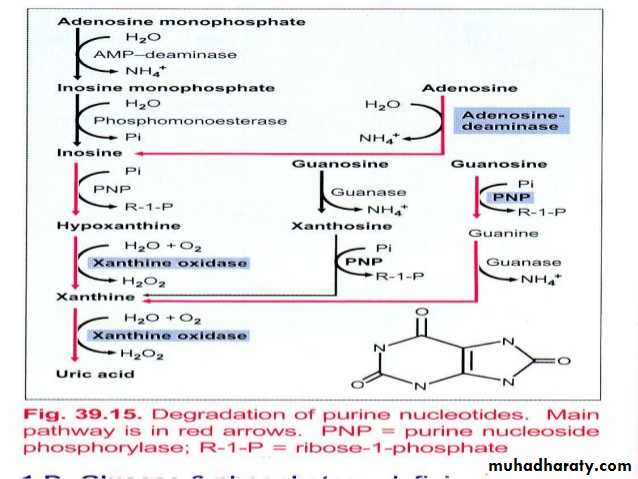
Synthesis of purine
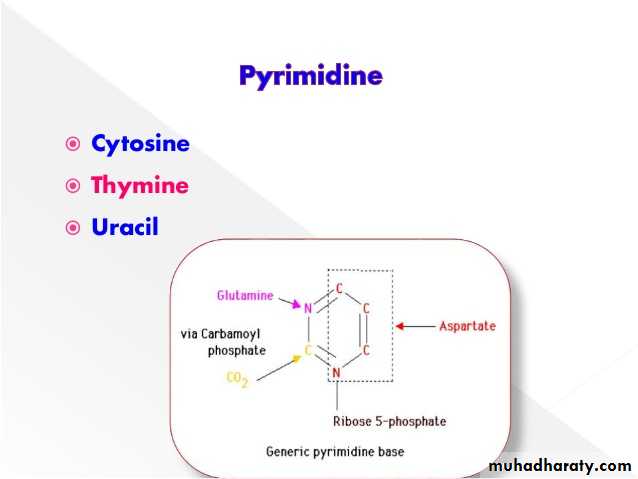
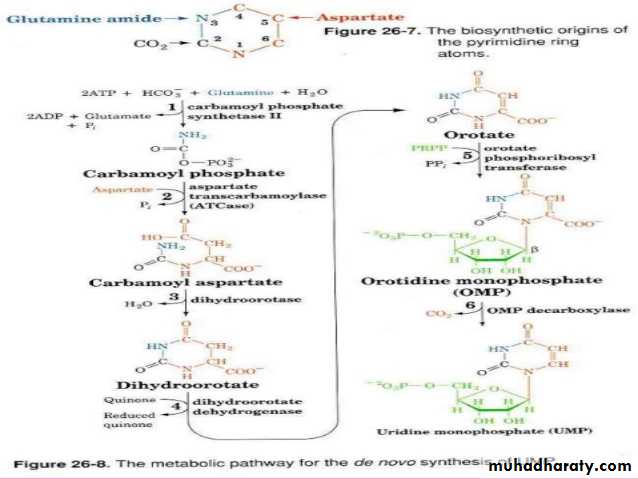
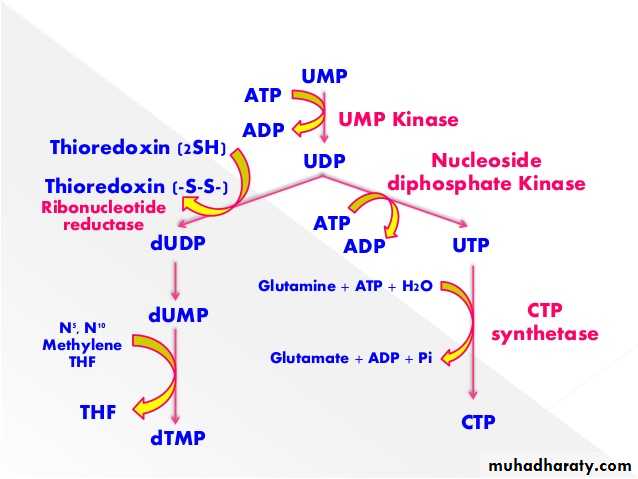
Pyrimidine biosynthesis
Unlike in purine biosynthesis, the pyrimidine ring is synthesized before it is conjugated to PRPP. The first reaction is the conjugation of carbamoyl phosphate and aspartate to make N‐carbamoylaspartate. The carbamoyl phosphate synthetase used in pyrimidine biosynthesis is located in the cytoplasm, in contrast to the carbamoyl phosphate used in urea synthesis, which is made in the mitochondrion. The enzyme that carries out the reaction is aspartate transcarbamoylase, an enzyme that is closely regulated.