بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
Nose and paranasal sinuses
ByDr. Adel Sahib Al-Mayaly
Nose
External nose
Nasal cavity
paranasal sinuses
Introduction
The nose is an integral part of the respiratory tract.It contains the peripheral organ of smell (Olfactory area).
It is a resonating chamber for voice
It includes the external nose and nasal cavity
The nasal cavity is divided into right and left cavities by the nasal septum (midline partition).
Functions of the nose
1- Olfaction (smelling).2- Respiration (breathing),
3- Filtration of dust.
4- Humidification of inspired air.
5- Reception and elimination of secretions from the paranasal sinuses and nasolacrimal ducts.
6- Resonating chamber.
Nasal profile
External Nose
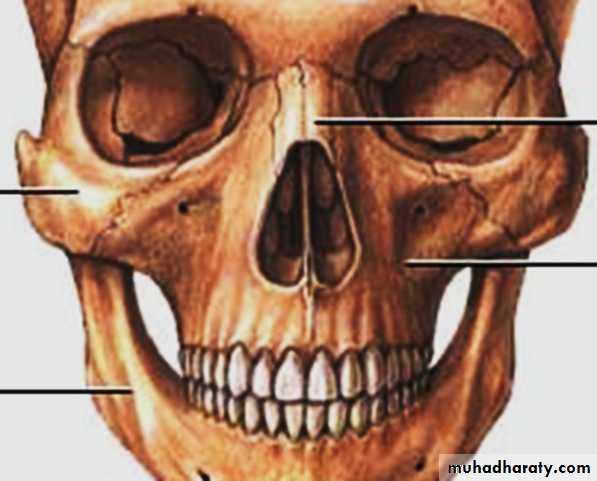
The external nose triangular-shaped projection in the center of the face .It consists of osteocartilaginous framework covered by muscles and skin.
Its upper end or root is continuous with the forehead
. At its lower end (base) are the nares (nostrils).The sides of the nose meet in the midline anteriorly to form the dorsum.
The upper part of the dorsum is the bridge and at the
lower end of the dorsum is the tip of the nose.
The lower flared part of the side of the nose is the ala.
The external nose
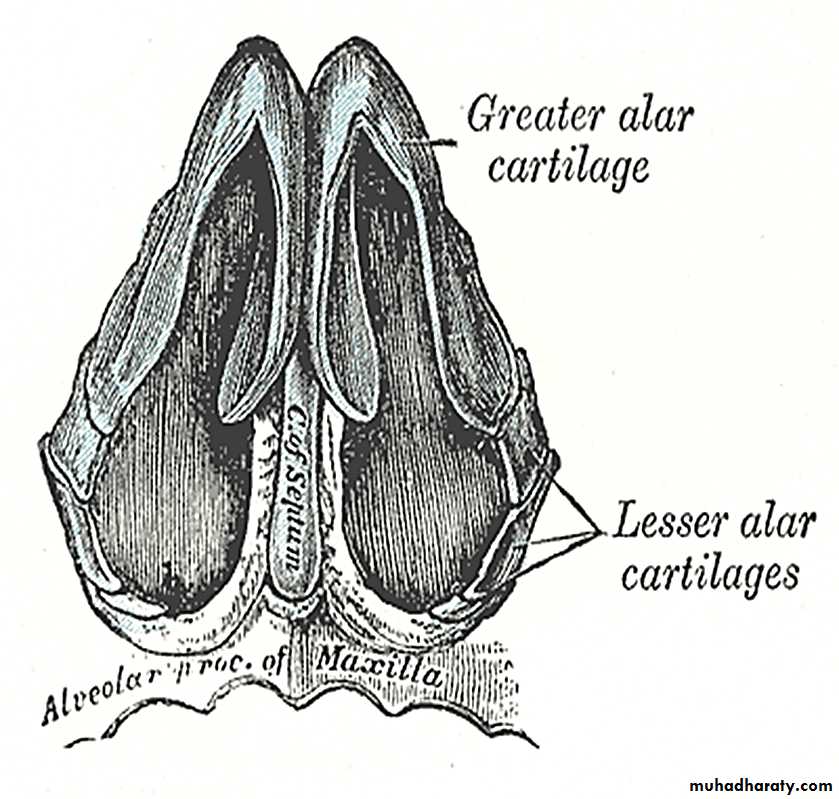
The framework of the external nose
It is made up1- Above by:- Bony
the nasal bones, the frontal processes of the maxillae, and the nasal process of the frontal bone
2- Below:- Cartilaginous
the framework is formed of plates of hyaline cartilage
( two upper lateral, two alar & septal process).
The external nose
Framework(bony)Blood Supply of the External Nose
The skin of the external nose is supplied by branches of the ophthalmic and the maxillary arteries
The skin of the ala and the lower part of the septum are supplied by branches from the facial artery.
Nasal Cavity
It extends from;-the nostrils in front to the posterior nasal apertures or choanae behind.
it is divided into two cavities by the nasal septum.
Each cavity has 4 walls:-
1- Medial & lateral.
2- Roof & floor
Nasal cavity
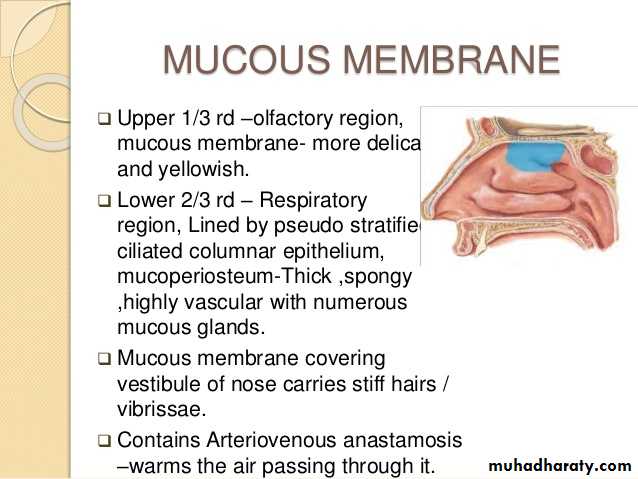
Nasal vestibule:- is the anterior and inferior part of nasal cavity.It is lined by skin and contains sebaceous glands,hair follicles and hair(vibrissae) easy to infection.
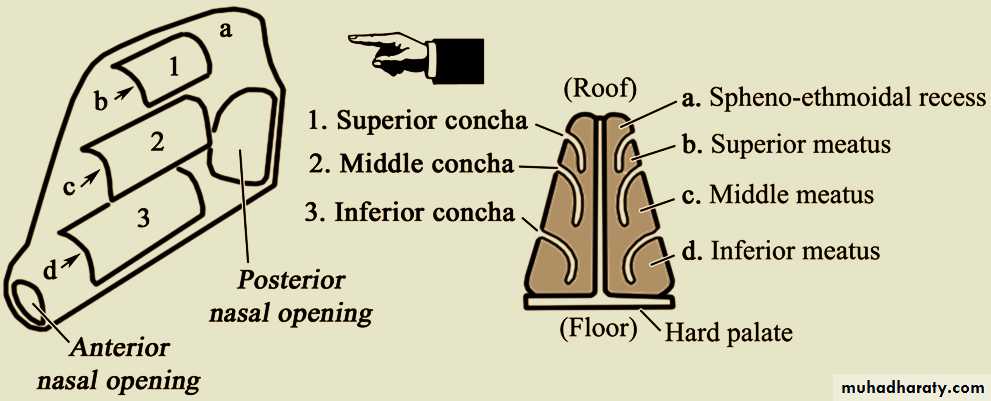
The lateral wall
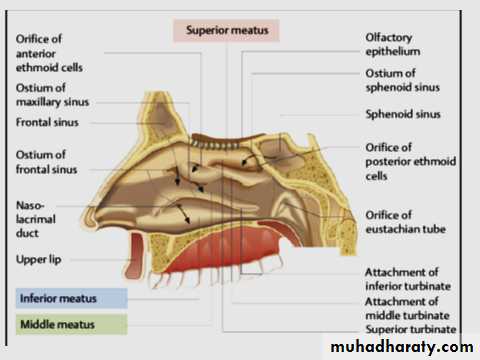
has three projections of bone called (turbinates or conchae) superior, middle, and inferior nasal conchaeThe space below each concha is called a meatus.
Inferior, Middle & Superior meati
Sphenoethmoidal Recess
is a small area above the superior concha. It receives the opening of the sphenoid air sinus
Lateral wall
Middle Meatus
The middle turbinate has by far the greatest functional importance.Most of the drainage tracts from the surrounding paranasal sinuses open into the middle meatus.
Maxillary , frontal & anterior ethmoid sinuses
Collectively called anterior group
Medial Wall (Nasal septum)
The nasal septum has a:
•Bony part
•Cartilaginous part•Membranous part
Components of nasal septumBony part:
•Posterosuperiorly: The perpendicular plate of the ethmoid.
•Posteroinferiorly: Vomer BONE
Cartilaginous part:
•Anteriorly quadrilateral septal cartilage
•Medial crus of the alar cartilage
Membranous part:•This is the anterior most part of the nasal septum lined by skin and fibrofatty tissue.
Septum deviation
Result in-
Nasal obstruction
Nasal bleeding
Headache
Anosmia
Sinusitis
External deformity
Roof & Floor
Roof :- Is by cribriform plate of ethmoidFloor:- Hard palate. a- palatal processes of palatine bone & horizontal plates of maxilla
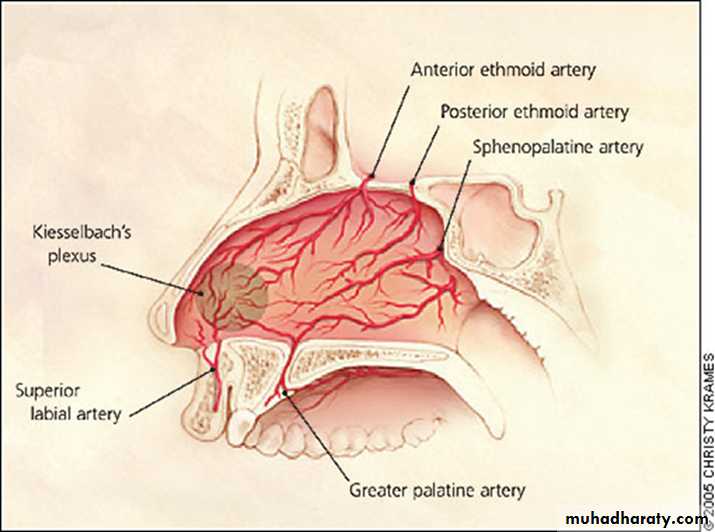
Arterial supply of the nose
Sphenopalatine artery;-- It is a branch from the maxillary artery (main arterial supply).
Septal branch of the superior labial artery from facial artery.
Septal branch of the superior labial artery from facial artery.
Arterial supply of the nose
3- Ascending branch of the greater palatine artery
4- Anterior & post. Ethmoidal Aa.
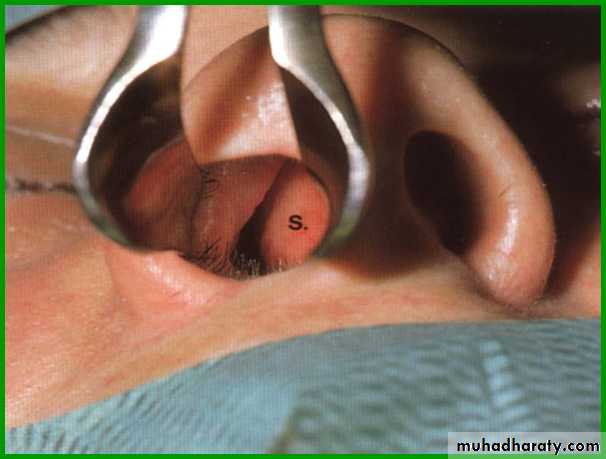
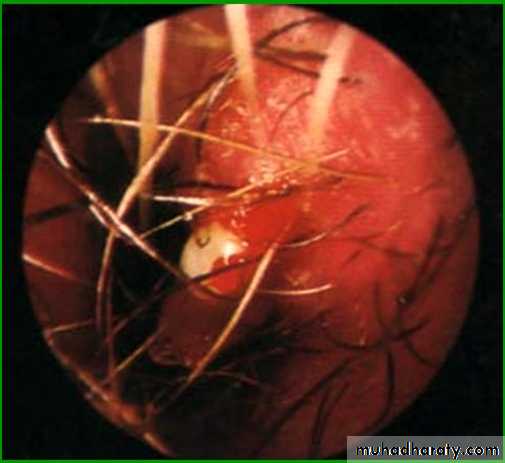
(Little’s area). Or “Kieselbach's plexus
This area is a common site for epistaxis (bleeding from the nose).Paranasal sinuses
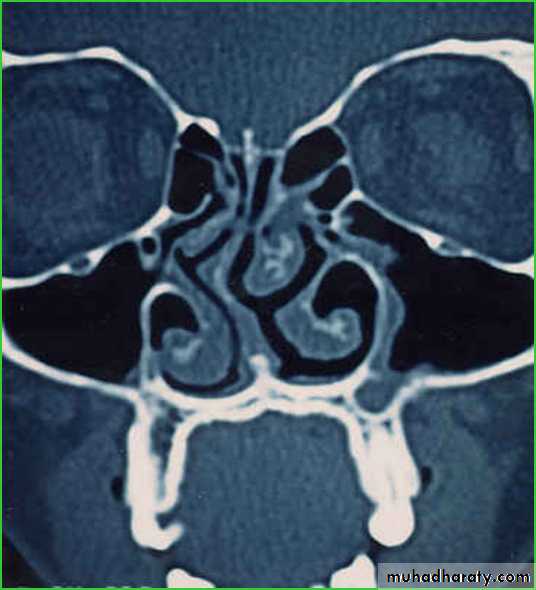
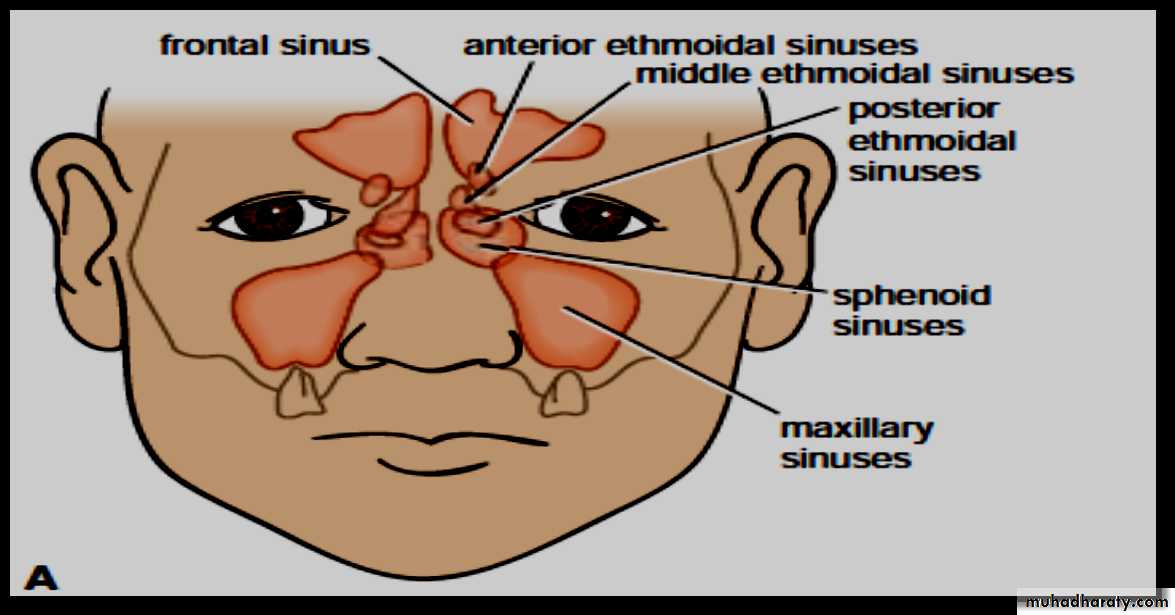
Are air-filled spaces in the facial & skull bonesThe paranasal sinuses consist of the paired frontal, ethmoid ,maxillary, and sphenoid sinuses.
Maxillary Sinus
The maxillary sinus usually is the largest of the paranasal sinuses and is situated in the body of the maxilla.Anterior wall:- The facial surface of maxilla.
Posterior wall:- The infratemporal surface.
Medial wall :- The nasal cavity.
The roof:- Floor of the orbit.
the floor is related to the roots of the premolars and molar
teeth.
The maxillary sinus drains into the middle meatus of the nasal cavity
Ethmoid Sinuses1he ethmoid sinuses consist of a variable number of separate cavities.
It lies between the upper part of the lateral nasal wall and the medial wall of the o:rbit.
Each sinus is divided into
1- anterior ethmoid sinus: - drains into middle meatus
2- posterior ethmoid :- drains into the superior meatus
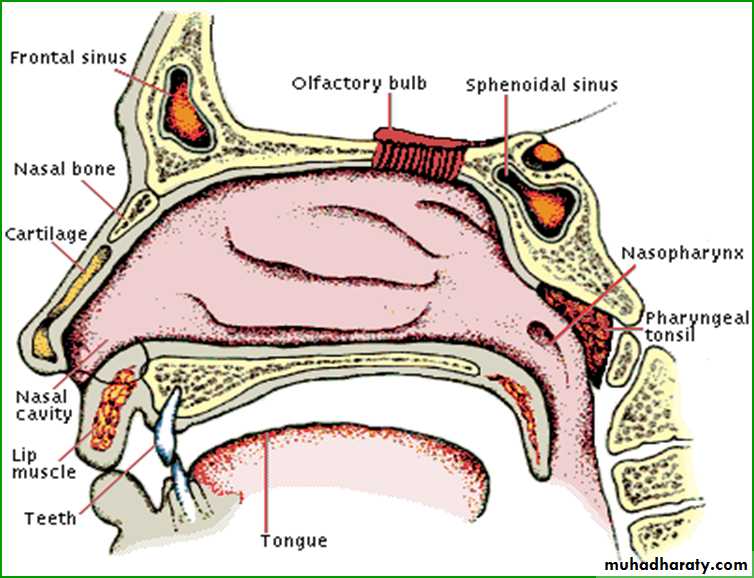
Frontal Sinuses
The two frontal sinuses are contained within the frontal bone.
They are separated from each other by
a bony septum.
Each sinus is roughly triangular.
Extending upward above the medial end of the eyebrow and backward into the medial part of the roof of the orbit.
Each frontal sinus opens into the middle meatus via the nasofrontal recess.
Sphenoid Sinuses
The two sphenoid sinuses lie within the body of the sphenoid boneEach sinus opens into the sphenoethmoidal recess above the superior concha.
Paranasal Sinuses and Their Site of Drainage into the Nose
Site of DrainageSinus
Middle meatus
1- Maxillary sinus
Middle meatus
2- Frontal sinuses
Sphenoethmoidal recess3- Sphenoid sinuses
4- Ethmoid sinuses
Middle meatus
Anterior
Superior meatusPosterior