PULMONARY FUNCTION TEST(PFT)
Proff. Amjad Fawzi
2017Objectives
By the end of the present lab, students should be able to:• Define different lung volumes and capacities.
• Define, perform and interpret the SPIROMETRY test.
• Obtain some of the significant spirometric parameters and compare them with those of a typical person of the same gender, height and age.
• Differentiate between normal, obstructive, and restrictive pattern spirograms.
Introduction
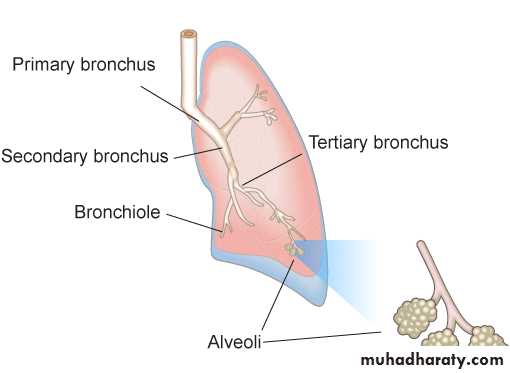
The efficiency of gas exchange between air and blood, which occurs in the alveoli, is dependent on ventilation (ulternating inflation and deflation of the lungs).The efficiency of ventilation, on the other hand, is dependent on the integrity of
airwaysalveoli
thoracic cage(bones and muscles)
respiratory control mechanisms.
Normal values of lung volumes &capacities depends on the following factors:
HeightWeight
Age
Gender
Race
Effort dependent
Normal values is obtained from special charts(NOMOGRAM) or special prediction equation depending on hight,weight and gender.
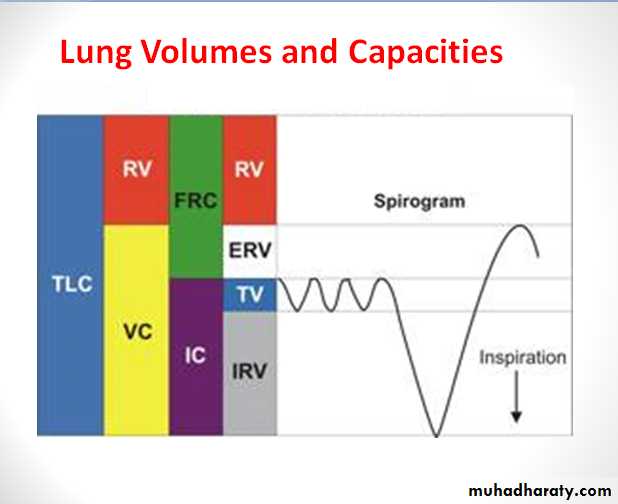
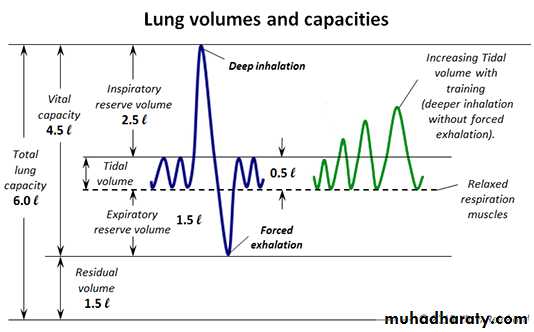
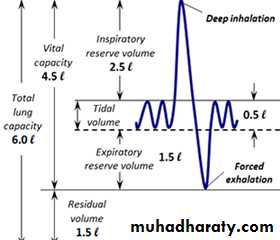
The vital capacity (VC)
This is the maximum amount of air that a person can expel from the lungs after filling the lungs first to their maximum extent(max expiration following max inspiration).The vital capacity (VC) = IRV + TV + ERV = 3000 + 500 + 1100 = 4600 ml.
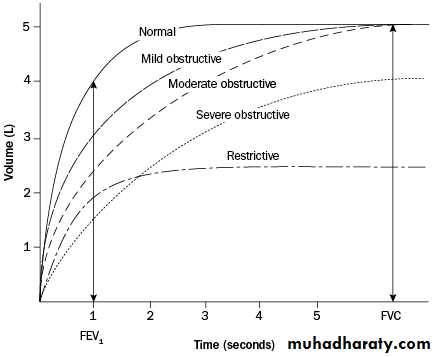
Vital capacity can be decreased markedly in restrictive lung diseases (paralysis of the respiratory muscles, pulmonary fibrosis) and may be normal in obstructive lung diseases (asthma, bronchitis, emphysema).
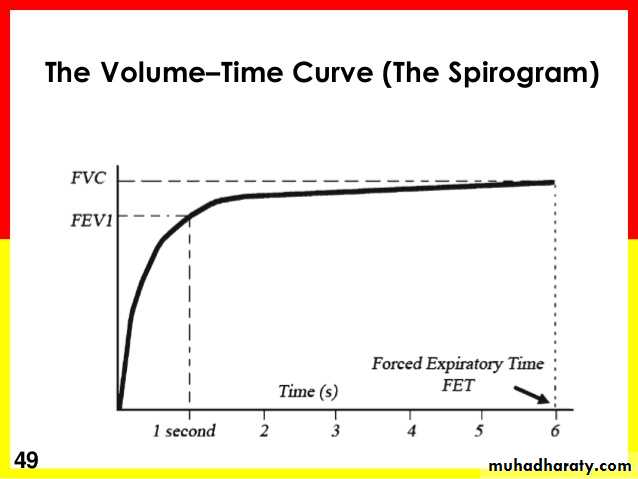
Timed vital capacity (forced expiratory volume-1 sec, FEV1): It is the volume of air expired during the first second of forceful expiration.
Percent vital capacity (FEV1%): [FEV1/VC] x 100. In normal subject, the FEV1% is at least 80%. However, in obstructive lung diseases like asthma, FEV1% is markedly reduced while normal in restrictive lung diseases.
Spirometry (measurement of breath)
The most common PFT.
It measures the volume and/ or the flow of air that can be inhaled and exhaled.
Other PFT includes:
Test for gas exchange(lung diffusing capacity-Dlco).Blood gas analysis.
Exercise test.
Special tests like bronchodilator test, PFT for children…..
Spirometry is used for:
Check upRotine health check up.
Physical fitness for certain jops(eg. Military).
Preoperative.
Diagnosis of lung diseases
Obstructive lung disease(asthma and chronic bronchitis).Restrictive lung disease(pulmonary fibrosis).
Follow up of treatment in chronic lung diseases.
Development of Spirometry
The water spirometer measuring vital capacity was developed by a surgeon named John Hutchinson, in 1846.
Spirometer was then developed into dry types.
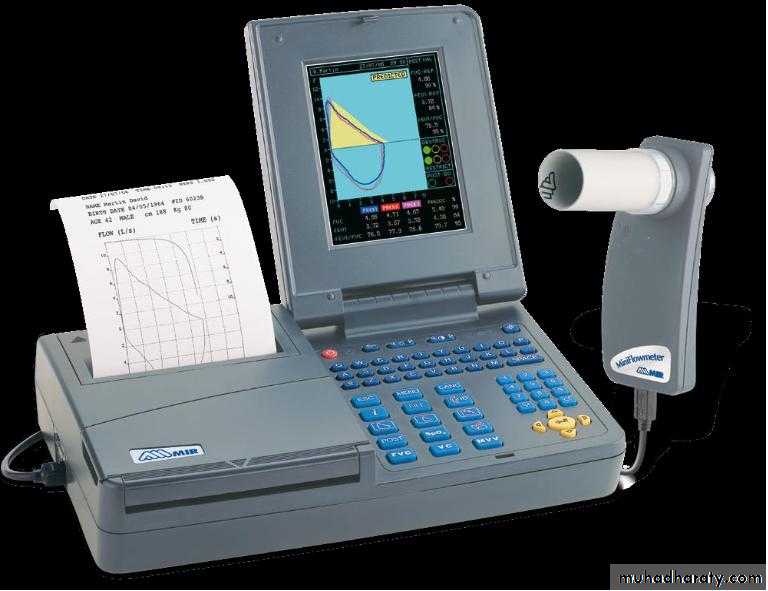
eg. VitalographModern Spirometers*Computer based*More accurate
Modern, computer based
spirometerTurbine
Whole body plethysmograph
more accurate measurement for the all lung volumes.SUBJECTS, APPARATUS AND PROCEDURE
SubjectsPre-test instructions and demonstration.
Apparatus
Use Spirometer to obtain the (FVC,FEV1,FEV1%).
Nose clip.
Tape measure(measurement of body hight).
Balance(measurement of body weight)
Spirogram
Classification of Lung Defects
OBSTRUCTIVE
Expiratory flow is below normal(reduced FEV1%)
Diseases:
Asthma
Bronchitis
Emphysema
RESTRICTIVE
Lung volumesare reduced(eg. FVC)Diseases:
Pulmonary fibrosis
Obesity
DISCUSSION
Enumerate the factors which affect the different lung function parameters.How you can use the forced spirogram to differentiate between obstructive and restrictive pulmonary diseases.