366
Dental implant
لثة \ خامس اسنان
د. زيد م(3)
3\ 4\ 2017
Dental implant
Is a non-biologic (artificial) device surgically inserted into the jaw bone to• Replace a missing teeth
• Provide support for a prosthetic denture
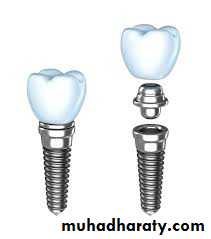
Component of endosseous dental implant
• Implant fixture• Transgingival abutment post
• Dental prosthesis
Component of endosseous dental implant
• Implant fixture:which is the portion of the Implant that is
surgically placed into bone that act as a root &needs 3-6 m. to be fully supported .by bone
2.Transgingival abutment post
is a titanium post that protrudes through tissue into mouth &support restorative prosthesis(crown or denture) to fixture.3.Fixed or removable dental prosthesis
which can be either fixed restoration (prosthetic crown)or removable (denture prosthesis).
Healing of endosseous dental implant
Osseointegration of the fixture (Bone cells grow around fixture until bone is in close contact with surface of fixture)Perimucosal seal (the epithelium adapts to transgingival post creating biological seal)
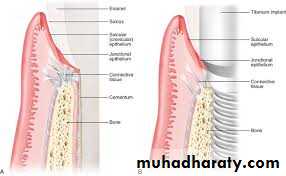
Peri-implant tissue
Tissues that surround implantare similar to periodontium of
natural tooth but there are
some important differences
Peri-implant tissue
Connective tissue fiber inserted to the root surface while in peri-implant tissue the fiber parallel or circular to implant surface
No periodontal ligament in peri-implant tissue
No cementum in peri-implant
Direct contact of alveolar bone
Implant to Epithelial tissue interface
Epithelial cells adhere to Implant surface via hemidesmosomes (theoretically)Junctional Epithelium form biological seal that function as a barrier b/w Implant & oral cavity
In natural teeth
Gngival fibers brace Gingival margin against tooth & strengthen attachment of Junctional Epithelium to tooth while periodontal ligament suspends tooth in its socket.Periodontal ligament serve as a physical barrier to bacterial invasion So lack of such protective function in Implant allow organisms to destroy bone much more rapidly.
• Implant to bone interface
Osseointegrationis direct contact of bone with Implant surface
Clinically, osseointegration is regarded as successful if there is :
1- absence of clinical mobility.
2- absence of inflammation of peri implant tissue.
3- no discomfort or pain when Implant is in function.
4- no increased bone loss or radiolucency around Implant on radiograph.
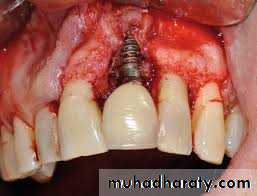
Pathological changes in peri-implant tissues
Plaque deposits Can accumulate on Implant & result in inflammation of soft tissue around Implant when disease process progresses further, partial or total loss of osseointegration can occur.
That is subdivided into:
Pathological changes in peri-implant tissues
• Peri-implant gingivitis• gingivitis without bone
• loss
• Peri-implantitis
• associated with bone
• loss
Peri implantitis Begins at coronal
portion while apical portion continues to be osseointegratedAdvanced lesion could be detected
as bone loss around Implant
Implant does not become mobile until final stages of peri-implantitis.
Etiology of peri-implant disease
• Bacterial infection
• Biomechanical force
• smoking
Bacterial infection
the pathogenesis in peri implant tissue & periodontal lesions in natural dentition progresses in Similar fashion (interaction).Rate of tissue destruction tend to be more rapid in peri implant tissue
Biomechanical factors
Excessive biomechanical forces have been suggested to induce bone stress & micro# at bone-Implant interface resulting in loss of osseointegration.Long term success of implant
Self-care education regarding implant care& home care tools.Soft tissue & radiographic examination checking occlusion
Demonstration on use of home care tools.
Maintenance therapy
• Maintenance of the bone supportX-ray evaluation at specific time intervals
Compare the hight & density with previous radiogragh
evaluated by long-cone paralleling techniqueat specific time intervals
Maintenance therapy
• Control of inflammation• Maintenance of functional implant
Check the implant component(as loose screws, cement washout ,material wear) screw or abutment # & proper adaptation.
Mobility require immediate consultation.
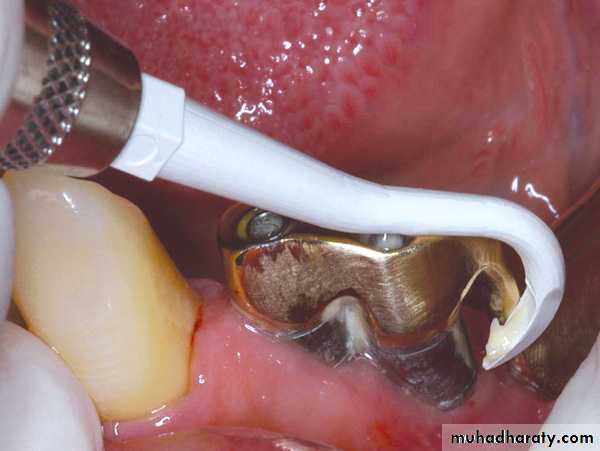
Debridment of the implant
use of metal, sonic ultrasonic curette contraindication.implant made of titanium that permanent
damaged if treated with metal instrument Such damage is plaque retentive
Metal instrument disturb surface coating implant that is decrease biocompatibility.
plastic instrument most commonly used
Peri-Implant probing
Baseline data should be present regarding fixed reference point for probingProbing should be avoided until about 3months after abutment connection.
Only light pressure applied during probing as
heavy force could penetrate weakly adhered
biological seal & introduce organisms into
peri-implant environment.