Mouth & Oropharynx
ByDr. Adel Sahib Al-Mayaly
Otolaryngologist
The Mouth(the oral cavity)
The mouth is for eating and talking through,
It also serves as an emergency airway in dyspnea or upper airway obstructionMouth
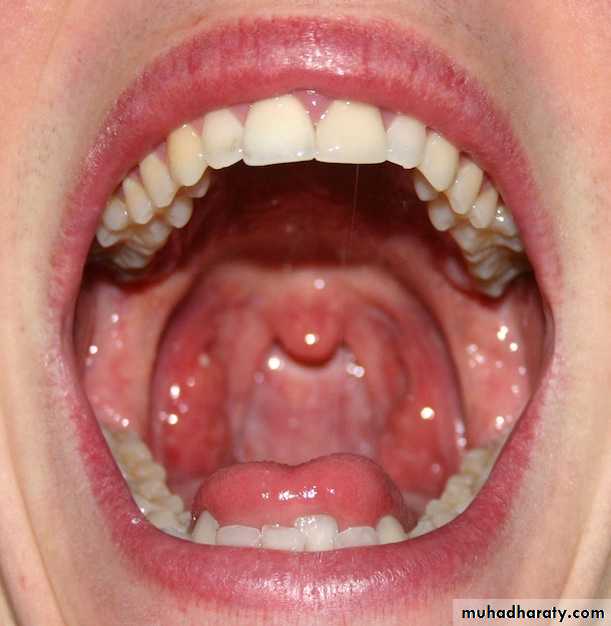
It is the hollow cavity that allows food and air to enter the body.
It extends from the lips to the palatoglossal arches (anterior pillars of the fauces).It is enclosed by the lips and cheeks.
Surface Anatomy of Mouth
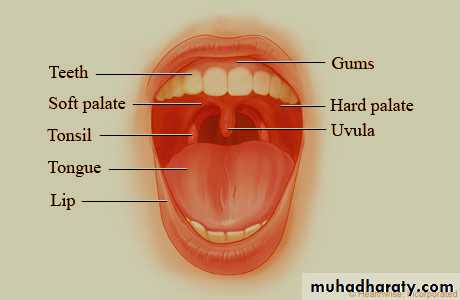
Anatomic structures of mouthIt is divided into:-
1- Vestibule:- slit-like space between lips/cheeks and teeth/gingivae (gums).
2- Mouth cavity proper:- The space inside the teeth and gums (alveolar processes).
It contains many other organs such as the teeth, tongue, and the ducts of the salivary glands
Mouth
The floor is the mylohyoid muscle & contains the anterior 2/3 of tongue (body).The roof is the hard palate.
The lips and cheeks are covered with hairy skin; except the red margin of the lips which is rich in capillary blood supply (vermilion border).
The red margin is highly sensitive and is represented by a large area in the sensory cortex
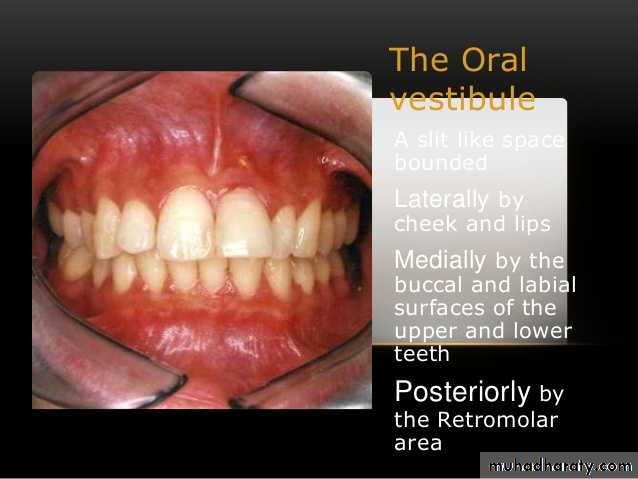
Vestibule
It lies between1- the lips and the cheeks externally and
2- the gums & the teeth internally.
It is slit-like space communicates with the exterior through the oral fissure between the lips.
When the jaws are closed, it communicates with the mouth proper behind the third molar tooth on each side
Vestibule
The lateral wall of the vestibule is formed by the cheek ; It is made up by the buccinator muscle and is lined with mucous membraneThe duct of the parotid salivary gland opens on a small papilla into the vestibule opposite the upper second molar tooth.
Mouth Proper
It has a roof and a floor.Roof:- Palate
Hard palate:-is the anterior 2/3 of palate & is vaulted (concave); this space is mostly filled by the tongue when it is at rest
Its bony skeleton is formed by:-
1- Palatine processes of maxilla
2- Horizontal plates of the palatine bone.
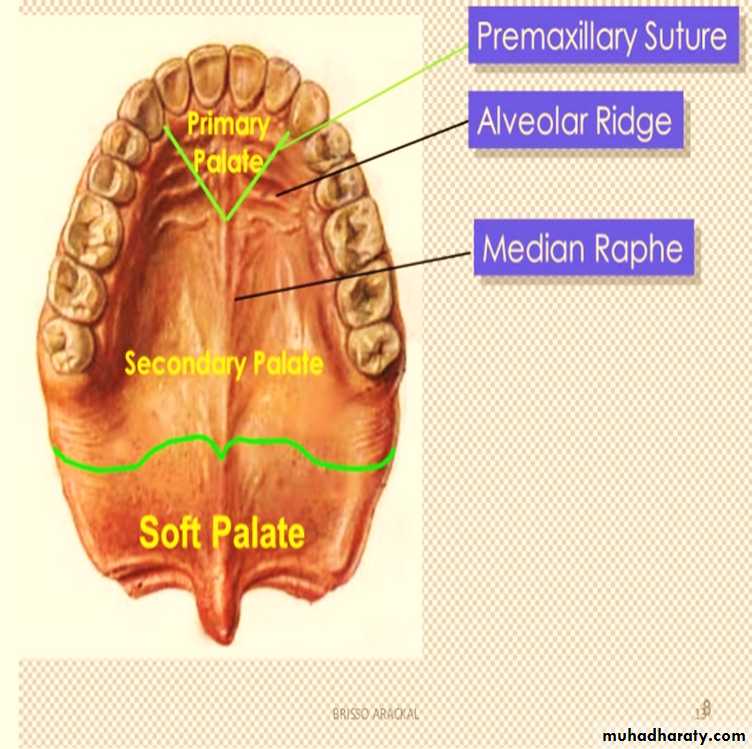
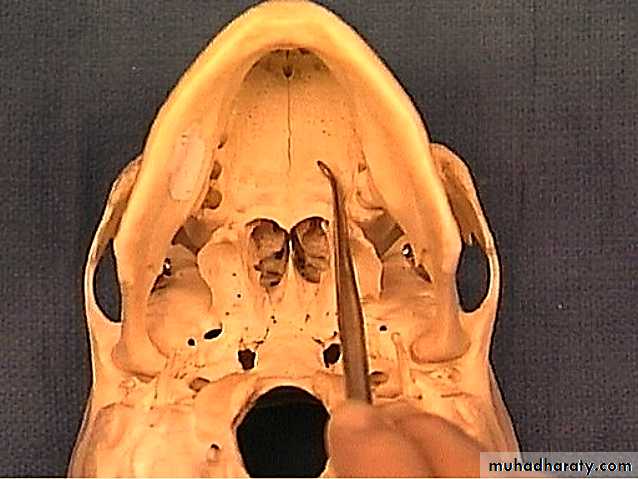
Surface Anatomy of Hard palate
In the midline; at the front of the hard palate lies the incisive fossa, posterior to the central incisor teeth into which the incisive canals open
Medial to the 3rd molar tooth, the greater palatine foramen pierces the lateral border of the bony palate.
The greater palatine vessels and nerve emerge from this foramen and run anteriorly on the palate.
The lesser palatine foramina lie posterior to the greater palatine foramen.
SOFT (Muscular)PALATE
It is the movable posterior third of the palateand is suspended from the posterior border of the hard palate.
Its free posterior border presents in the midline a conical projection called the uvula.
soft palate is composed of
1- mucous membrane,
2- palatine aponeurosis and
3- palatal muscles
Soft palate
Palatine Aponeurosisis a fibrous sheet attached to the posterior
border of the hard palate. It is the expanded tendon of the tensor veli palatini muscle.
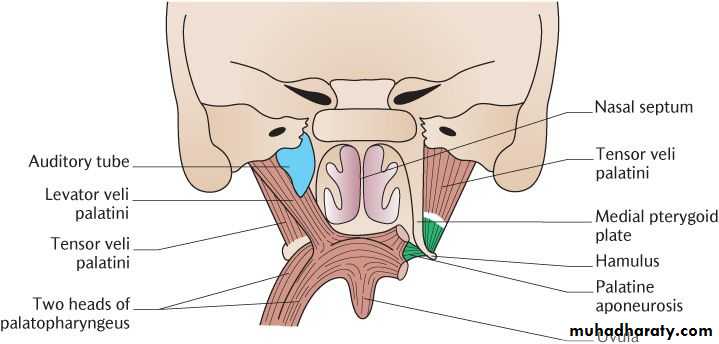
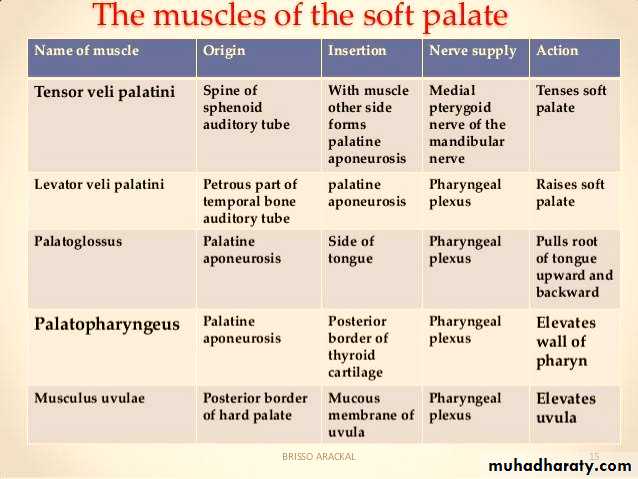
Muscles of the Soft Palate:-
1- tensor palati.
2- levator palati.
3- palatoglossus.
4- palatopharyngeus.
5- Musculus uvulae.
Blood Supply of the Palate
1-The greater palatine branch of the maxillary artery.2- ascending palatine branch of the facial artery.
3- ascending pharyngeal artery.
The sensory nerves of the palate
The greater and lesser palatine nerves (maxillary nerve).
The nasopalatine nerve (maxillary nerve).
Tongue
TongueThe tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth.
It manipulates food for mastication.
is used in the act of swallowing.
Is used during articulation.
It is the primary organ of taste in the gustatory system
Structure
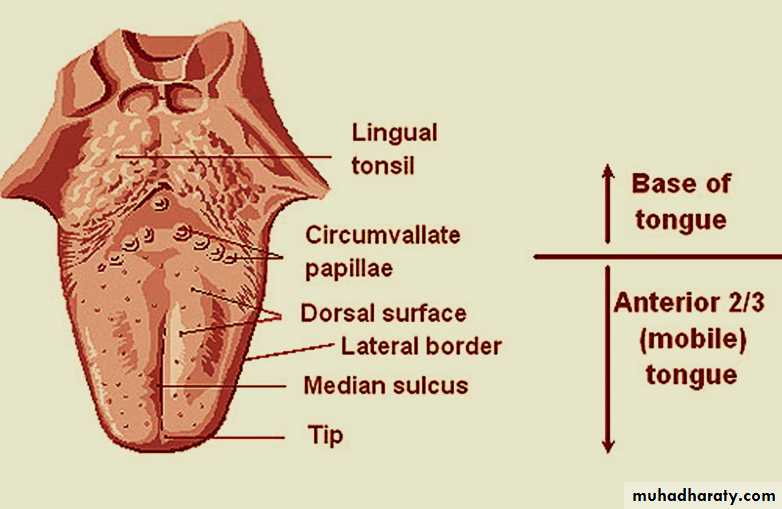
The tongue is mass of striated muscle covered with mucous membrane that occupies the floor of mouth.It is divided into right and left halves by a median fibrous septum (the median sulcus) .
It is of two parts:-
1- Oral part (anterior 2/3 body);- the mobile part
2- Pharyngeal part(posterior 1/3):- is also called base of tongue or root of tongue.
Structure
The two parts are divided by V-shaped sulcus called terminal sulcus.
The apex of the sulcus contains the Foramen cecum (the embryologic origin of thyroid gland).
The anterior end of tongue is thin and narrow & is directed forward (tip of tongue).
The posterior part is, its root, directed backward,
Surface of tongue
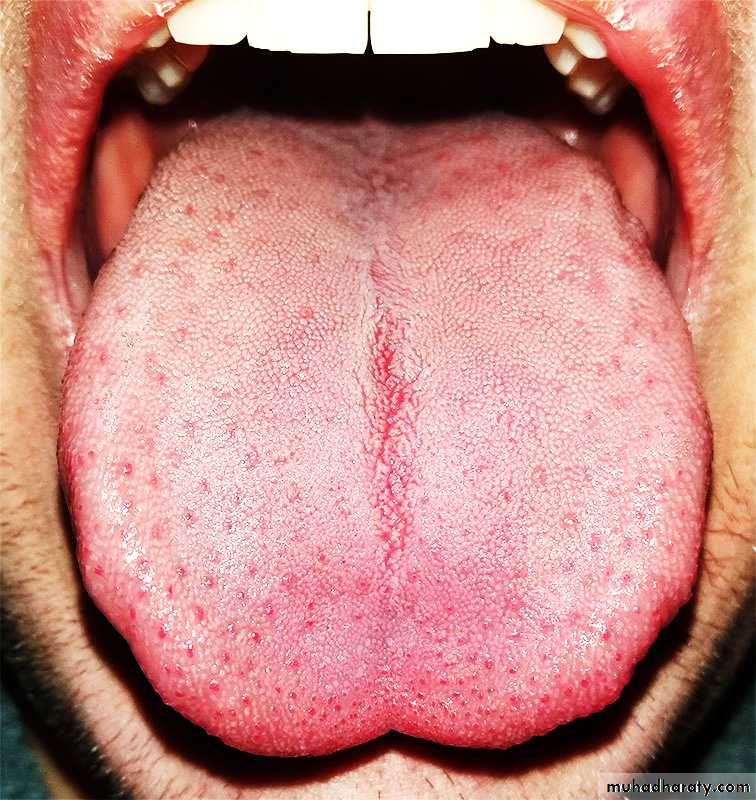
the tongue has two surfaces:-1- Dorsal surface:- (masticatory surface).
It is covered by keratinized stratified squamous epithelium & is characterized by mucosal projections called lingual papillae.
lingual papillae house the taste buds and their taste receptors. They consist of filiform, fungiform, vallate and foliate papillae.
The lingual papillae covers the dorsal side of the tongue
Surface of tongue
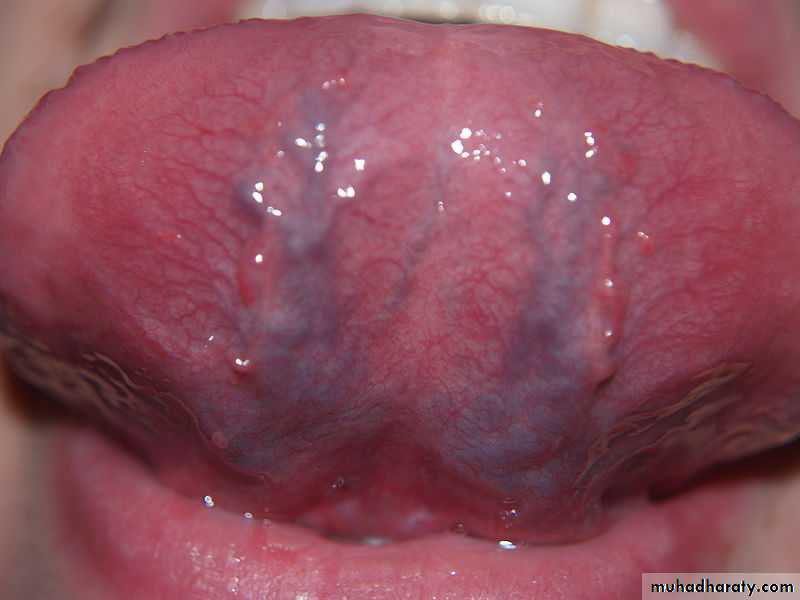
The ventral surface (underside) is stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium which is smooth.Sublingual Region
1- Frenulum of tongue.2- Sublingual fold.
3- Sublingual papilla.
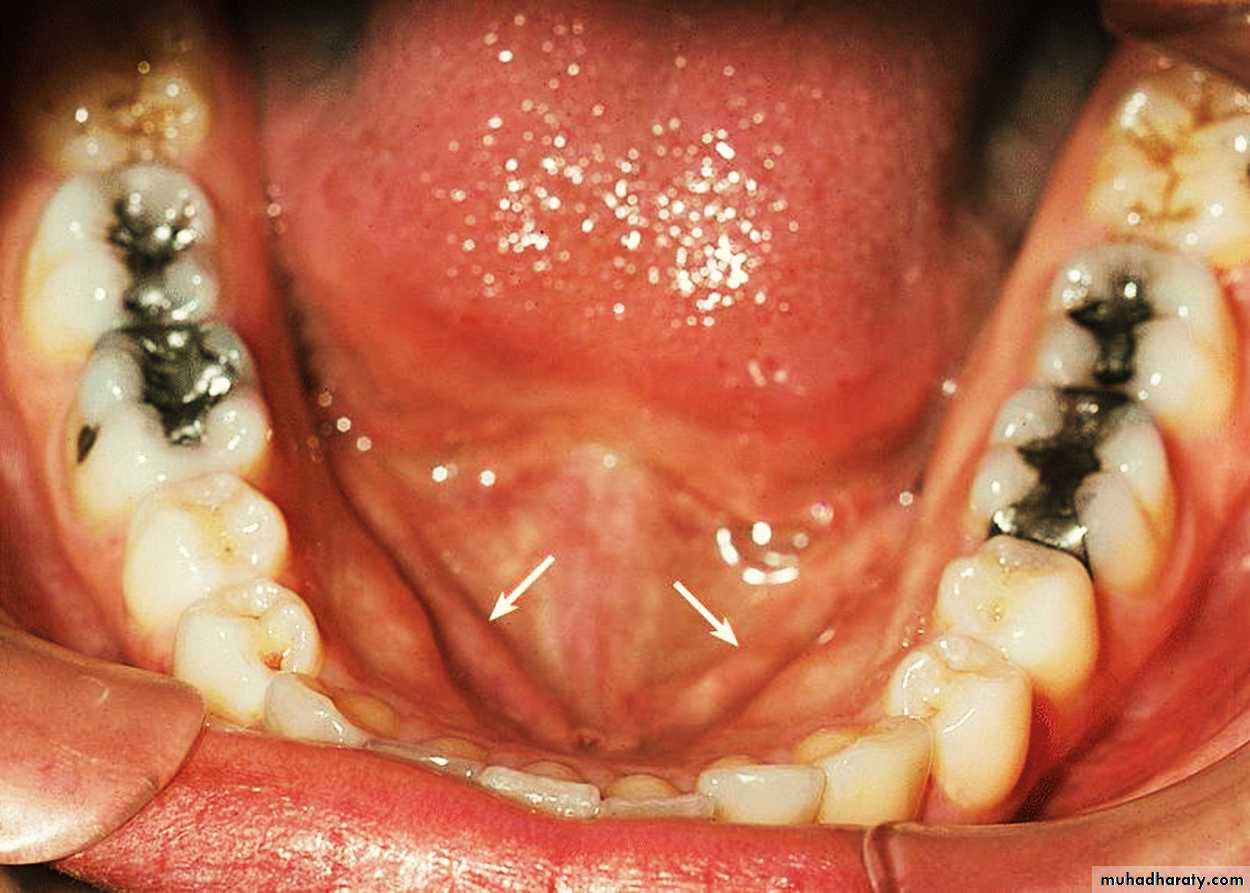
4- Opening of submandibular duct
Muscles of Tongue
The eight muscles of the human tongue are classified as either intrinsic or extrinsic.The four intrinsic muscles act to change the shape of the tongue.
They are not attached to any bone.
The four extrinsic muscles:-
They act to change the position of the tongue.
They are anchored to bone
Extrinsic muscles
The four extrinsic muscles originate from bone and extend to the tongue.
Their main functions are altering the tongue's position allowing for protrusion, retraction, and side-to-side movement.
They are
1- genioglossus
2- hyoglossus
3-styloglossus
4- palatoglossus
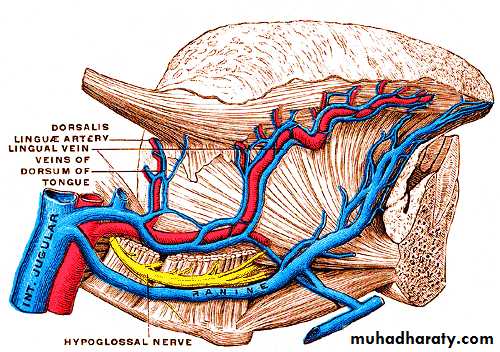
Blood supply
Primary supply is facial artery branch of ECA.Secondary supply is1- tonsillar branch of facial A.
2- ascending pharyngeal A.
Venous drainage:-
lingual vein
Extrinsic muscles
1- The genioglossus arises from the mandible and protrudes the tongue.2- The hyoglossus, arises from the hyoid bone and retracts and depresses the tongue.
3-The styloglossus arises from the styloid process of the temporal bone and draws the sides of the tongue up to create a tongue for swallowing.
4- Palatoglossus Pulls roots of tongue upward
and backward
Nerve supply
Motor fibers, Special sensory fibers for taste, and General sensory fibers for sensation.
Motor supply :- All intrinsic & extrinsic muscles by hypoglossal nerve except palatoglossus m. (vagus nerve)
Nerve supply
Sensory :-1- anterior 2/3:-
a- taste:- chorda tympani branch of the facial nerve (CN VII.
b- Sensation:- lingual branch of the mandibular division (V3) of the trigeminal nerve
Nerve supply
2- posterior 1/3:-Taste and sensation: glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX).
3- Base of tongue:-
Taste and sensation: internal laryngeal nerve (branch of CN X, vagus nerve).
Action
Nerve Supplyinsertion
Origin
Muscle
Protrudes apex of tongue
through mouth
Hypoglossal nerve
Blends with other muscles
of tongue
Superior genial spine of
mandible
Genioglossus
Depresses tongue
Hypoglossal nerve
Blends with other muscles
of tongue
Body and greater cornu
of hyoid bone
Hyoglossus
Draws tongue upward and backward
Hypoglossal nerve
Blends with other muscles
of tongue
Styloid process of temporal
bone
Styloglossus
1-Pulls roots of tongue upward
and backward, 2- narrows
oropharyngeal isthmus
Pharyngeal plexus
Side of tongue
Palatine aponeurosis
Palatoglossus
Muscles of Tongue