D.Rasha L2
1
Body of uterus
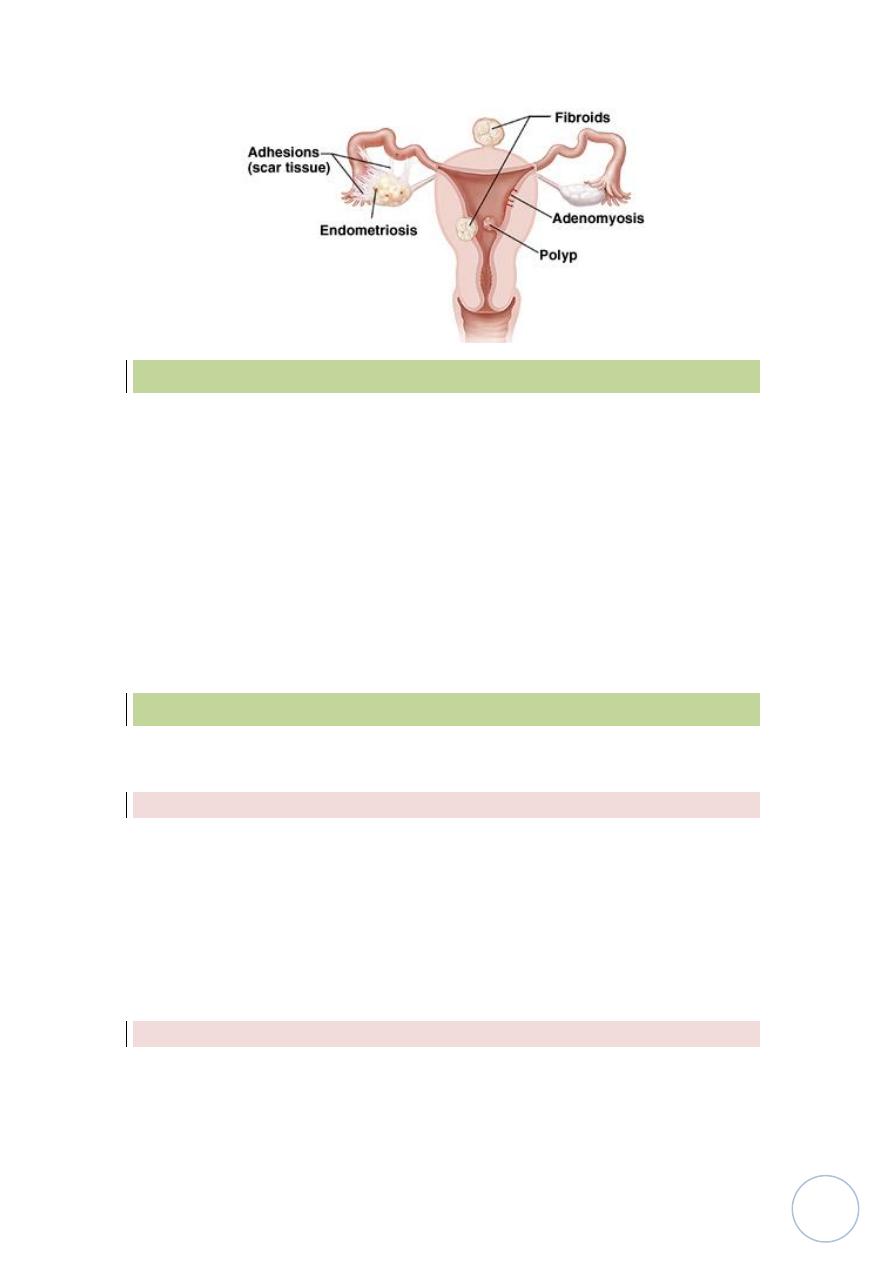
Endometritis:
It's either acute bacterial inflammation or chronic one which occur after
abortion or normal delivery, in cases of use IUDs and miliary TB which's
seen histologically as irregular proliferation of endometrial glands and
chronic inflammatory cells infiltrated of stroma.
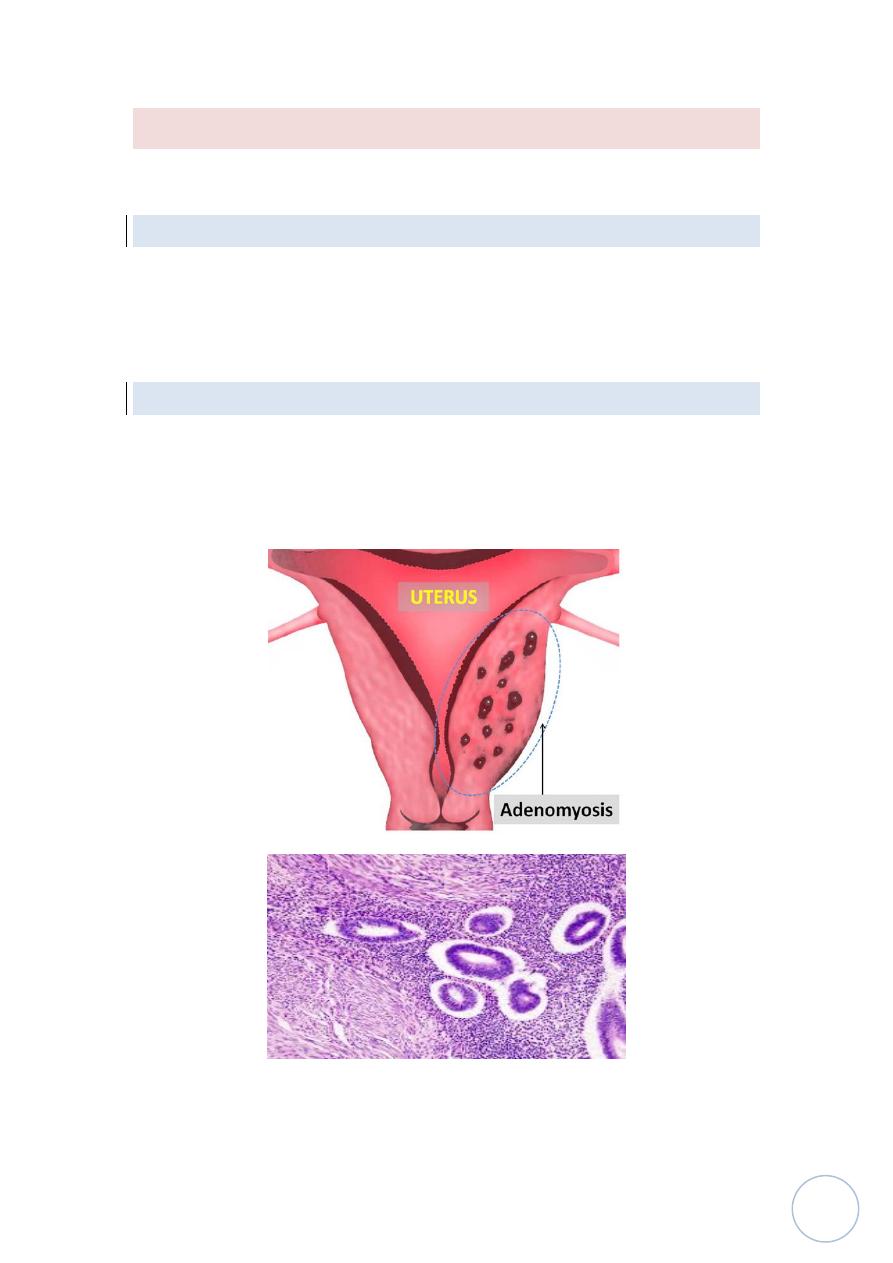
Adenomyosis:
This condition is characterized by implantation of both endometrial glands
and stroma from basal layer of endometrium between myometrial layers
which cause reactive hypertrophy of myometrium, menorrhagia,
dysmenorrhea and pelvic pain.
D.Rasha L2
2
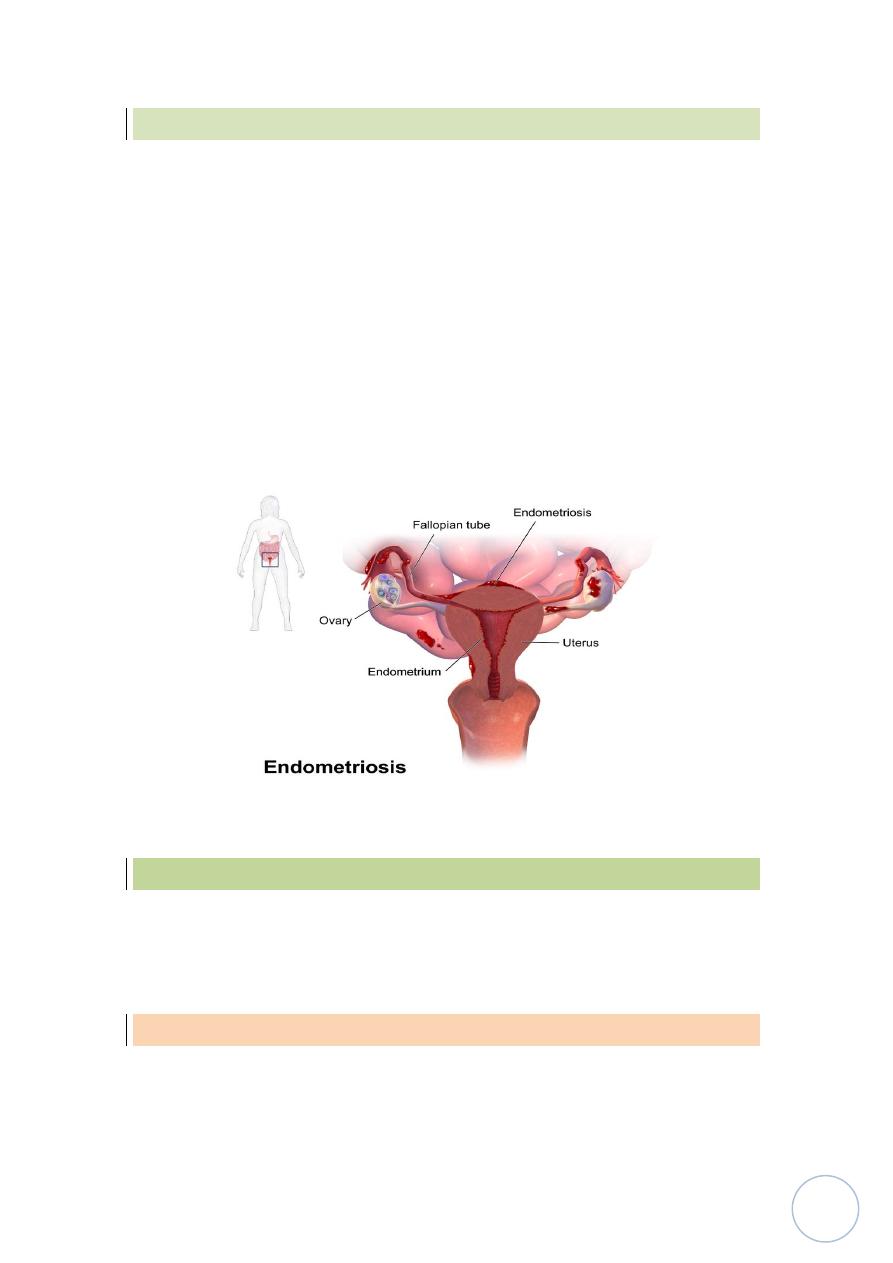
Endometriosis:-
end, it often causes infertility, dysmenorrhea and pelvic pain, this
condition consist of functioning endometrial tissue in the pelvis ( ovaries,
pouch of Douglas, uterine ligaments, tubes and rectovaginal septum also
may be seen in peritoneal cavity, about the umbilicus also can be seen then
in LN, lungs, heart and bone.
So it's suffering from cyclic changes of menstrual cycle, in ovaries it will
form large blood filled cysts which's called chocolate cyst as the blood
ages, the organization of the blood leads to fibrosis and adherence of pelvis
structure so cause infertility.
The
microscopically diagnosis
depend on finding 2 of following 3 features,
endometrial glands, stroma and hemosiderin pigment.
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding
DUB:-
It's defined as abnormal bleeding in the absence of a well-defined organic
lesion in the uterus.
Endometrial hyperplasia:-
An excess of estrogen relative to progestron if prolonged and marked
induce endometrial hyperplasia which is ranging from simple hyperplasia
to moderate, complex hyperplasia and atypical hyperplasia these changes
D.Rasha L2
3
depend on level and duration of exposure to estrogen effect, the
imporatance of hyperplasia especially complex and atypical which is
caused abnormal uterine bleeding and it's a premalignant codition cause
adenocarcinoma of endometrium.
Tumors
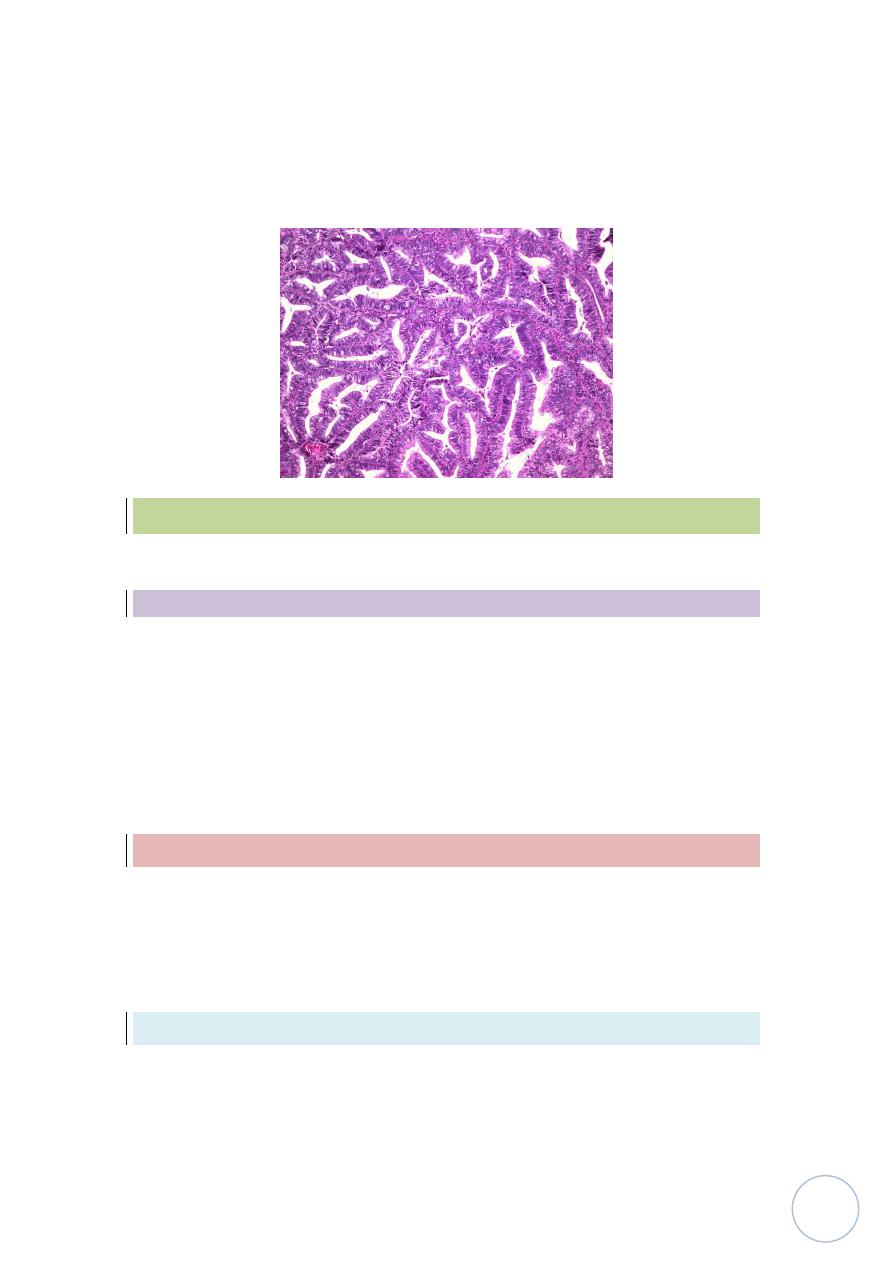
Endometrial polyps:-
Which is small sessile mass project from endometrium.
Histologically
seen as polyp lined by columnar epithelium and contain in
stroma endometrial glands which are sometimes showing cystically
dilated glands on fibrosed stroma.
The clinical manifestation of endometrial polyps in producing uterine
bleeding and rarely progress to adenocarcinoma.
Leiomyoma:-
It's most common benign tumor occur in female during reproductive life,
it's effected by estrogen and oral contraceptive, so that it's shrink in size in
menopause, it's a benign tumor of smooth muscle cells of myometrium but
because of firm consistency called fibroid
.
Morphology:-
Macroscopically:
it appear as sharply circumscribed, firm, grey to white
mass with whorled cut surface, it may occur singly but more often as
multiple masses either "transmural" in wall or submucosal or subserosal.
D.Rasha L2
4
Microscopically:
appear as proliferated myocytes arranged in interlacing
bundles forming whorles with no atypia of proliferated myocytes.
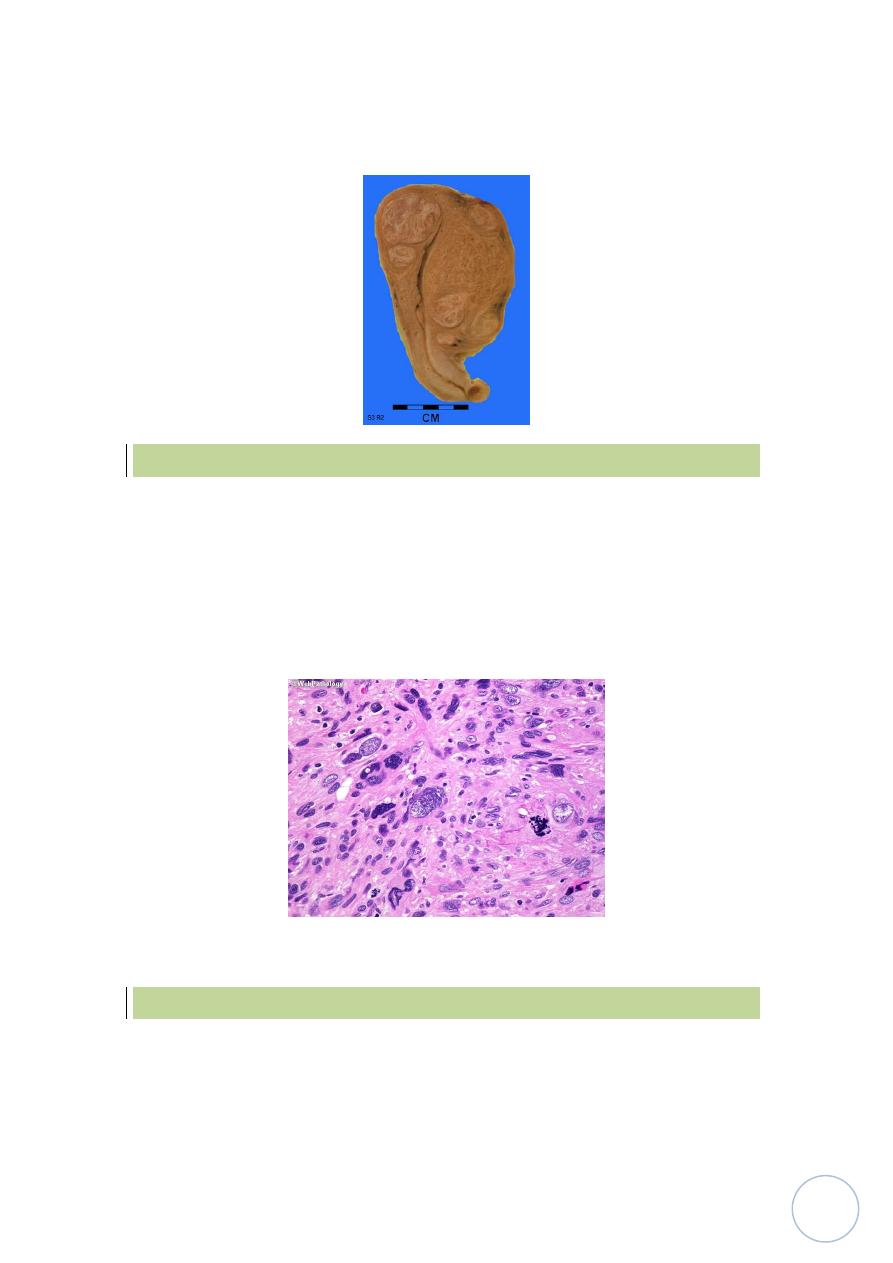
Leiomyosarcoma:-
It's a malignant tumor arise from leiomyocytes of uterus and not from
leiomyoma, it's unlike leiomyoma usually arise as single mass.
Histologically:
It's represent a wide range of differentiaition, from those
that closely resemble leiomyoma to anaplastic tumors, diagnostic features
of leiomyosarcoma include relatively frequent mitoses with or without
cellular atypia or less numerous mitoses with cellular atypia.
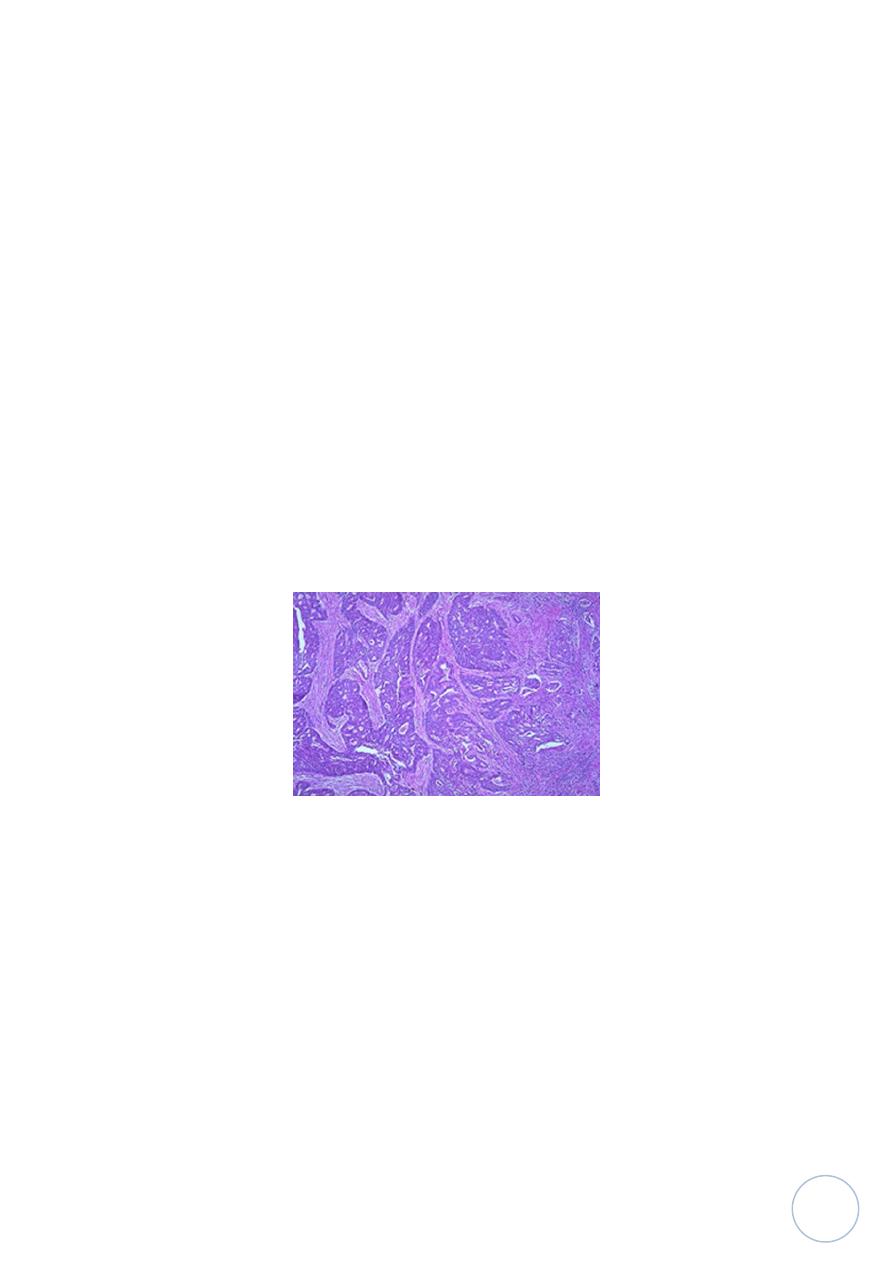
Endometrial carcinoma:-
It's most frequent cancer of female genital tract after early detection and
treatment of CIN.
Pathogenesis:-

D.Rasha L2
5
Endometrial carcinoma usually occur in post menopausal women, so it's
uncommon below the age of 40 years.
The main risk factor is increased estrogen stimulation as in endometrial
hyperplasia and this also depend on dosage and duration of estrogen
stimulation.
Morphology:-
Endometrial carcinoma occur on one of 2 forms either appear as
infiltrative
causing diffuse thickening of the affected uterine wall or appear
as
exophytic
form.
Microscopiaclly:
most of these tumors are adenocarcinomas with either
well defined glands resembling the endometrial glands from which arose
or less well differentiated tumors forming solid sheets of cells with nuclear
atypia and mitotic activity.
So
grading
of carcinoma according to differentiation into grade I to III from
well differentiated to undifferentiated.
Staging
system is most widely used.
StageI:
confined to uterine corpus.
StageII:
involvement of corpus and cervix.
StageIII:
extension outside of the uterus but not outside the true pelvis.
StageIV:
extension beyond stage III.
D.Rasha L2
6
Fallopian tubes:-
Inflammations ( Salpingitis )
Are almost always caused by bacteria and may be affected by T.B in
combination with infection of endometrium.
The importance of chronic inflammation in causing of obstruction of tubal
lumen and caused perminant infertility,
Other diseases of F.T
are
ectopic (tubal) pregnancy and endometriosis
Neoplasms:
primary adenocarcinoma, it's rare neoplasm and usually can't
discovered until spread.
Ovaries
Primary inflammation of ovary is very rare condition
.
Follicular and luteal cysts:-
It's a common condition, that is physiologic in nature, it's caused by
unruptured Graafian follicles, they are often multiple, may reached 4-5 cm
in diameter filled by serous fluid and
microscopically
lined by granoulosa
or luteal cells.
The clinical importance of this cyst, it's may be ruptured and producing
intraperitoneal bleeding and acute abdominal symptom.
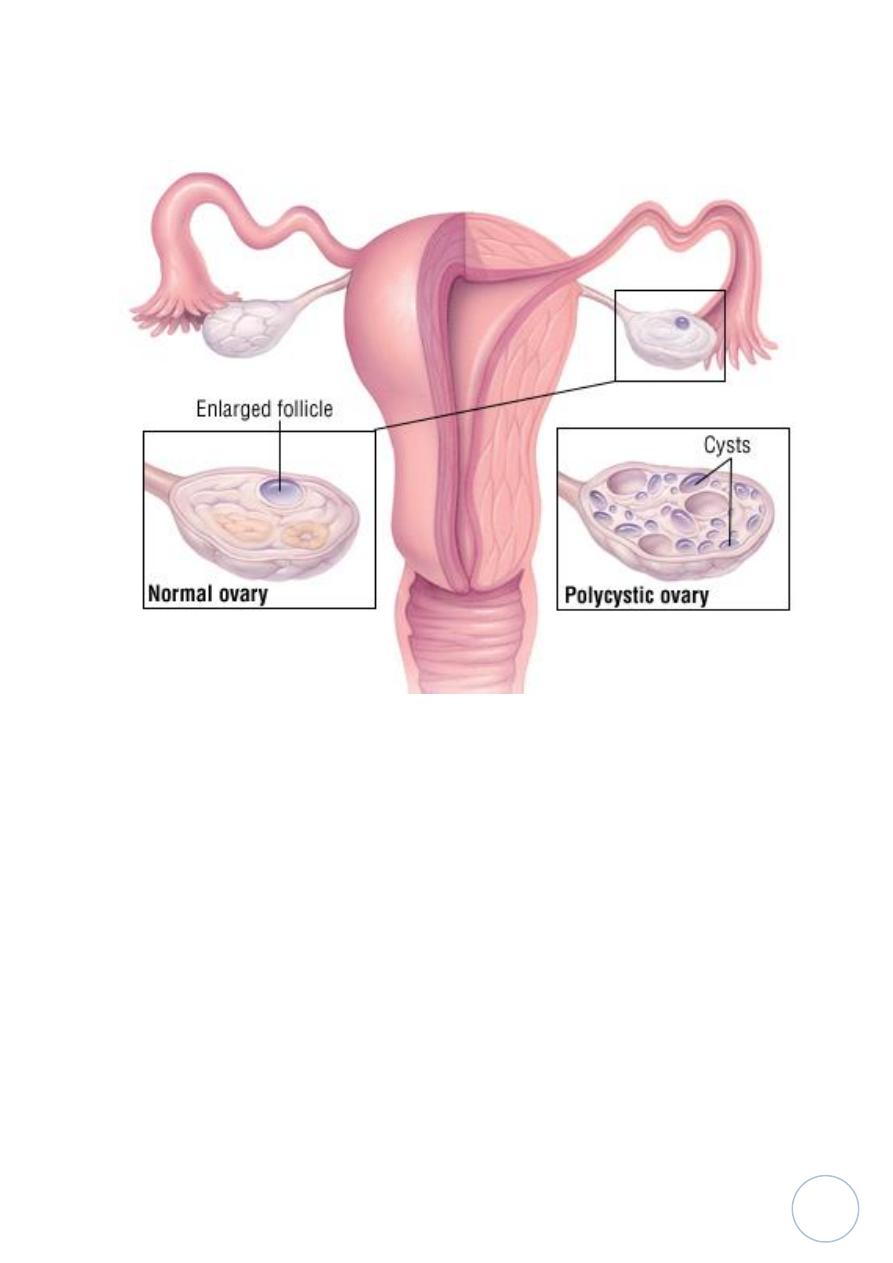
Polycystic ovaries:-
It's a syndrome also called Stein-Leventhal syndrome, that's caused
oligomenorrhea, hirsutism, infertility and obesity in young women
because of multiple cysts in ovaries produced estrogens and androgen.
D.Rasha L2
7
This appear in ovary as multiple subcortical cysts measured 0.5 to 1.5 cm and
appear
microscopically
as cyst lined by granulosa cells.
