
Dr. Akeel Al-yacopy
M.B.Ch.B
Baghdad
M.R.C.P London
M.R.C.P UK
F.R.C.P Glasgow

Ascrobic acid is the major dietary antioxidant in the aqueous
phase of the body. The best established biochemical
consequence of its deficiency is impaired reduction of amino
acid Proline to Hydroxyproline.
Hydroxyproline is an uncommon amino acid except in
collagens of which it makes up an indispensable 12%.
Impaired collagen formation is the biochemical basis of
Scurvy.
Small dose of vitamin C will cure scurvy, 30mg of vitamin C
is more than enough to prevent scurvy.
*Daily requirement for healthy adults: 40-60mg

Black carrots, guavas.
Rosehip syrup, green peppers.
Oranges, other citrus fruits, strawberries.
Cauliflower, broccoli.
Sprouts, cabbages.
Potatoes.
Liver and milk.

Normally 40 to 60mg is enough for healthy adults. But there
are some situations in which the doses must be increased
either because of decreased absorptions of vitamin C or
because of increased catabolism by diseases.
Trauma and surgery increase the need for vitamin C for
collagen synthesis. Several drugs antagonise vitamin C:
Corticosteroids.
Aspirin.
Indomethacin.
Phenylbutazone.
Tetracycline.
Smoking also antagonises vitamin C.
In these situations it is advisable to give a supplement of up
to 250mg vit.C/day to cover major surgery.

-There is doubt about the efficacy of large doses of vitamin C in
preventing flu.
-Vitamin C increases the absorption of iron (which is beneficial).
-Vitamin C is easily destroyed by cooking and also by alkaline, for
example sodium bicarbonate, it is also destroyed by light.
Clinical features of scurvy:
Swollen gums which bleed easily.
Perifollicular and petechial haemorrhage.
Ecchymosis.
Gastrointestinal bleeding.
Anaemia.
Poor wound healing.
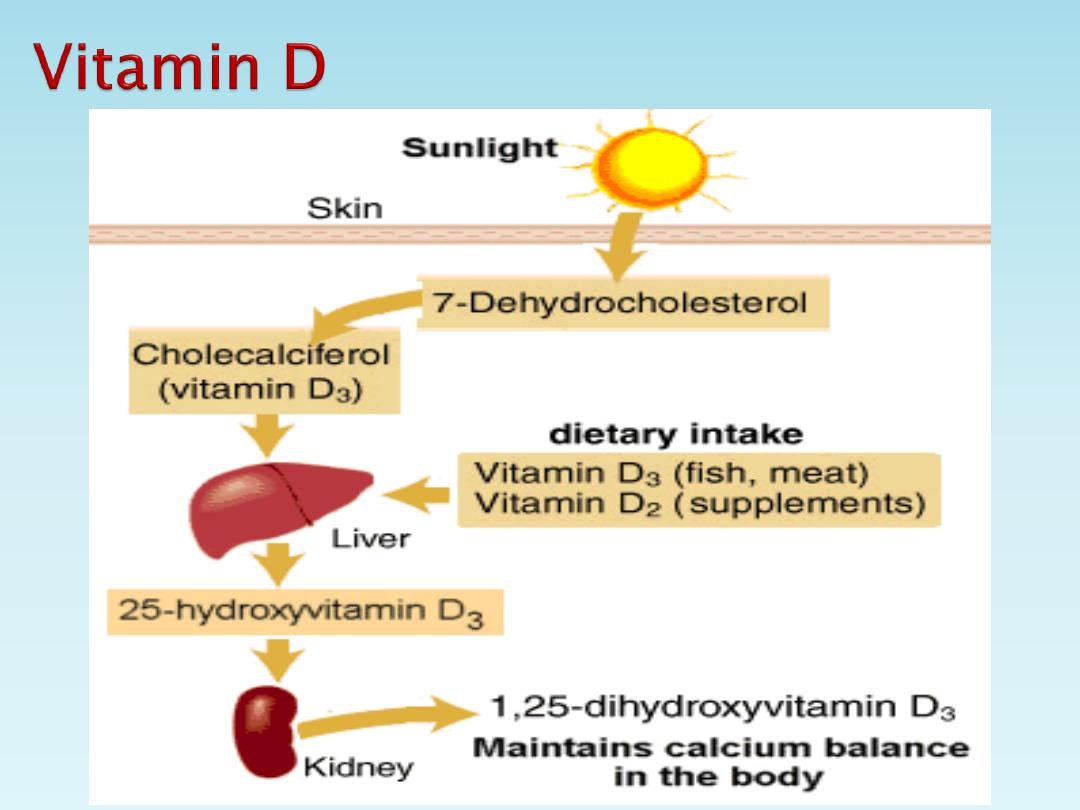

The natural substance Cholecalciferol was
originally called vitamin D3, vitamin D2 is the
artificially produced Ergocalciferol.
The natural and usual source of cholecalciferol is
by the action of short wave length UV light from
the sun on the companion of cholesterol in the skin
7-dehydrocholesterol, cholecalciferol also occur in
a small minority of our foods.
*Daily requirement for healthy adults: 5μg.

Fish liver oil.
Fatty fish (Sardines, tuna, salmon).
Margarine (fortified).
Infant milk (fortified).
Egg, liver.

Deficiency in infants causes rickets and in matures causes
osteomalacia.
The small dietary contribution of vitamin D is lost in:
Malabsorption.
Chronic biliary obstruction.
Long term anticonvulsant (phenobarbitone and phenytoin)
increase metabolic loss.
In these situations vitamin D is indicated.
In CRF and hypoparathyroidism, 1 α hydroxylation to the
active metabolite is impaired and renal bone disease respond
only to 1,25(OH)2D3 (calciferol) or 1 α OHD3
(affacalcidol).

Overdose with vitamin D causes:
Hypercalcaemia (thirst, anorexia, polyuria, with
risk of metastatic calcification).
One international unit 1U (not used now) of
vitamin D = 0.025 of cholecalciferol or
ergocalciferol, to convert 1U to microgram divide
by 40.
Therapeutic dose for rickets and osteomalacia 25-
100μg vitamin D.

α-Tocopherol is the most active of 8 very similar
compounds with vitamins E activity.
Being fat soluble, vitamin E is present in all cell
membranes where it acts as an antioxidant. It is thought to
reduce peroxidation of unsaturated fatty acid, by free
oxygen radicals.
*Daily requirement for healthy adults: 10mg.
It is thought that the requirement is proportional to the
intake of polyunsaturated fat.

Vegetable oils, wheat germ (oil
is the richest).
Margarines, mayonnaise.
Nuts and seeds.

Deficiencies:
Mild anaemia.
Ataxia.
Loss of tendon jerk.
Pigmenting retinopathy.
The most severe cases of deficiencies occur in patients with
chronic fat malabsorption especially fibrocystic disease of the
pancreas and abetalipoproteinaemia
Many people take vitamin E supplements on their own
initiative in large doses as treatment for infertility. But double
blind trial did not confirm this.
There is still doubt about whether vitamin E as antioxidant
can reduce atherosclerosis.

It is called the Koagulation by (Dam 1935).
It comes in two chemical forms, vitamin K1
(Phytomenadione) is found mainly in vegetables.
The K2 vitamin (Menaquinone) are a series produced by
bacteria, for example in the gut.
Deficiency of vitamin K manifests itself as
hypoprothrombinaemia and bleeding.
*Daily requirement for healthy adults: 70μg.
Food sources of vitamin K:
• Turnip greens.
• Broccoli.
• Cabbage, lettuce.
• Liver.

Cord blood level of vitamin K are very low and breast milk
contains little of the vitamin, unless the mother has been
dosed with vitamin K.
To prevent haemorrhagic disease of the newborn, 1mg of
vitamin K1 (by injection or by mouth) is given either to all
infants or to those at increased risk (low birth weight or
difficult delivery), depending on hospital policy. The single
IM injection of vitamin K1 prevents both early and late
vitamin K deficiency bleeding. Oral vitamin K prevents early
but not late haemorrhagic diseases.
In adults vitamin K deficiency is to be expected in
obstructive jaundice, malabsorption syndrom. Vitamin K1
must be given before surgery for these conditions.
Anticoagulants of Warfarin group owe their therapeutic
action to antagonism of vitamin K, and vitamin K1 is the
antidote for overdose.

Thank you
for your attention.
