ASSESSING THE EYES
Assessing The EyesDR. ALI ALIBRAHIMI
M.B.Ch.B
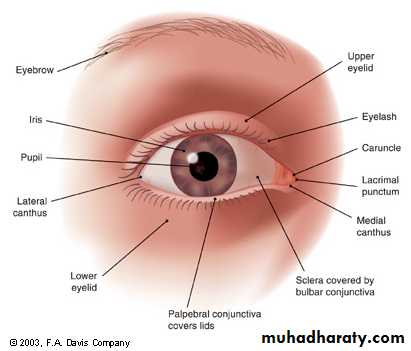
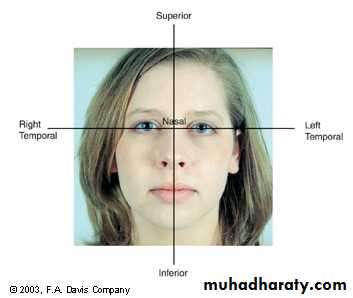
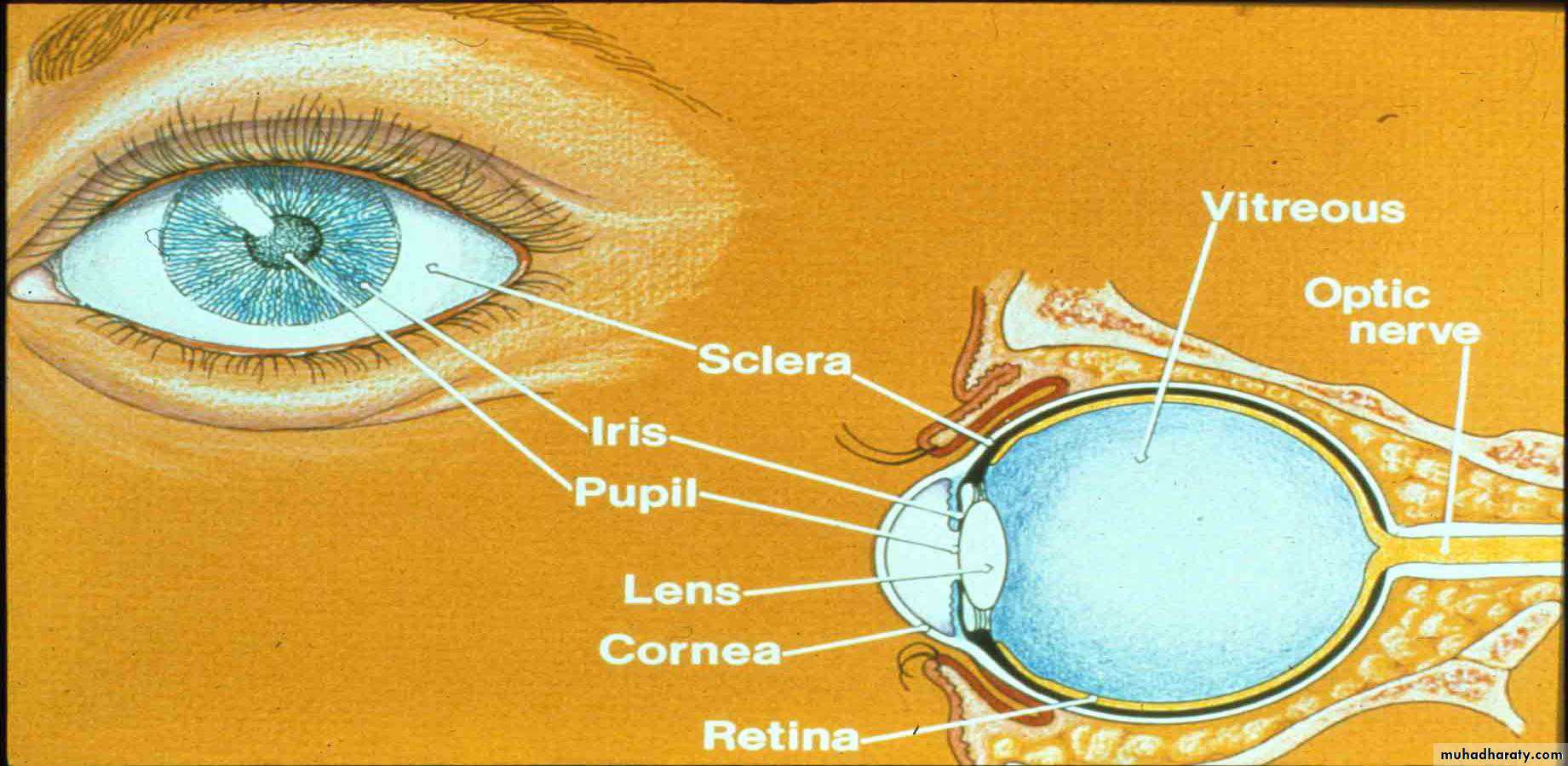
Structure & Functions External Structures
Eyelids and lashes:Protect the eyes
Lacrimal glands and ducts:
Produce tears
Conjunctiva:
Provide lubrication
Sclera:
Gives shape and structure to eyeIris:
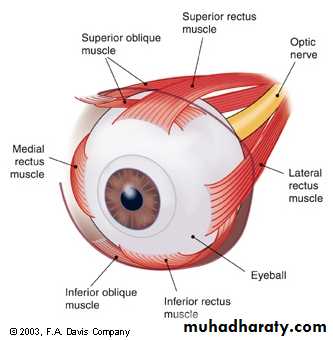
Controls amount of light entering eye; provides eye colorExtraocular muscles:
Control eye movement
Cornea:
Transparent, avascular outer layer of the eyeballAnterior chamber:
Filled with aqueous humor
Pupil:
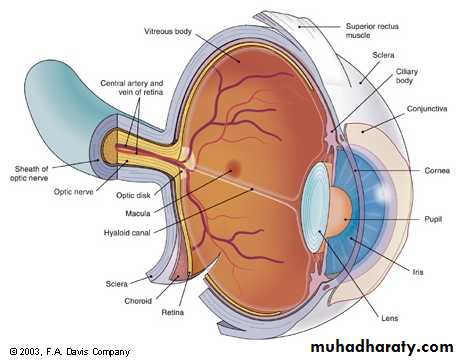
The aperture of the irisStructure & Functions Internal Structures
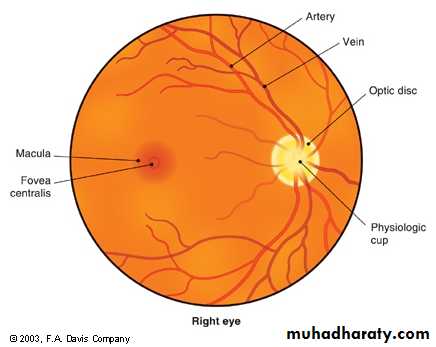
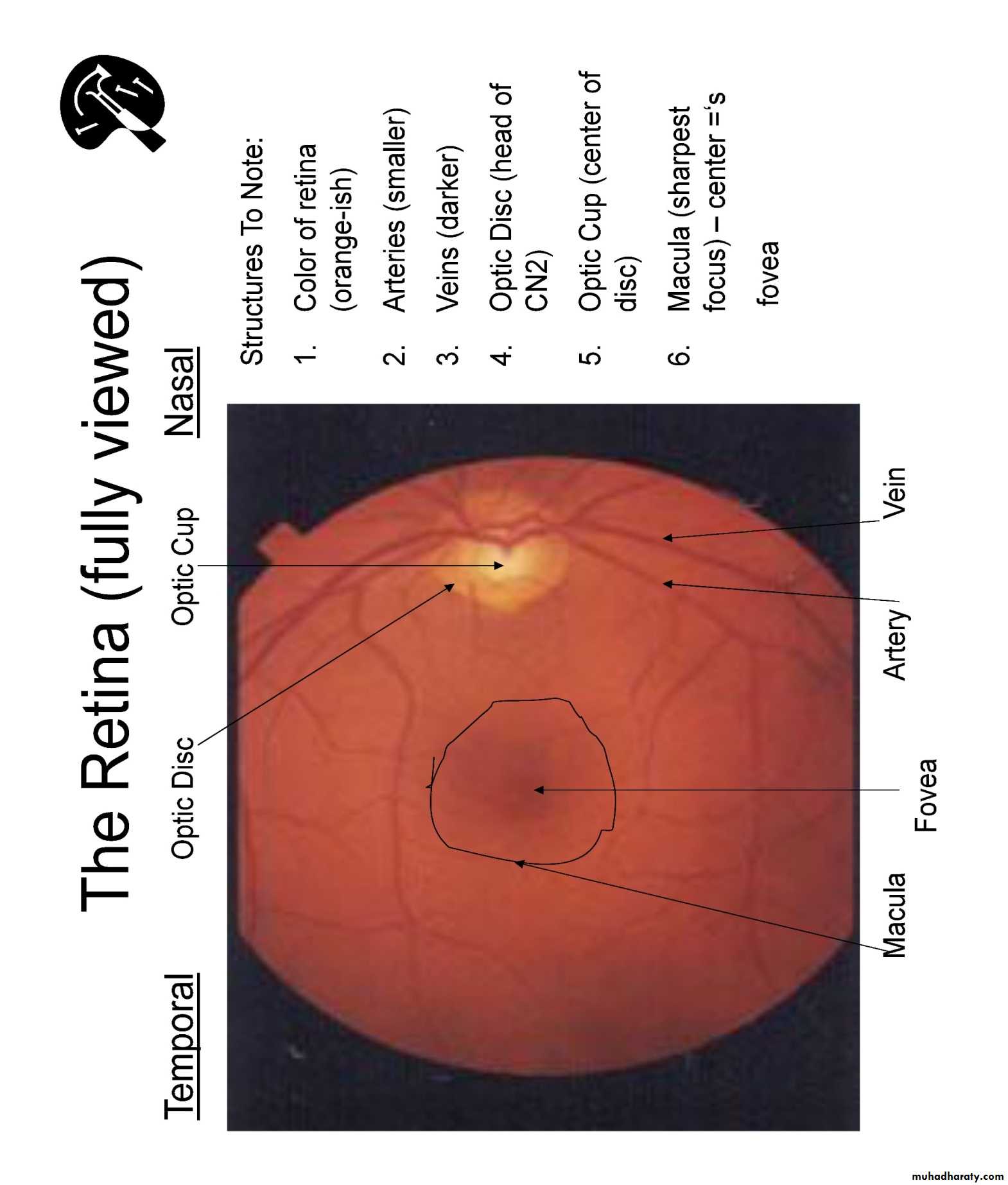
Optic disc and physiological cup:Area where the optic nerve and the blood vessels enter the eye
Retinal blood vessels:
Blood supply to eye
Retina:
Inner layer; receives light waves that are sent to brain and converted into visible perceptions
Macula:
Avascular, darker area of central vision
Visual Acuity
Far vision: Snellen eye chartNear vision: read newsprint 13 to 15” from eyes
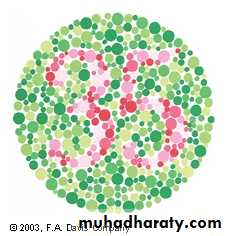
Color vision: identify color bars on Snellen or use color plates
Peripheral vision: come in from the periphery in all fields and note field cuts
Retinoscopical examination
Means examination of the retina(visualization of ocular fundus)3 methods of fundal examination :
1- direct ophthalmoscopy ; by which a magnification of about 15 times is obtained2- indirect ophthalmoscopy: by which a larger field is obtained , but with magnification 0f 4-5 times
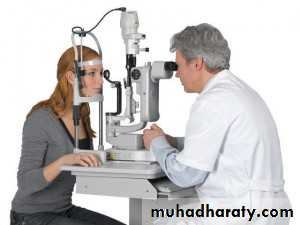
3- slit lamp bio microscopy : combined with a condensing lens to neutralize the corneal refractive power .
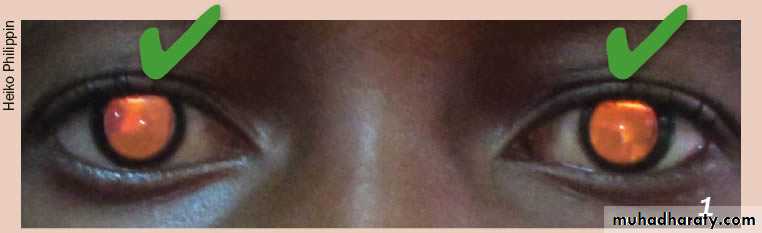
The red reflex: refers to the reddish-orange reflection of light from the eye's retina that is observed when using an ophthalmoscope or retinoscope from approximately 30 cm / 1 foot. This examination is usually performed in a dimly lit or dark room.
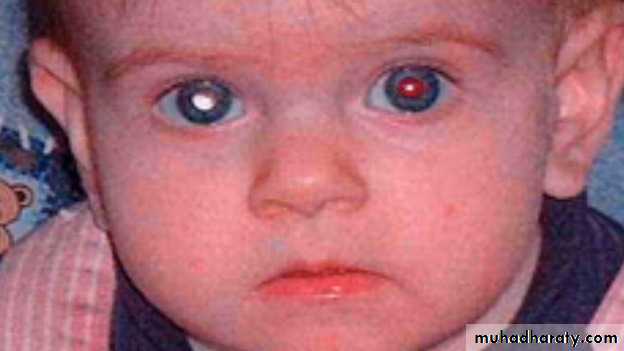
Many eye problems may be detected by this test, such as:
Cataracts - show leukocoria, or white coloration of the eye which may be from rubella or other maternal infections
Retinoblastoma - shows leukocoria.
Newborns are regularly screened for retinoblastomas with an ophthalmoscope
What You Should See by ophthalmoscope
•Magnified view of surface structures (pupil, iris, sclera, contact lenses)– using ophthalmoscope like a magnifying glass•To view retina, must see through intervening structures (powered view )
***if no obstruction red reflex visualized when look from a distance to the pupil.
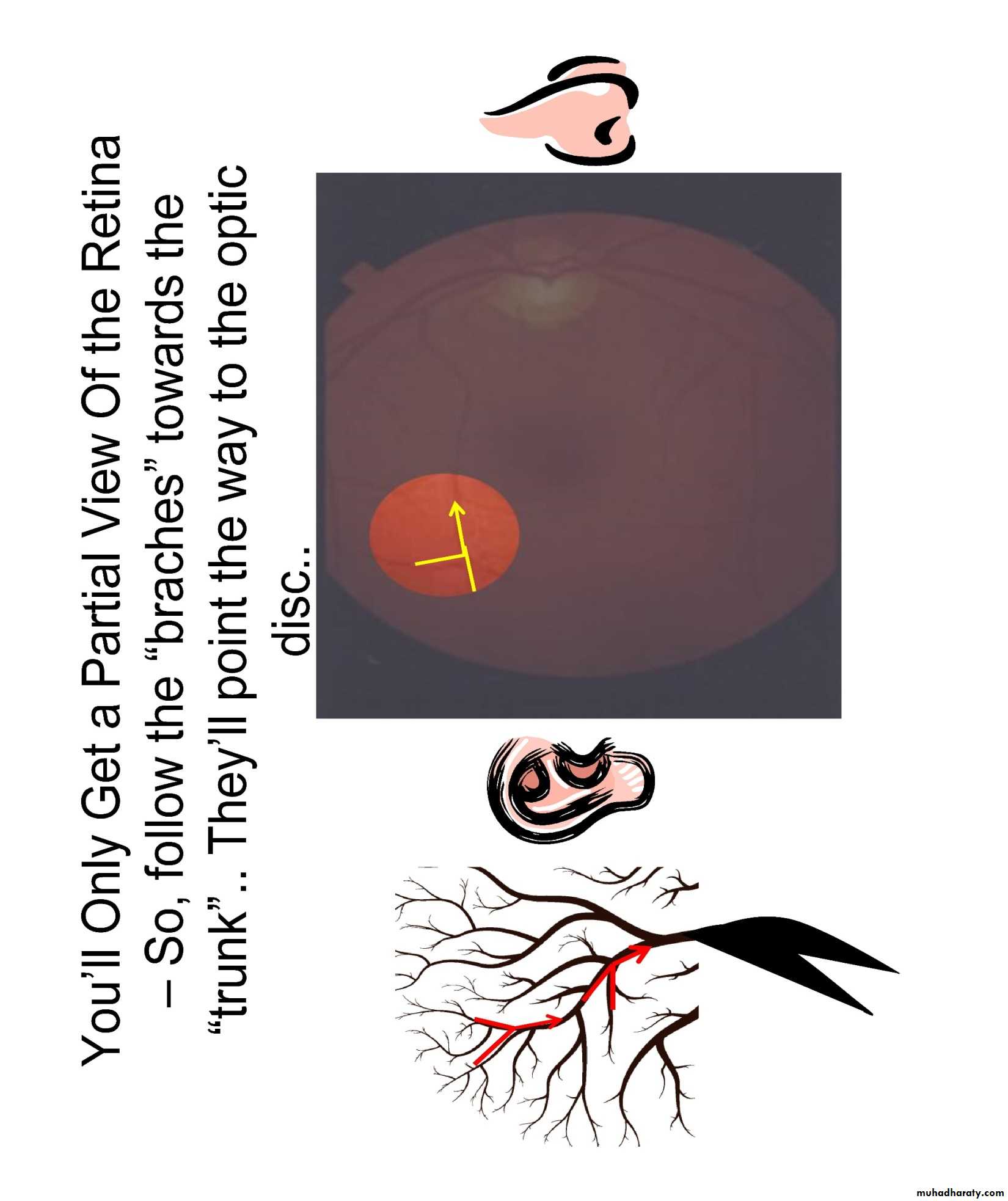
Viewing The Retina
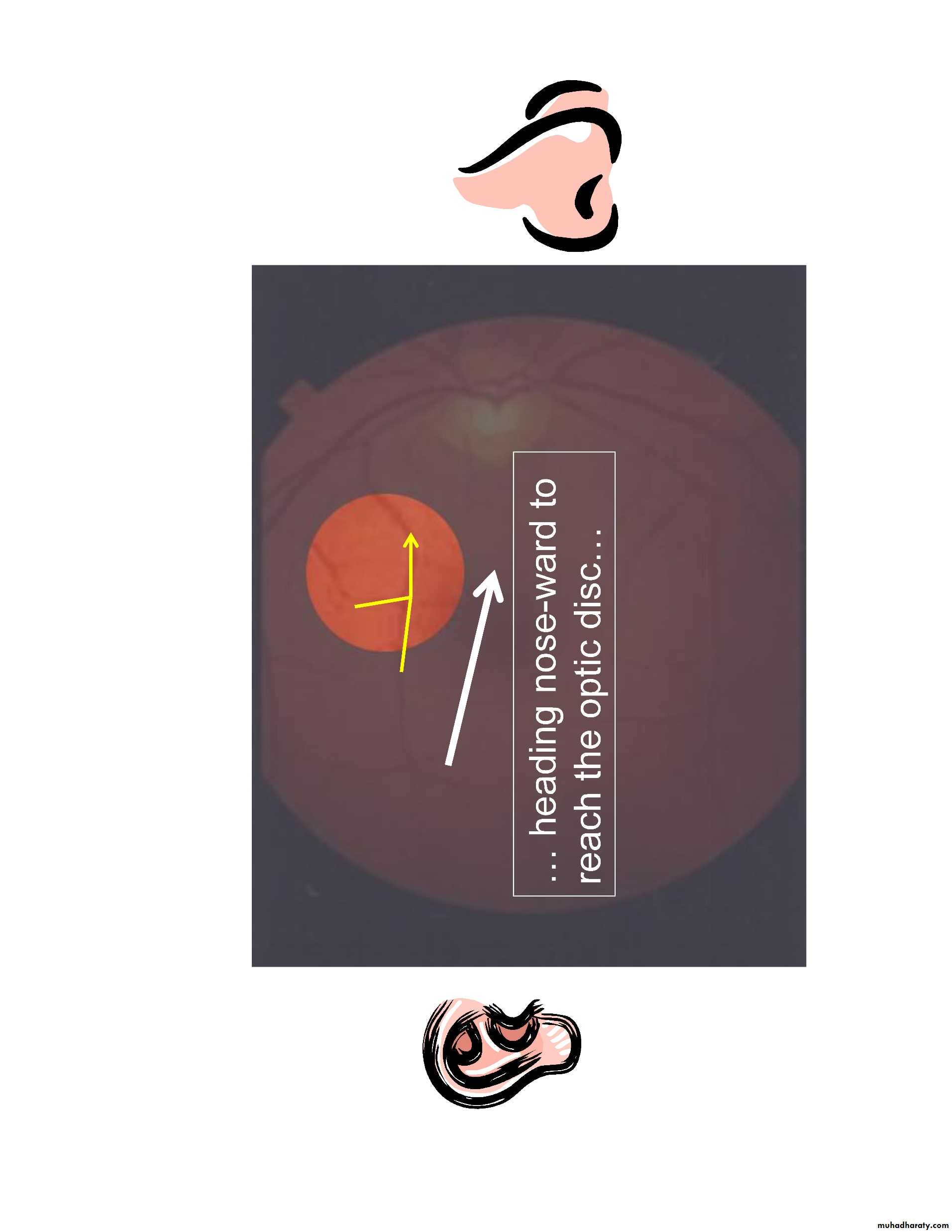
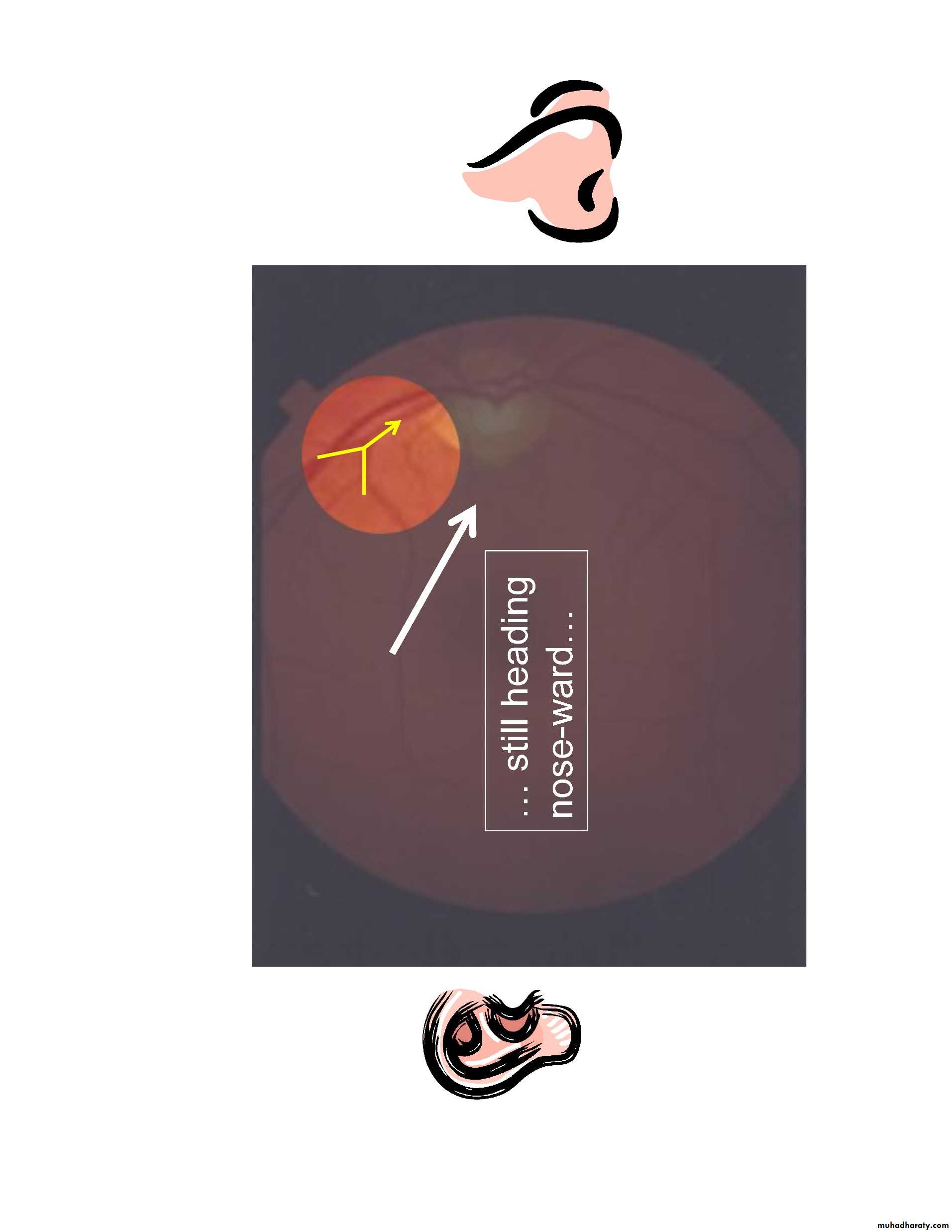
•at any time, only 15% of retina visible( without pupillary dilatation) while with pupillary dilatation about 50% of the fundus is visualized•Follow vessels (branches of tree trunk) optic disc
•Be systematic:
–Optic disc
–Vessels (veins & arteries)
–Retina (in quadrants)
–Macula ask the patient to look @ your light
Clinical application
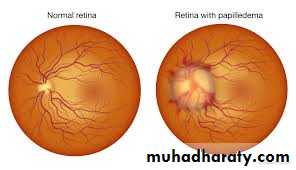
Papilledema is optic disc swelling that is caused by increased intracranial pressure. The swelling is usually bilateral and can occur over a period of hours to weeks. Unilateral presentation is extremely rare. Papilledema is mostly seen as a sign resulting from another pathophysiological process.In intracranial hypertension, papilledema most commonly occurs bilaterally. When papilledema is found on fundoscopy, further evaluation is warranted as vision loss can result if the underlying condition is not treated. Further evaluation with a CT or MRI of the brain and/or spine is mandatory
Signs and symptoms
venous engorgement (usually the first signs)loss of venous pulsation
blurring of optic margins
elevation of optic dis
hemorrhages over and / or adjacent to the optic disc
Causes :
CPAP therapy
Brain tumor
Malignant hypertension
Respiratory failure or sleep apnea