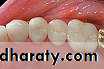
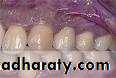
Provisional restoration of crown & bridgeAss. Prof Dr Talal Al-Salman2011 - 2012presented by dr. manaf basil
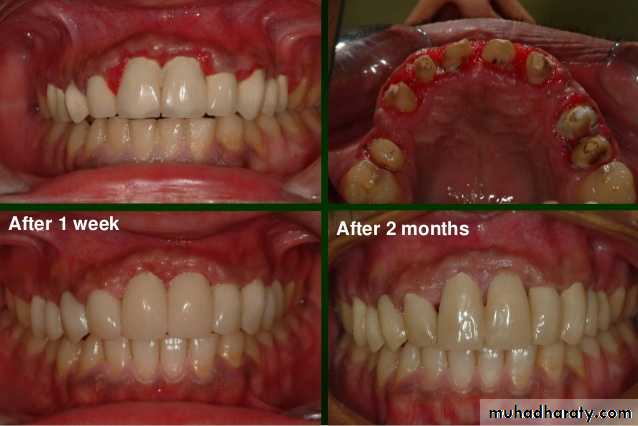
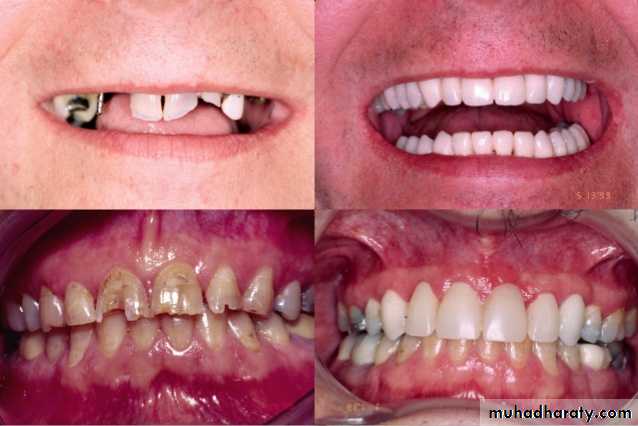
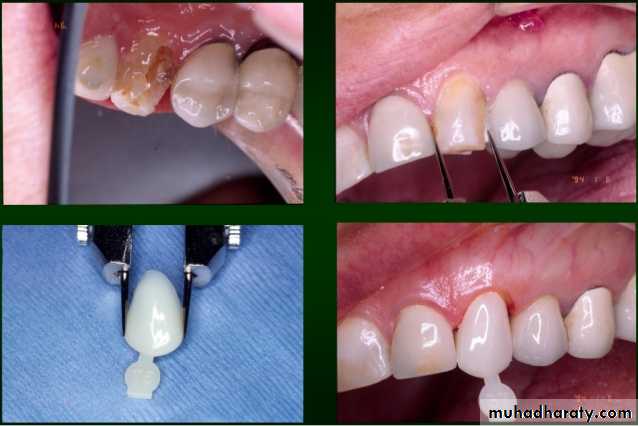
Provisional crown or fixed partial denture is essential to prosthodontic therapy. . Prepared abutment teeth must be restored temporarily while the final prosthesis is being fabricated in order to provide protection to pulp, periodontium, positional stability, mastication, & esthetic & to obtain certain diagnostic information.
1. Pulp protection:During preparation, the enamel is removed completely and this leading to dentin exposure, so through the time of permanent restoration fabrication and due to different physical, chemical and thermal stimuli in the oral invironment the pulp may be traumatized leading to pulp inflamation or pulp death. Fracture of the prepared tooth is a common complication and lastly trauma to the periodontium due to lack of normal contour of the tooth
2. Positional stability:
Crown preparation completely remove of all undercuts, axial contours, contacts with the adjacent teeth and providing free occlusal space with the opposing teeth. This condition if lift for a long period of time leading to changes in the position of the prepared tooth, the adjacent and the opposing teeth3. Mastication & esthetic
After tooth preparation and at the time of final restoration construction, the site of the preparation will be functionally impaired ( mastication & esthetic ).for that reason, the use of provisional restoration will rehabilitate the area and permit normal use of the quadrant.4. Certain diagnostic information
The use of provisional restoration will give an idea to the dentist and the patient about the effect of fixed prosthesis on esthetic and function and give a time to the patient to adapt on a foreign body in his mouth.Requirement of Provisional restoration:
The temporary restoration should satisfy the following requirements:1: it should not irritating & protect the prepared tooth from injury.
2: it should protect & maintain the health of periodontium.
3: it should maintain the position of prepared, adjacent & opposing teeth.
Requirement of Provisional restoration:
4: it should provide esthetic, phonetic & masticatory function as indicated.5: it should have adequate strength & retention to withstand the forces.
6: it should have accurate marginal fit & surface finish.
7: it should be designed with physiologic axial contour & open embrasures to allow the restoration to function as healing matrix for surrounding tissues.
Types of provisional restoration:
A: Prefabricated crown: several types of prefabricated crown are available commercially, however this type is rarely satisfy the requirements of good provisional restoration, most preformed crowns need some modifications like internal relief, axial recontouring & occlusal adjustment before cementation. Prefabricated crowns are generally limited to use as single restoration more than for bridges, there are several types:
A: Prefabricated crown:
1: Polycarbonate crown: it has the most natural appearance of all the preformed crown materials, it is mostly available in single shade, they are supplied as incisors, canines & premolars.A: Prefabricated crown:
2: cellulose acetate crown: it is a thin transparent material available in all teeth shapes & sizes, the color are depend on the self curing resin, once the resin is polymerized the cellulose acetate is withdrawn & discarded.A: Prefabricated crown:
3: Aluminum & tin-silver crown: this type is suitable for posterior teeth, the more preferable crown forms have anatomically shaped occlusal surfaces, the others are merely cylindrical caps.A: Prefabricated crown:
4: Nickel chromium crown: it is often used as a restoration in children, it has high strength & hardness & thus is useful for longer-term provisional restoration.B: Fabricated (tissue form) crowns and bridges:
There are three methods to make the tissue surface forms of provisional restorations:1: Indirect method: an impression is made for the prepared teeth & is poured with dental stone, the provisional crown or bridge is fabricated outside the mouth, this have an advantage like that there is no contact of free monomer with prepared tooth or gum. This type of procedure avoid subjecting the prepared tooth to the heat generation during polymerization of resin & the margins of the restoration is better than in direct procedure because it can be better controlled extra-orally.
Advantages of indirect method
1- There is no contact of free monomer with the prepared tooth or gingiva, which might cause tissue damage and an allergic reaction or sensitization.2- The procedure avoids subjecting a prepared tooth to the heat created from polymerizing resin.
Advantages of indirect method
3-The marginal fit of provisional restorations that have been polymerized undisturbed on stone casts is significantly better than that of provisionals that have been removed from the mouth before becoming rigid .This is because:(a) the stone restricts resin shrinkage during polymerization and
(b) separating the resin from the tooth causes distortion.
Directly made long-span or multi-abutment FPDs are likely to have unacceptable marginal discrepancies caused by shrinkage and distortion
3: Direct procedure:
the patient tissues provide the tissue surface form & thus the intermediate steps of the indirect technique are eliminated. This is convenient when assistant training and office laboratory facilities are inadequate for efficiently producing an indirect restoration. However, the direct technique has significant disadvantages: potential tissue trauma from the polymerizing resin and inherently poorer marginal fit. Therefore, the routine use of directly formed provisional restorations is not recommended when indirect techniques are possible2: Indirect-direct method: this method include a correctly contoured thin walled restoration made in laboratory before tooth preparation, a sufficient space is allowed internally for additional resin. The restoration is made on diagnostic cast has an approximate fit on the clinically prepared tooth & then lined directly in the mouth with resin, this procedure having advantage like less chairside time & less heat generation from polymerization on the teeth.
Advantages of indirect-direct method
1- Chairside time is reduced. Most of the procedures are completed before the patient's visit.2- Less heat is generated in the mouth. The volume of resin used during lining is comparatively small.
3- Contact between the resin monomer and soft
tissues is minimized compared to the direct
procedure. Because pontic ridge areas do not
normally require lining, there is a reduced risk of allergic reaction.