Lec. 7 Biology
HistologyBone
Bone is a hard connective tissue that consists of living cells and a mineralized matrix.Functions of bone:
Support and protection- The skeletal system provides structural support for the entire body. Bones can serve to protect internal organs, such as the brain and the heart.
Movement-Bones work in conjunction with skeletal muscle and other skeletal system components to assist in enabling body movement.
Blood Cell Production -Formed elements of the blood are produced in red marrow of the bones.
Storage - Bones store important minerals, including calcium and phosphorus. Bone also stores fat in yellow bone marrow.
Bone Matrix
Bone matrix consists of two major components:The organic component
The organic component accounts for about 1/3 of the mass of a bone, and it is called the osteoid. Collagen fibers are the major component of the osteoid.Inorganic Component:
The inorganic component accounts for about 2/3 the mass of a bone, and it is composed mainly of calcium and phosphorus, along with other components including bicarbonate, citrate, magnesium, sodium, and potassium.
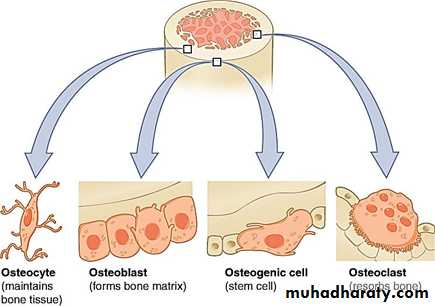
Bone Cells
There are four types of cells:Osteogenic cells : stem cells that divide and give rise to the next type of cell, the osteoblast. Osteogenic cells are elongated have pale nuclei.
Osteoblasts: Bone-forming cells that are derived from osteogenic cells and forms the bone matrix. They are roughly cuboidal or angular, and line up in a single layer on the bone surface .
Osteocytes : are mature bone cells that originate from osteoblasts. They reside in tiny cavities called lacunae, which are interconnected by slender channels called canuliculi , Osteocytes project cytoplasmic extensions into the canaliculi, and gap junctions connect neighboring osteocytes Their functions include formation of bone, maintenance of matrix and homeostasis of Calcium.
Osteoclasts : The bone removing cells, they multinucleated giant cells, they have numerous nuclei . Osteoclasts attach to bone surfaces and use acids and enzymes to decompose bone .
(Bone cells)
(Bone Cells )(Bone cells)
(Bone Cells )
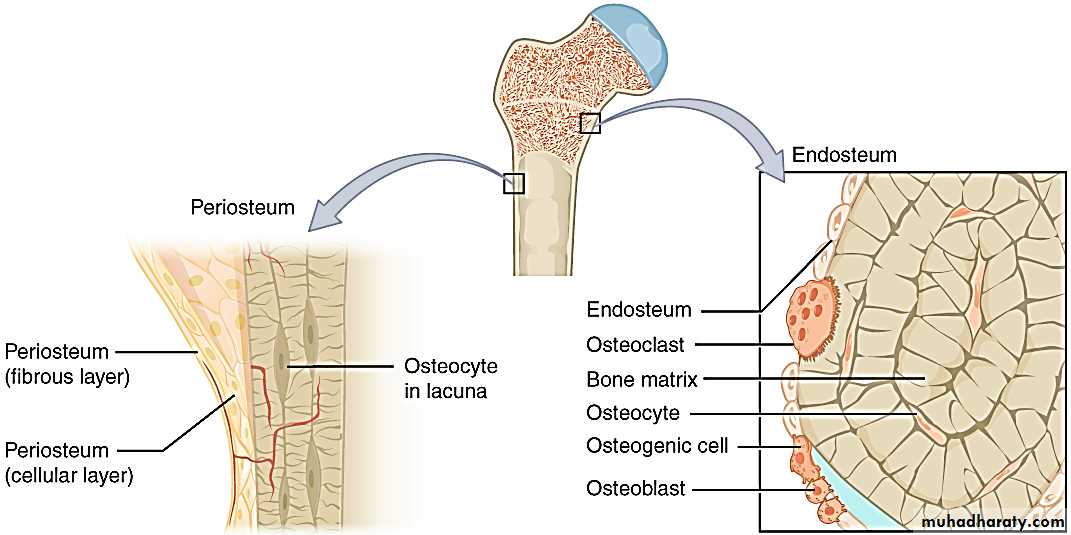
Periosteum and Endosteum
Periosteum: Each bone is surrounded by fibrous sheath called “periosteum”, It consists of two layers, the outer layer is dense fibrous connective tissue and contained blood vessels, the inner layer is composed of more loosely arranged connective tissue contains numerous spindle shaped cells called osteogenic cells which on stimulation becomes activated and gives osteoblasts.Endosteum: It is lines marrow cavity within the bone and composed of a single layer of flattened osteogenic cells and a very small amount of connective tissue.
( Periosteum and Endosteum )
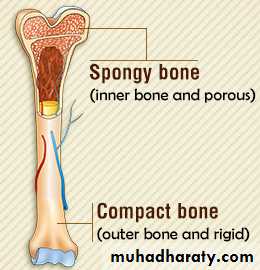
Bone types
There are two primary types of bone tissue:Compact bone .
Spongy bone.
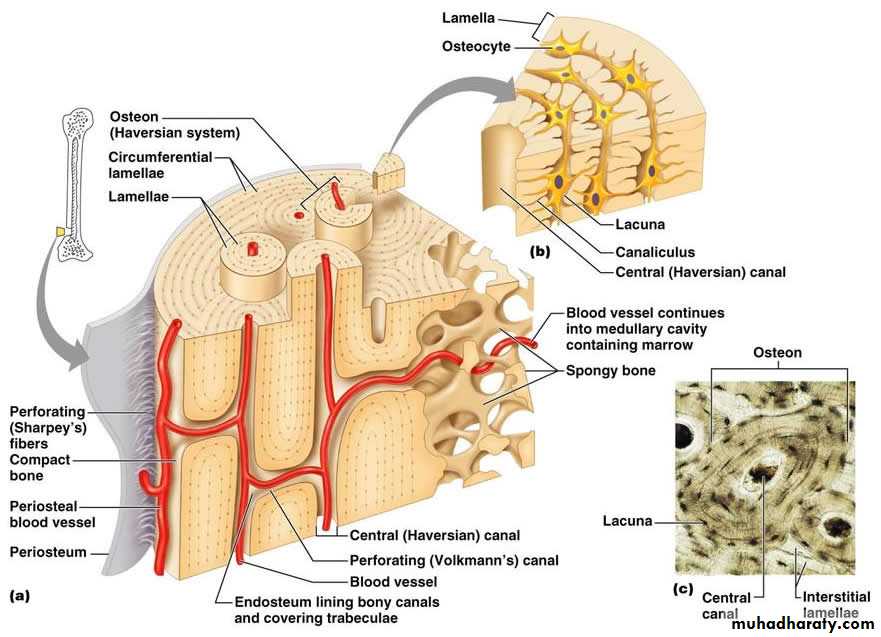
1-Compact bone
Makes outer hard shell of the bone and has more matrix than spaces . The basic unit of compact bone is an osteon or Haversian system. Each osteon has four parts : The lamellae ; concentric rings of extracellular matrix that consist of mineral salts (mostly calcium and phosphates). The lamellae are responsible for the compact nature of this type of bone tissue. Lacunae ; small spaces between lamellae that contain mature bone cells called osteocytes. Canaliculi : networks of minute canals that project from lacunae containing the processes of osteocytes. Canaliculi provide routes for nutrients to reach osteocytes and for wastes to leave them. A central (haversian) canal contains blood vessels and nerves. The Haversian canal provides a passageway for blood vessels and nerves.
Haversian canal run along the length of the bone, branched, and anastomoses with each other. They also communicate with marrow cavity and with external surface through channels that called (Volkmann canals). Blood vessels and nerves pass through all these channels.
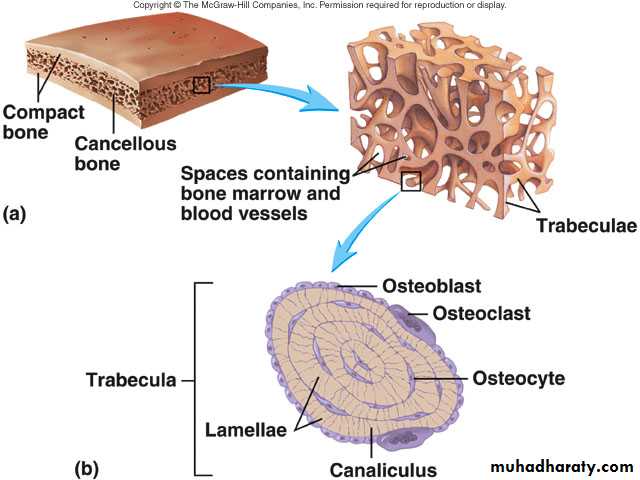
2.Spongy bone:
It is located in the interior of the bone. Contain more space than matrix . Instead of being completely solid, spongy bone contains spaces, and the bone connective tissue forms a latticework structure called trabeculae which contain lamellae, osteocytes, lacunae, and canaliculi. Spaces between trabeculae are filled with red bone marrow which is site for hemopoiesis .
(Spongy bone)
Difference Between Compact and Spongy Bone:
Compact bone is also called cortical bone while spongy bone is also called cancellous bone.
Compact bones are made of osteons while spongy bones are made of trabeculae.
Compact bones are heavy while spongy bones are light.
Compact bones fill the outer layer of most of the bones while spongy bones fill the inner layer of the bones.