Lec. 8 Histology
Bone DevelopmentOssification
Bone appears in the 6-week-old embryo and growth of bone continues till about 25 years old. Bone formation may still occur but involves remodeling. The process of bone formation is called ossification. There are two types of ossification: intramembranous ossification and endochondral ossification .1- Intramembranous Ossification:
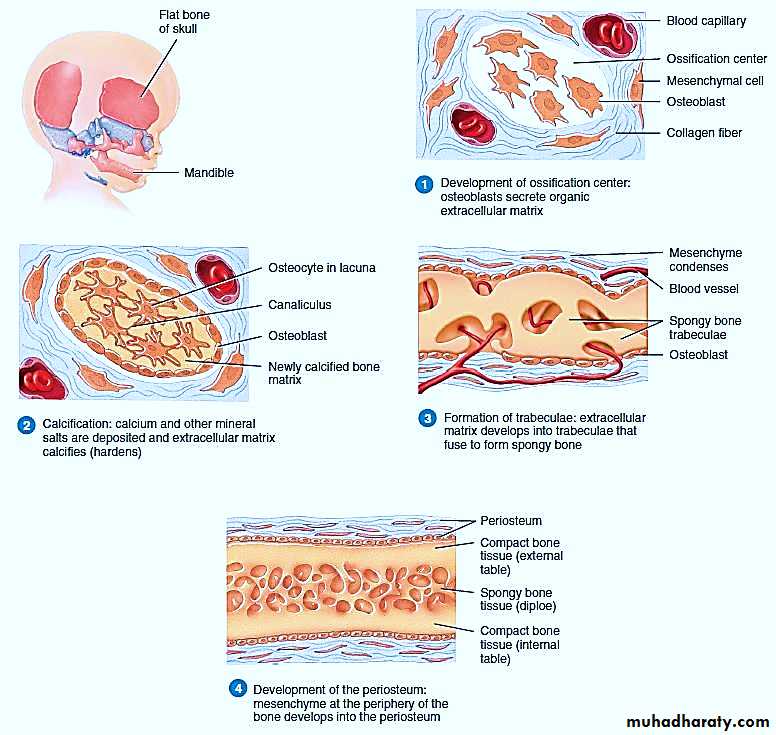
Intramembranous ossification is the process of bone development from mesenchyme or fibrous connective tissue, example, is the flat bones of the skull.The following steps occur during this development ( Figure 1) :
Development of ossification Center
Calcification
Formation of Trabeculae
Development of Periosteum and Formation of Compact Bone
Figure 1: Intramembranous Ossification
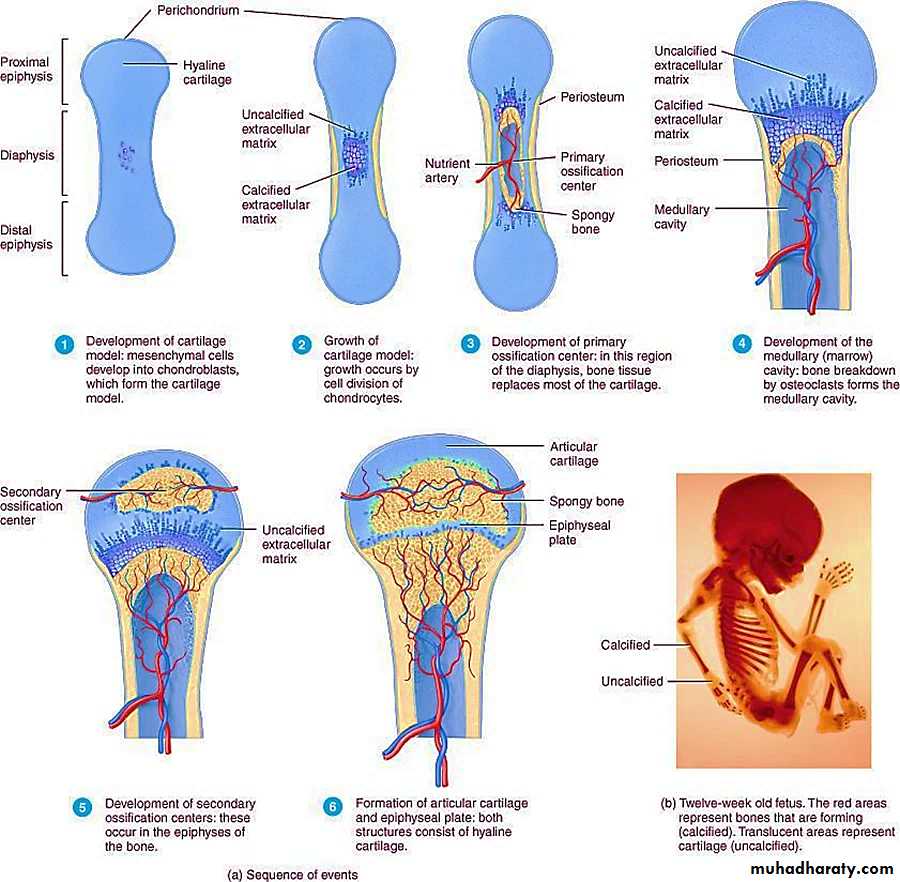
2- Endochondral OssificationEndochondral ossification is the process of bone development from hyaline cartilage , examples are long bones of the limbs, basal bones of the skull, vertebral column and ribs.
The following steps occur during this development (Figure 2) :
Development of the cartilage model
Growth of the cartilage model
Development of the primary ossification center
Development of marrow cavity
Development of the secondary ossification center
Formation of the articular cartilage and epiphyseal plate
Figure 2 : Endochondral ossification
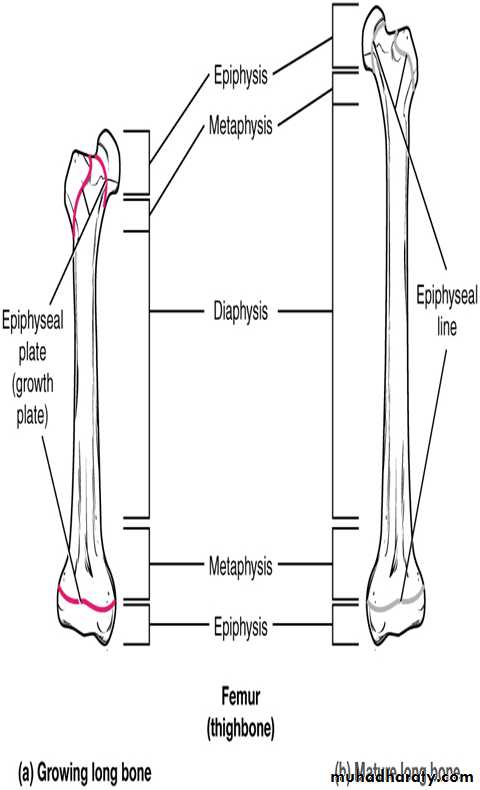
Growth in lengthThe epiphyseal plate is the area of growth in a long bone. It is a layer of hyaline cartilage where ossification occurs in immature bones. The epiphyseal plate is composed of 5 zones of cells and activity (Figure 3).
1. Zone of reserve or resting cartilage : It consists of small chondrocytes. These chondrocytes do not participate in bone growth.
2. Zone of proliferation : The chondrocytes undergo cell division and arrange themselves in distinct columns that are parallel to the direction of growth.
3. Zone of hypertrophy : Chondrocytes in this zone stop dividing and undergo growth in size.
4. Zone of calcification : Chondrocytes are mainly dead here because the extracellular matrix has calcified.
5. Zone of ossification : Osteoclasts digest the calcified cartilage , and osteoblasts replace it with bone tissue.