Cardiac
Arrhythmia

Arrhythmias
•
Disturbance of heart rhythm and/or
conduction.
•
Arrhythmia :
–
Tachyarrhythmia
–
bradyaahythmia
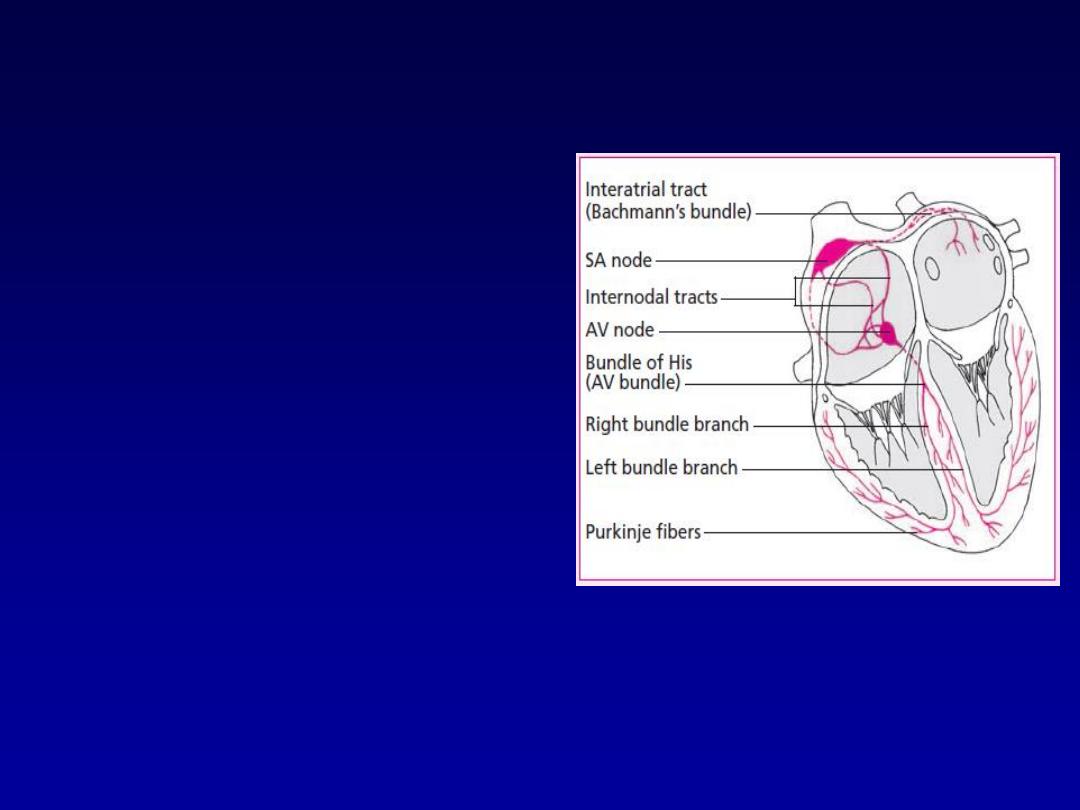
Conductive system of the heart
•
SA Node
- Dominant
pacemaker with an
intrinsic rate of 60 -
100 beats/minute.
•
AV Node
- Back-up
pacemaker with an
intrinsic rate of 40 -
60 beats/minute.
•
Ventricular cells
-
Back-up pacemaker
with an intrinsic rate
of 20 - 45 bpm.

Mechanism of tachyarrhythmia
•
Increased automaticity.
•
Re-entry.
•
triggered activity
For more presentations www.medicalppt.blogspot.com

Antiarrhythmic drugs
• Digoxin
• Adenosine
• Atropine

pot.com
Arrhythmias
•
Sinus Rhythms
•
Premature Beats
•
Supraventricular Arrhythmias
•
Ventricular Arrhythmias
•
AV Junctional Blocks

spot.com
Sinus Rhythms
•
Sinus Bradycardia
•
Sinus Tachycardia
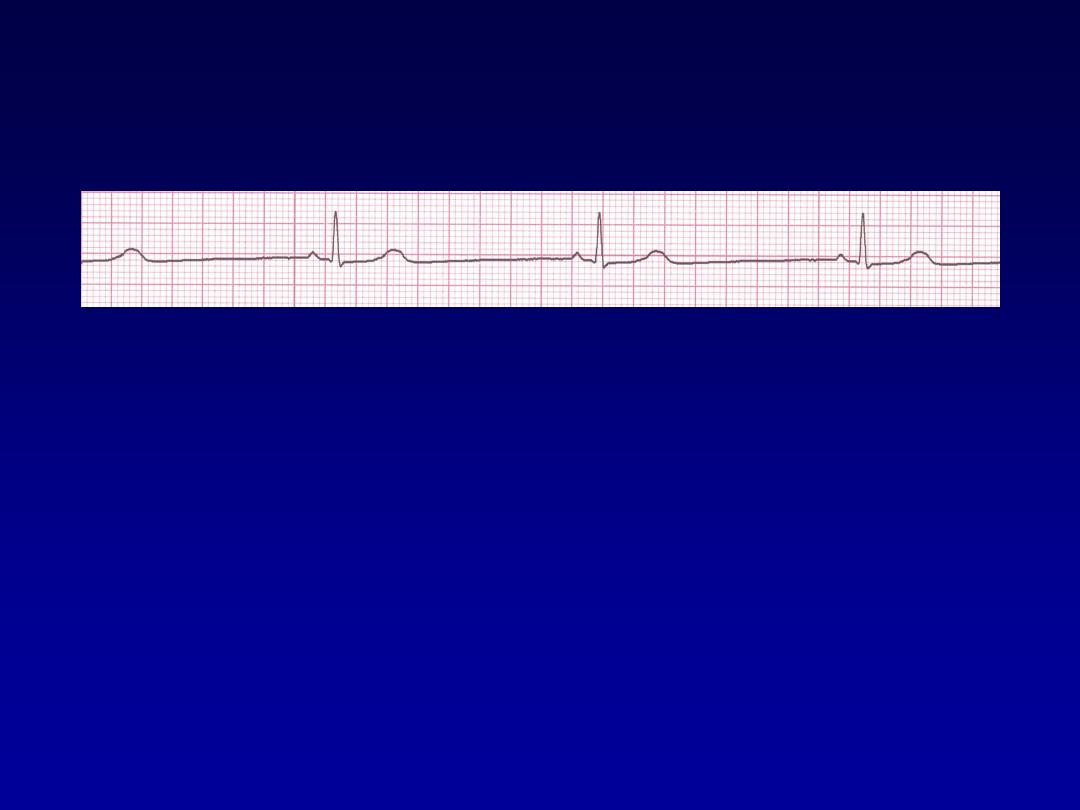
Sinus Bradycardia
•
Deviation from NSR
A sinus rate of less than 60/min

Causes of Sinus Bradycardia
•
MI
• Sinus node disease (sick sinus syndrome)
• Hypothermia
• Hypothyroidism
• Cholestatic jaundice
• Raised intracranial pressure
• Drugs, e.g. β-blockers, digoxin, verap
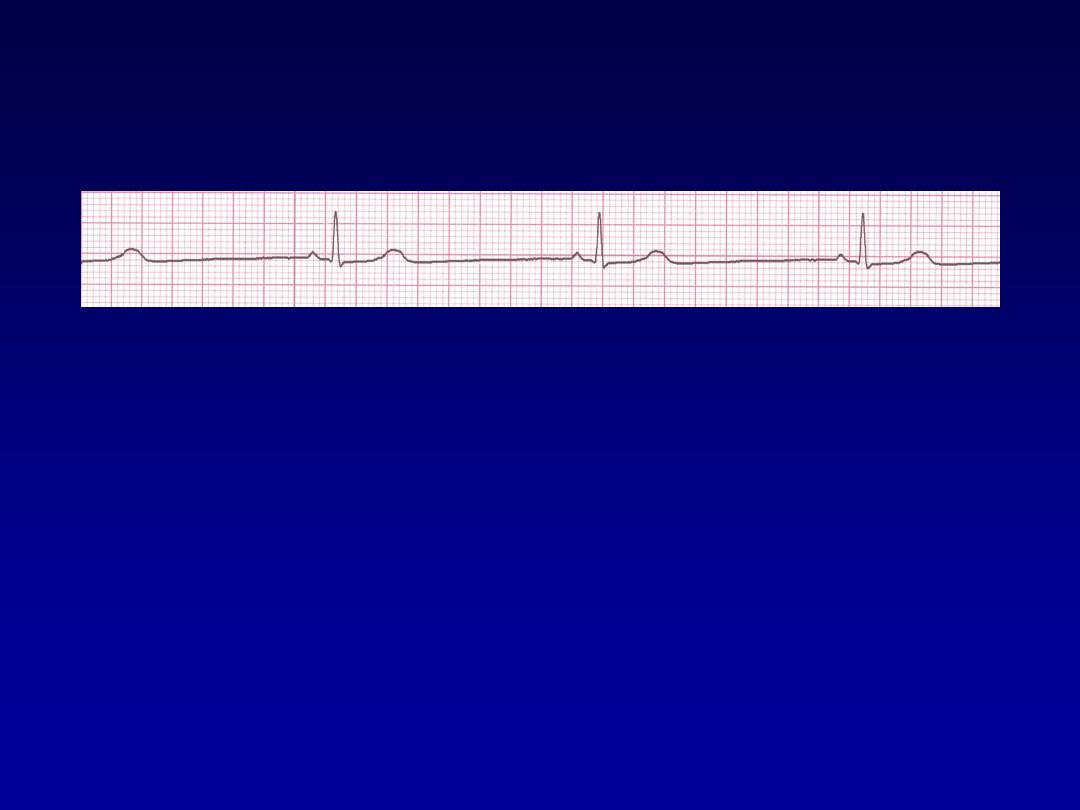
Rhythm
30 bpm
• Rate?
• Regularity?
regular
normal
0.10 s
• P waves?
• PR interval?
0.12 s
• QRS duration?
Interpretation?
Sinus Bradycardia
Sinus Tachycardia
•
Deviation from NSR
-
a sinus rate of more than 100/min

Causes of Sinus Tachycardia
* Anxiety
• Fever
• Anaemia
• Heart failure
• Thyrotoxicosis
• Phaeochromocytoma
• Drugs, e.g. β-agonists (bronchodilators)
Rhythm
130 bpm
• Rate?
• Regularity?
regular
normal
0.08 s
• P waves?
• PR interval?
0.16 s
• QRS duration?
Interpretation?
Sinus Tachycardia

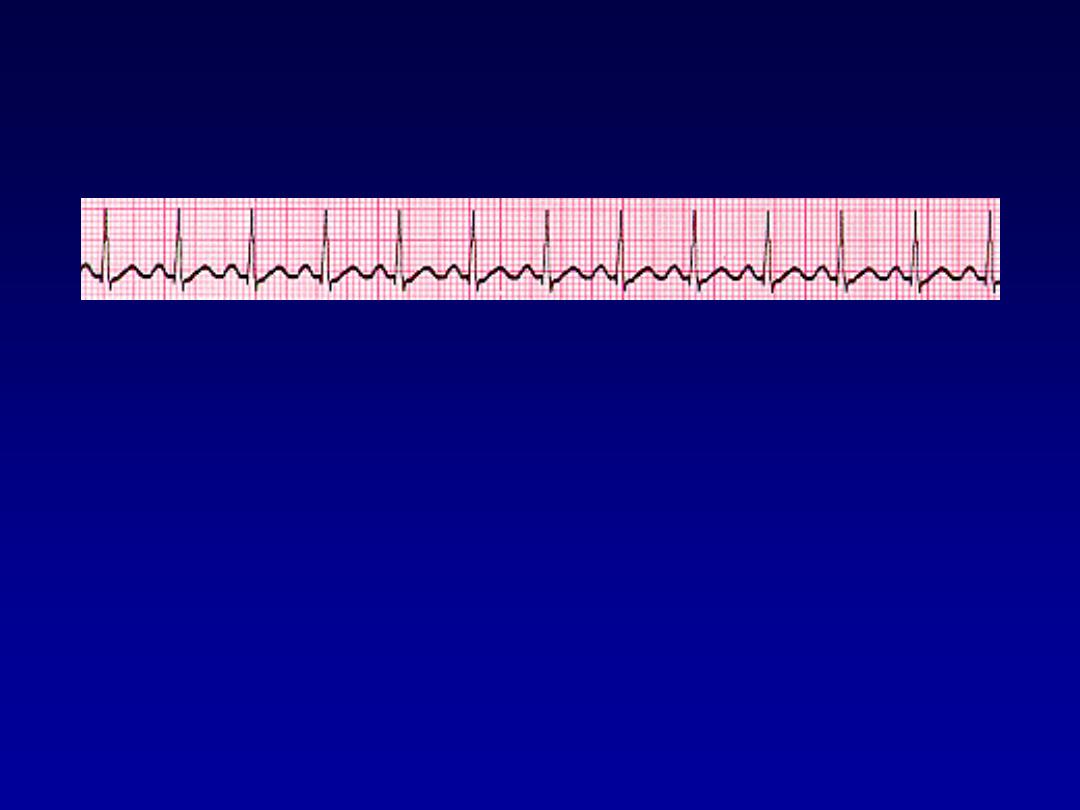
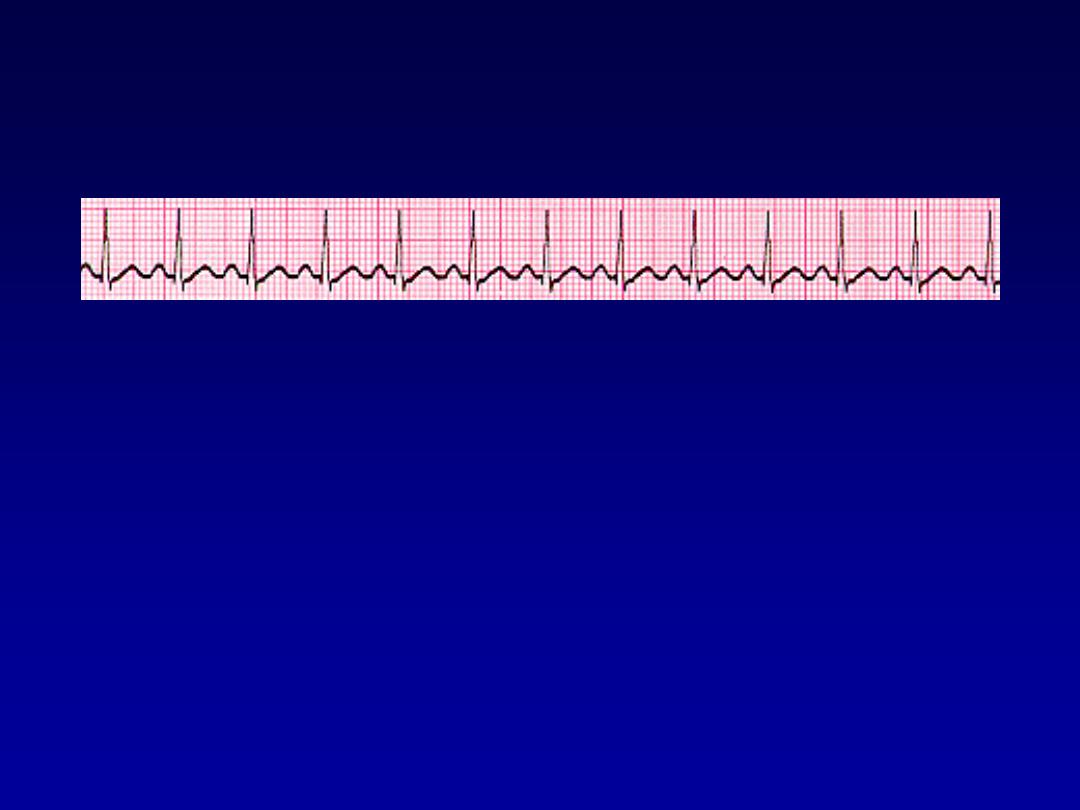
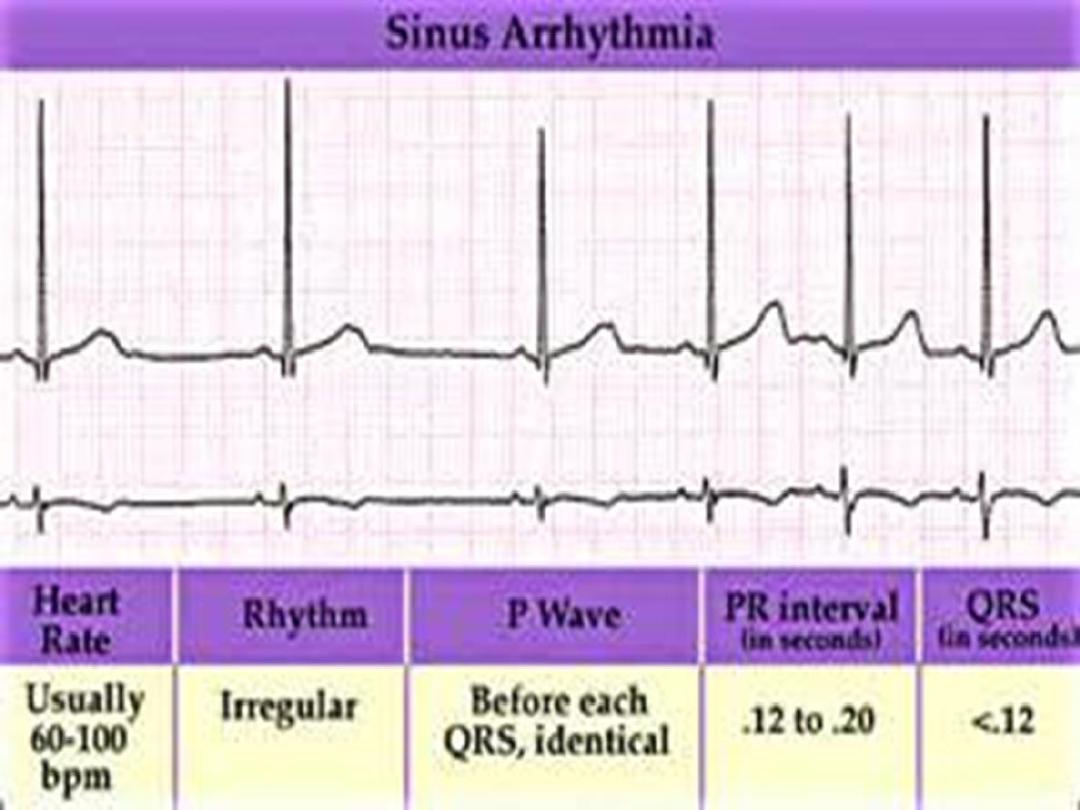
Sinus arrhythmia
•
Phasic alteration of the heart rate during
respiration (the sinus rate increases
during inspiration and slows during
expiration
For more presentations www.medicalppt.blogspot.com
Sick Sinus Syndrome(SSS)

Supraventricular Arrhythmias
•
Atrial Fibrillation
•
Atrial Flutter
•
Paroxysmal Supraventricular
Tachycardia

Premature Beats
•
Premature Atrial Contractions
(PACs)
•
Premature Ventricular Contractions
(PVCs)
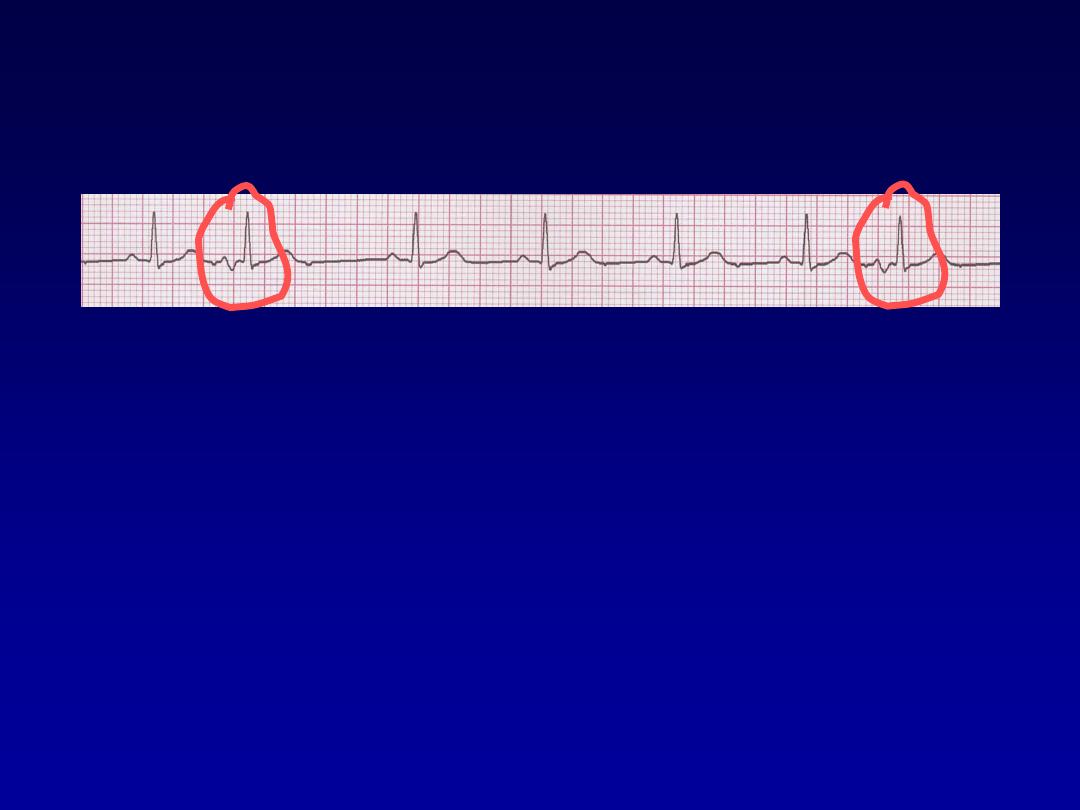
Premature Atrial Contractions
•
Deviation from NSR
–
These ectopic beats originate in the
atria (but not in the SA node),
therefore the contour of the P wave,
the PR interval, and the timing are
different than a normally generated
pulse from the SA node.

Atrial Fibrillation
•
The most common sustained cardiac arrhythmia.
•
AF can cause palpitation, breathlessness and fatigue.
In patients with poor ventricular function or valve
disease, it may precipitate or aggravate cardiac
failure.
•
AF
is
associated
with
significant
morbidity
(
Thromboembolic )and a twofold increase in mortality .
•
AF can be classified as paroxysmal (intermittent
episodes
which
self-terminate
within
7
days),
persistent
(prolonged
episodes
that
can
be
terminated by electrical or chemical cardioversion) or
permanent.

Common causes of atrial fibrillation
•
Coronary artery disease (including acute MI)
•
Valvular heart disease, especially rheumatic mitral
valve disease
•
Hypertension
•
Sinoatrial disease
•
Hyperthyroidism
•
Alcohol
• Cardiomyopathy
•
Congenital heart disease
•
Chest infection
•
Pulmonary embolism
•
Pericardial disease
•
Idiopathic (lone atrial fibrillation)
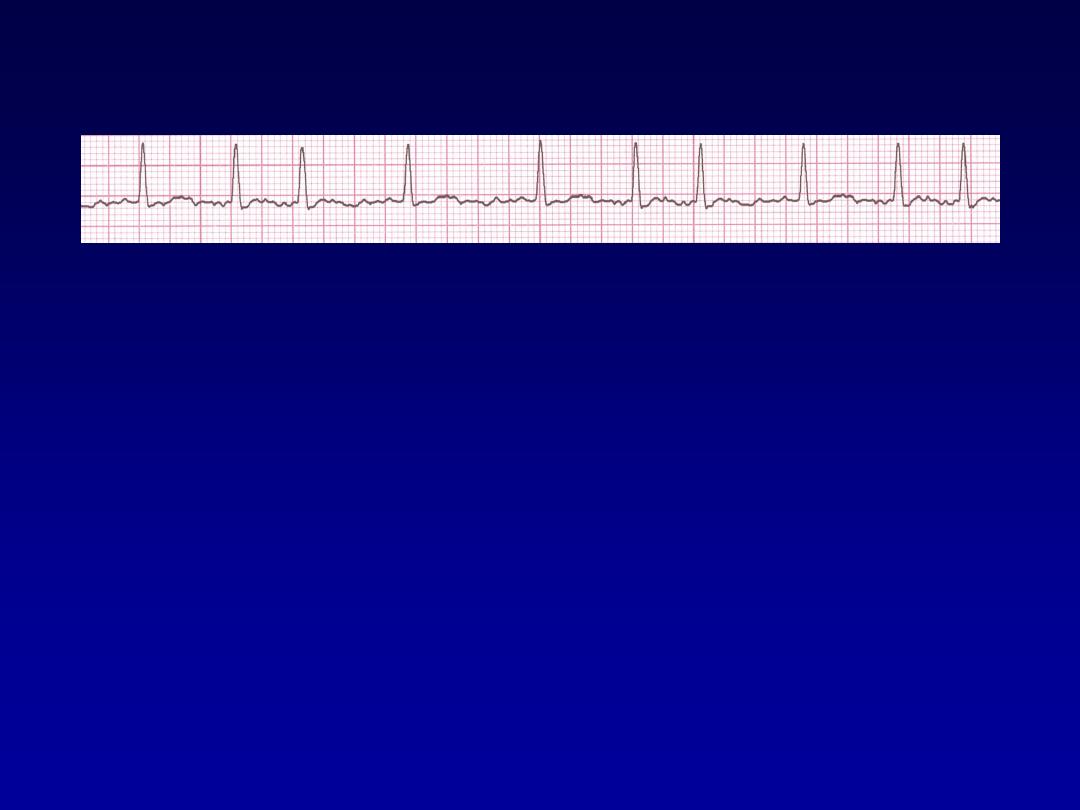
Atrial Fibrillation
•
Deviation from NSR
–
No organized atrial depolarization, so
no normal P waves (impulses are not
originating from the sinus node).
–
Atrial activity is chaotic (resulting in an
irregularly irregular rate).
–
Common, affects 2-4%, up to 5-10% if
> 80 years old
AF

• Rhythm control
• Pharmacologic cardioversion
Flecainide
,Propafenon,Amiodaron
• Electrical cardioversion
- Less than 48 hours direct cardioversion.
- More than 48 hours +Anticoagulates for 4 weeks
prior and 3 months after.
Rate control
•
Using Digoxin, β-blockers and calcium
antagonists, such as verapamil or diltiazem
•
Catheter ablation in refractory cases
Management

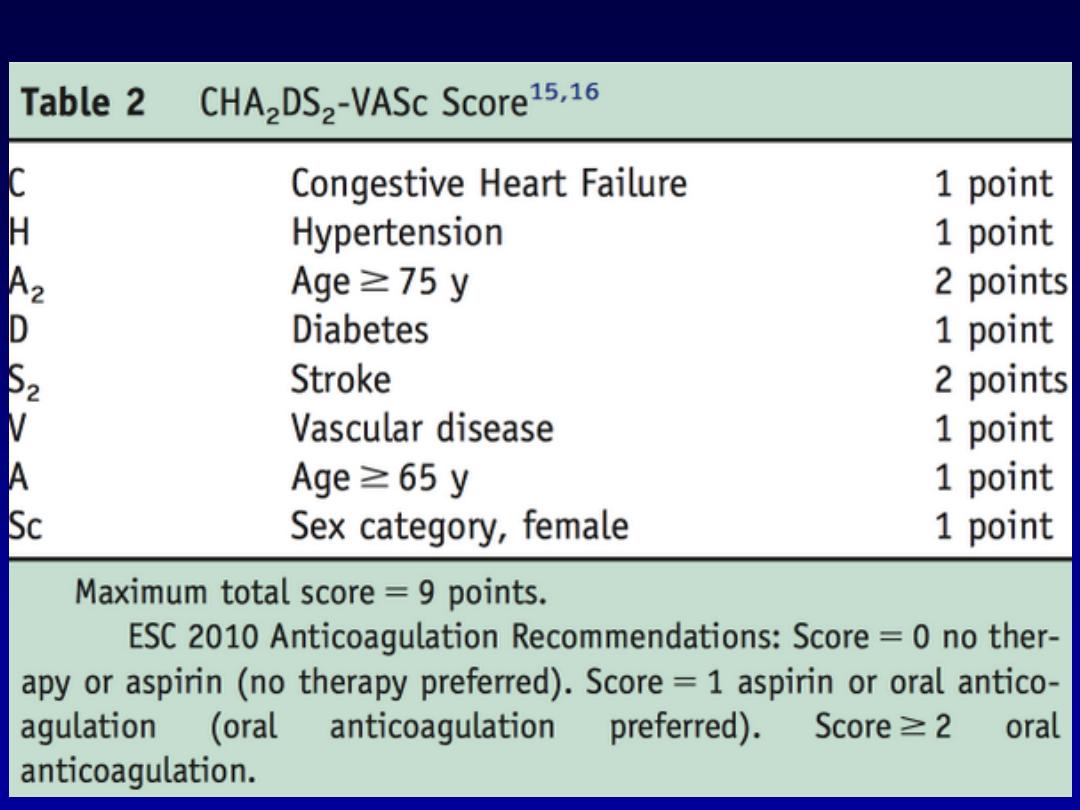
Prevention of
thromboembolism
•
Risk stratification is based on clinical
factors using the CHA2DS2-VASc
scoring system.
•
Warfarin INR 2-3
•
Aspirin
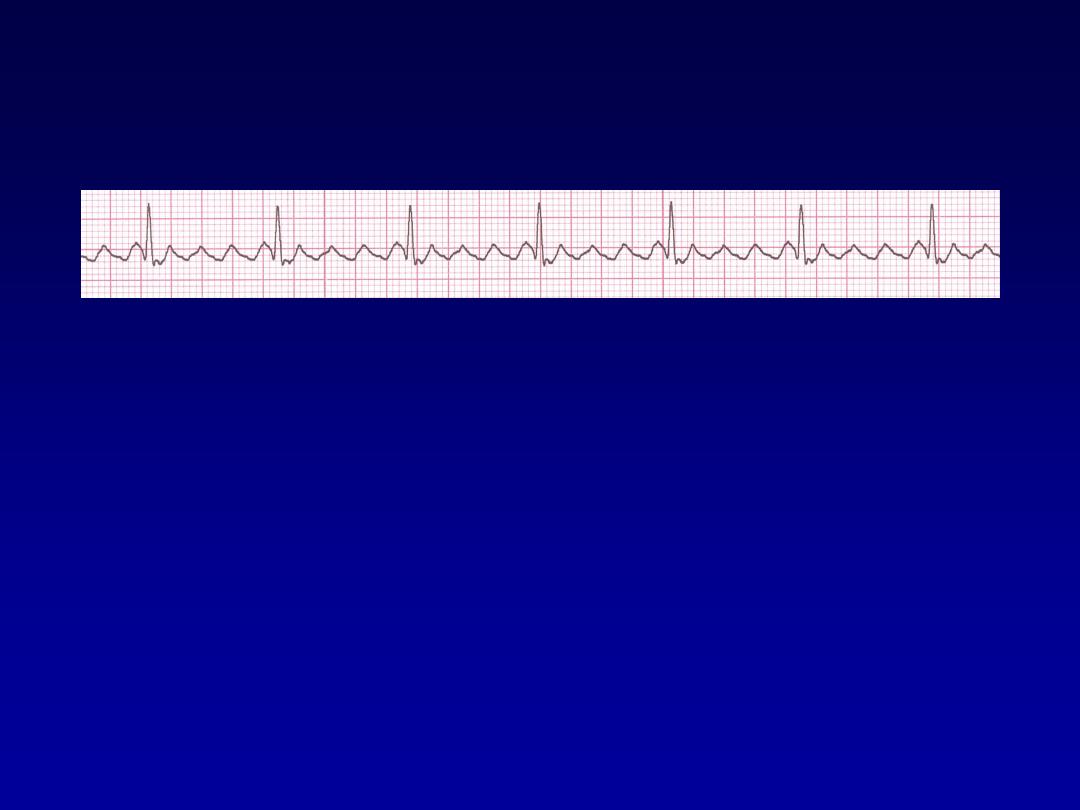
Atrial Flutter
•
Etiology:
a large (macro) re-entry circuit,
usually within the right atrium encircling
the tricuspid annulus with every 2nd,
3rd or 4th impulse generating a QRS
(others are blocked in the AV node as
the node repolarizes).
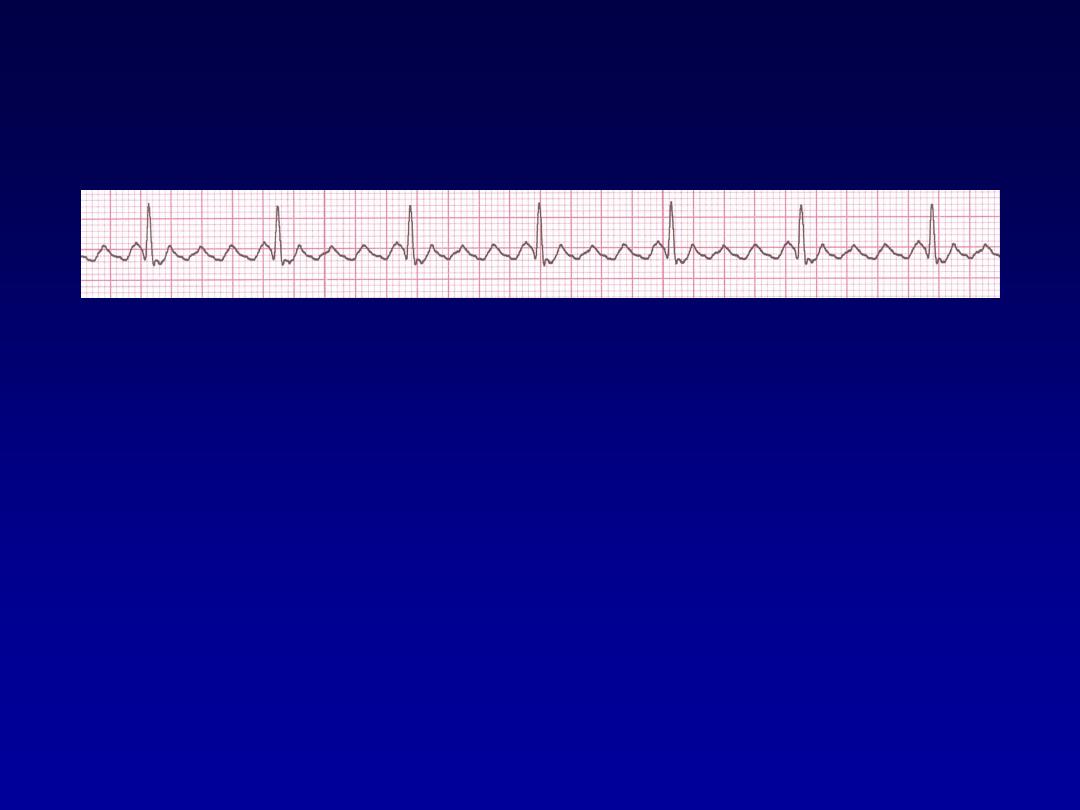
Atrial Flutter
•
Deviation from NSR
–
No P waves. Instead flutter waves (note
“sawtooth” pattern) are formed at a rate
of 250 - 350 bpm.
–
Only some impulses conduct through
the AV node (usually every other
impulse)
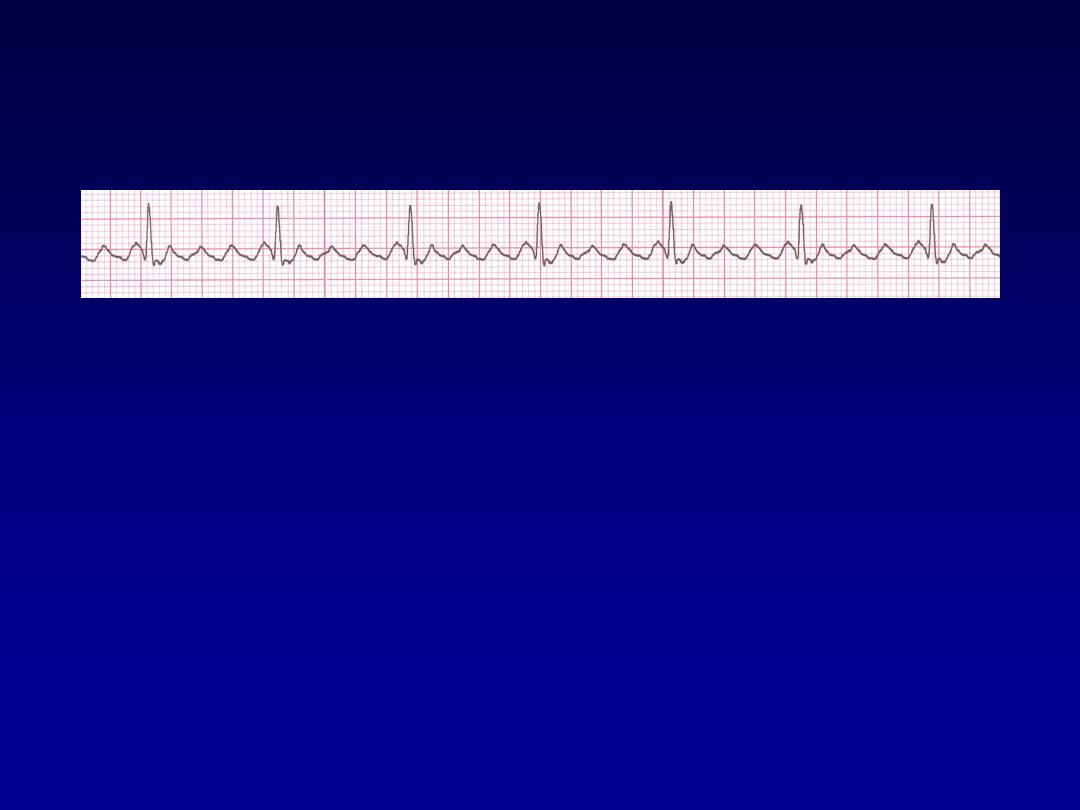
Atrial F
70 bpm
• Rate?
• Regularity?
regular
flutter waves
0.06 s
• P waves?
• PR interval?
none
• QRS duration?
Interpretation?
Atrial Flutter
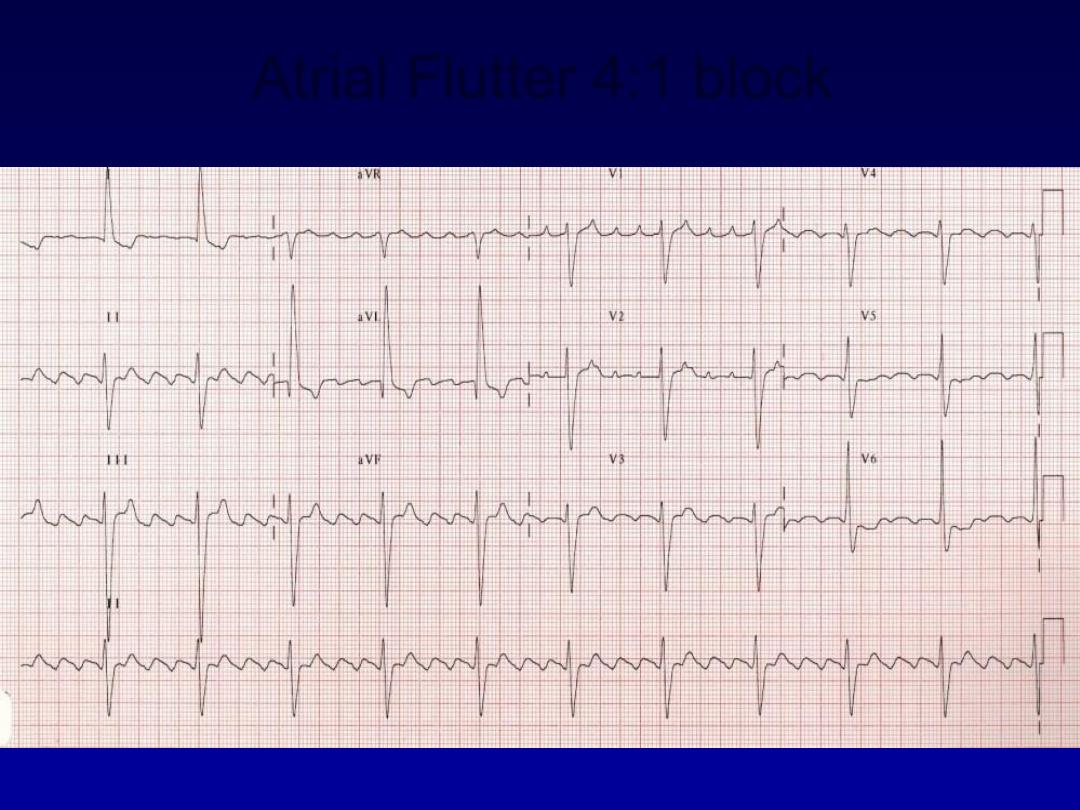
Atrial Flutter 4:1 block

Causes and Symptoms
•
Similar to atrial fibrillation
•
Managemen
t
•
Treat the cause
•
Rate control -Digoxine B blocker,verapamil.
•
Rhythm control
–Amiodaron ,DC
•
Maintanance B- Blocker or amiodarone
•
Anticoagulant
•
Catheter ablation offers a 90% chance of complete cure
and is the treatment of choice for patients with persistent
symptoms
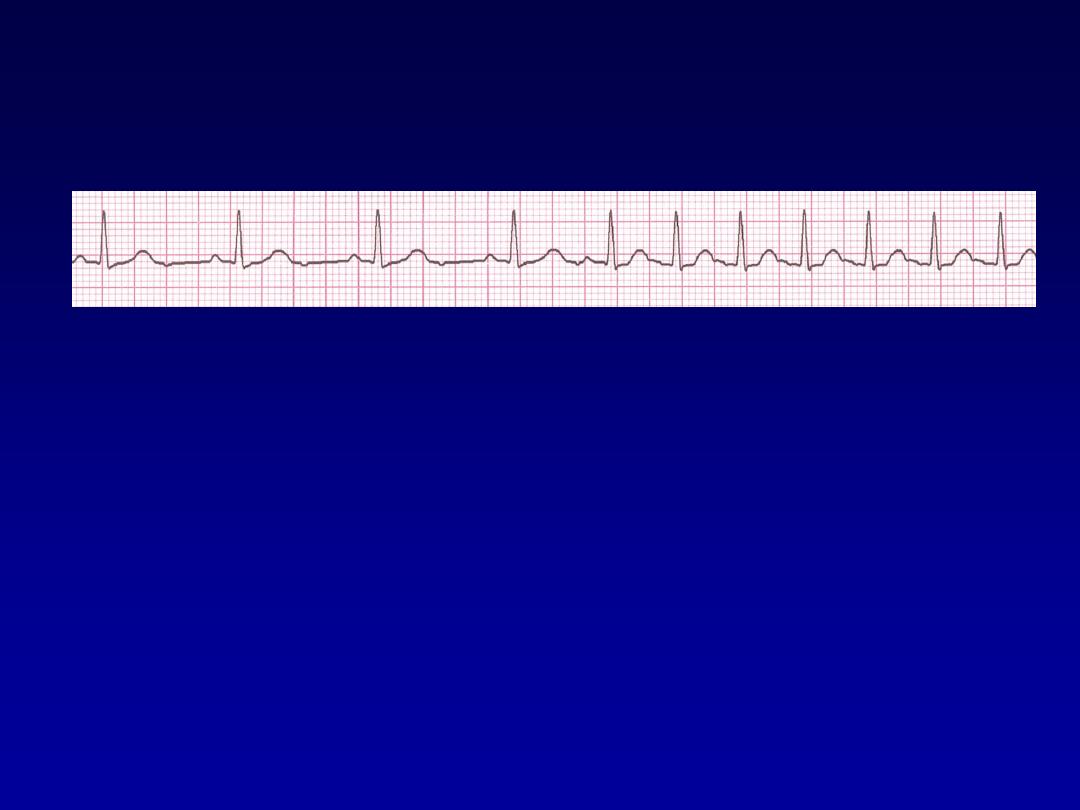
Paroxysmal Supraventricular
Tachycardia (PSVT)
•
Deviation from NSR
–
The heart rate suddenly speeds up,
often triggered by a PAC (not seen
here) and the P waves are lost.
–
Tends to occur in normal heart.
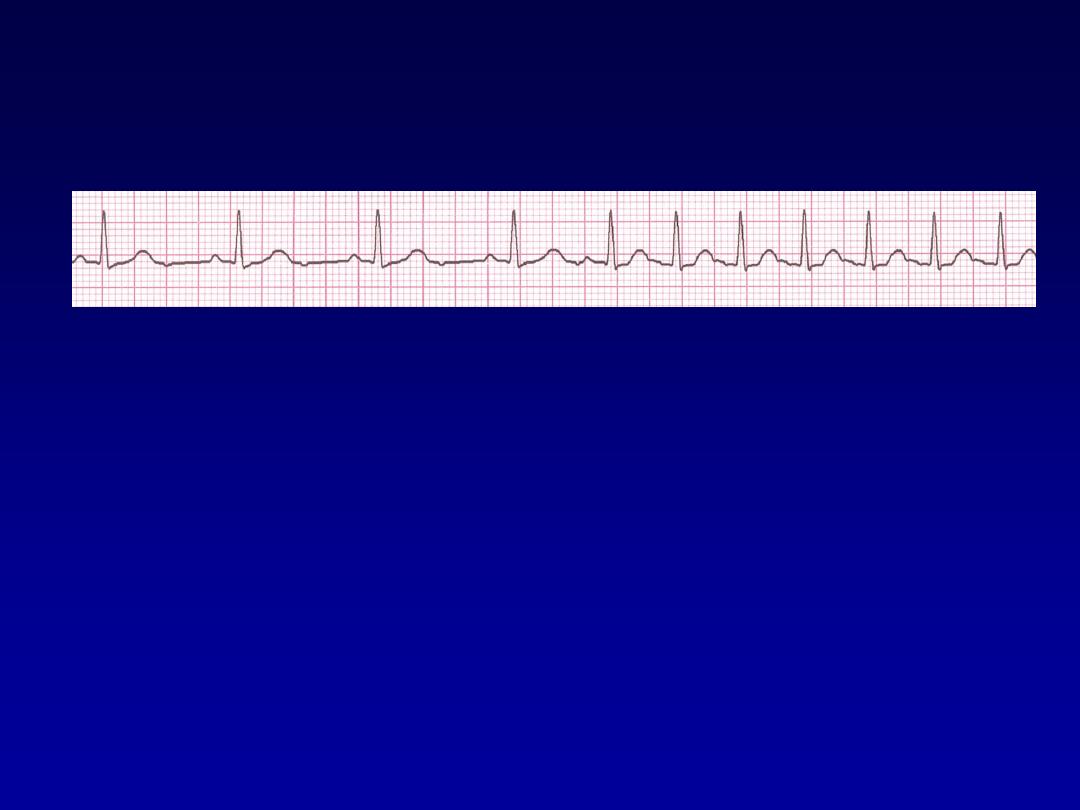
PSVT
•
Etiology:
There are several types of
PSVT but all originate above the
ventricles (therefore the QRS is narrow).
•
Most common: abnormal conduction in
the AV node (reentrant circuit looping in
the AV node).
•
Rate 150-250
PSVT
For more presentations www.medicalppt.blogspot.com

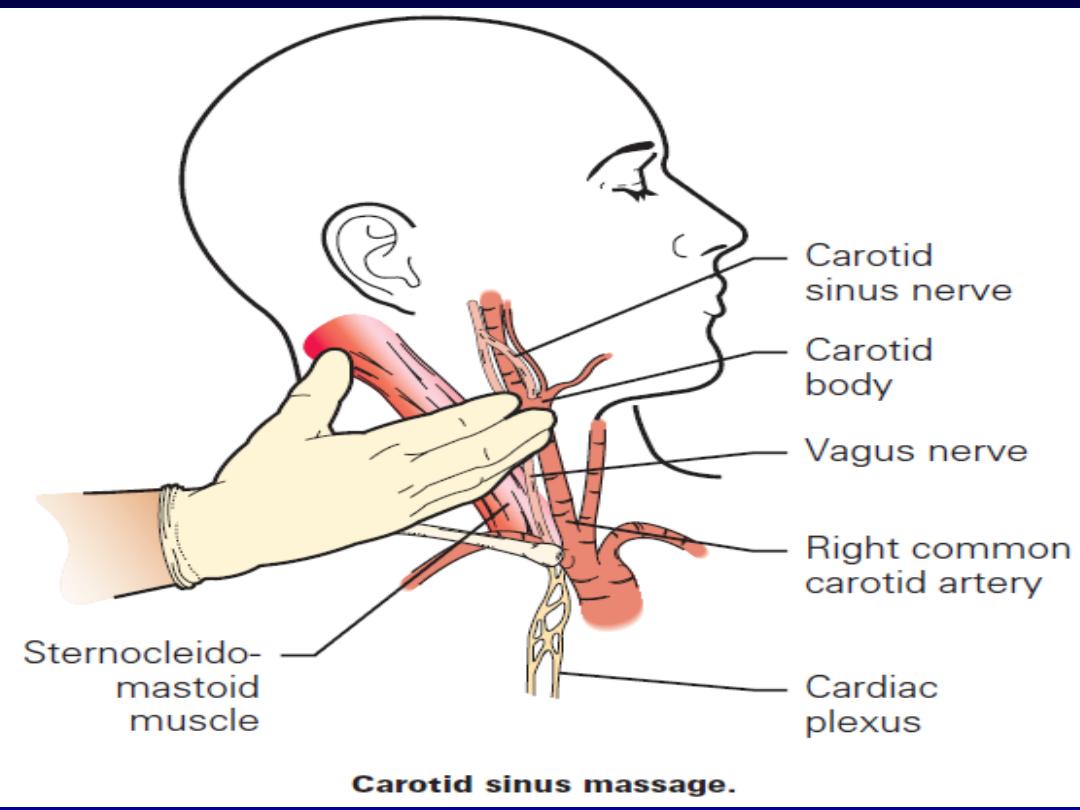
Managment
•
Episode may be terminated by carotid sinus
pressure or by the Valsalva manœuvre.
Adenosine (3
–12 mg rapidly IV in incremental
doses until tachycardia stops) or verapamil (5
mg IV)
•
Recurrent SVT, catheter ablation is the most
effective therapy and will permanently
prevent SVT in more than 90% of cases
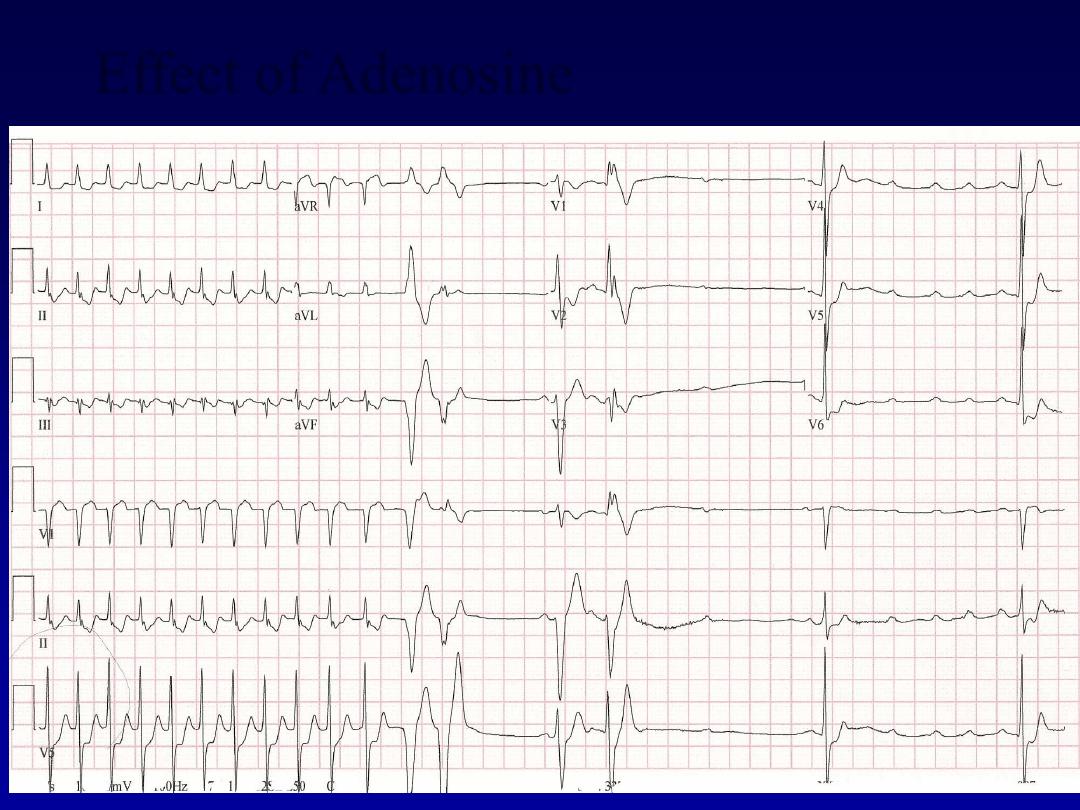
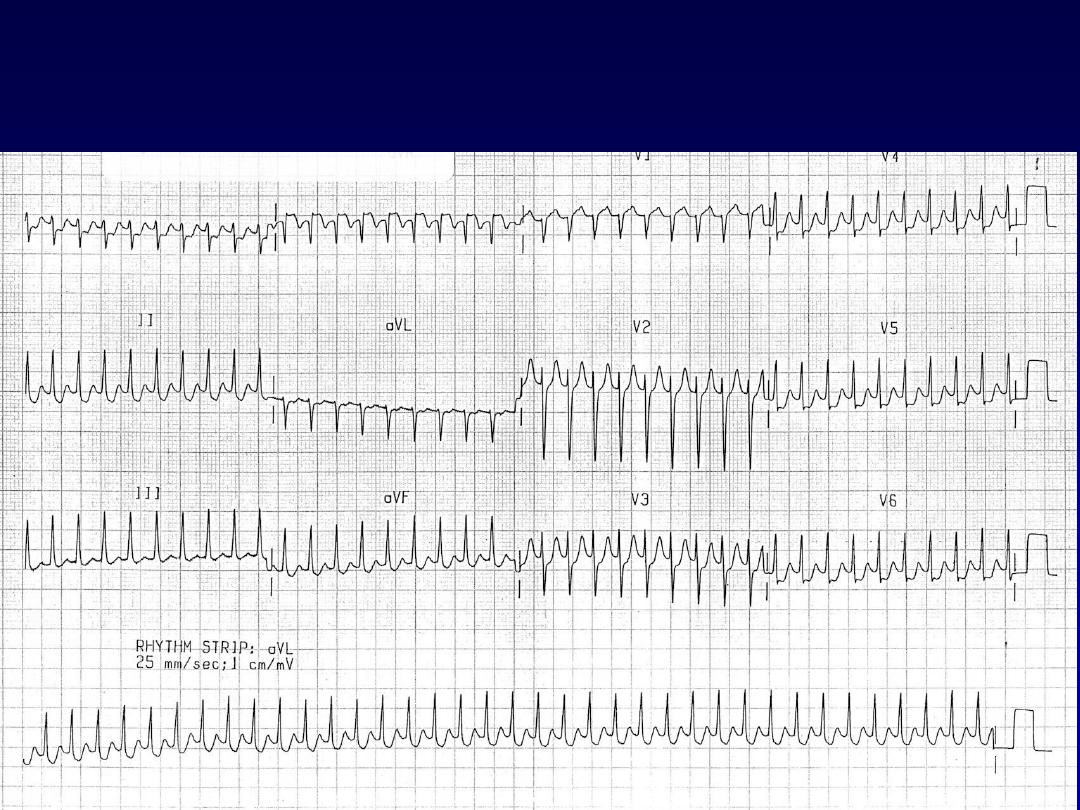
Effect of Adenosine
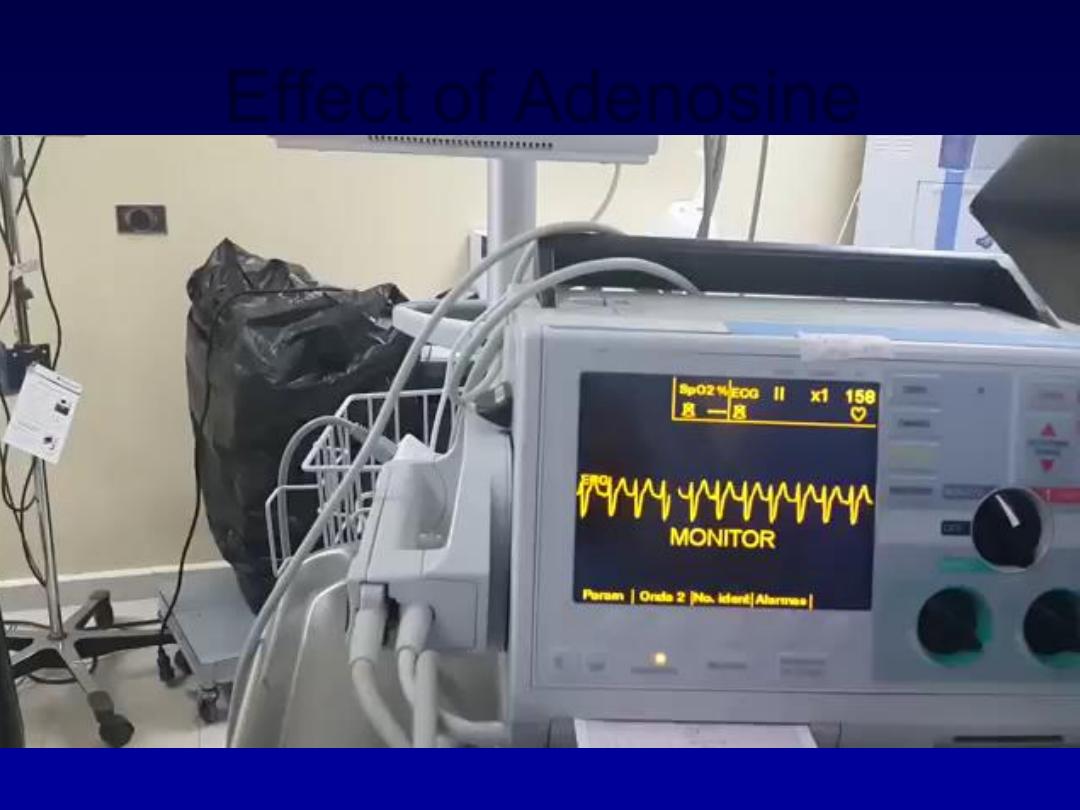
Effect of Adenosine

Ventricular Arrhythmias
•
Premature Ventricular Contractions
•
Ventricular Tachycardia
•
Ventricular Fibrillation
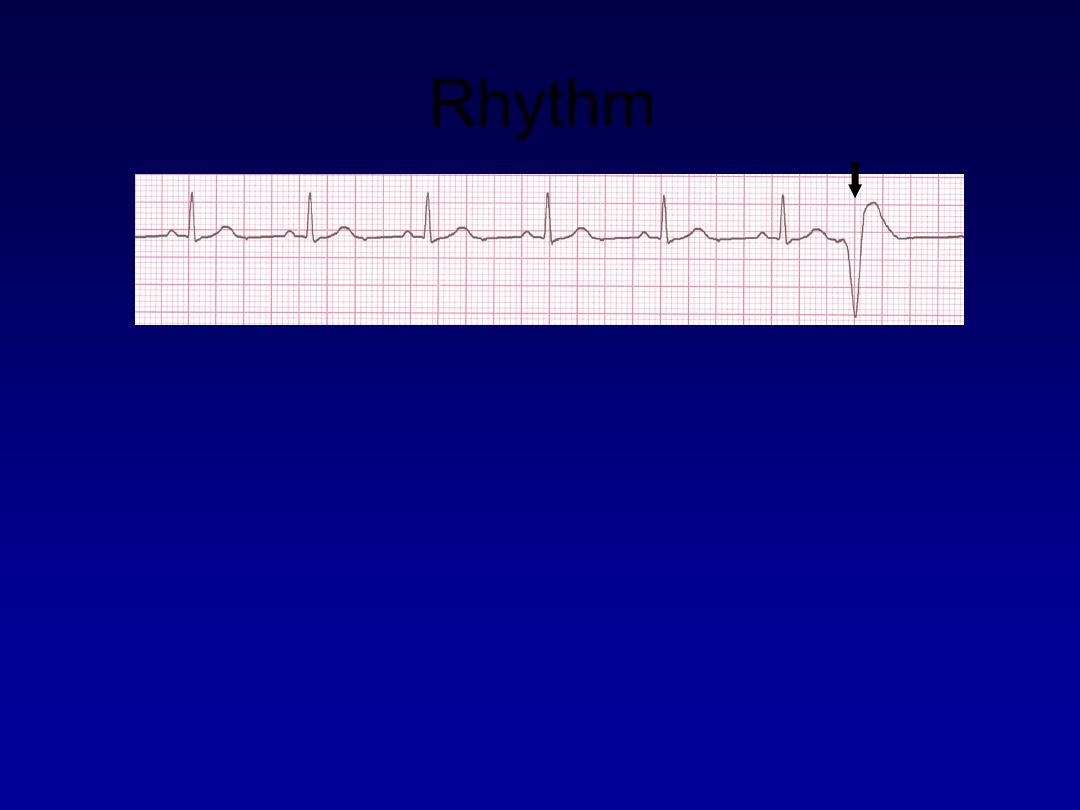
Rhythm
60 bpm
• Rate?
• Regularity?
occasionally irreg.
none for 7
th
QRS
0.08 s (7th wide)
• P waves?
• PR interval?
0.14 s
• QRS duration?
Interpretation?
Sinus Rhythm with 1 PVC
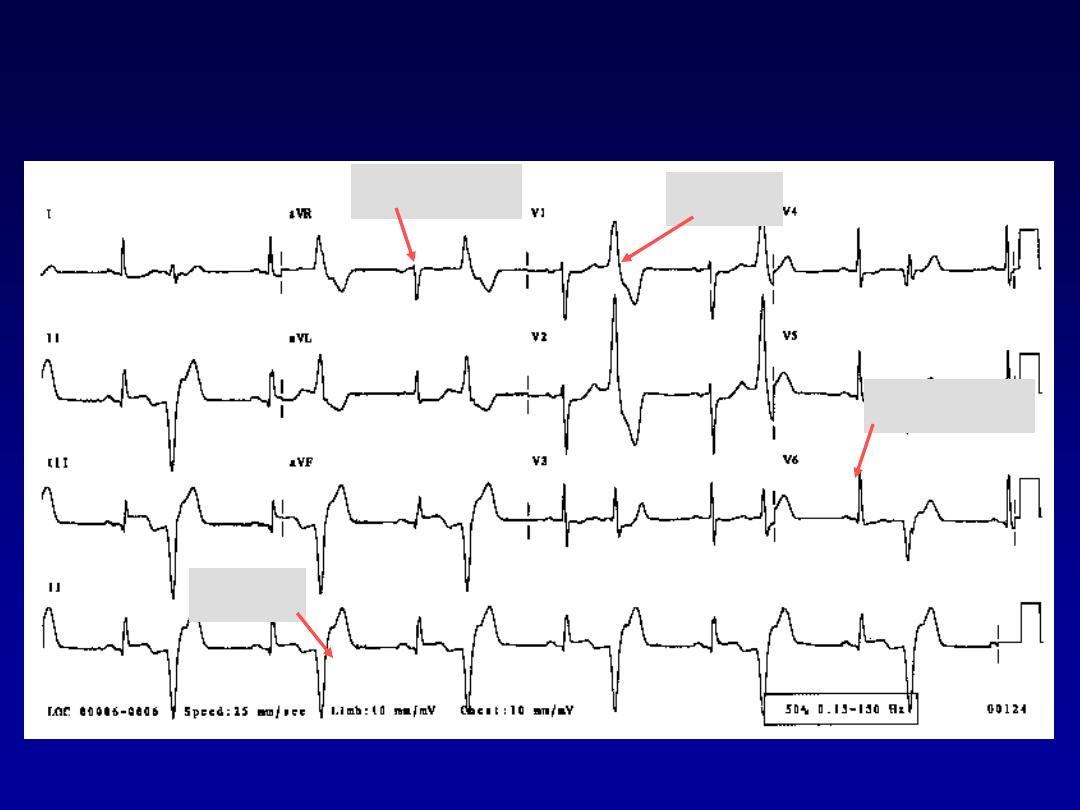
41
Ventricular Bigeminy
Normal
VPC
VPC
Normal

Ventricular Tachycardia
•
Dangerous.
•
Nearly in abnormal heart.
•
3 or more successive PVC at rate of
more than 120.
•
Can occur in normal heart.
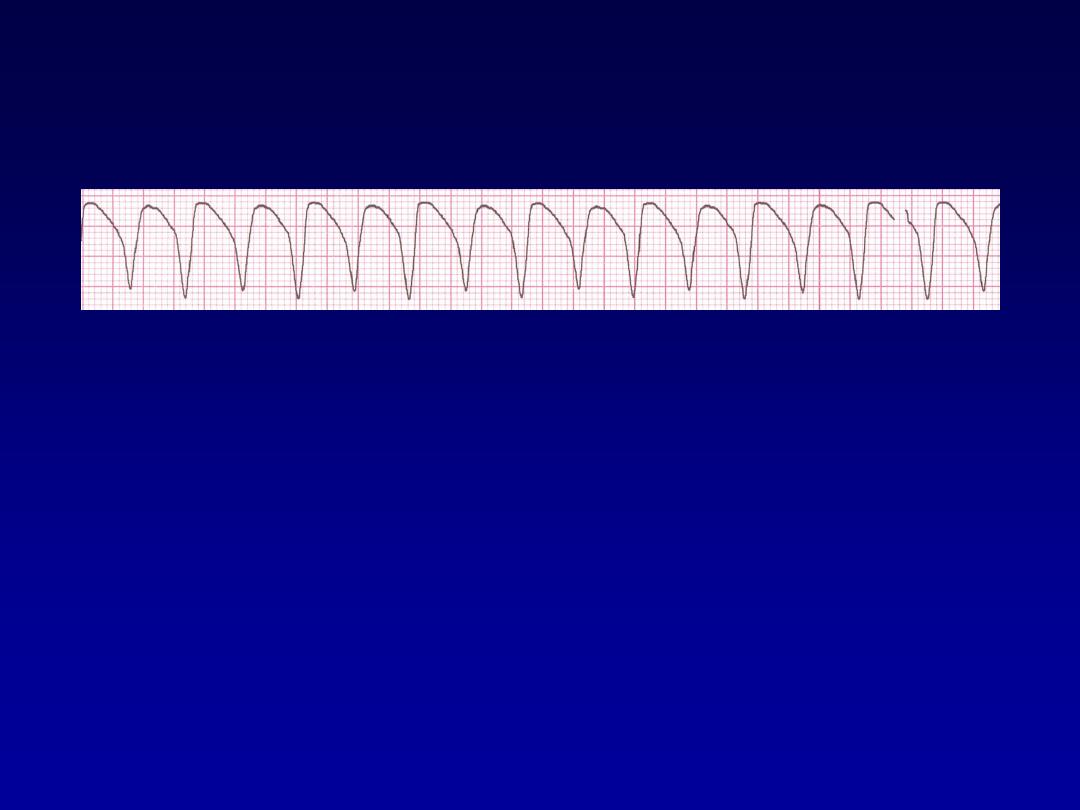
Ventricular Tachycardia
•
Deviation from NSR
–
Impulse is originating in the ventricles
(no P waves, wide QRS).
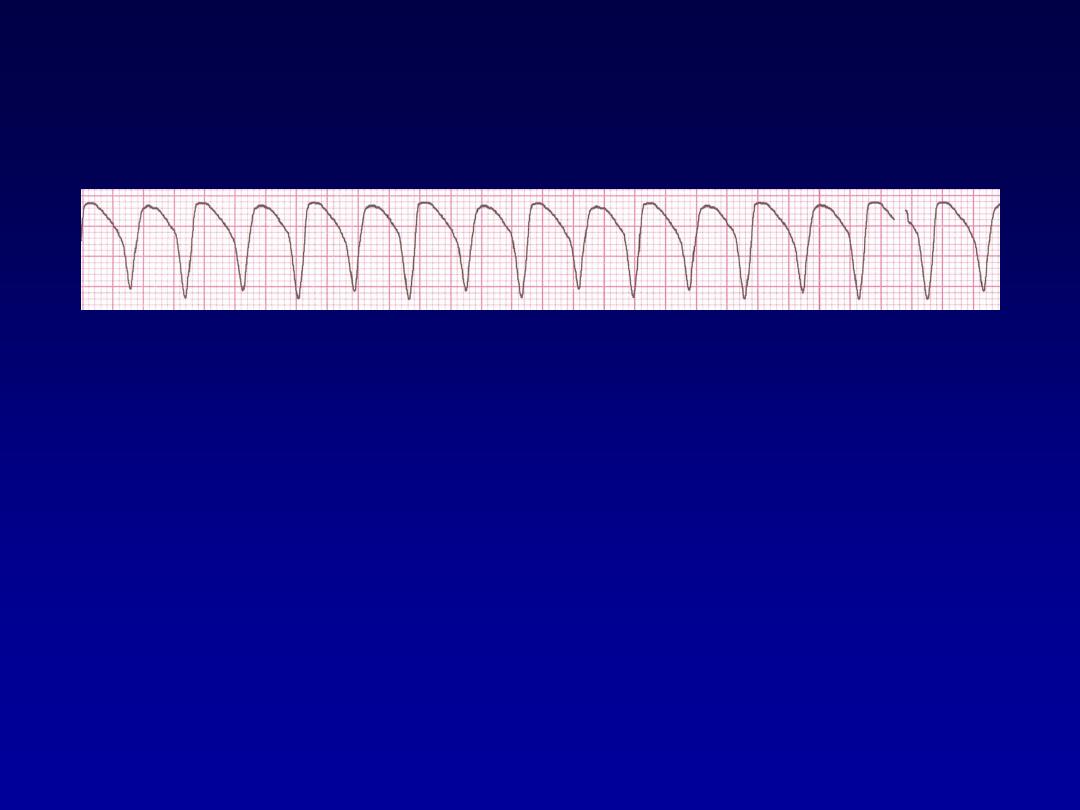
Ventricular Tachycardia
•
Etiology:
There is a re-entrant pathway
looping in a ventricle (most common cause).
•
Ventricular tachycardia (VT) occurs most
commonly in the settings of acute MI,
chronic coronary artery disease, and
cardiomyopathy.
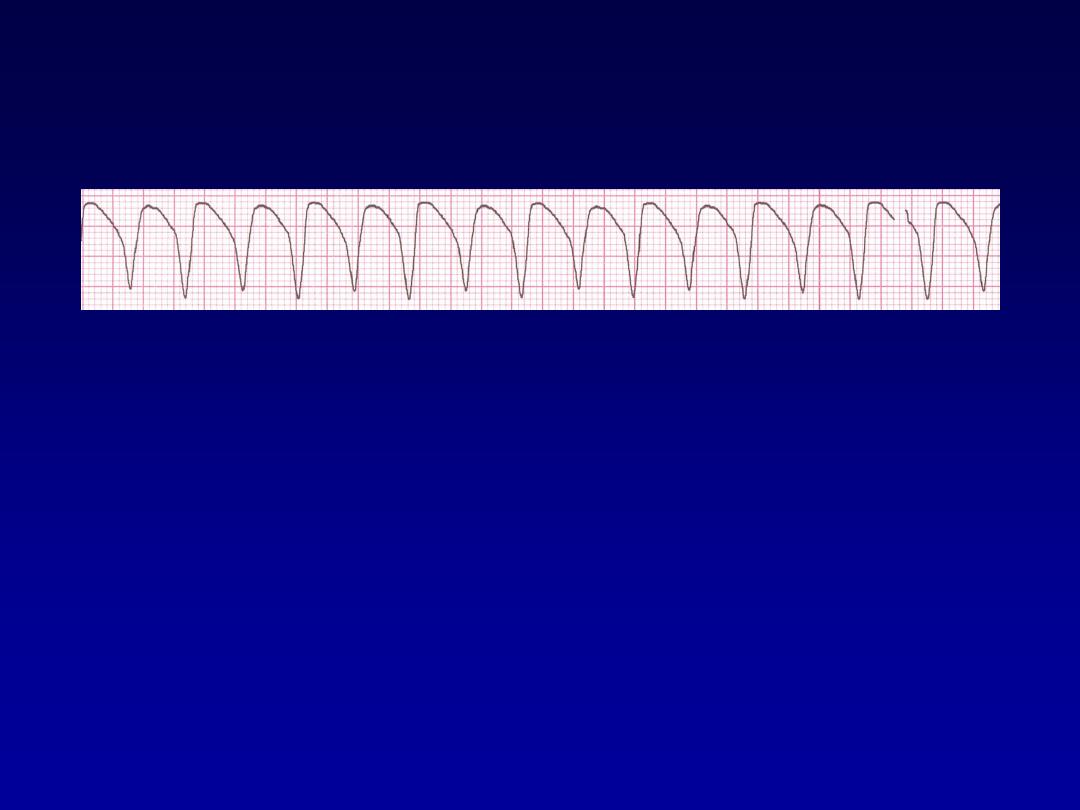
Rhythm
160 bpm
• Rate?
• Regularity?
regular
none
wide (> 0.12 sec)
• P waves?
• PR interval?
none
• QRS duration?
Interpretation?
Ventricular Tachycardia
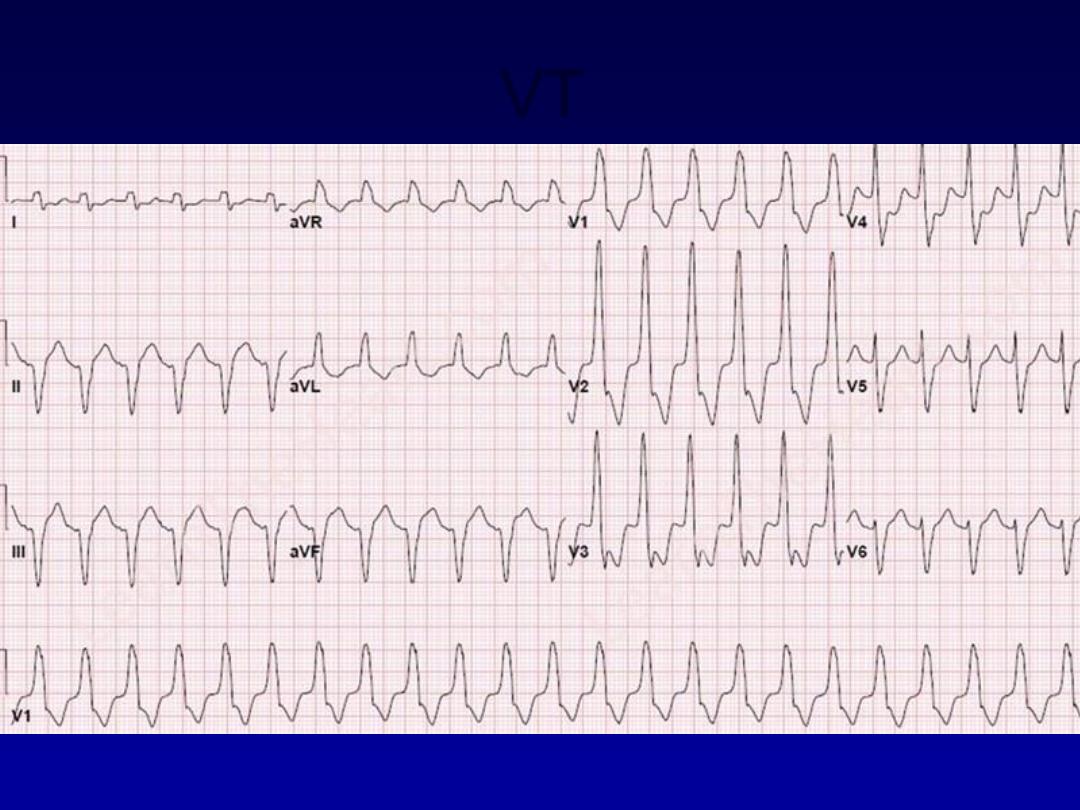
VT

Management
•
Treat cause.
•
Hemodynamically unstable DC
•
Stable IV amiodarone or lidocaine.
•
With poor LV function indication for ICD
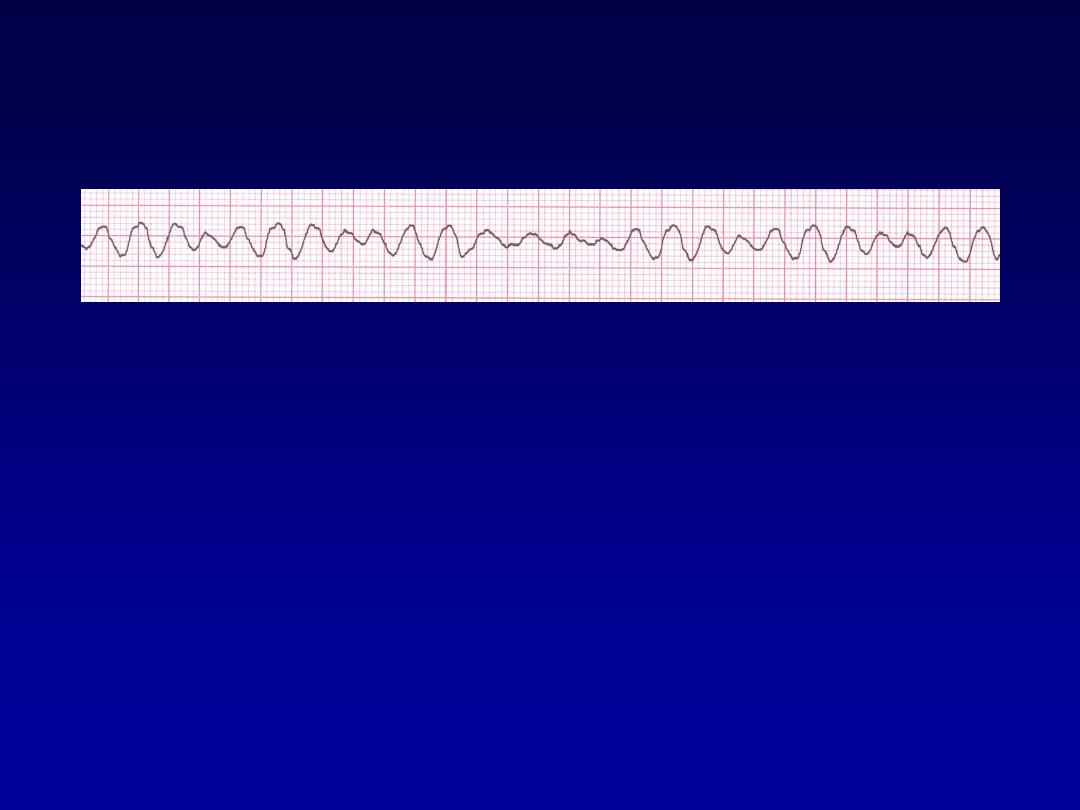
Ventricular Fibrillation
•
Deviation from NSR
–
Completely abnormal.
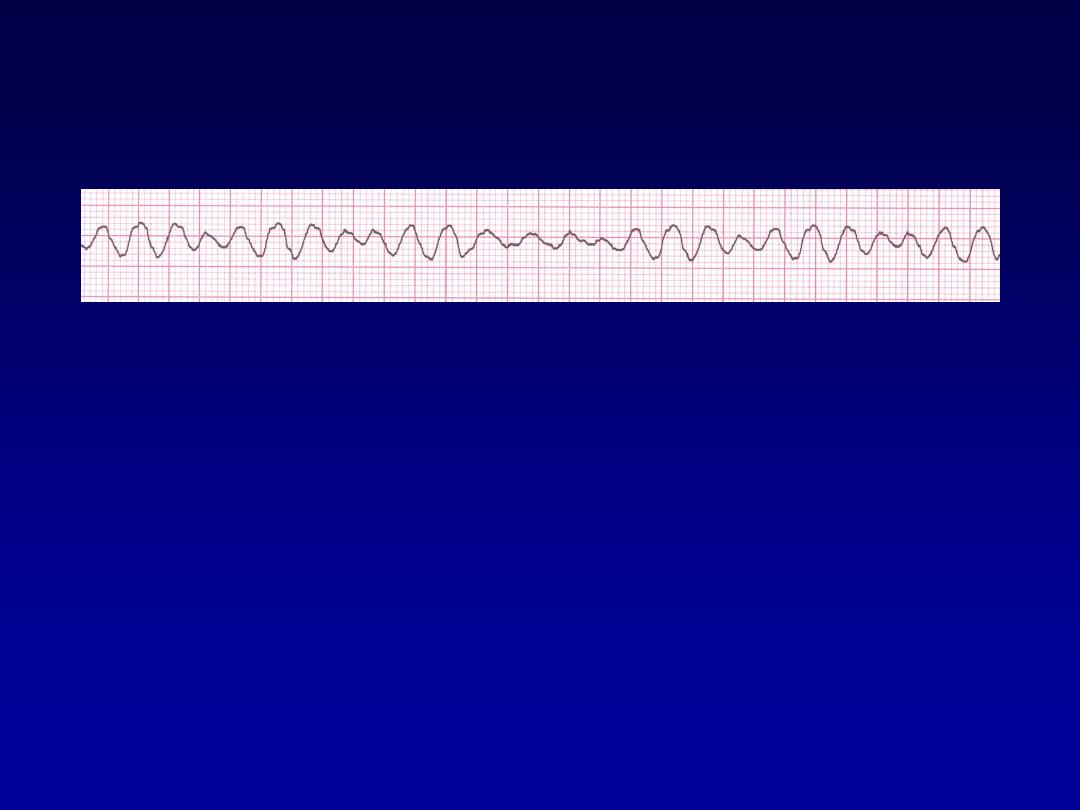
Ventricular Fibrillation
•
Etiology:
The ventricular cells are
excitable and depolarizing randomly.
•
Rapid drop in cardiac output and death
occurs if not quickly reversed
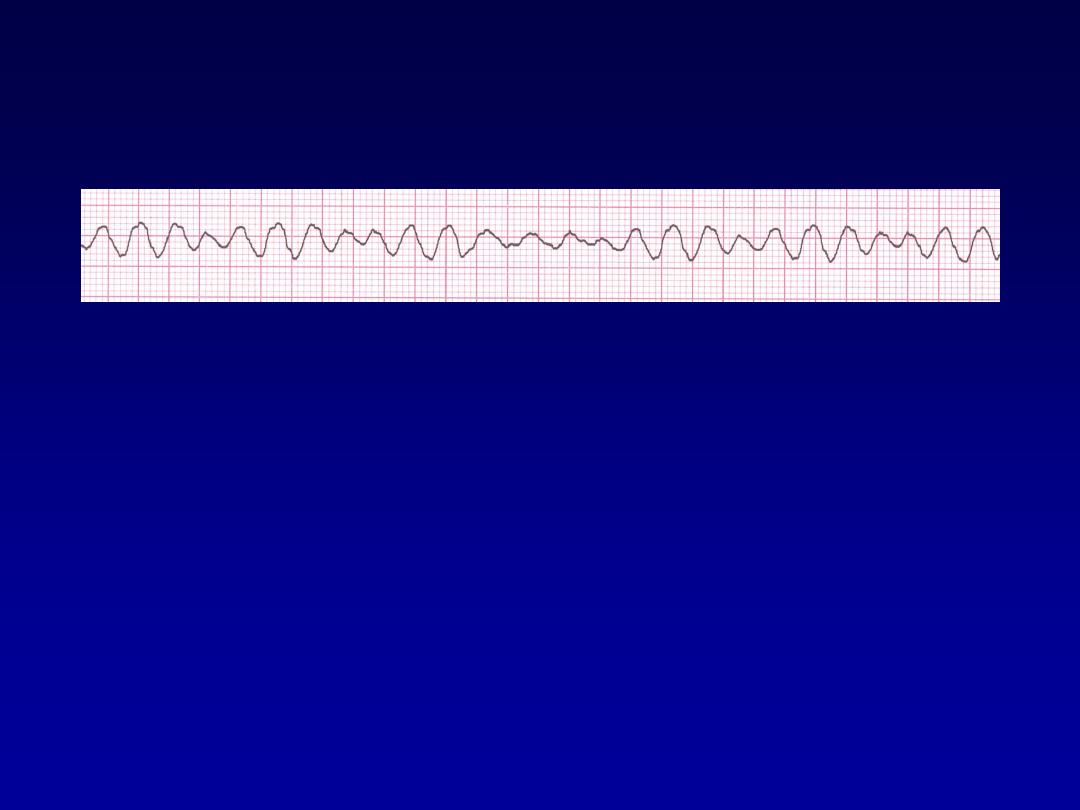
Rhythm
none
• Rate?
• Regularity?
irregularly irreg.
none
wide, if recognizable
• P waves?
• PR interval?
none
• QRS duration?
Interpretation?
Ventricular Fibrillation
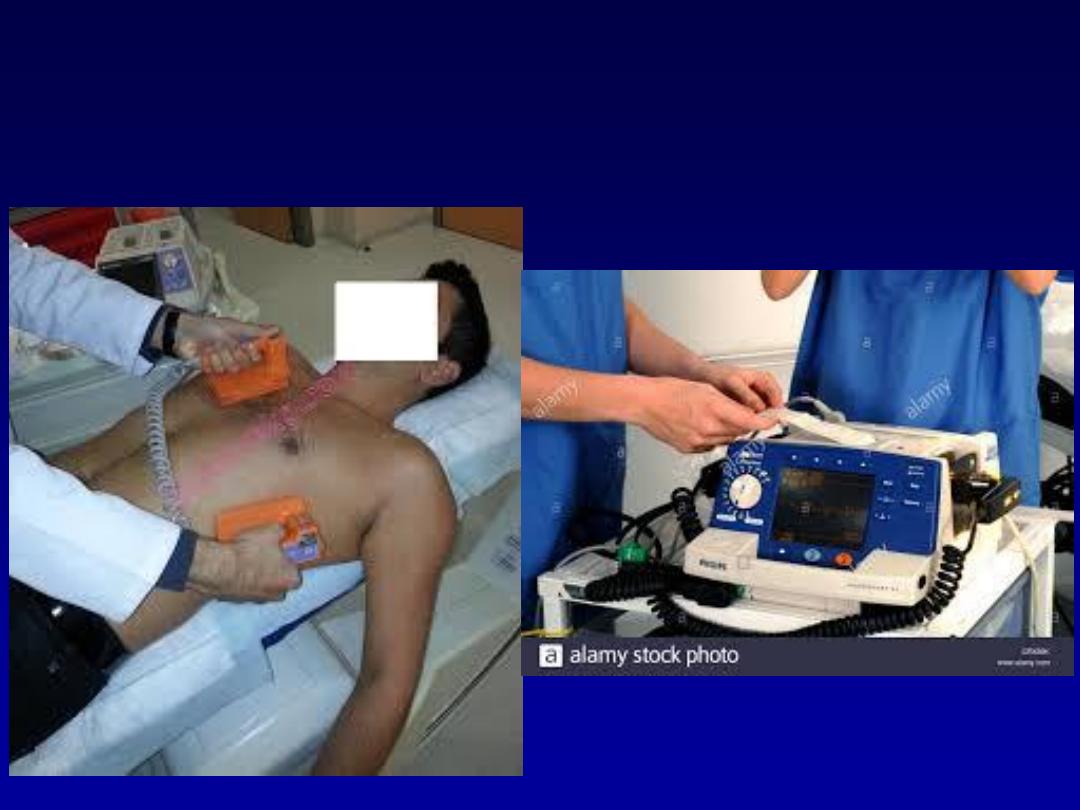
Management
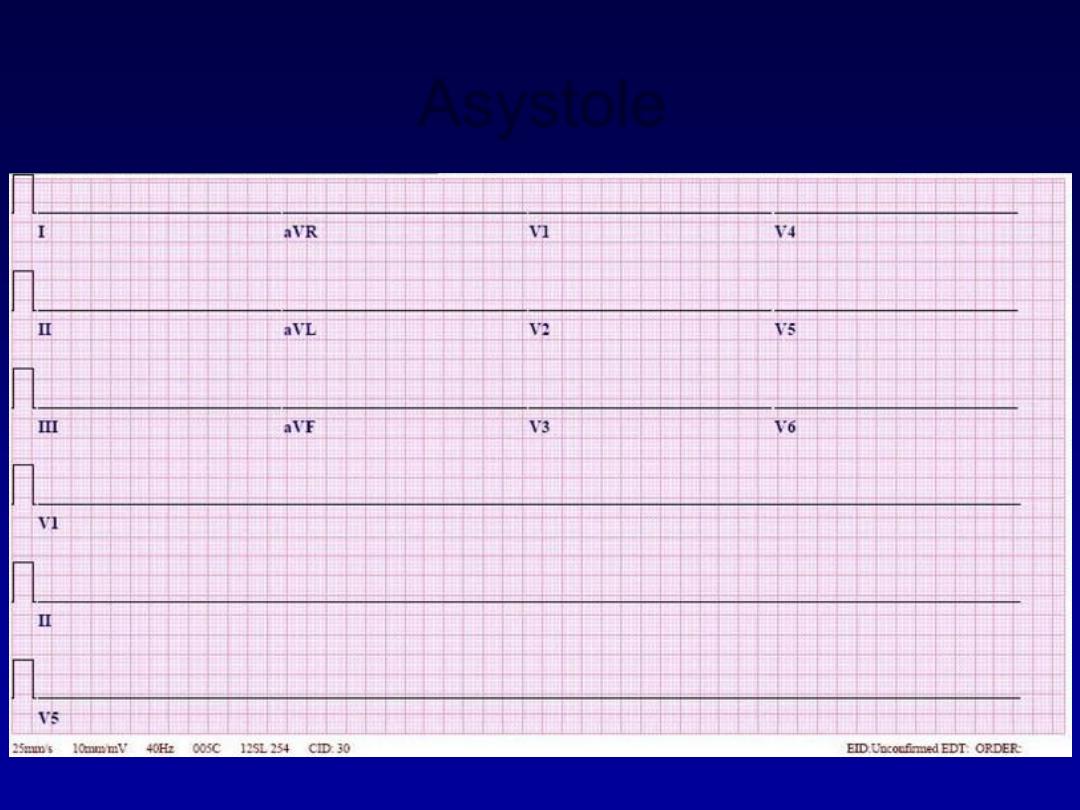
Asystole
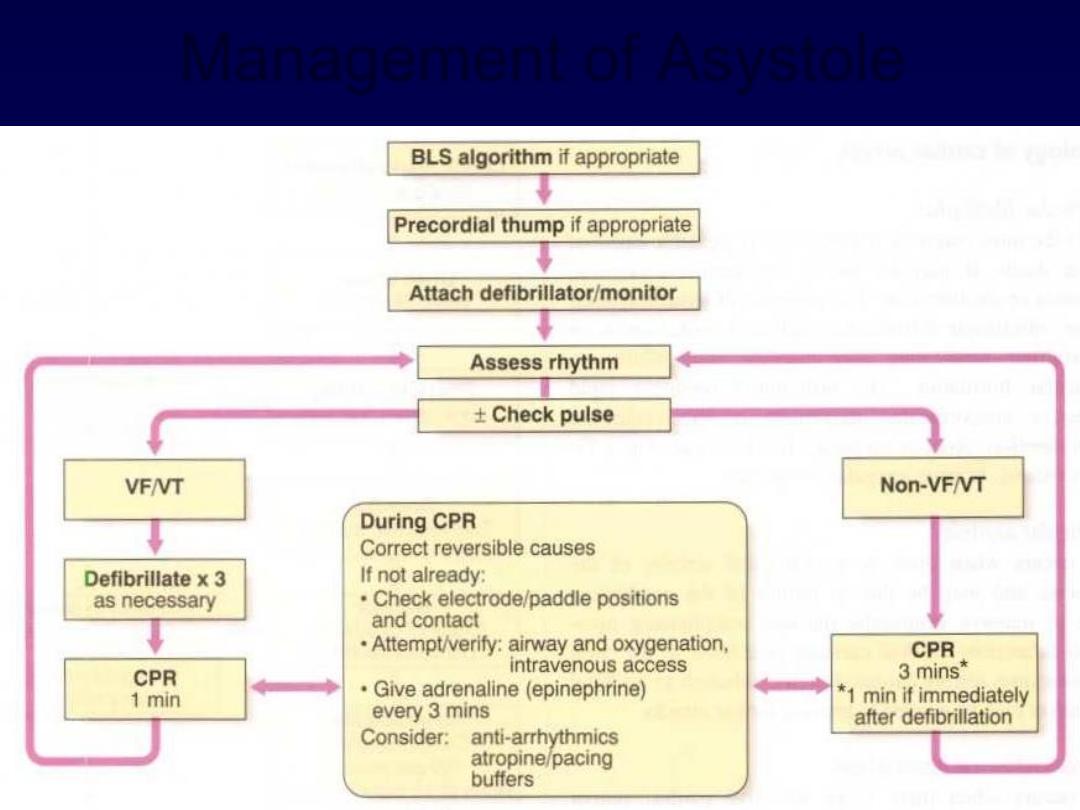
Management of Asystole

AV Nodal Blocks
•
1st Degree AV Block
•
2nd Degree AV Block, Type I
•
2nd Degree AV Block, Type II
•
3rd Degree AV Block
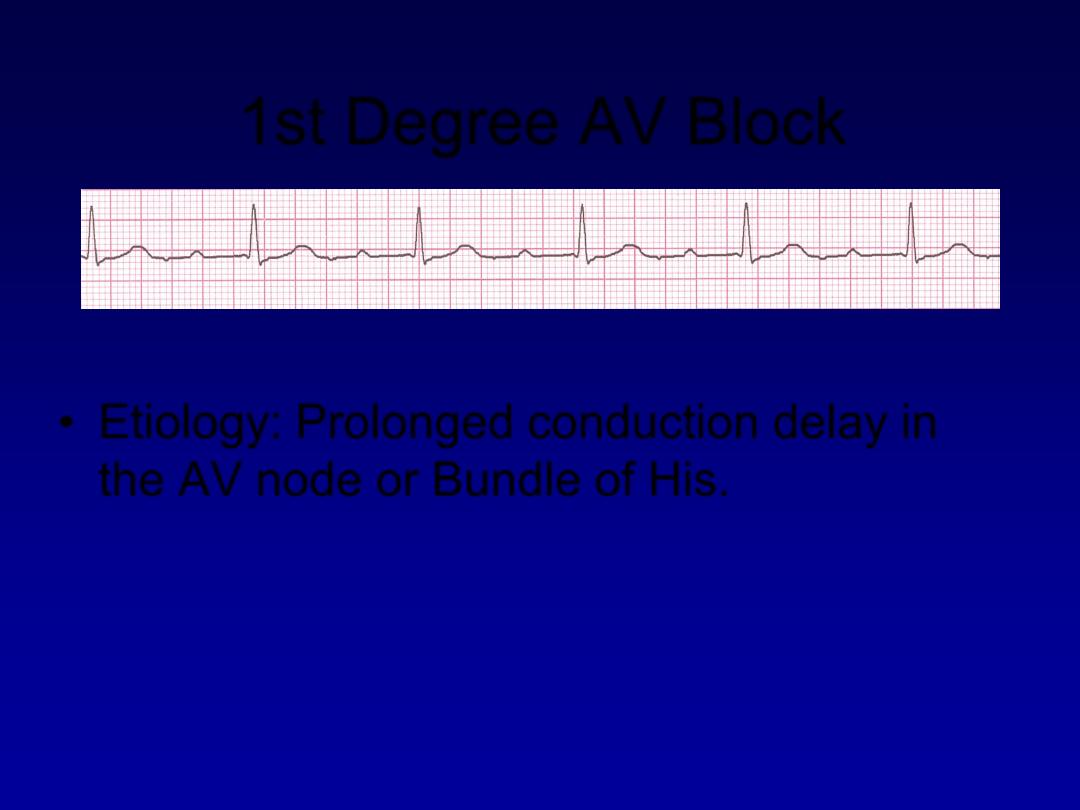
1st Degree AV Block
•
Etiology:
Prolonged conduction delay in
the AV node or Bundle of His.
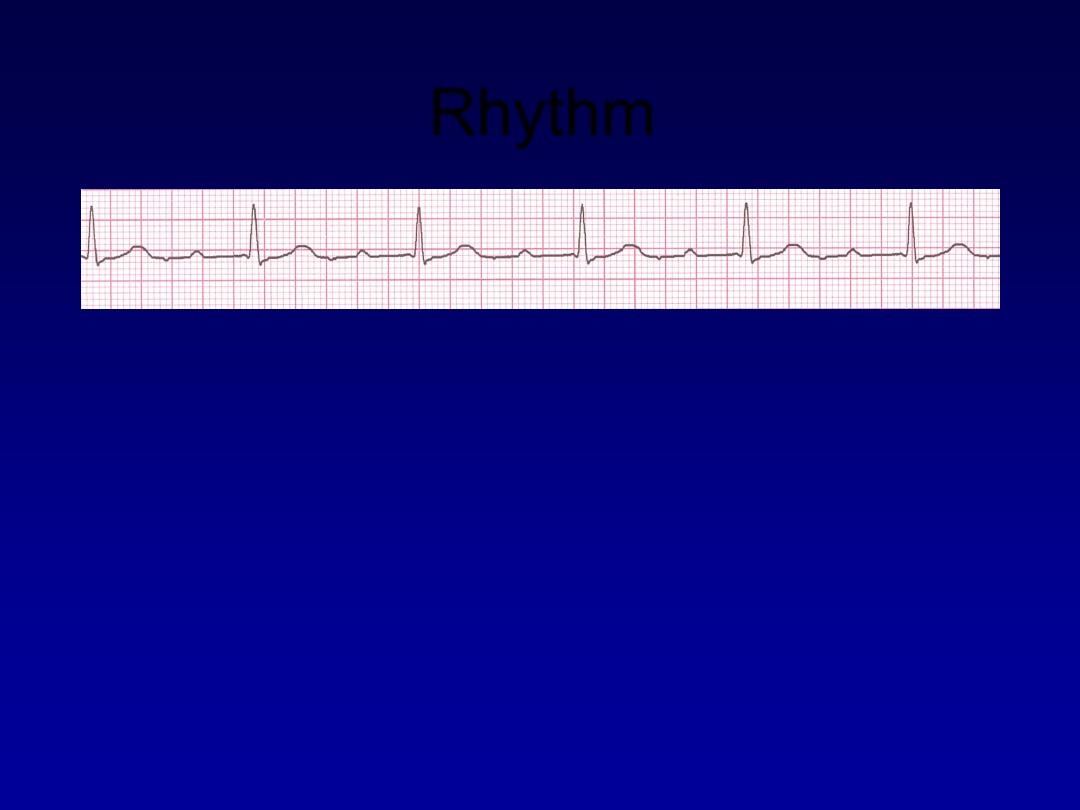
Rhythm
60 bpm
• Rate?
• Regularity?
regular
normal
0.08 s
• P waves?
• PR interval?
0.36 s
• QRS duration?
Interpretation?
1st Degree AV Block
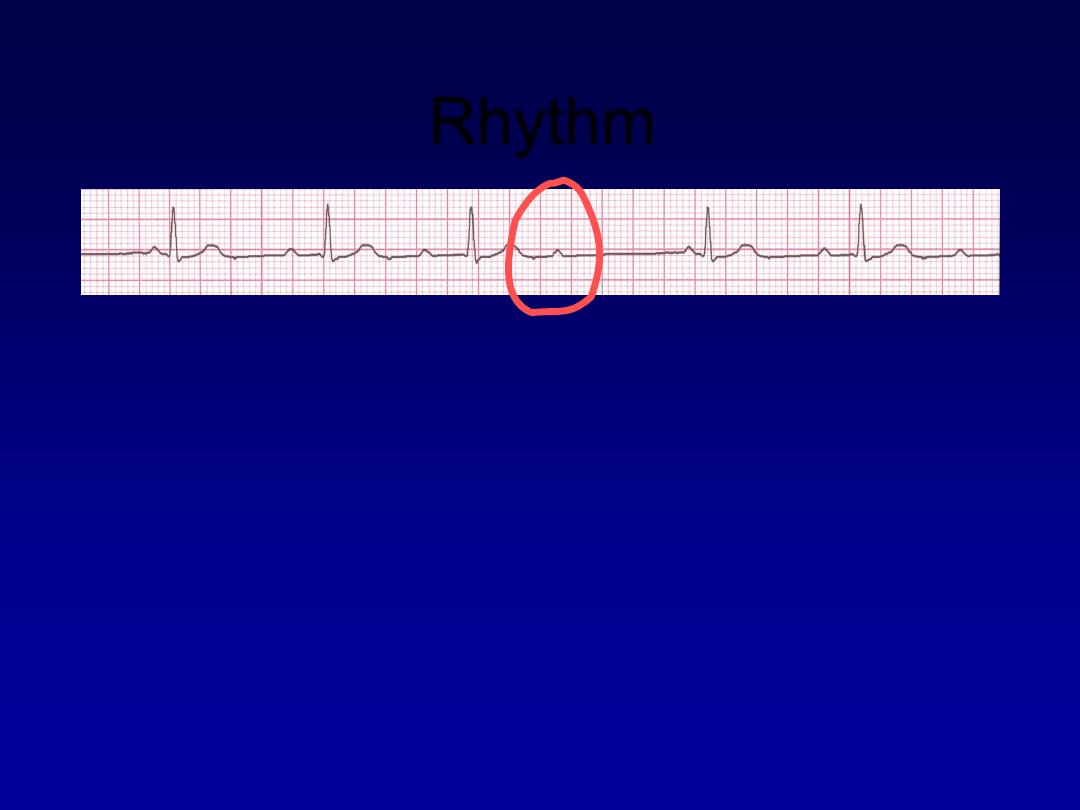
Rhythm
50 bpm
• Rate?
• Regularity?
regularly irregular
nl, but 4th no QRS
0.08 s
• P waves?
• PR interval?
lengthens
• QRS duration?
Interpretation?
2nd Degree AV Block, Type I
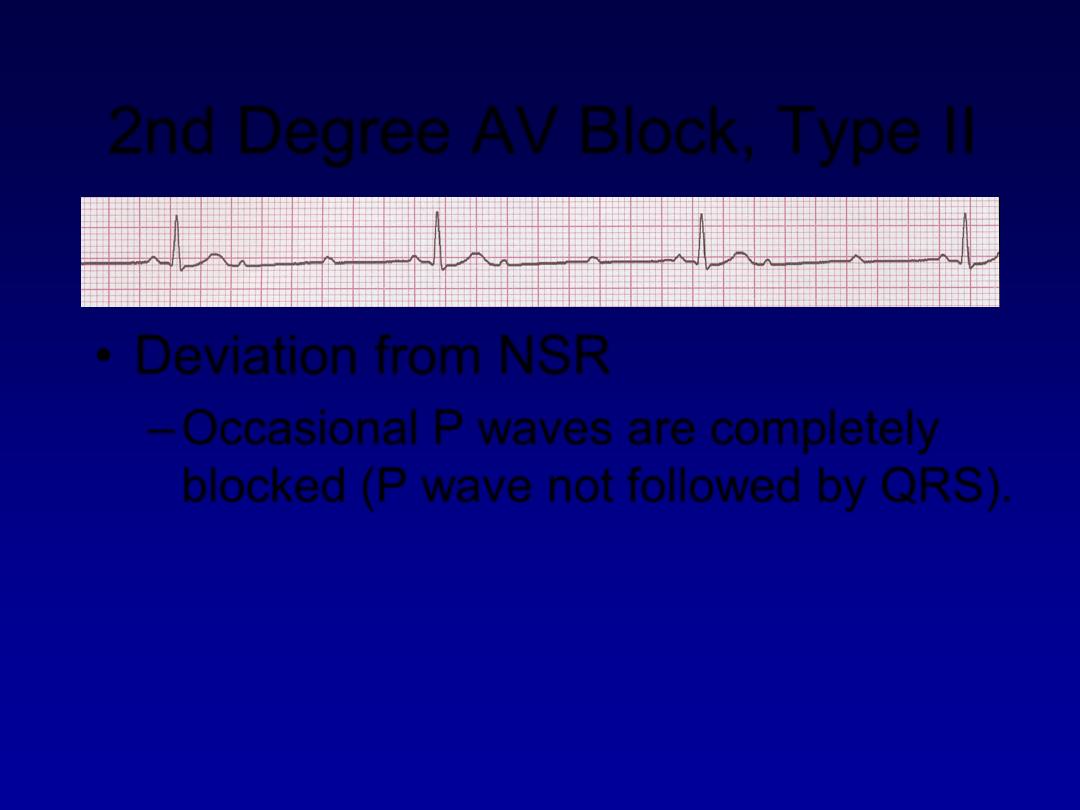
2nd Degree AV Block, Type II
•
Deviation from NSR
–
Occasional P waves are completely
blocked (P wave not followed by QRS).
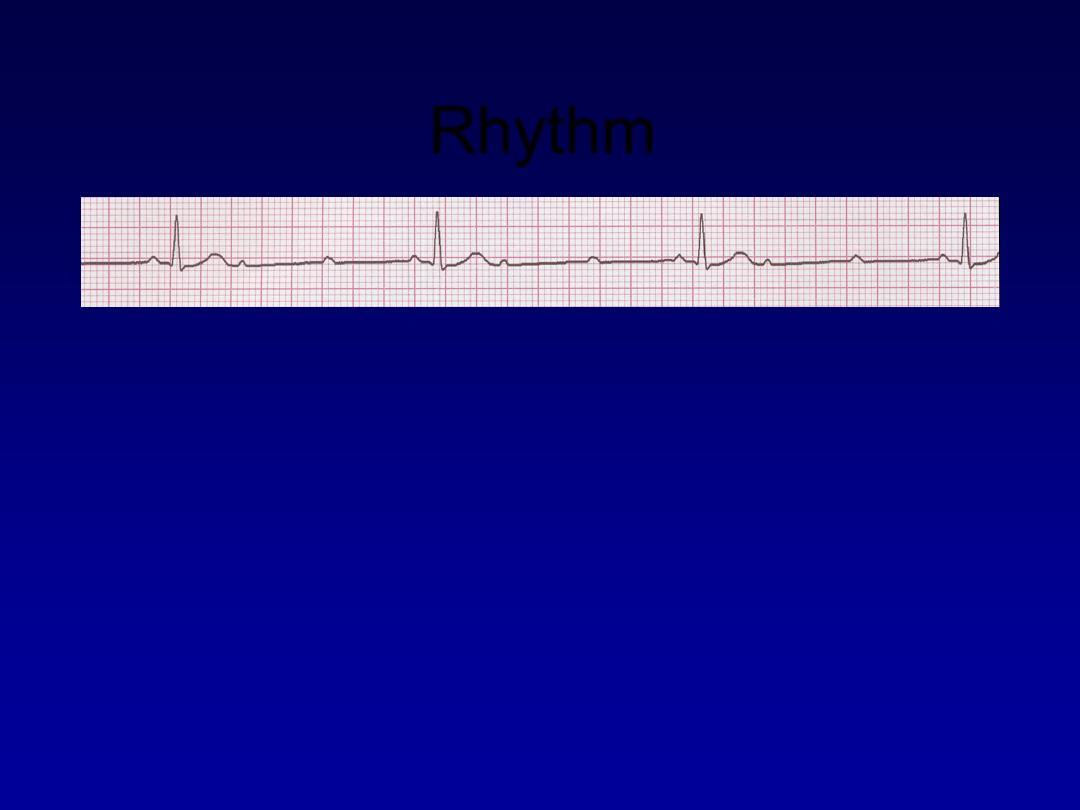
Rhythm
40 bpm
• Rate?
• Regularity?
regular
nl, 2 of 3 no QRS
0.08 s
• P waves?
• PR interval?
0.14 s
• QRS duration?
Interpretation?
2nd Degree AV Block, Type II

3rd Degree AV Block
•
Deviation from NSR
–
The P waves are completely blocked in
the AV junction; QRS complexes
originate independently from below the
junction.
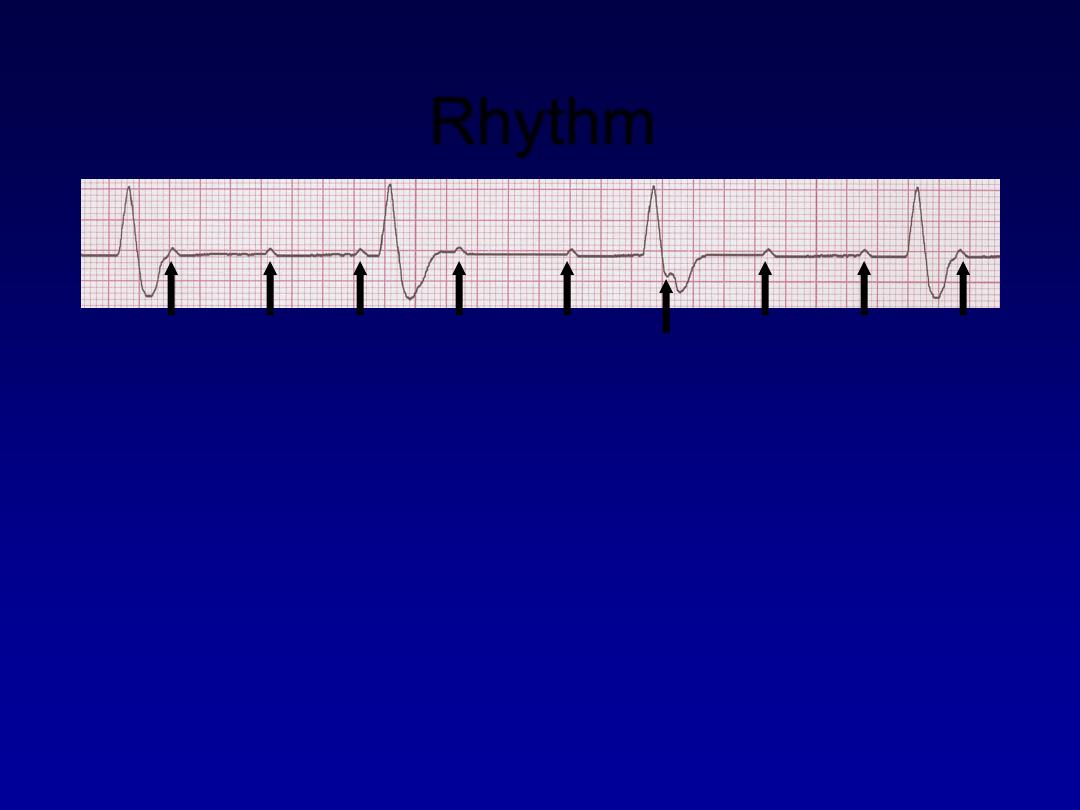
Rhythm
40 bpm
• Rate?
• Regularity?
regular
no relation to QRS
wide (> 0.12 s)
• P waves?
• PR interval?
none
• QRS duration?
Interpretation?
3rd Degree AV Block

Management of symptomatic heart
block

Bundle branch block and hemiblock
•
Left bundle branch block LBBB
•
Right bundle branch block RBBB
For more presentations www.medicalppt.blogspot.com
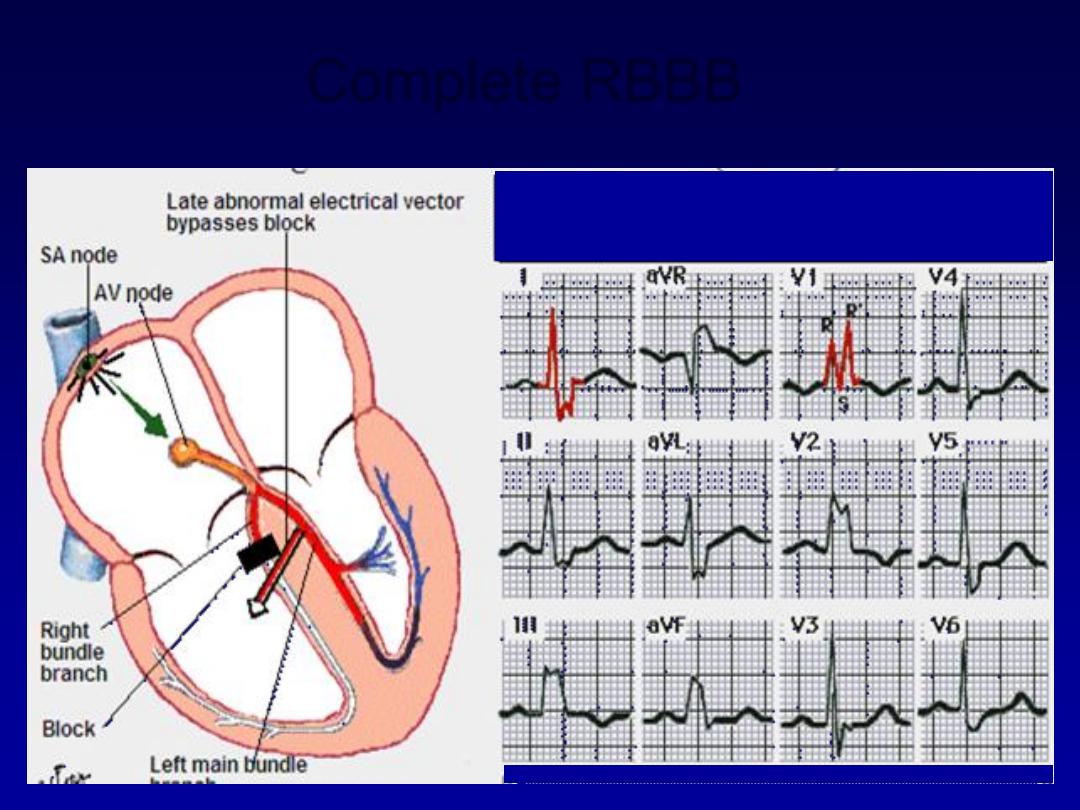
Complete RBBB
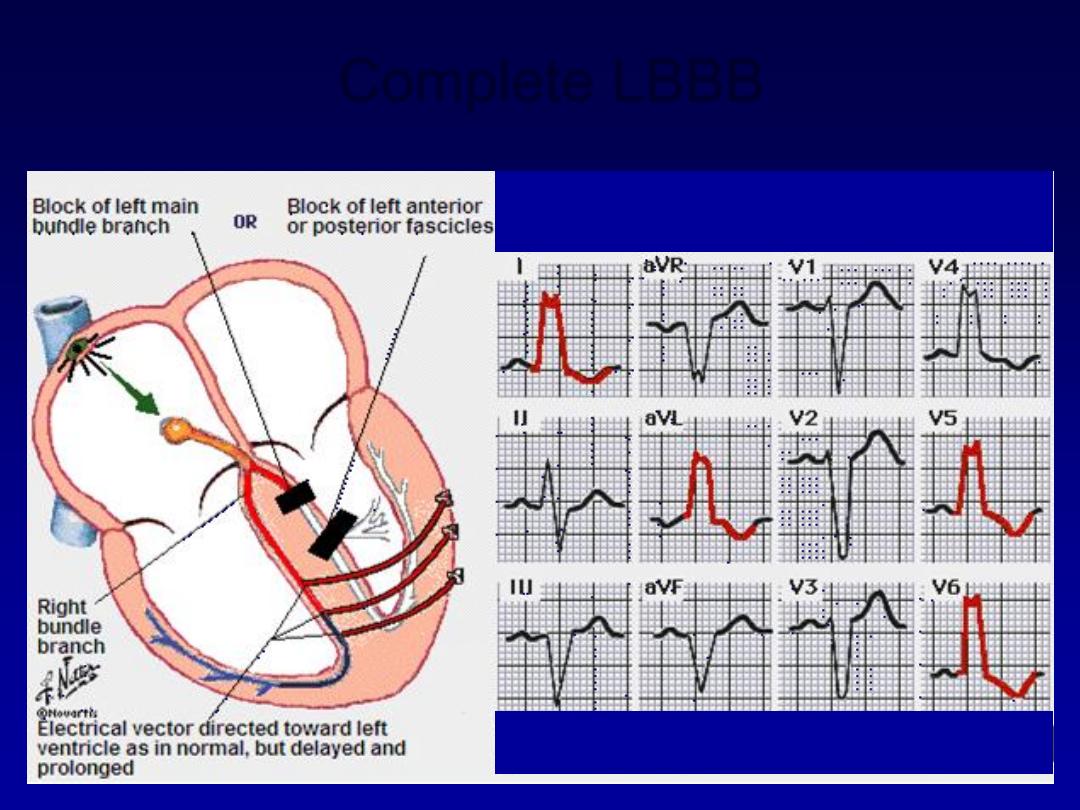
Complete LBBB
65

Questions
