
Diagnosis of TB
TB diagnostic tests—history
❖ • Microscopy (1880s)
❖ • Culture (1880s)
❖ • Chest x-ray (1930s)
❖ • Tuberculin skin test (Mantoux-1907; PPD-
1939
)
)
❖ • Nucleic acid amplification tests (1990s)
❖ • Interferon release assays (2000
Diagnosis of TB
❖ The key to the diagnosis of tuberculosis is a high index of suspicion.
❖ X-Ray
❖ Skin Test
❖ Direct demonstration of AFB in sample
❖ • Growth of TB bacilli in culture
Role of Chest X-ray
❖ No chest X-ray pattern is absolutely typical of TB.
❖ 10-15% of culture-positive TB patients not diagnosed by X-ray
❖ 40% of patients diagnosed as having TB on the basis of x-ray alone do not
have active TB
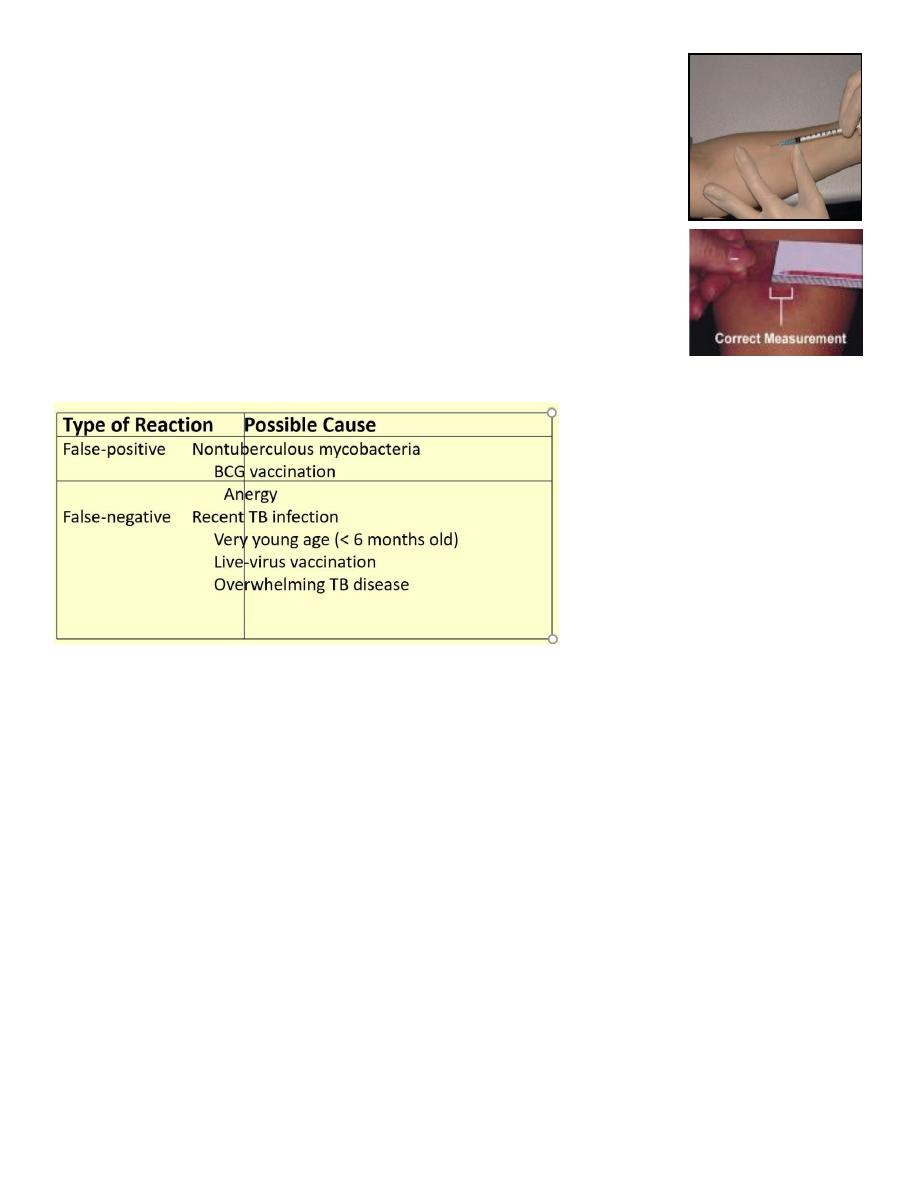
Administering Tuberculin Skin Test
• Purified protein derivative (PPD)
• TU PPD tuberculin.
• Read reaction 48-72 hours after injection
• Measure only induration
• Record reaction in millimet
Factors that affect the PPD Reaction
AFB Smear Microscopy
❖ Microscopy is a simple convenient test Requires minimal infrastructure and
equipment
❖ • Highly accurate, inexpensive and fast .
❖ • Accessible to the majority of patients Prioritizes infectious cases
❖ Fluorescence acid-fast staining is more expensive than conventional Ziehl–
Neelsen staining but is associated with a higher rate of detection because the
slides can be examined faster at lower magnifications.
Limitations of Microscopy Limitations of Microscopy
❖ Can not distinguish between dead or live bacteria .
❖ • High bacterial load >3000–5000 AFB 5000 AFB/mL is required for etection
• Can not do species identification •
❖ Can not perform Drug Sensitivity Test.
Culture Media main types
Egg = LJG, LJP, Stone brink, Ogawa
❖ Agar = 7H10, 7H11, Blood
❖ Liquid = Kirchner, 7H9, 7H12, Dubos
❖ New Types=
Bactec 460, MGIT, MB BacT . BACTEC 9000 MB system
❖ Septi-Chek AFB system (Becton Dickinson)
Radiometric Technology
❖ The only well established rapid radiometric method for detecting
mycobacteria in clinical specimens is the BACTEC 460TB system (Becton-
Dickinson Diagnostic Instruments Systems, Maryland).
❖ This system is based on the detection of radioactive carbon-dioxide produced
by bacterial metabolism of palmitic acid labelled with carbon 14.
❖ Growth of the mycobacteria can be detected within as few as 3 days, and
the mean time to detect the M. tuberculosis complex is about 14 days (87-
96%)
❖ BACTEC system, which employs a superscript 14C-labeled substrate medium
that is almost specific for mycobacteria. Instrument Systems, Sparks, Md. has
been reported to significantly decrease the time required for detection of
mycobacterial TB
❖ BACTEC method has provided more rapid growth (average, 9 -14days),
specific identification of M. tuberculosis (5 days), and rapid drug
susceptibility testing (6 days).
Non-Radiometric Technology
❖ BACTEC 9000 MB system (Becton Dickinson).This system uses MYCO/F
medium, a modified Middlebrook 7H9 broth.(8-13 days)
❖ The system responds to changes in oxygen concentration. Each vial contains
a silicon rubber disk, impregnated with a ruthenium metal complex, which
serves as an oxygen-specific sensor. Oxygen quenches the fluorescent output
of the sensor.
❖ Oxygen consumption by microorganisms can be detected by the increase in
fluorescence.
▪ BACTEC 960 MGIT ,MGITstands for Mycobacteria Growth Indicator Tube,
and 960 indicates the total number of culture tubes it can hold at any given
time

▪ Evaluation of mycobacteria recovery from the fluorometric BACTEC 960 and
the radiometric BACTEC 460 TB system have shown that they are more
sensitive in recovery of mycobacteria than the conventional L-J and smear
microscopy.
▪ There is no significant difference between the radiometric BACTEC 460 TB
and the fluorometric BACTEC 960 with 91.9% positivity and 95.1% positivity
respectively.
❖ Results available in 7-14 days
Cytokine Release Assays
QuantiFERON-TB GOLD test .
❖ Blood samples must be processed within 12 hours after collection while
white blood cells are still viable.
❖ followed by measurement of Interferon-gamma Assays released by
sensitized lymphocytes in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
At present, the QuantiFERON-Gold TB test is recommended for screening for
latent tuberculosis infection .
After incubation of the blood with antigens for 16 to 24 hours, The white blood
cells will release IFN-gamma in response to contact with the TB antigens ,the
amount of interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) is measured.
❖ QuantiFERON-TB GOLD test
❖ Should not give false-positive result due to:
❖ BCG vaccination
❖ Nontuberculous mycobacteria.
❖ The test’s performance may be enhanced by the use the Early
Secreted Antigen Target -6 (ESAT-6 ) and Culture Filtrate Protien-
10 (CPF-10).

The Xpert MTB/RIF TB Test
❖ Mean time for Detection of MTB
• GeneXpert = < day,
• Microscopy = 1 day,
• Liquid culture - MGIT = 17 days,
• Solid Culture = > 30 days
❖ Mean time for Detection of Rifampicin Resistance
• GeneXpert = < 1day
• Liquid DST = 30 days
• Conventional DST ( Solid proportional Method) = 75 days
How does the test work?
• Detects DNA sequences specific for Mycobacterium Tuberculosis and
Rifampicin resistance by PCR
• Based on Nucleic Acid Amplification Test (NAAT). The Xpert® MTB/RIF
❖ purifies
❖ concentrates
❖ amplifies (by real-time PCR) and
❖ identifies targeted nucleic acid sequences in the Mycobacterium
tuberculosis genome,
The Xpert MTB/RIF TB Test
The Xpert MTB/RIF is a cartridge-based, automated diagnostic test that can
identify Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) and resistance to rifampicin (RIF).
In December 2010 WHO endorsed the Xpert MTB/RIF technology and released a
recommendation and guidance
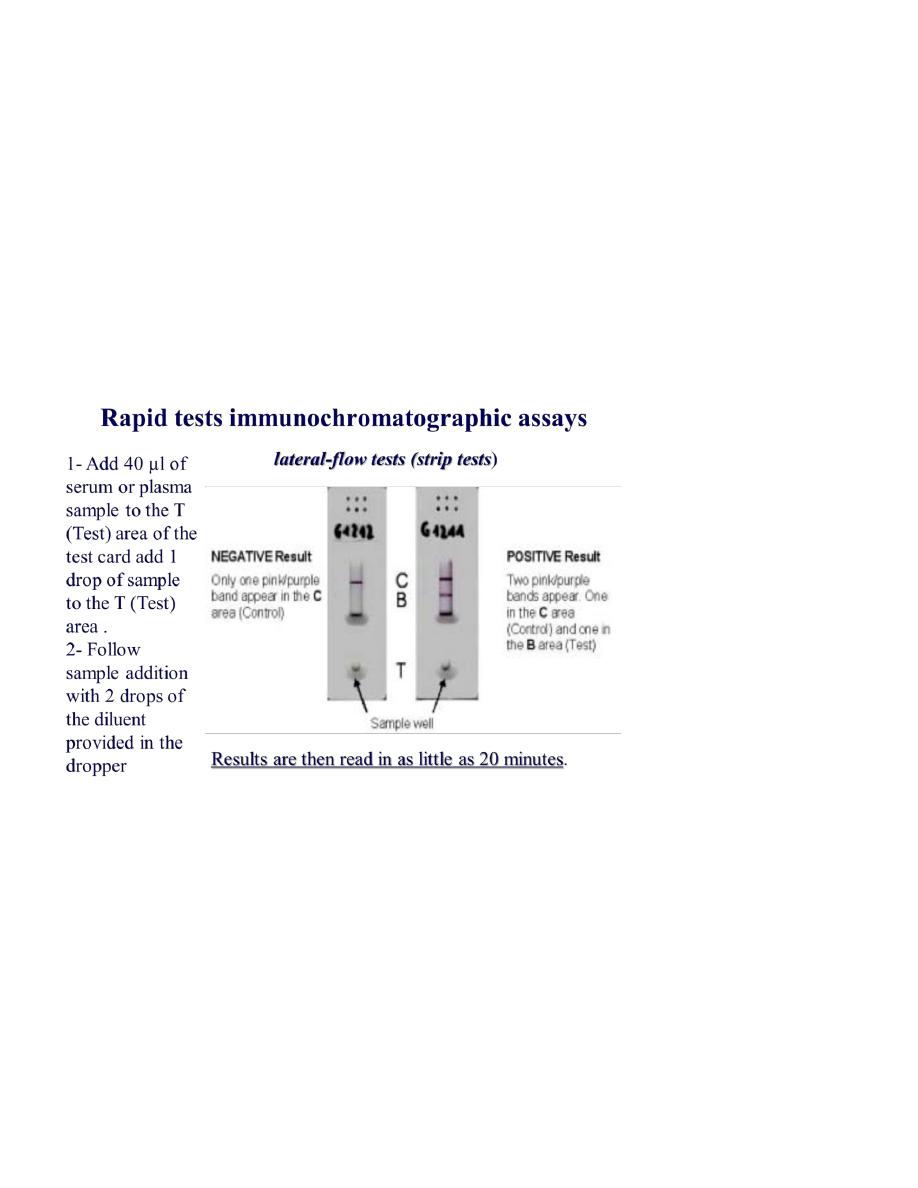
Rapid tests immunochromatographic assays
lateral-flow tests or simply strip tests
❖ 1- Add 40 µl of serum or plasma sample to the T (Test) area of the test card
add 1 drop of sample to the T (Test) area .
❖ 2- Follow sample addition with 2 drops of the diluent provided in the dropper
❖ bottle by holding the bottle vertically over the T (Test) Area.
❖ 3- Results are then read in as little as 20 minutes.
ESAT-6 and CFP10
❖ Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific antigens (ESAT-6 and CFP10) in
experimental animals as well as during natural infection in humans and
cattle.
❖ combination of ESAT-6 and CFP10 was found to be highly sensitive and
specific for both in vivo and in vitro diagnosis.

❖ In humans, the combination had a high sensitivity (73%) and a much higher
specificity (93%) for active tuberculosis than PPD (7%).
Enzyme-linked immunospot assay
T-cell–based interferon-γ release assay
❖ The ELISpot
PLUS
assay incorporates a novel region of difference-1 encoded
antigen, Rv3879c, alongside the ESAT-6 and CFP10.
❖ ELISpot
PLUS
sensitivity is 89%
higher than that of the standard ELISpot.
❖ The combined sensitivity
of ELISpot
PLUS
and tuberculin skin testing in
confirmed and
highly probable cases of TB was 99%.
Serologic Diagnosis of Tuberculosis
ELISA measurement of Ig antibody to mycobacterial antigens
❖ Antigen 60 IgG measurement
❖ Antigen 38kda IgG Antigen Kp90 IgA &measurement
❖ Antigen 60 IgG seemed to be superior to the others (i.e., the cutoff value
was justified by both the sensitivity and the specificity .
❖ Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med., Volume 156, Number 3, September 1997, 906-
911
❖ Antituberculous glycolipid antigen TBGL.
❖ The lipoarabinomannan (LAM) polysaccharide antigen.
❖ Antigen 60 (A60), which is derived from purified protein derivatives.
❖ The combination of LAM, A60, and TBGL appears to be the best choice of
antigens for the serodiagnosis of TB

Chemical Detection of Biologic Compounds
❖ Adenosine deaminase, a host enzyme produced by activated T cells and
easily detected by a colorimetric procedure, was shown to increase in
concentration during the active stages of tuberculous meningitis and to
decrease to normal levels after effective antituberculosis therapy.
❖ A more complicated technology detects the presence of tuberculostatic acid
in the spinal fluid or serum of patients.
Gen-Probe AMPLIFIED TM
❖ The MTT&MTD are chemical tests, the amplification is to produce sufficient
nucleic acid, within a few hours, these tests can recognize MTC in an AFB-
positive specimen, with nearly 96% sensitivity and 100% specificity.
❖ The NAA result can be falsely negative if there are very few tubercle bacilli,
❖ NAA test can amplify DNA from both viable and non-viable organisms.
❖ Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
❖ Yield 95% of smear+ and only 50% of smear negatives.
❖ main advantages: speed + sensitivity
❖ sensitivity :
❖ in principle able to pick up 1 TB bacillus
❖ in practice : less sensitive than culture
❖ Serve only the diagnosis not monitor the treatment outcome
❖ Cannot replace culture
❖ Not able to determine infectiousness.
❖ Very expensive ($50-$100 per assay)

Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction Techniques
❖ Real-time PCR methods are based on hybridization of amplified nucleic acids
with fluorescent-labelled probes spanning DNA regions of interest and
monitored inside thermal cyclers.
❖ The main advantage of real-time PCR methods is its speed in giving
results,1.5-2.0 h after DNA extraction.
Non-molecular Techniques
The FastPlaque Tuberculosis Assay
❖ The FastPlaque TB assay , relies on the ability of M. tuberculosis to support
the growth of an infecting mycobacteriophage. The assay have shown a
sensitivity of 50-65% in smear-negative specimens with specificity of 98% .
❖ It is a rapid, manual test, easy to perform and has a higher sensitivity than
microscopy, in newly diagnosed smear +ve pts.
Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 1998;2: 160
