

• 45 yr-old-male
• Asymptomatic
• Abnormal liver enzymes
– ALT
55 (<40)
– AST
42 (<40)
– Bili, Alk, GGTP
WNL

• What do you want to know ?
• Risk factors for hepatitis ?
• What do you do next ?

• What do you want to know ?
• Risk factors for hepatitis ?
• What do you do next ?
More detailed history
Recent viral infection
Co-morbid conditions
Recent surgeries
Family history
Medications
Recreational drugs
ETOH use
Occupation

• What do you want to know ?
• Risk factors for hepatitis ?
• What do you do next ?
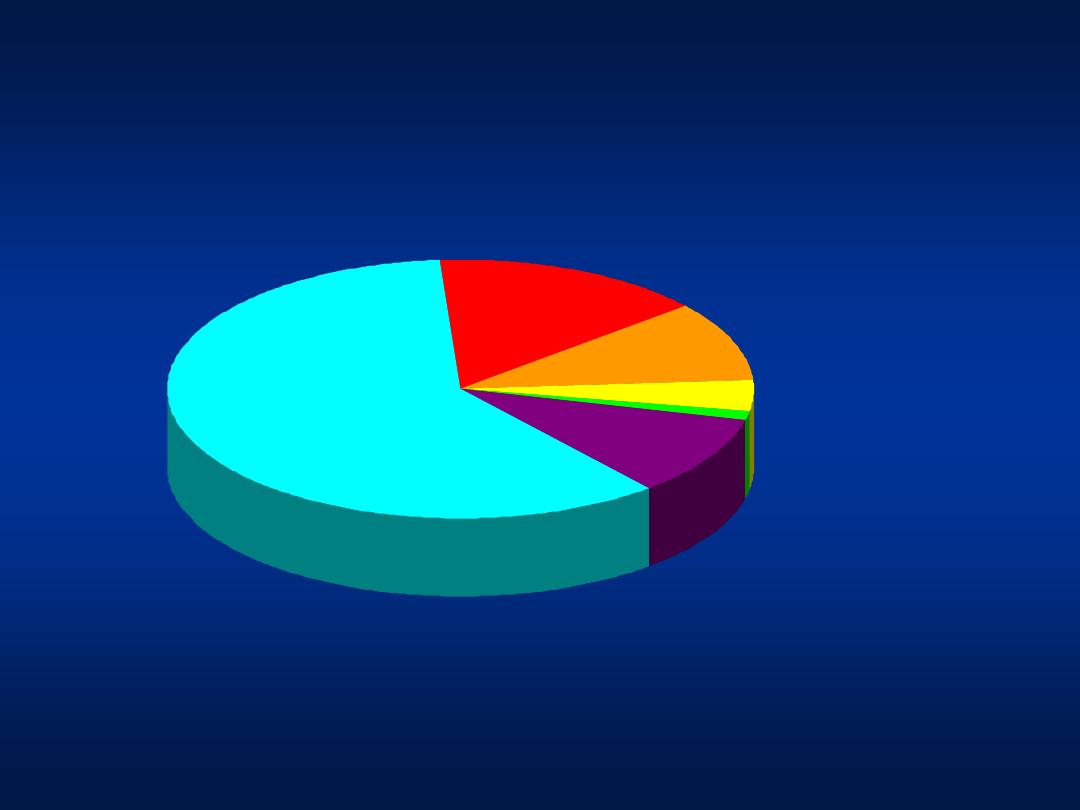
Sources of Infection
Sexual 15%
Other 1%*
Unknown 10%
Injecting drug use 60%
Transfusion 10%
(before screening)
*
Nosocomial; iatrogenic; perinatal
Occupational 4%
Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
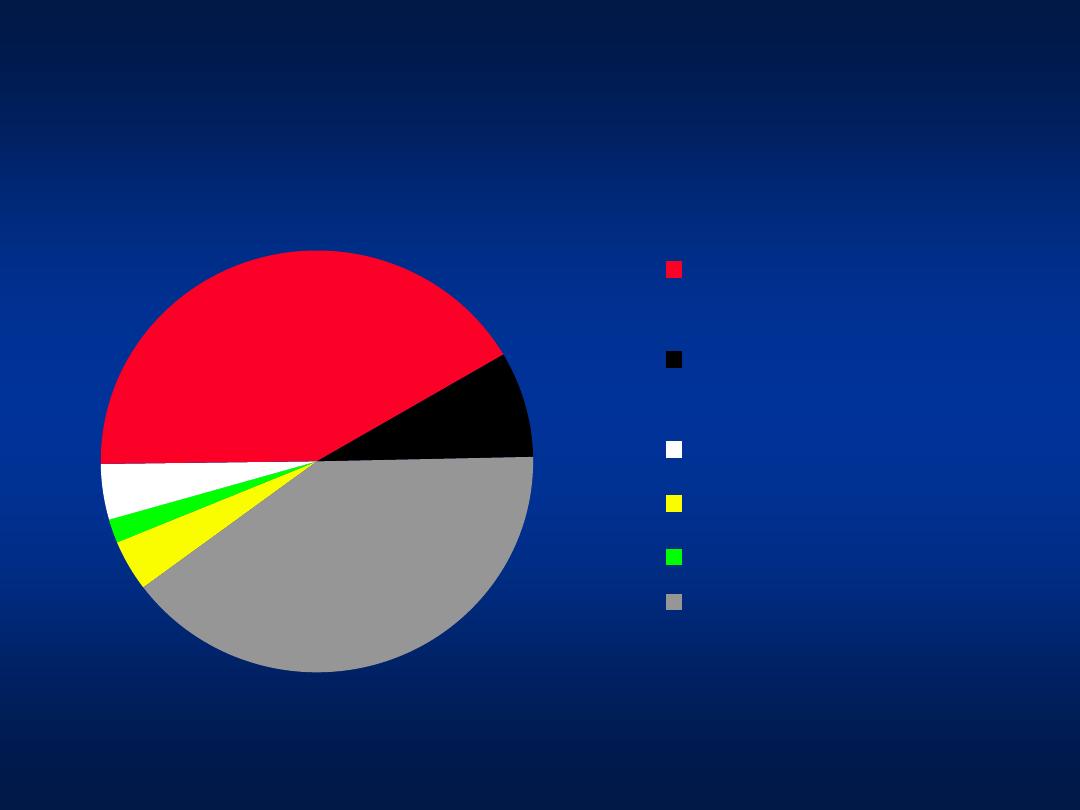
Modes of Transmission
Blood
Transfusion
prior to 1995
Blood transfusion
after 1995
Tattooing
Hemodialysis
IVDA
Unknown
4%
2%
4%
42%
8%
40%
Khatib et al, Unpublished data 2004
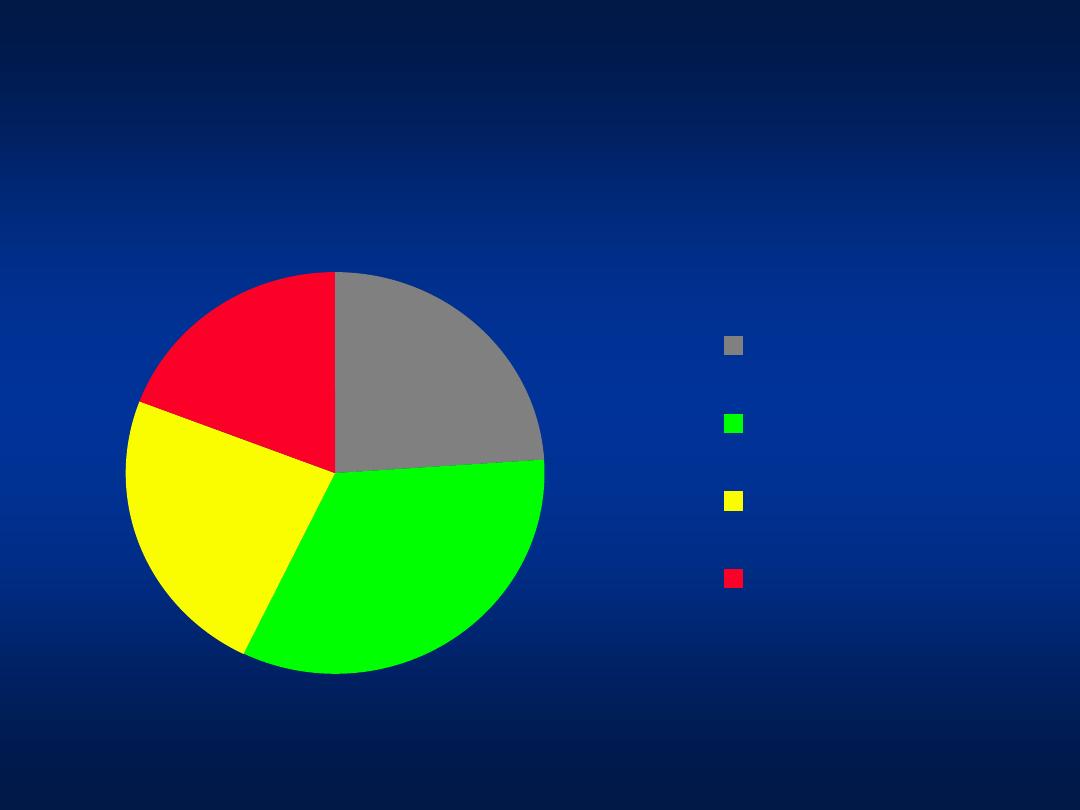
Modes of transmission
24%
33%
24%
19%
No risk factors
Circumcision at
home
Minor Surgical
procedure
Dental procedure
Khatib et al, Unpublished data 2004
Patients with unknown risk factors

• What do you want to know ?
• Risk factors for hepatitis ?
• What do you do next ?

• HBsAg
• HCV ab
• RUQ ultrasound
• ANA
• ASMA
• Anti LKM ab
• Lipid profile
• Fasting blood sugar
• Complete physical
examination

• HBsAg
+
• HBeAg
-
• Anti-HBe
+
• Anti-HBc
+
HCV ab -
RUQ US WNL
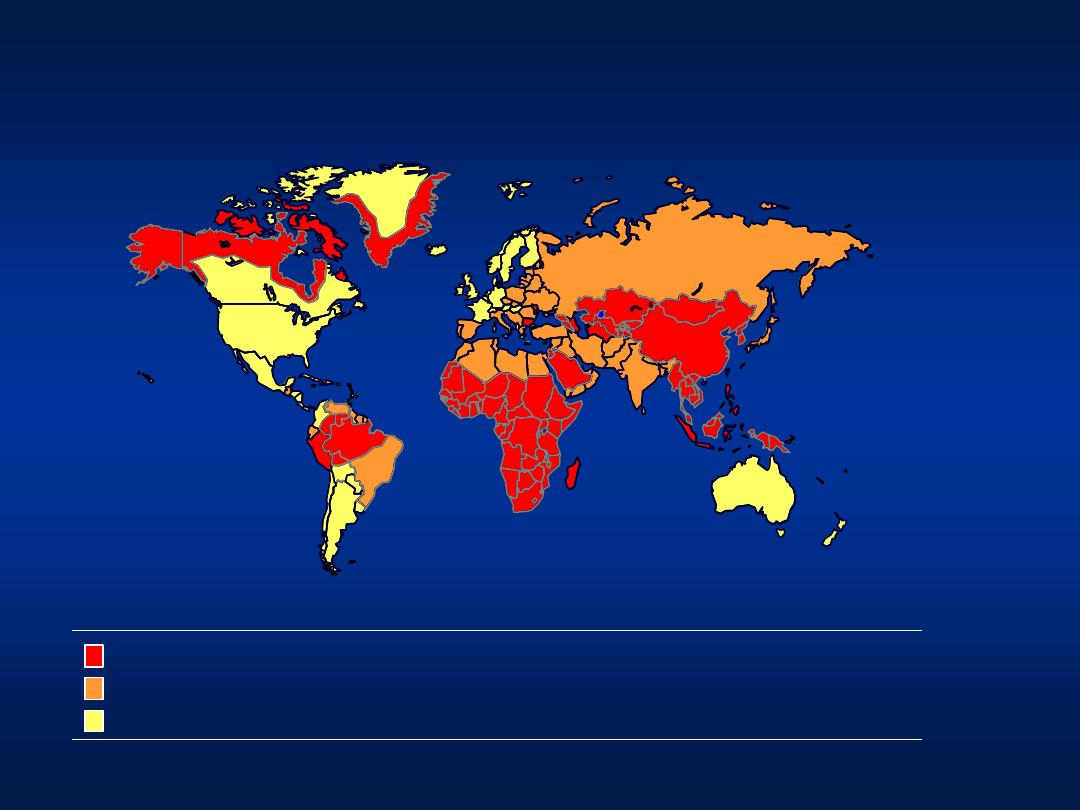
HBV Distribution
Chronic infection
prevalence
8% – High
2
–7% – Intermediate
< 2%
– Low
Predominant age at infection
Early childhood
Perinatal and early childhood
Adult
Past infection
prevalence
40
– 90%
16
– 55%
4
– 15%
CDC, 1991
HBsAg Prevalence in Arab Countries
Bahrain
0.9-1.3%
Tunisia
7%
UAE
2-5%
Kuwait
2%
Oman
2-10%
Morocco
6%
Jordan
3-10%
Palestine
5-6%
Iraq
4-5%
S. Arabia
6-8%
Egypt
3-11%
Yemen
12-18%
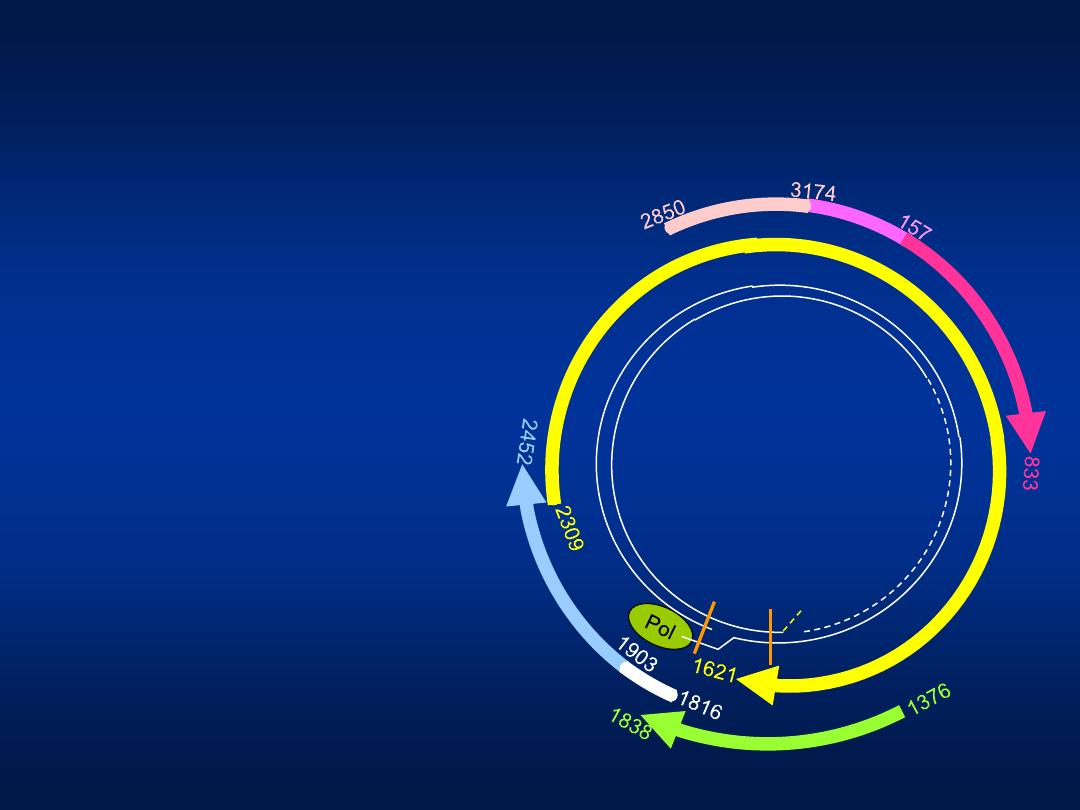
preS2
(+)
(-)
DR1 DR2
POL
preS1
S
X
Pre-core
Core
The HBV Genome
•
The HBV genome contains
only four potential genes
(S, C, P, and X), which
overlap
•
S: surface : envelope
(HBsAg)
•
C: core: nucleocapsid
(HBcAg)
•
Pre-core: HBeAg
•
P: polymerase
•
X: transcription activator
Lee WM. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997; 337:1733
–45

Hepatitis B
Mutations
• Precore mutation (G1896A)
– Abolishes HBeAg production
• Core promotor mutation (A1762T, G1764A)
– Down-regulates HBeAg production
• Treatment-induced mutations
– YMDD: Induced by Lamivudine (20%/year)1
– N236T: Induced by Adefovir (1.7%/year)2
1 Lai C. Clin Infec Dis 2003;36;687-696
2 Xiang S. et al. J Hepatol 2003;38(2);102
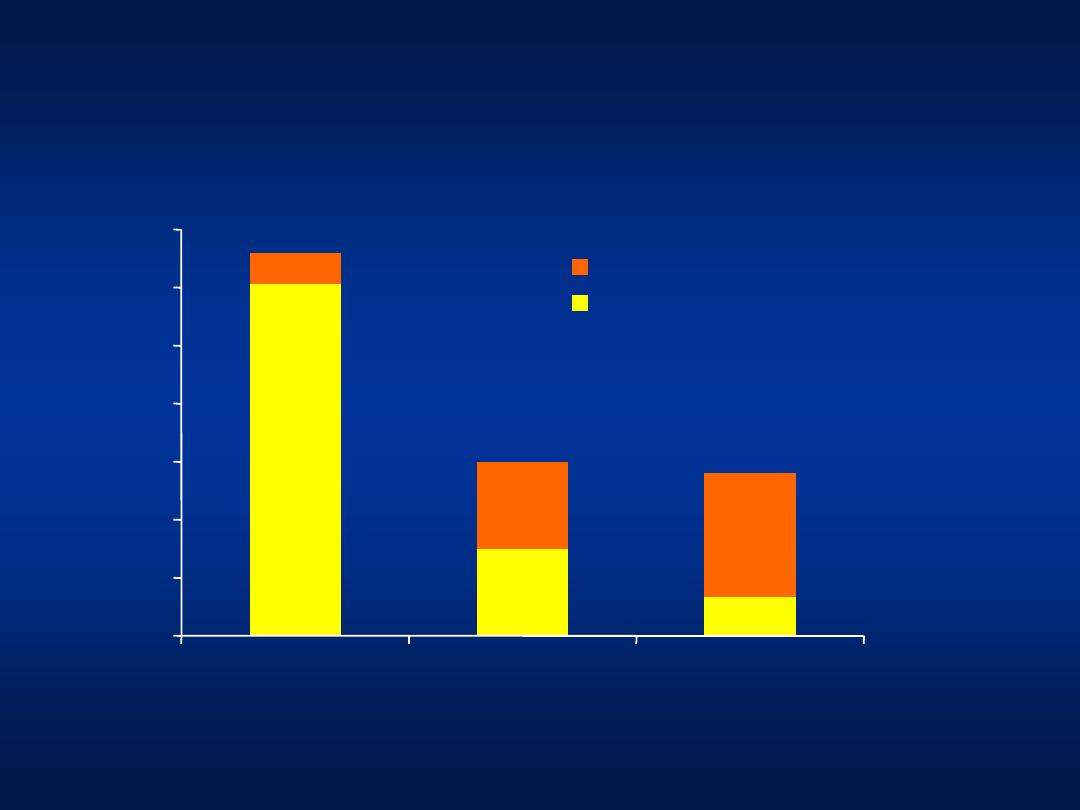
Hepatitis B
Prevalence of HBeAg-Negative
Funk ML, et al. J. Viral Hep. 2002; 9:52
–61
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
Mediterranean
Asia Pacific
USA and Northern
Europe
Percent
o
f
CHB
p
atie
nts
HBeAg-negative CHB
Pre-core stop variant
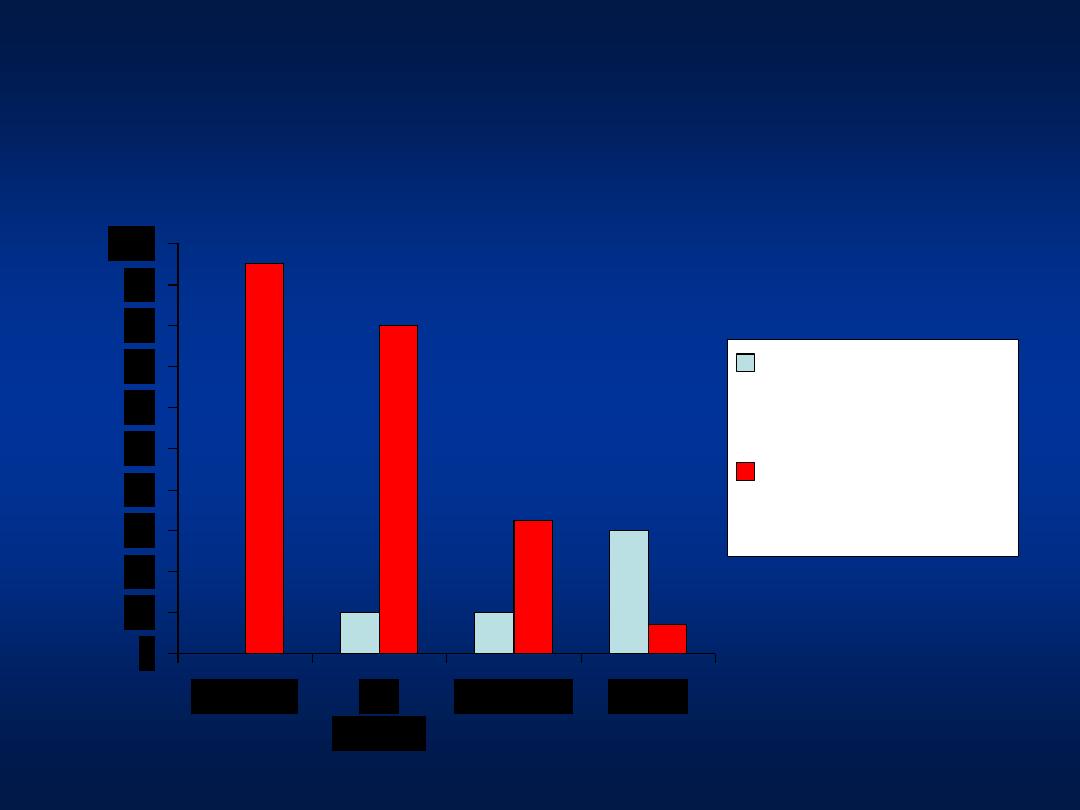
Age Factor in Acute HBV Infection
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
Neonate
< 6
months
1-4 years
Adults
Frequency of
clinically apparent
acute hepatitis B
Frequency of
subsequent chronic
infection
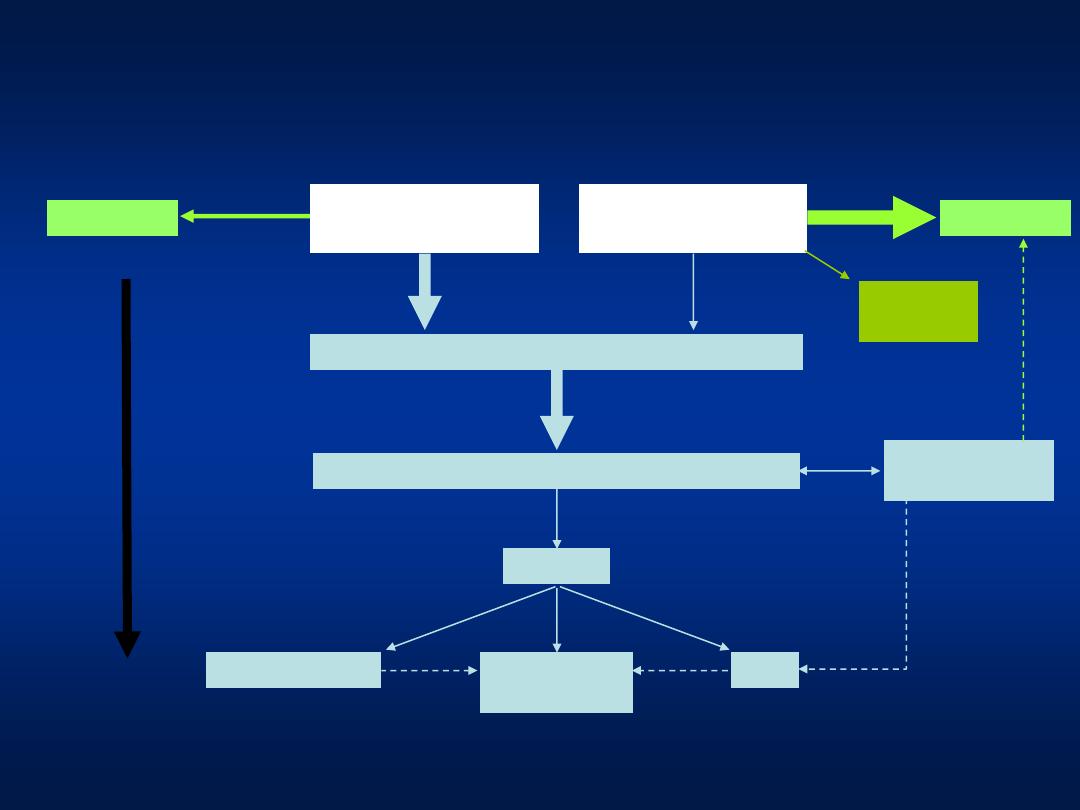
The Clinical Outcomes of HBV Infection
Adapted from EASL Consensus Statement. J. Hepatol. 2003; 39 (S1):S3
–25
Chronic infection
Cirrhosis
HCC
Decompensation
Inactive carrier
state
Adult
acute infection
Recovery
Fulminant
hepatitis
95%
< 1%
30–90%
5–50
years
Transplant
or Death
Perinatal/childhood
acute infection
Recovery
10–70%
< 5%
Mild, moderate or severe chronic hepatitis
1*
0.1*
2–10*
4*
3*
2–8*
*
per 100 patient-years
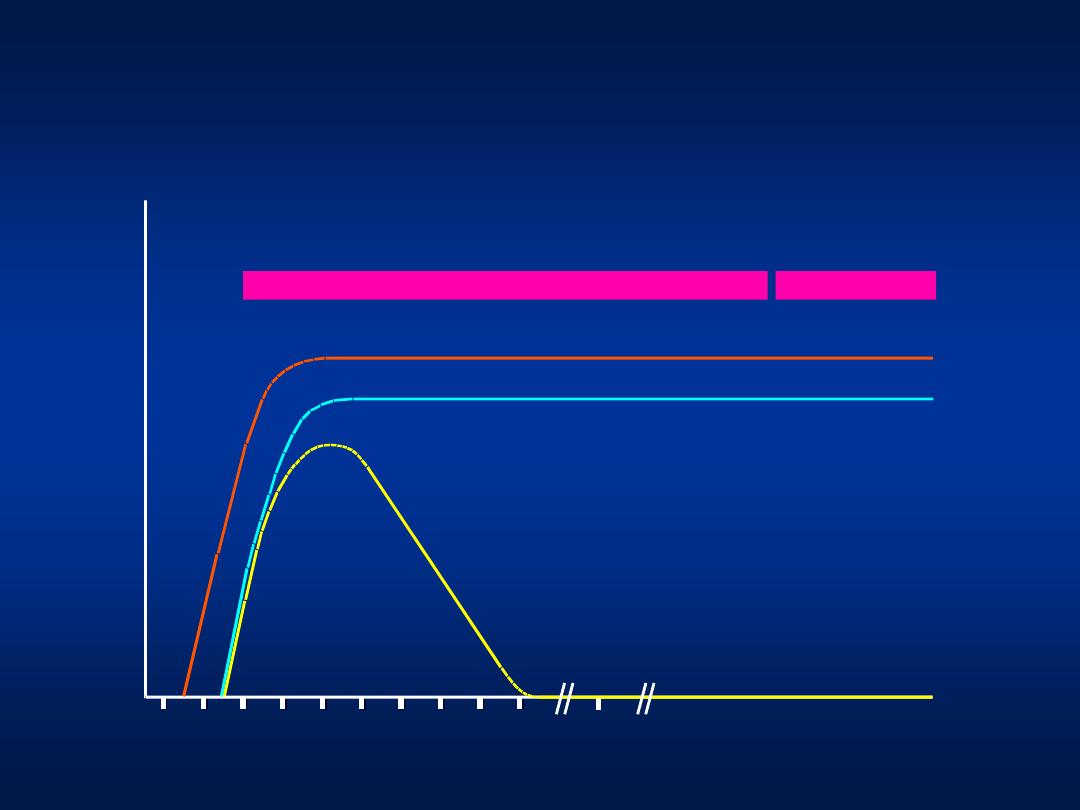
Weeks after exposure
Titer
IgM anti-HBc
Total anti-HBc
HBsAg
Acute
(6 months)
HBeAg
Chronic
(years)
anti-HBe
0
4
8 12 16 20 24 28 32 36
52
Years
Serologic Course of Chronic HBV
Infection

Phases of Chronic HBV Infection
• Replicative Phase (Immunoactive):
– Immune Tolerance Phase: only in perinatally
acquired disease, lasts 10-30 years. No active liver
disease.
HBeAg+ve, high HBV DNA, but normal ALT and
biopsy
– Immune Clearance Phase: Chronic hepatitis B.
Active liver disease present.
HBV DNA in serum, high ALT, abnormal biopsy
(HBeAg positive/ HBeAg negative)
• Non-replicative Phase
– HBeAg –ve, anti-Hbe +ve, undetectable HBV DNA

Replicative Phase
• HBeAg positive and anti-HBe negative (wild
Type)
• HBeAg negative and anti-HBe positive
(precore or core promotor mutants)
• HBV DNA high: 10
4
-10
8
copies/ml
• ALT persistently or intermittently elevated
• Symptoms presents or absent

Non-replicative Phase
• HBeAg negative and anti-HBe positive
• HBV DNA low 10
2
-10
4
copies/ml
• ALT persistently normal
• HBsAg may later become negative
(with development of anti-HBs)

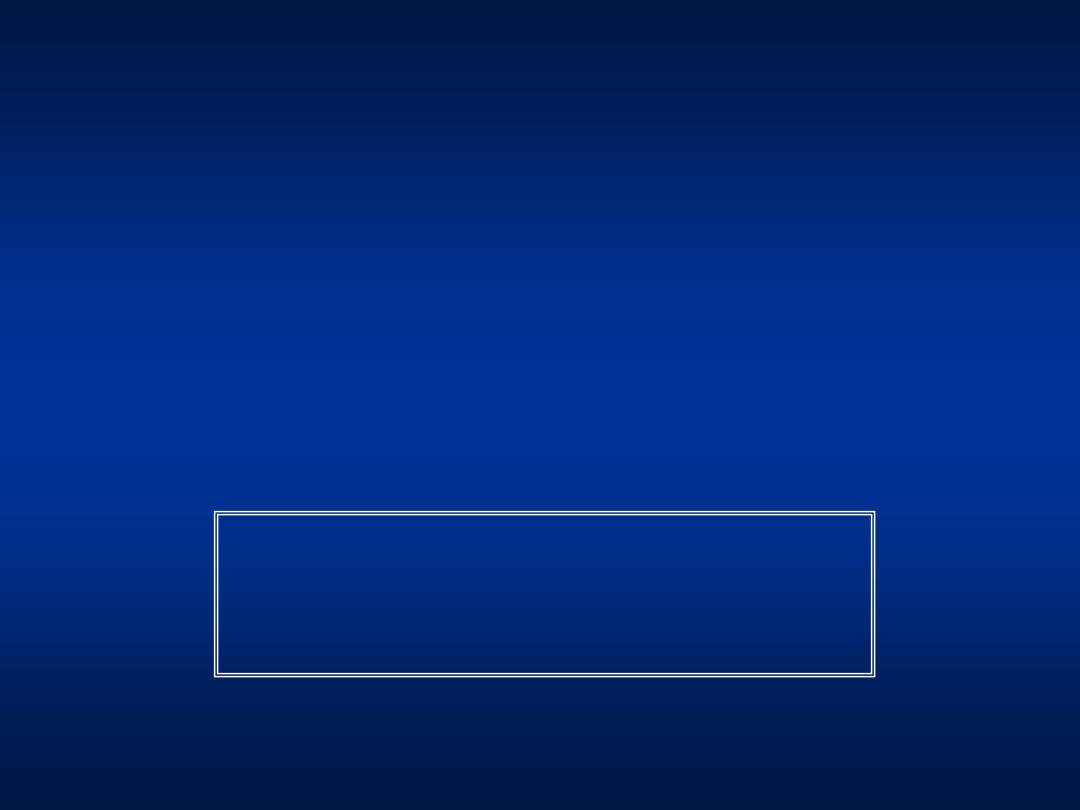
• HBsAg -
• Anti-HBs +
• Anti-HBc +
• HBeAg -
Previous Infection
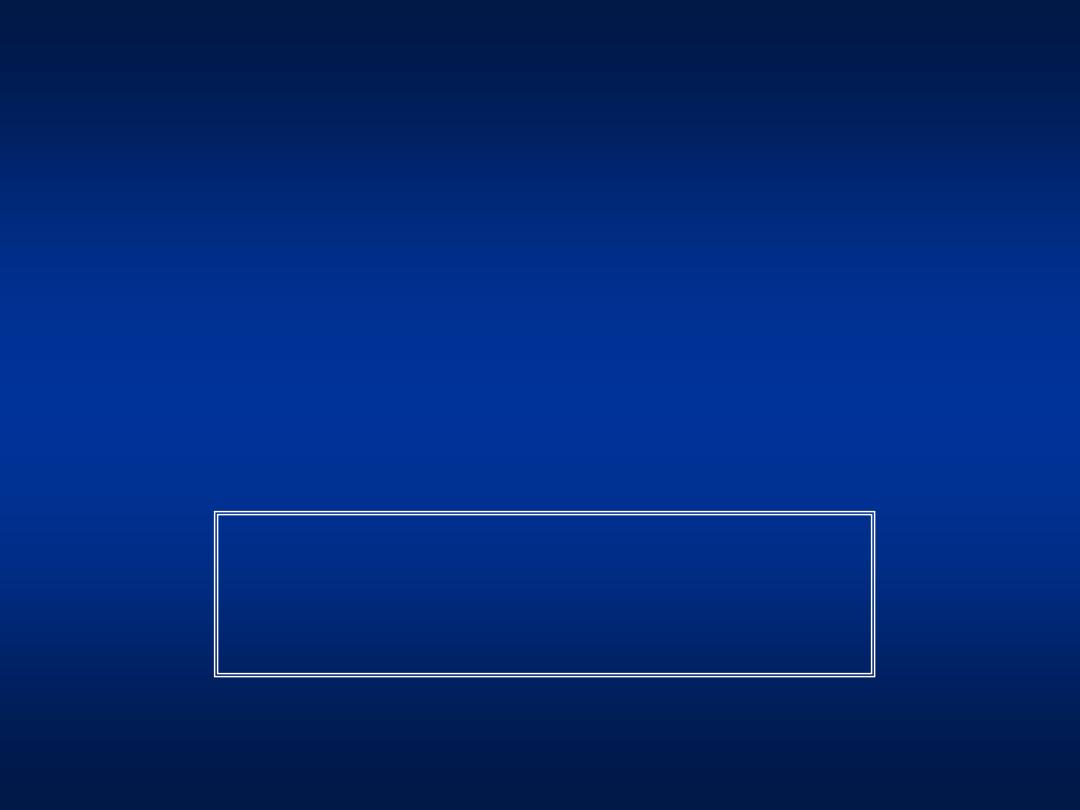
• HBsAg -
• Anti-HBs +
• Anti-HBc -
• HBeAg -
Vaccinated

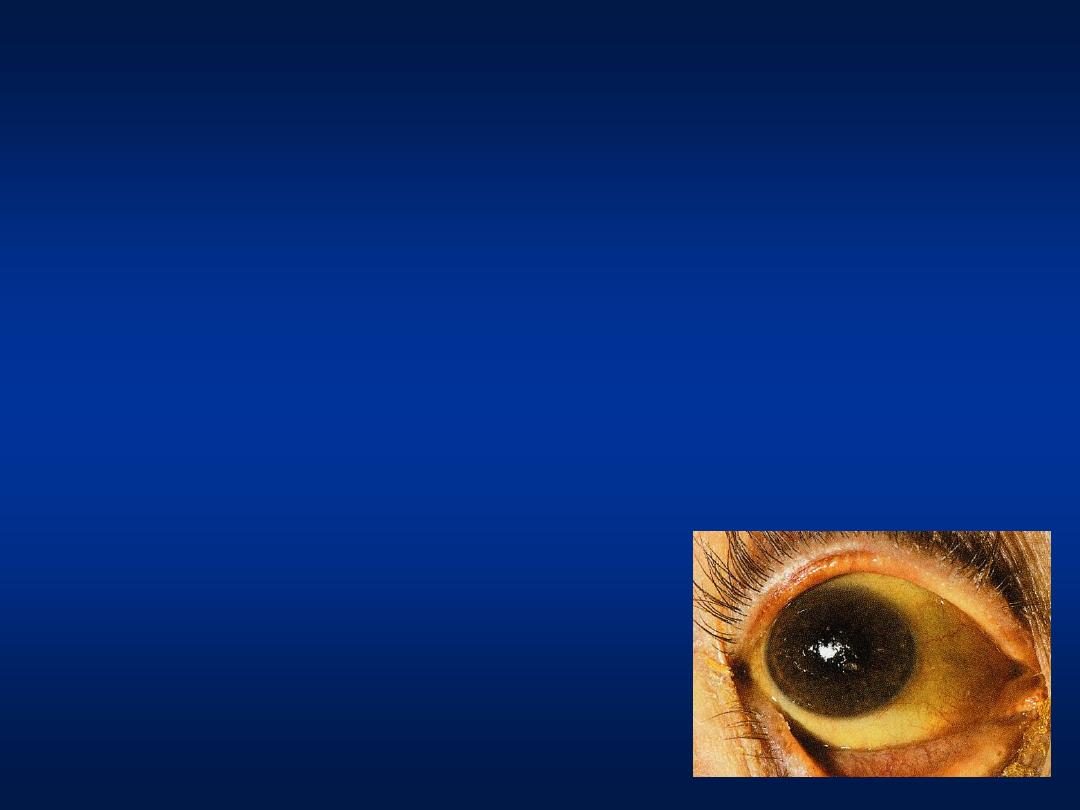
• A 19 year-old University student,
presented with flu-like symptoms of 1
week duration, followed by lethargy and
confusion.
• Clinically, she appeared jaundiced, with
decreased level of consciousness, but did
not have stigmata of chronic liver disease.

• HBsAg
• Anti-HBc IgM
• HCV ab
• HAV IgM
• ANA
• Ceruplasmin
• RUQ U/S

• PT/INR 2.2
• Albumin 3.9
• HBsAg Negative
• HCV ab Negative
• HAV IgM Positive
• Diagnosis
Fulminant Liver Failure
Acute Hepatitis A
Case 1
Labs showed:
AST
1198
ALT
1400
ALK
1189
T. Bili
16
Ammonia 225

Questions
• Is Hepatitis A a fatal disease ?
• Do we need to get Vaccinated ?
• What kind of immunization do we
have and is it effective?

Questions
• Is Hepatitis A a fatal disease ?
• Do we need to get Vaccinated ?
• What kind of immunization do we
have and is it effective?
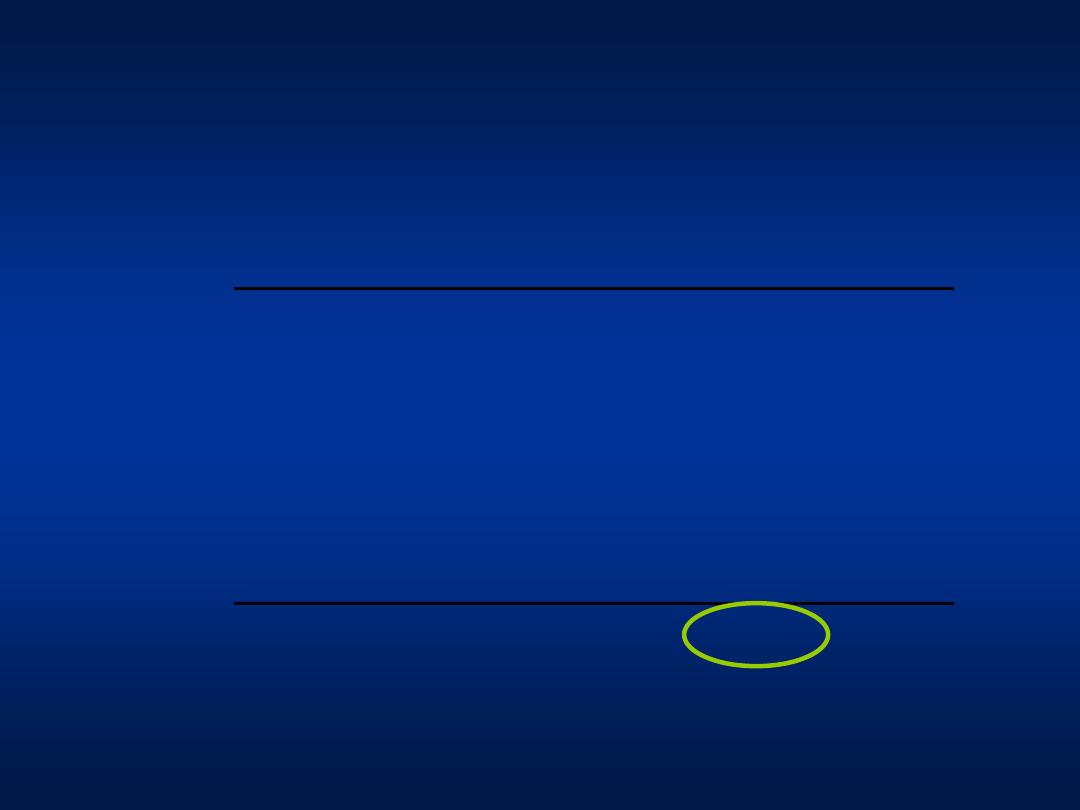
Hepatitis A
Age
– specific fatality
Age group (years)
Case-fatality (per 1000)
<5
3.0
5-14
1.6
15-29
1.6
30-49
3.8
>49
17.5
Total
4.1
CDC Viral Hepatitis Surveillance Program, 1983-1989

Questions
• Is Hepatitis A a fatal disease ?
• Do we need to get Vaccinated ?
• What kind of immunization do we
have and is it effective?

Endemicity
Peak Age
Transmission Pattern
High
Early
Childhood
Person to person,
Outbreaks uncommon
Intermediate
Late
childhood/
young adults
Person to person
Food and water outbreaks
Low
Adults
Travelers,
Outbreaks uncommon
Hepatitis A
Transmission and Epidemics
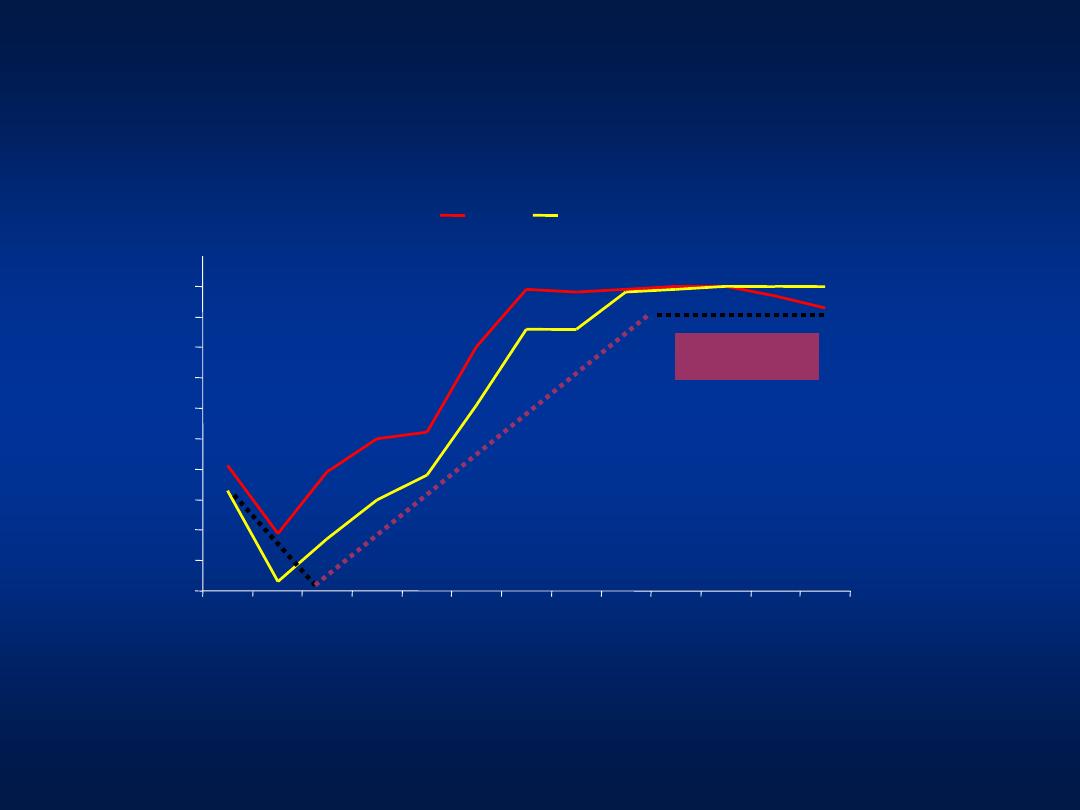
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
0-1
1-2
2-3
3-4
4-5
5-10
10-
15
15-
20
20-
30
30-
40
40-
50
50-
60
>60
Age (years)
Pro
p
o
rtion
(%)
1988
1996
Hepatitis A
Age-Prevalence Shift in Hepatitis A
Now !!!
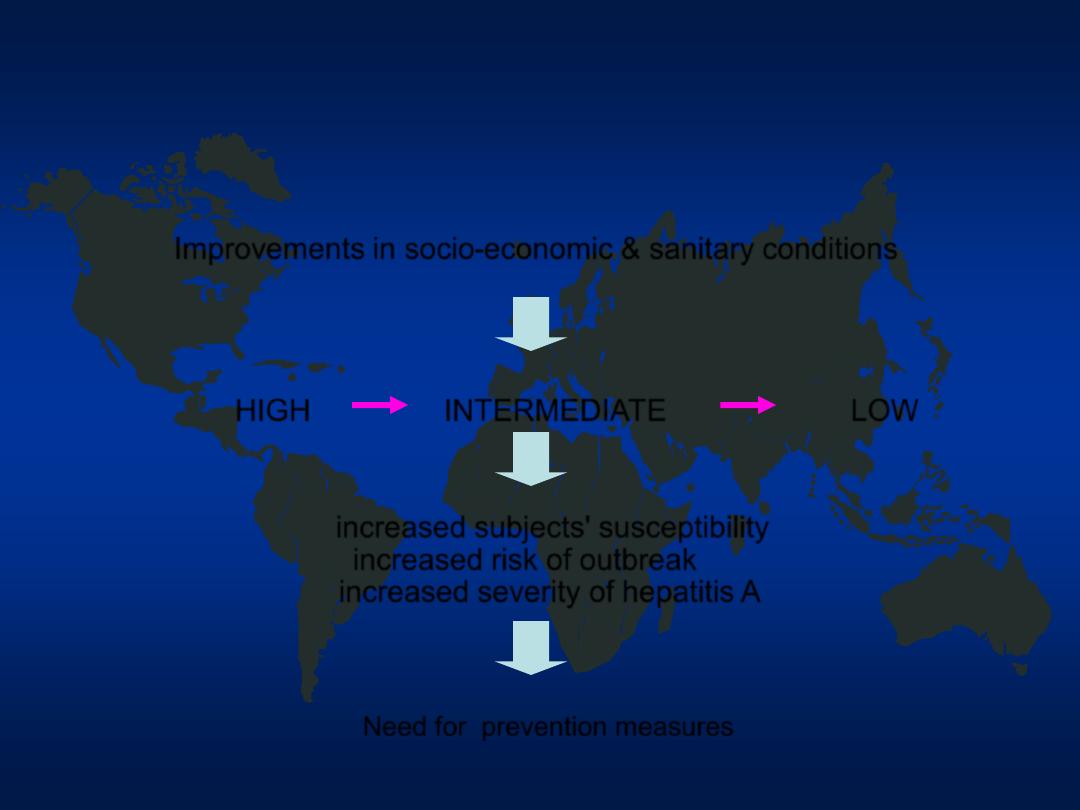
Improvements in socio-economic & sanitary conditions
HIGH
INTERMEDIATE
LOW
increased subjects' susceptibility
increased risk of outbreak
increased severity of hepatitis A
Need for prevention measures
Hepatitis A
Changing Epidemiology in Jordan

Questions
• Is Hepatitis A a fatal disease ?
• Do we need to get Vaccinated ?
• What kind of immunization do we
have, and is it effective?
Hepatitis A
Prevention
Few
Few
Systemic
Several
2
number of
injections
Mild
Mild
Local
Side effects
Day 1
<14 days
Onset of protection
3-5 months
10 years
Duration
85%
97%
Efficacy
Immunoglobulin
Vaccination

• A 35 year-old male gentleman presented to
the clinic after a pre-employment test. He
was found to be HBsAg positive.
• He is asymptomatic and his physical exam
is normal.
• Labs
– ALT
65
– AST
48
– ALK
88
– T.Bili
1.0
– INR
1.1
– Albumin 4.2
Case 2
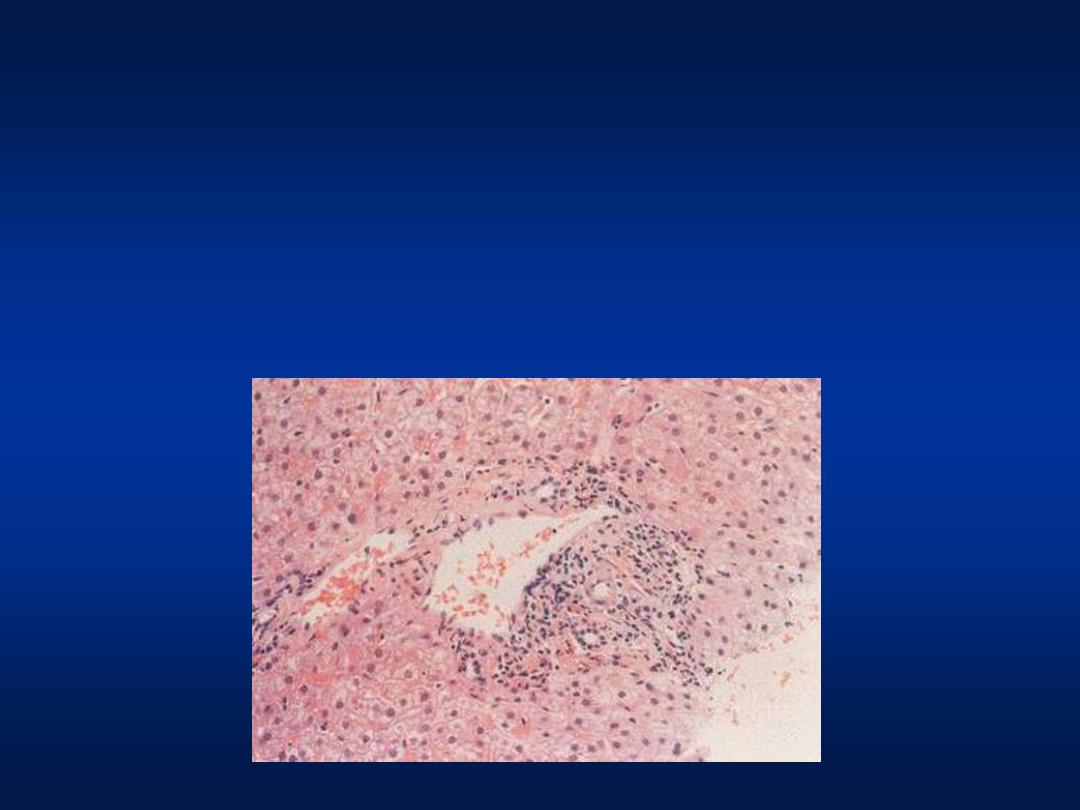
• HCV RNA PCR
Positive
• Liver Biopsy Grade II stage III
• Diagnosis
Chronic Hepatitis C
Case 3

Questions
• What are risk factors for Hepatitis
C transmission?
• Did he acquire the infection from
blood transfusion?
• Is hepatitis C a treatable disease?
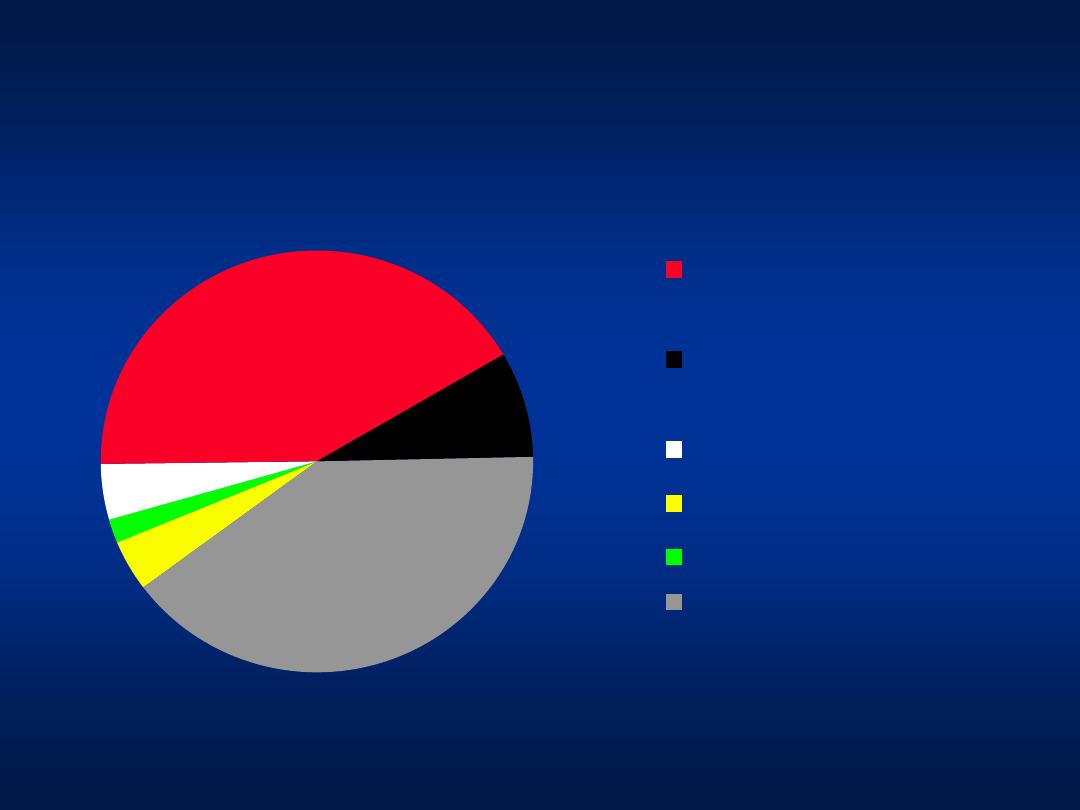
Hepatitis C
Modes of Transmission
Blood
Transfusion
prior to 1995
Blood transfusion
after 1995
Tattooing
Hemodialysis
IVDA
Unknown
4%
2%
4%
42%
8%
40%
Khatib et al, Unpublished data 2004
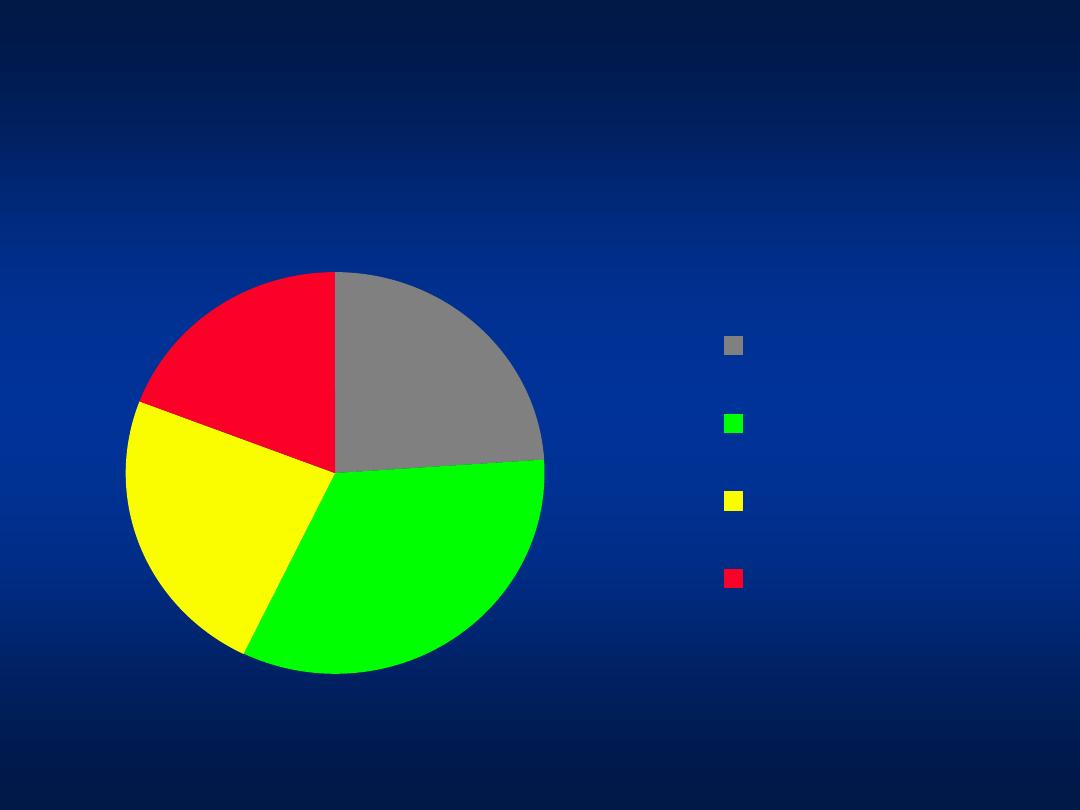
Hepatitis C
Modes of Transmission
24%
33%
24%
19%
No risk factors
Circumcision at
home
Minor Surgical
procedure
Dental procedure
Khatib et al, Unpublished data 2004
Patients with unknown risk factors
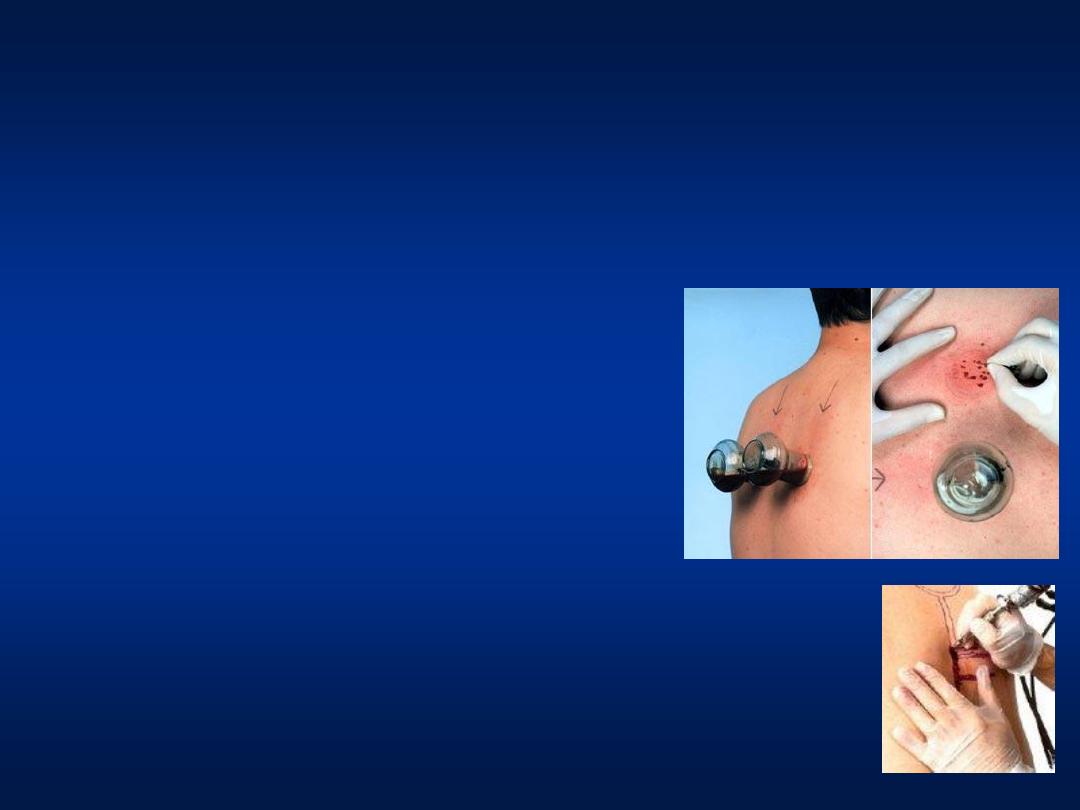
Hepatitis C
Additional Sources of Infection
• Traditional practices using unsterilized tools:
– Barbering
– Tattooing
– Circumcision
– Body piercing
– Dental procedures
– Hejama
• Use of unsterilized injection equipment

Questions
• What are risk factors for Hepatitis
C transmission in Jordan ?
• Did he acquire the infection from
blood transfusion?
• Is hepatitis C a treatable disease?
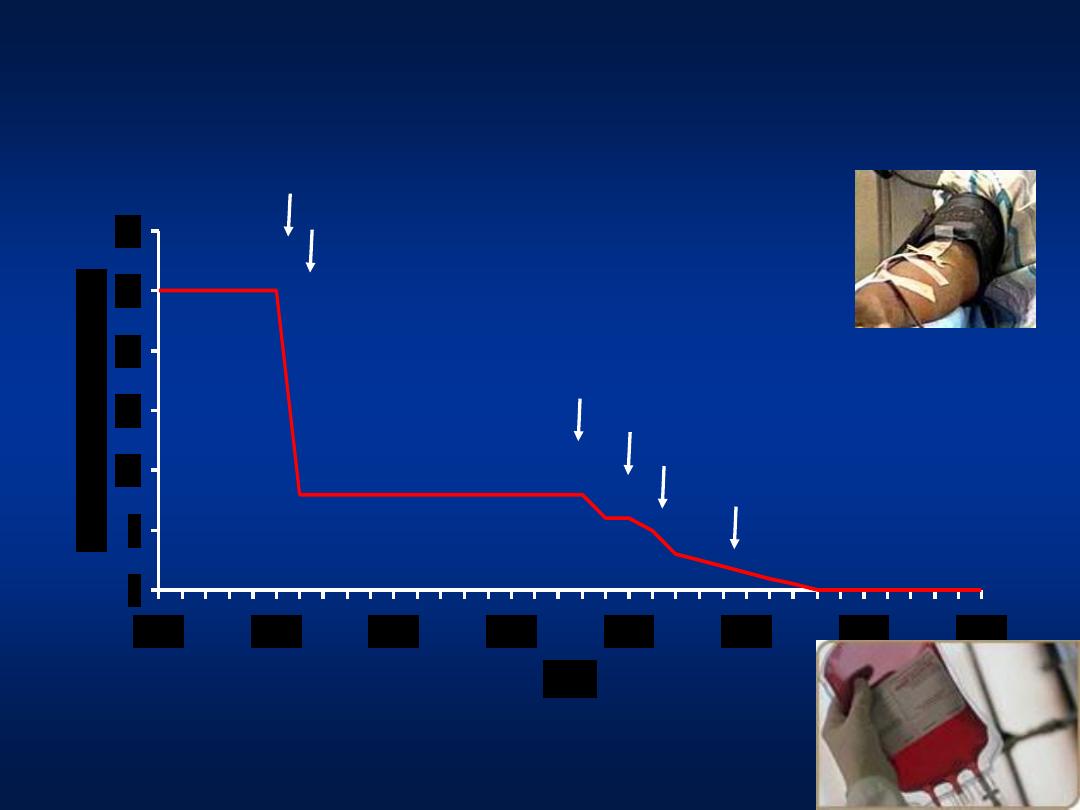
All volunteer donors
HBsAg
Donor Screening for HIV Risk Factors
Anti-HIV
ALT/Anti-HBc
Anti-HCV
Improved
HCV Tests
Adapted from HJ Alter and Tobler and Busch, Clin Chem 1997
Post-transfusion Hepatitis
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
1965
1970
1975
1980
1985
1990
1995
2000
Year
%
o
f
R
e
c
ip
ie
n
ts
I
n
fe
c
te
d

Questions
• What are risk factors for Hepatitis
C transmission in Jordan ?
• Did he acquire the infection from
blood transfusion?
• Is hepatitis C a treatable disease?
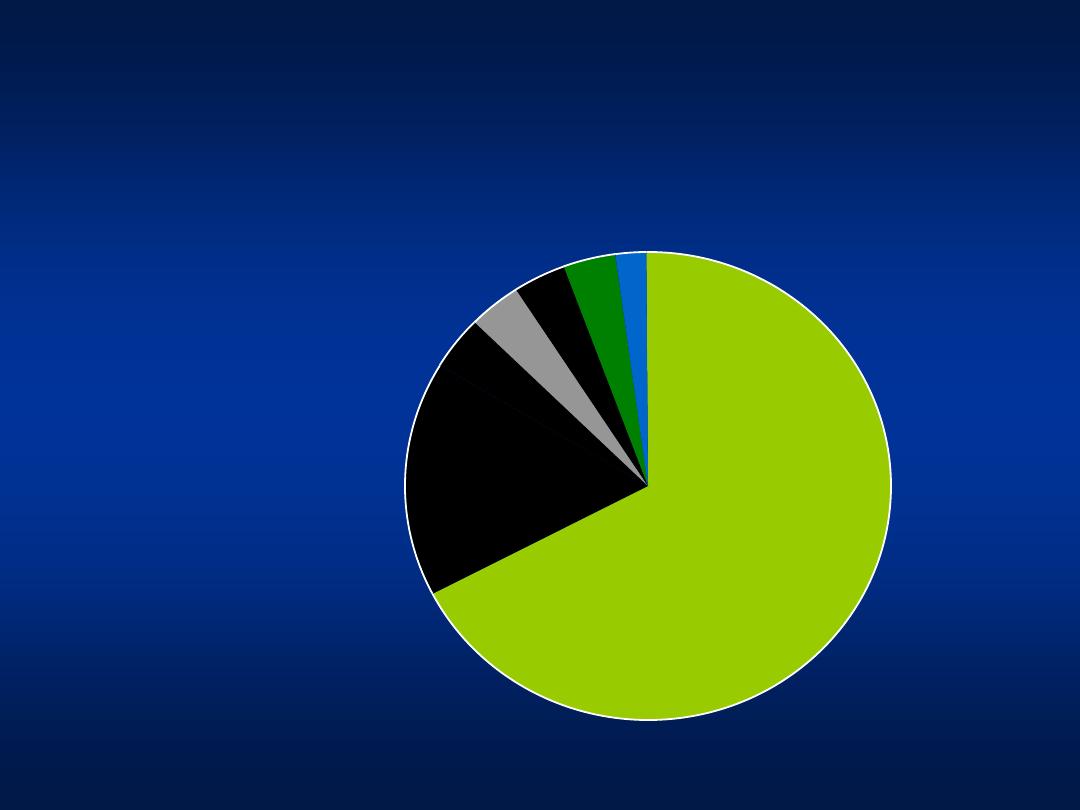
Hepatitis C
Genotypes
Genotype 4
66%
Genotype 4+ 1b
16%
Genotype 1a 4%
Genotypes 2 and 3 4%
Genotype 4+ 2a/c 4%
Un-typable4%
Genotype 1b+3a 2%
Genotype 4
– 66%
Genotype 4 +1b
– 16%
Genotype 4+ 2a/c- 4%
Genotype 2,3
– 4%
Genotype 1b
– 4%
Khatib et al, Unpublished data 2004
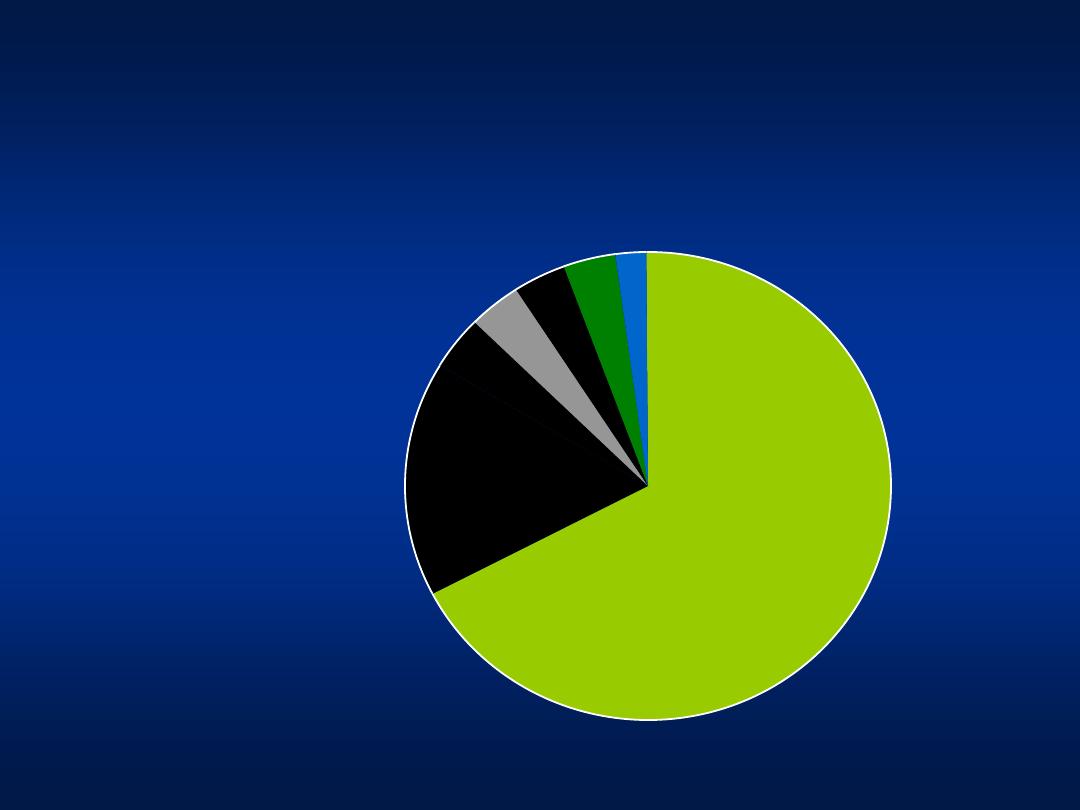
Hepatitis C
Genotypes
Genotype 4
66%
Genotype 4+ 1b
16%
Genotype 1a 4%
Genotypes 2 and 3 4%
Genotype 4+ 2a/c 4%
Untypable 4%
Genotype 1b+3a 2%
Genotype 4
– 66%
Genotype 4 +1b
– 16%
Genotype 4+ 2a/c- 4%
Genotype 2,3
– 4%
Genotype 1b
– 4%
Khatib et al, Unpublished data 2004
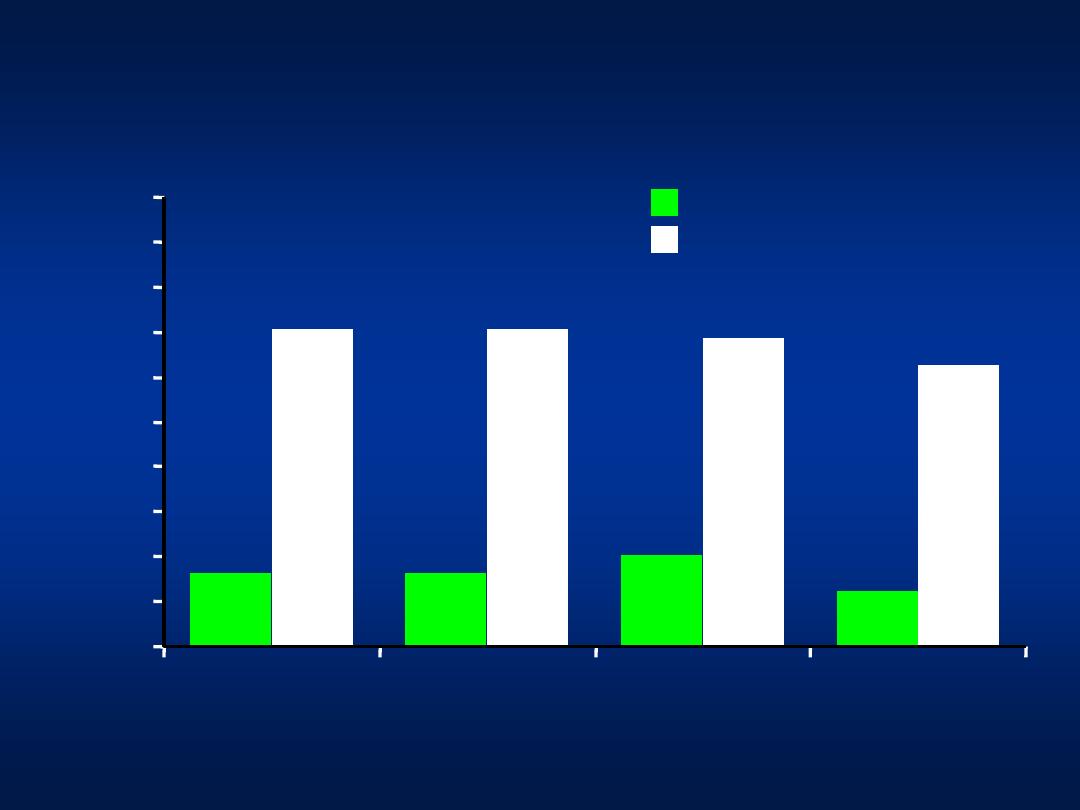
At Wks 12 & 24 = HCV RNA negative or drop of
2 log
10
PCR
Hepatitis C
Combination Therapy for Genotype 4
Interferon/Ribavirin (N = 49)
PEG Interferon+ Ribavirin (N = 51)
0
Thakeb F, et al. 2003.
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
V
ir
o
lo
g
ica
l Re
sp
o
n
se
(
%
o
f P
a
tie
n
ts
)
Wk 12
Wk 24
Wk 48 (EOT)
Wk 72 (SVR)
16.4
20.4
12.3
70.6
70.6
68.6
62.7
16.4
N = 8
N = 8
N = 6
N = 10
N = 36
N = 36
N = 35
N = 32

Thank You
